Systemic Anatomy - The Respiratory System
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture and lab
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
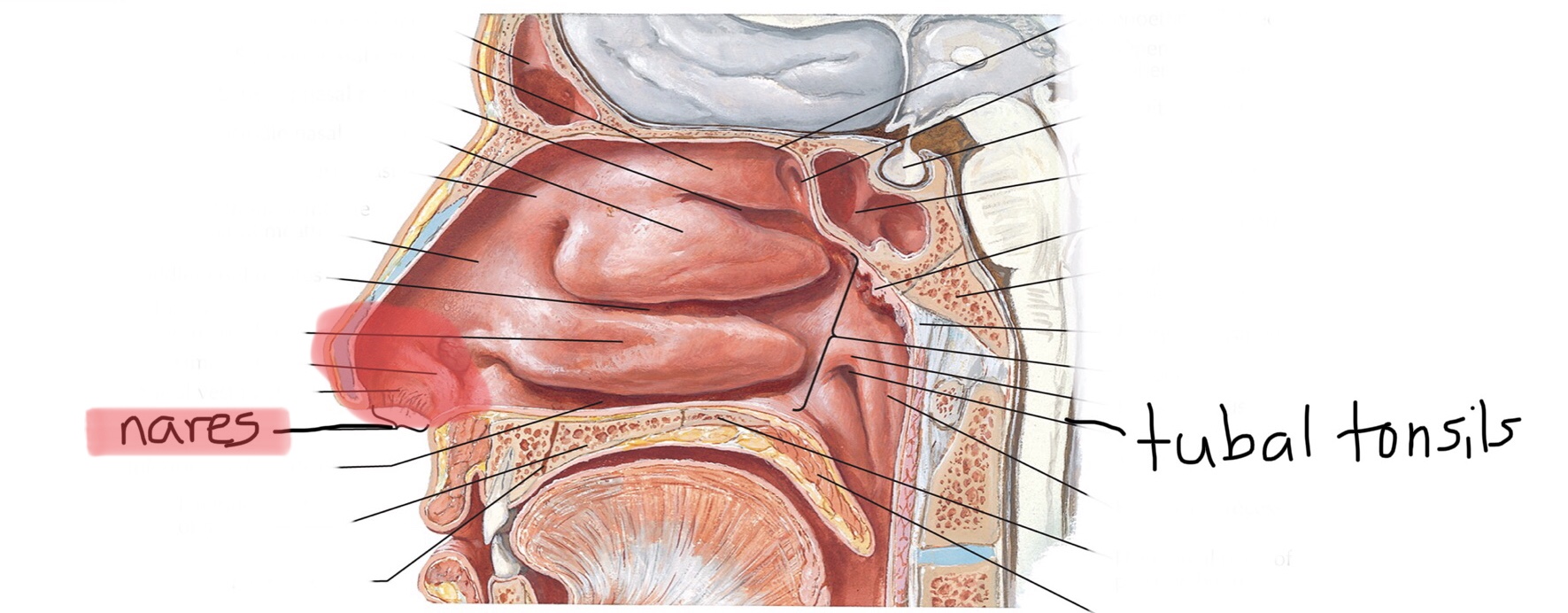
Identify the nares.
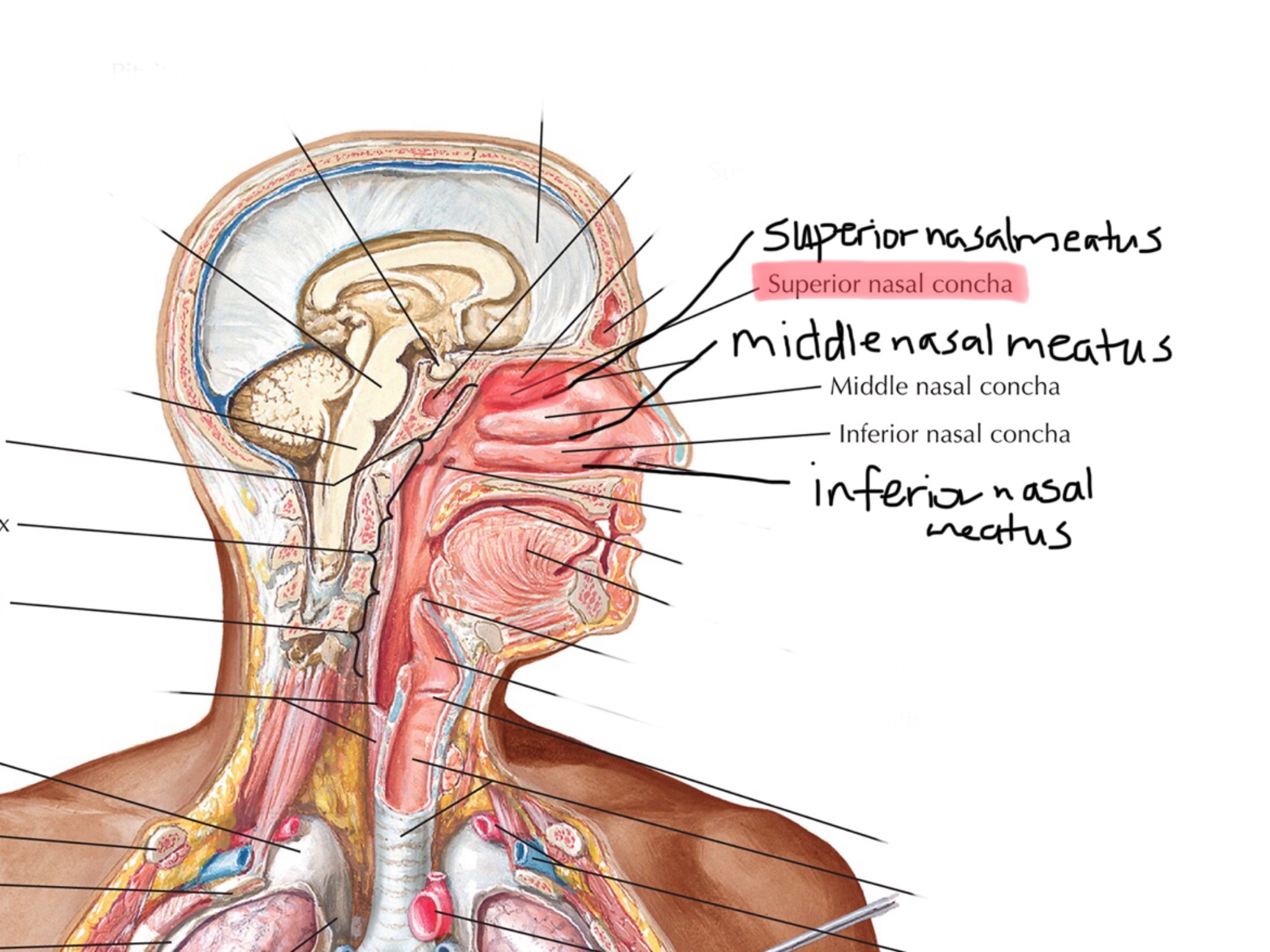
Identify the superior concha.
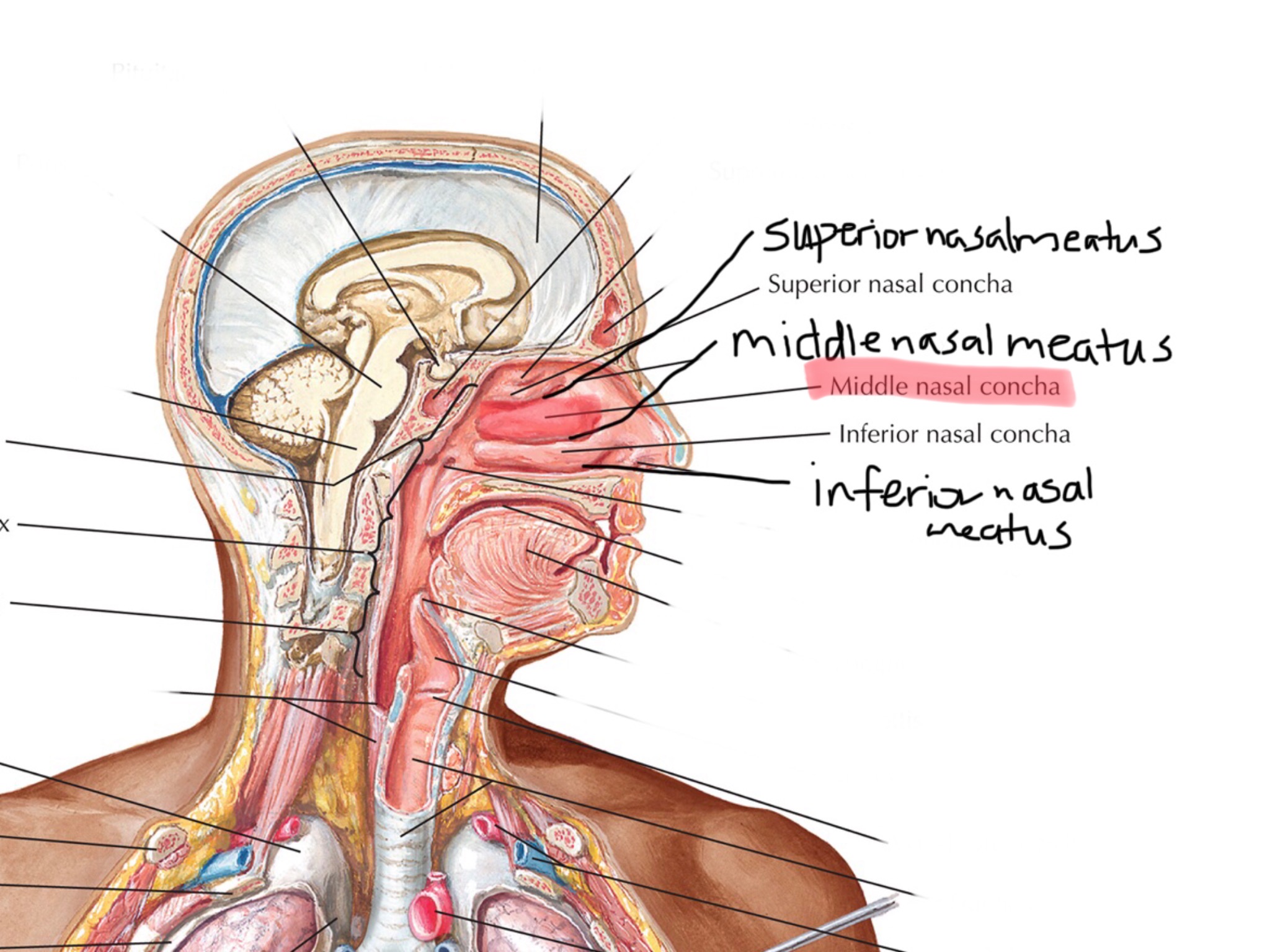
Identify the middle concha.
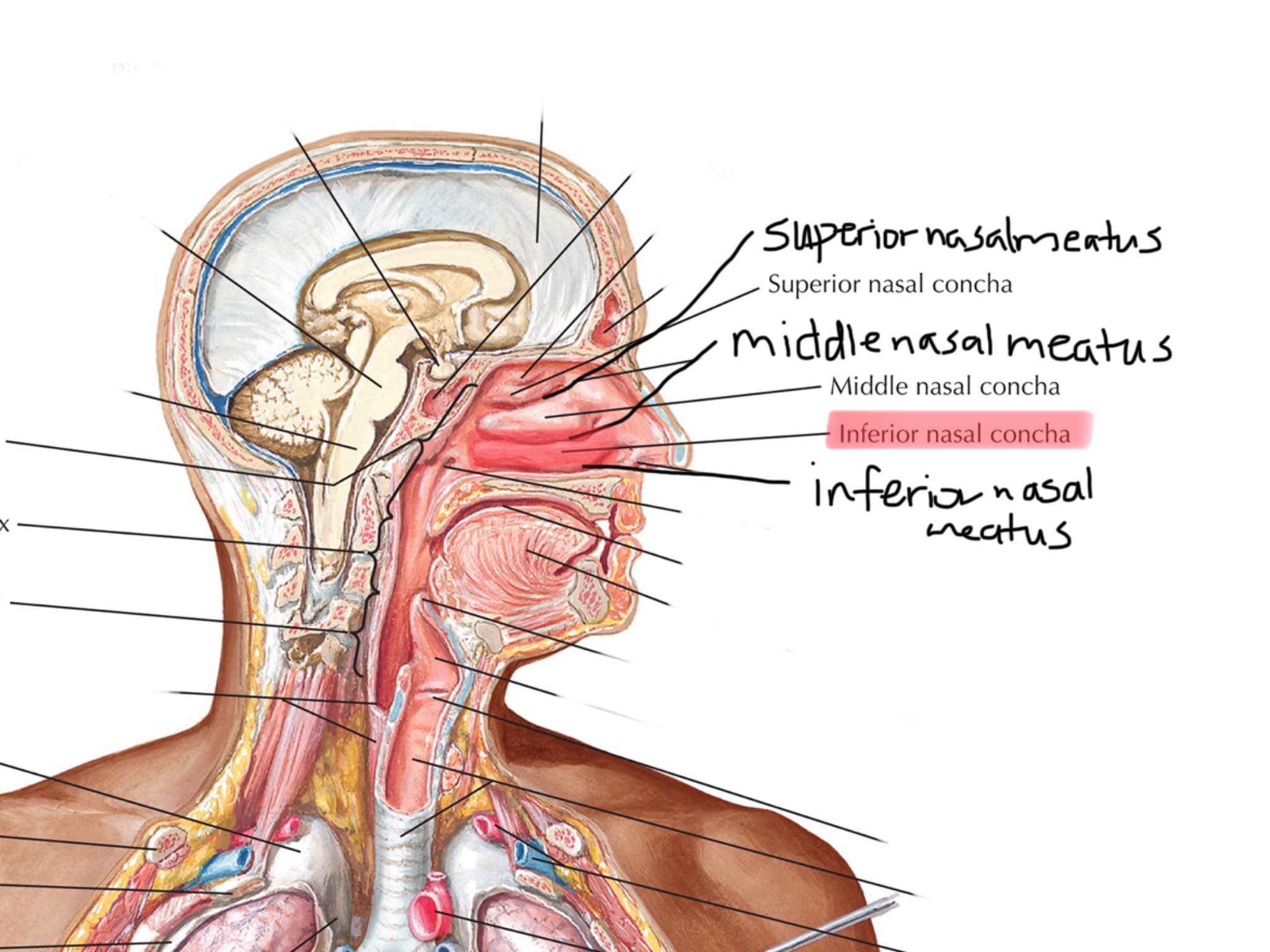
Identify the inferior choncha.
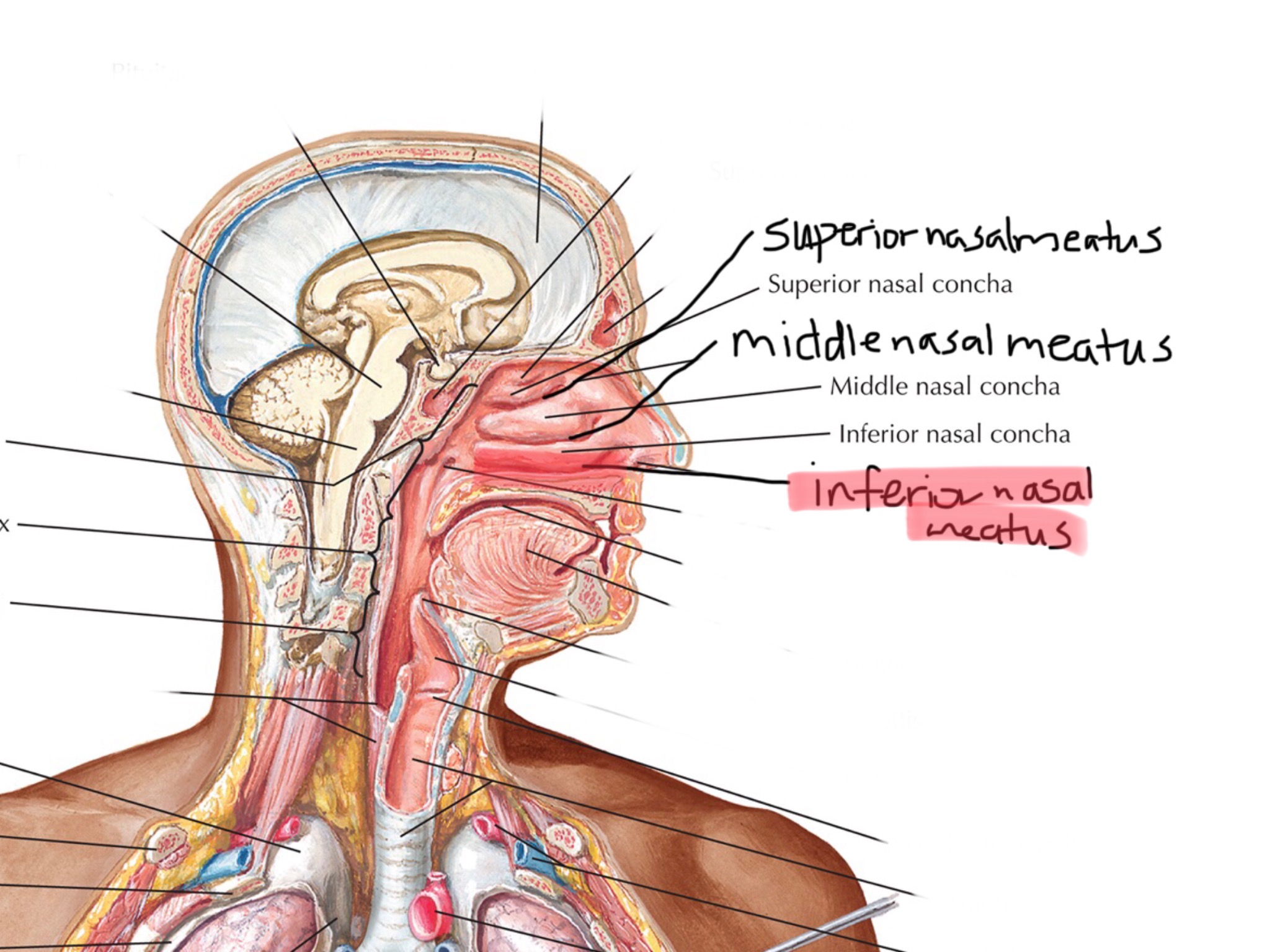
Identify the superior nasal meatus.
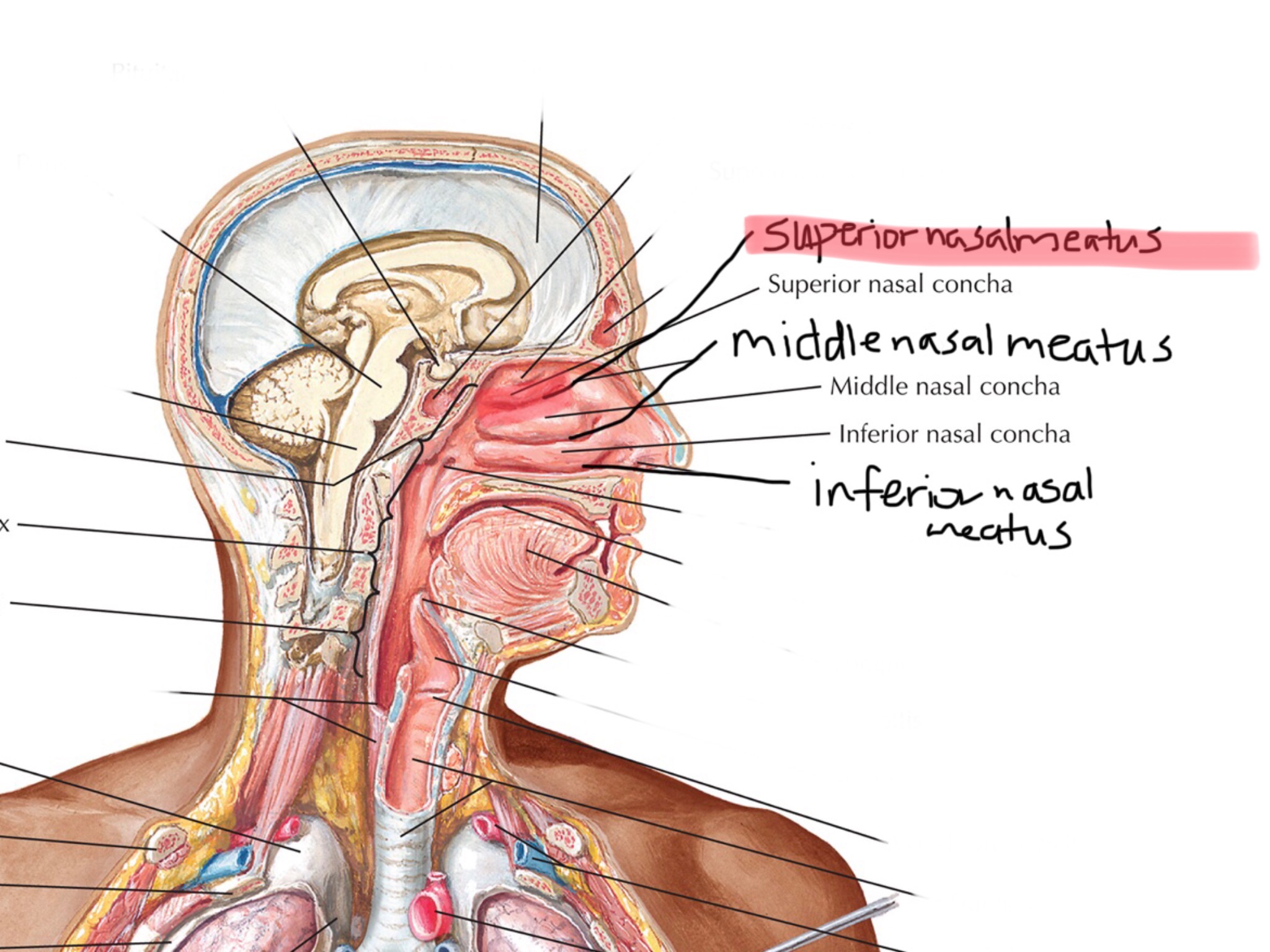
Identify the middle nasal meatus.
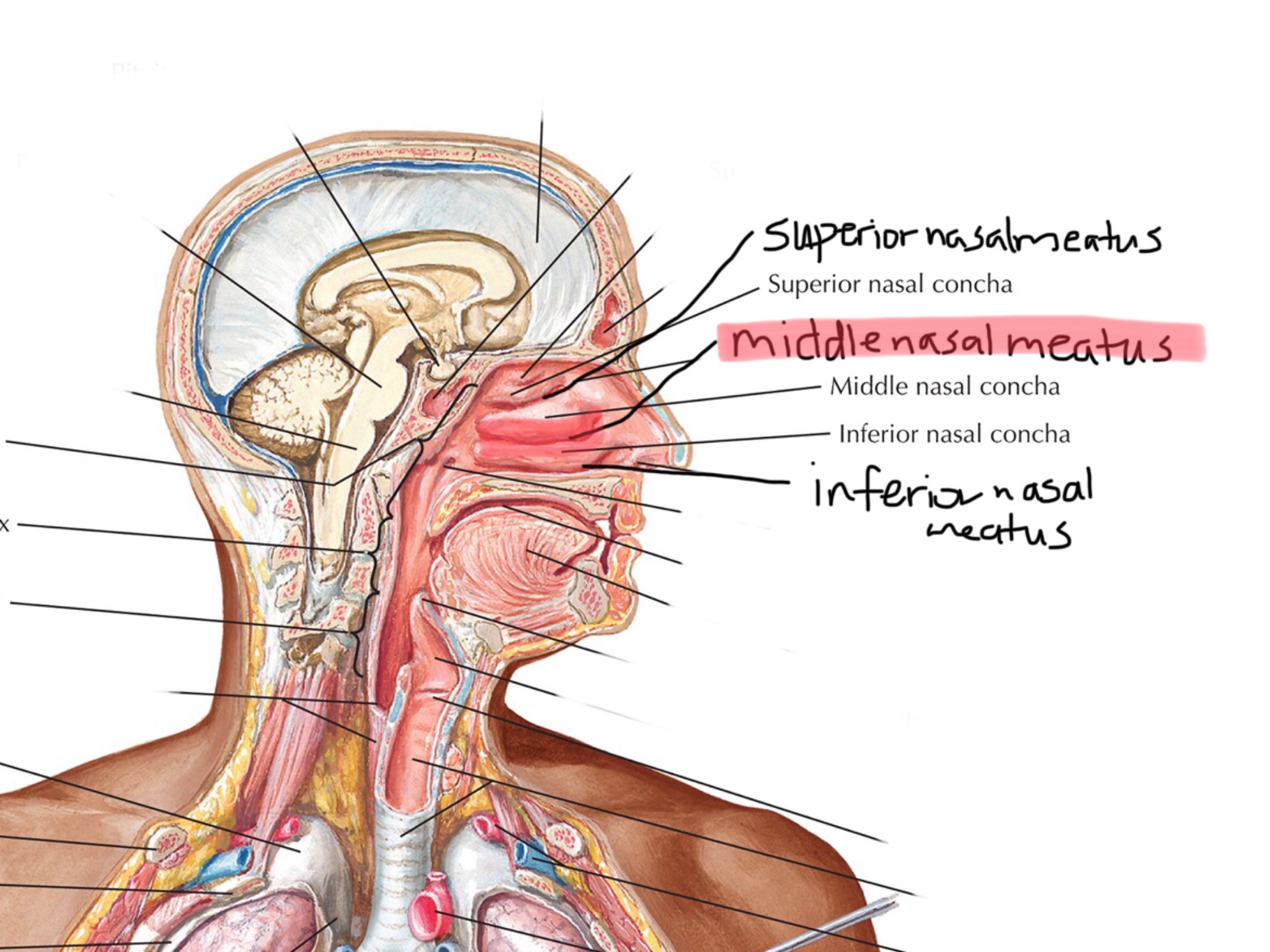
Identify the inferior nasal meatus.
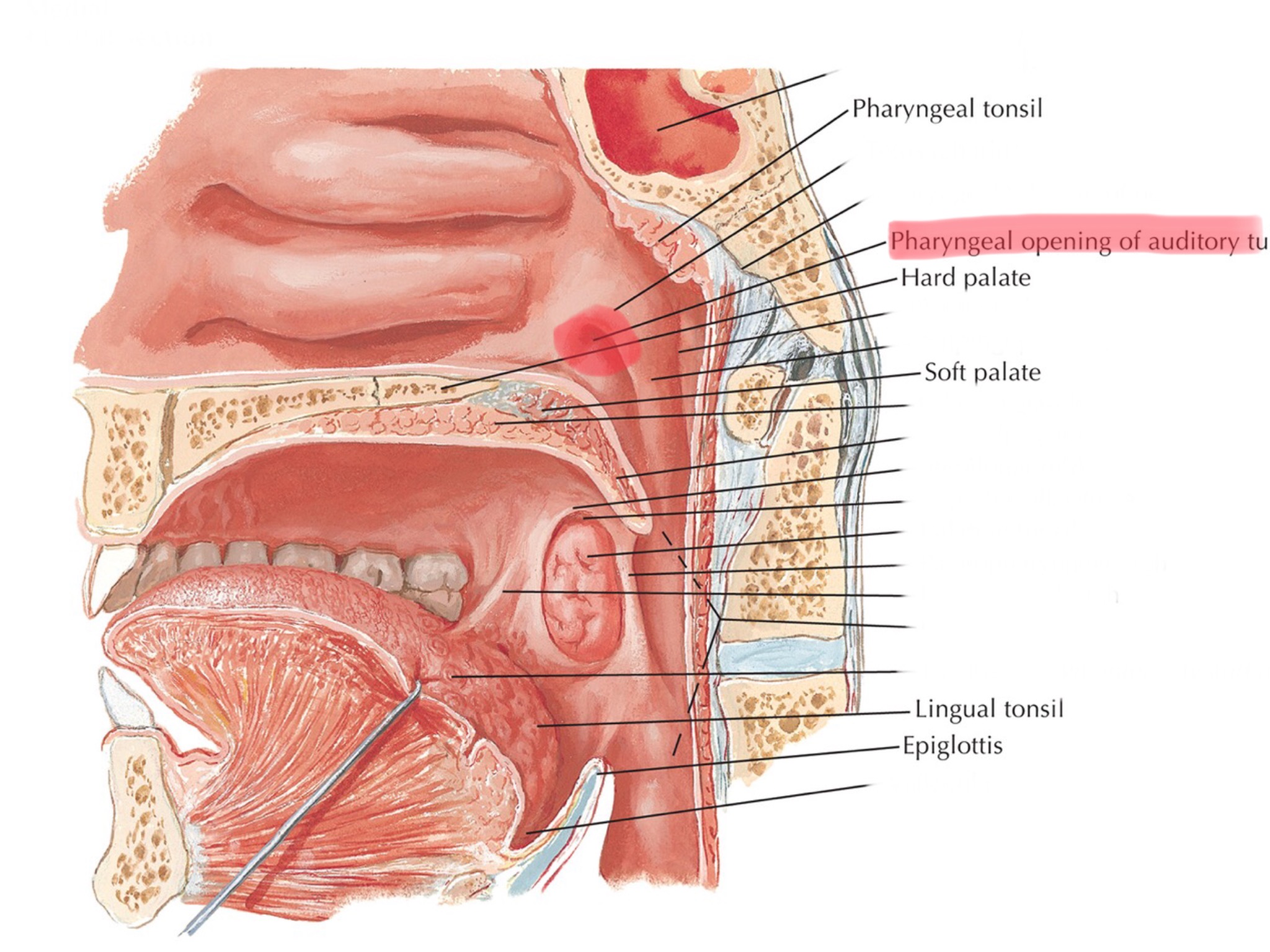
Identify the opening of the pharyngotympanic tube.
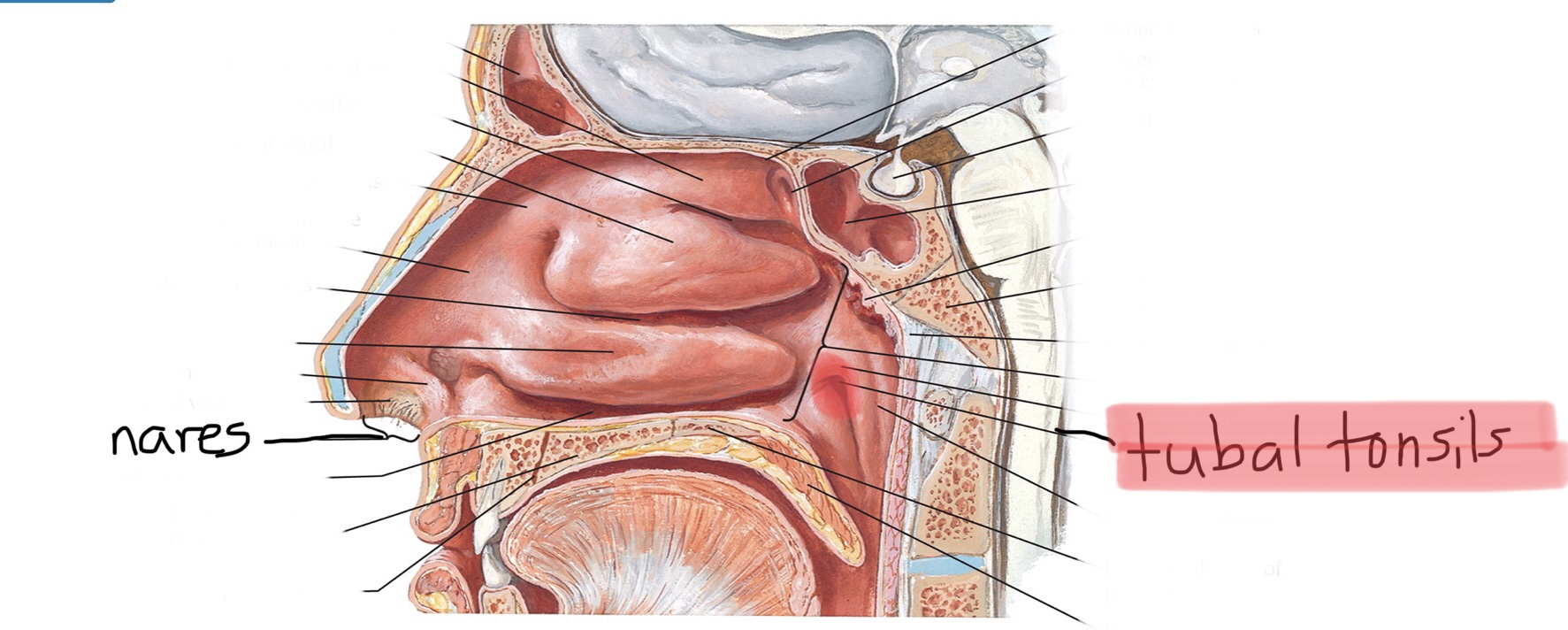
Identify the tubal tonsils.
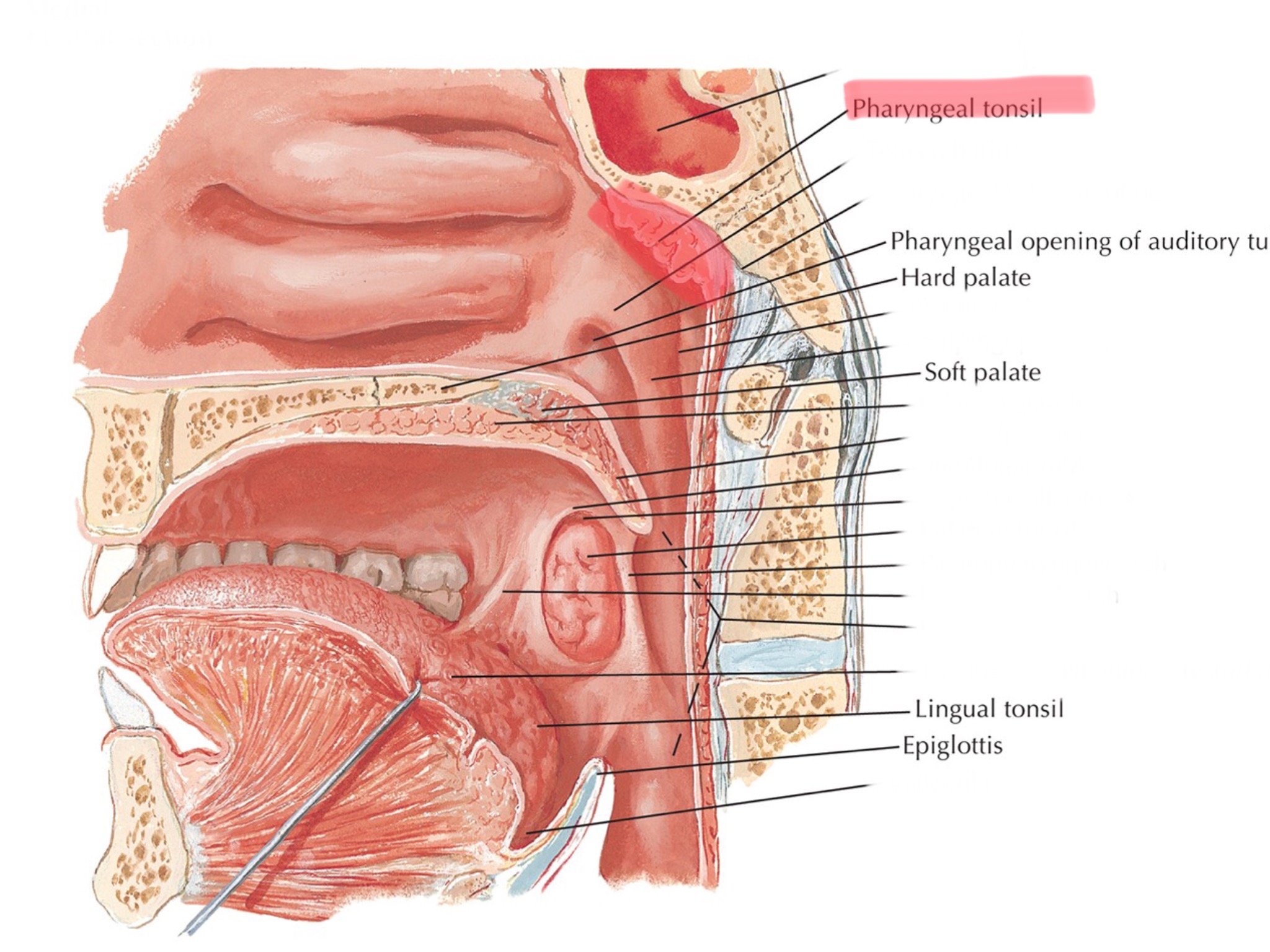
Identify the pharyngeal tonsil.
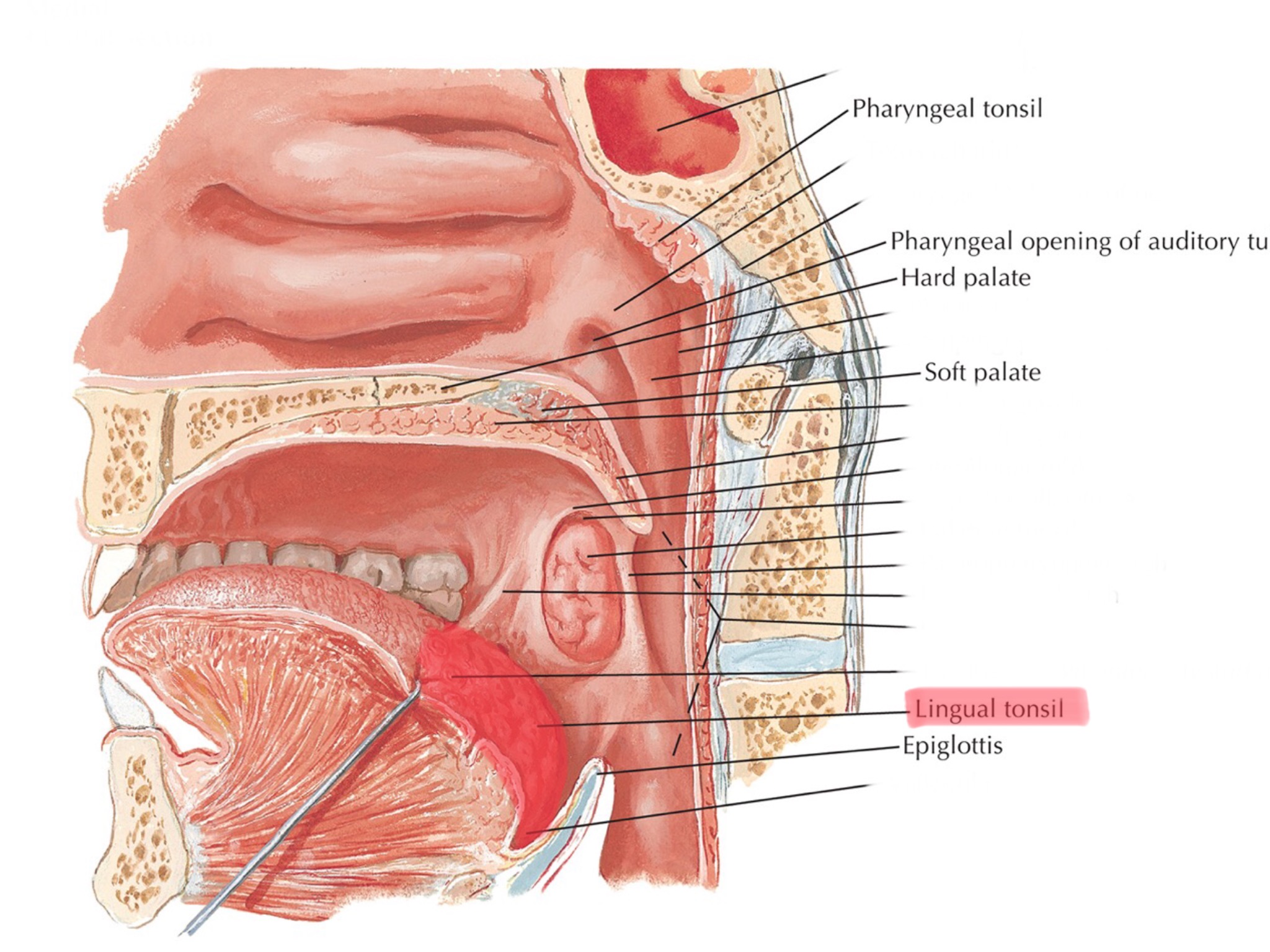
Identify the lingual tonsil.
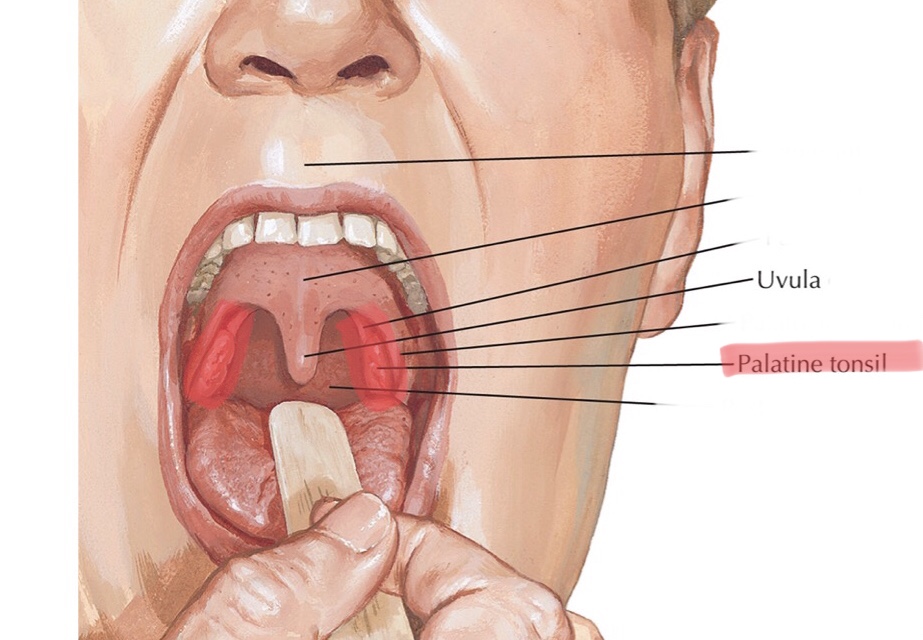
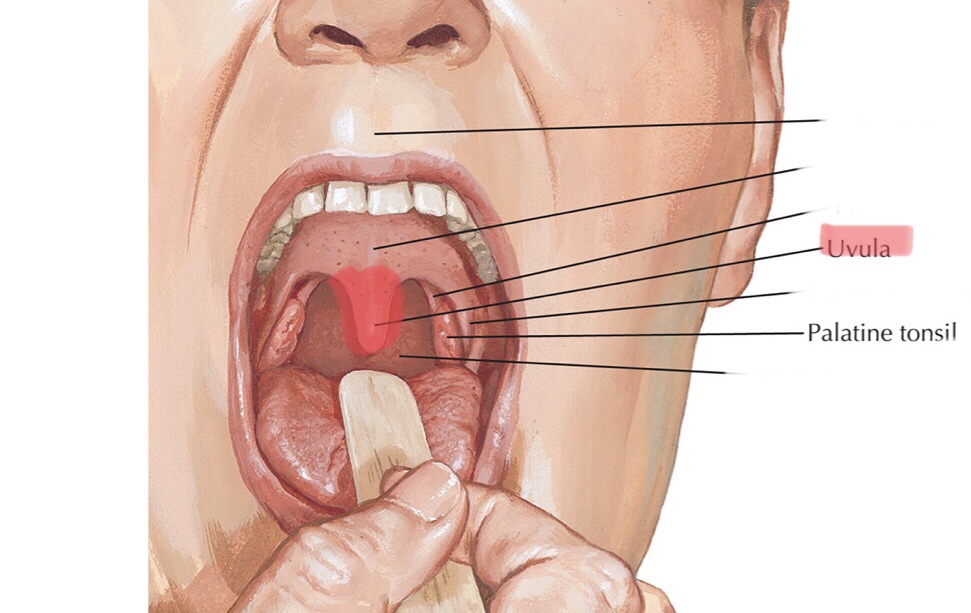
Identify the palatine tonsils.
Identify the nasopharynx.
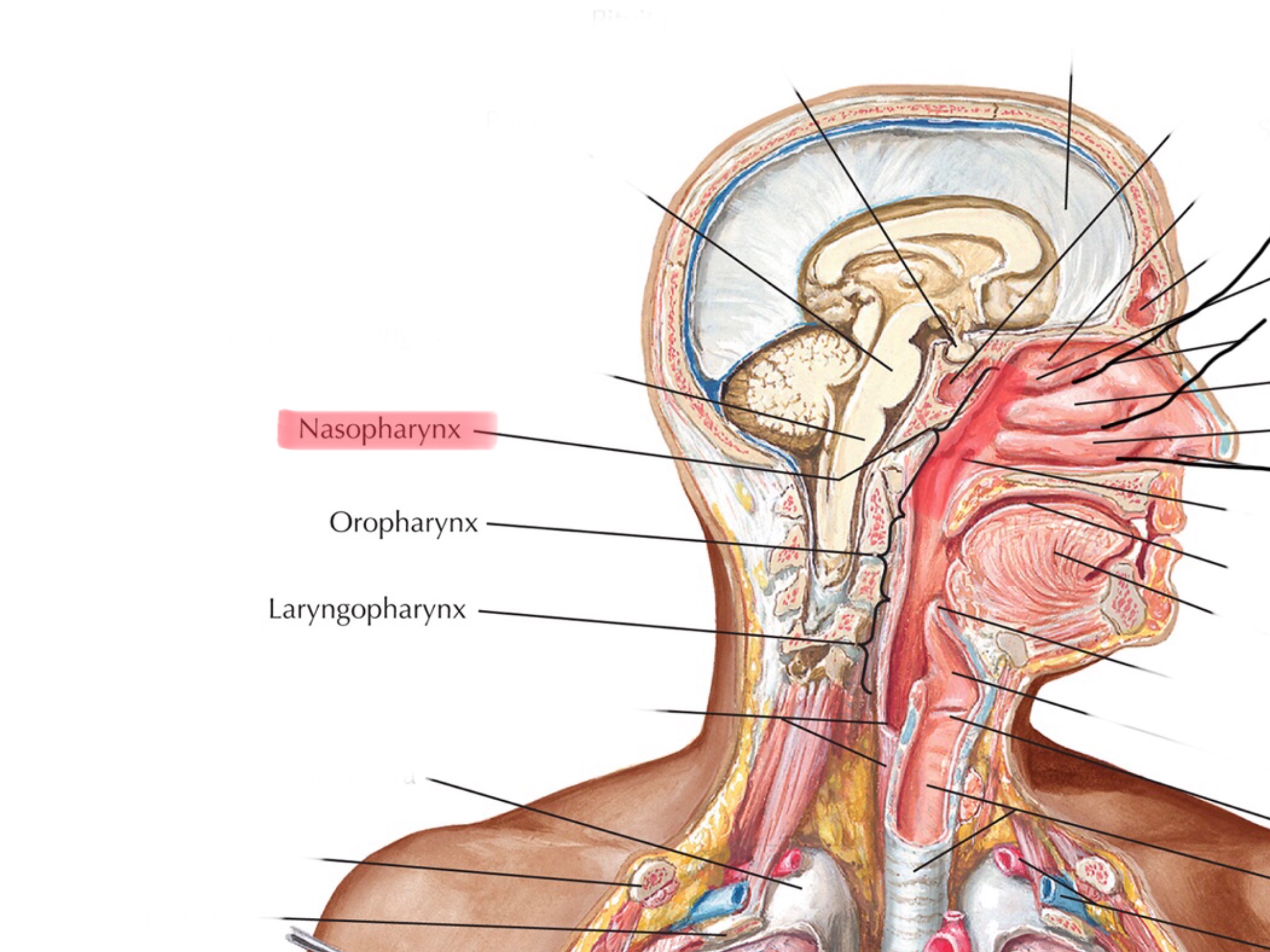
Identify the oropharynx.
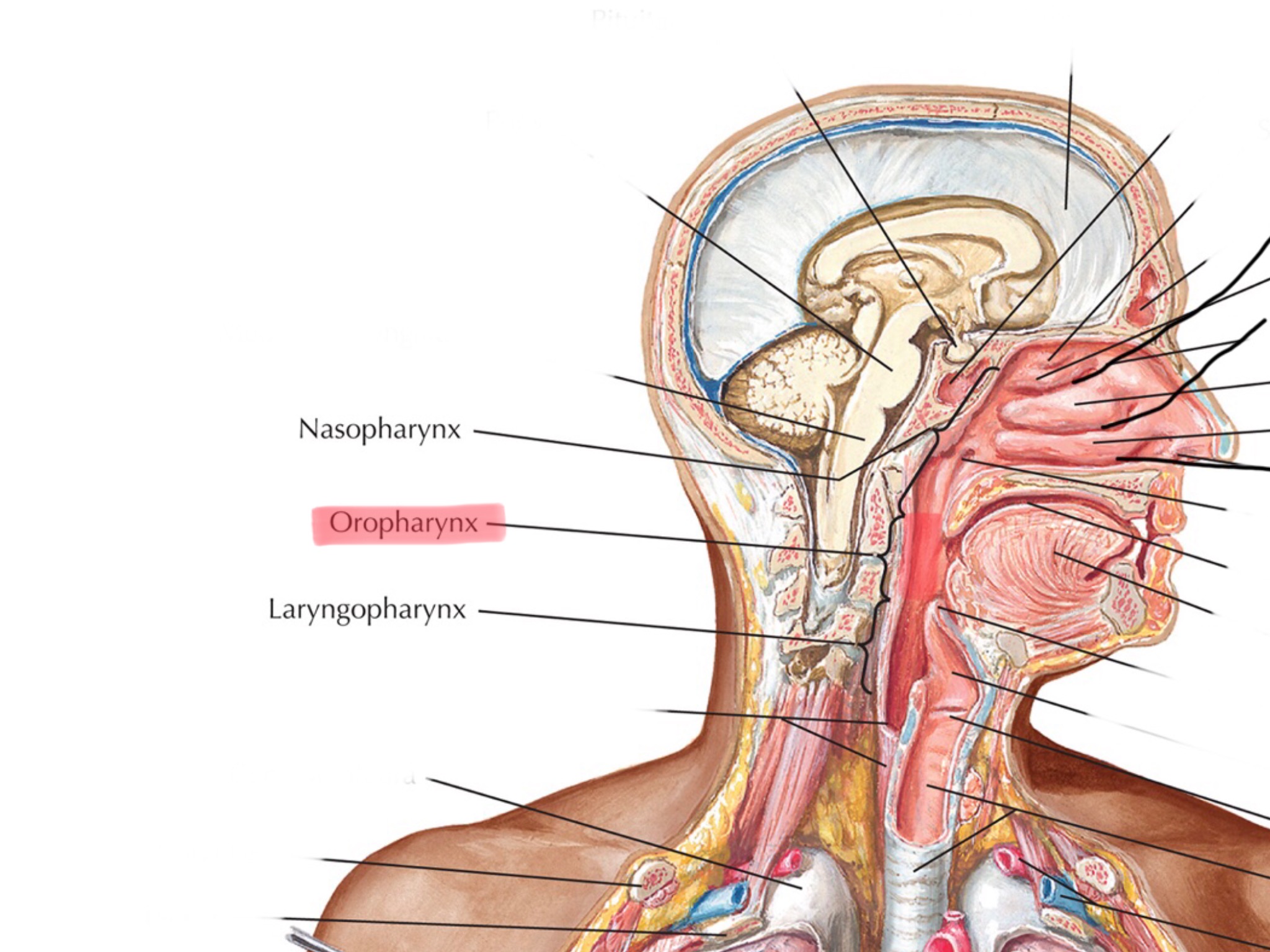
Identify the laryngopharynx.
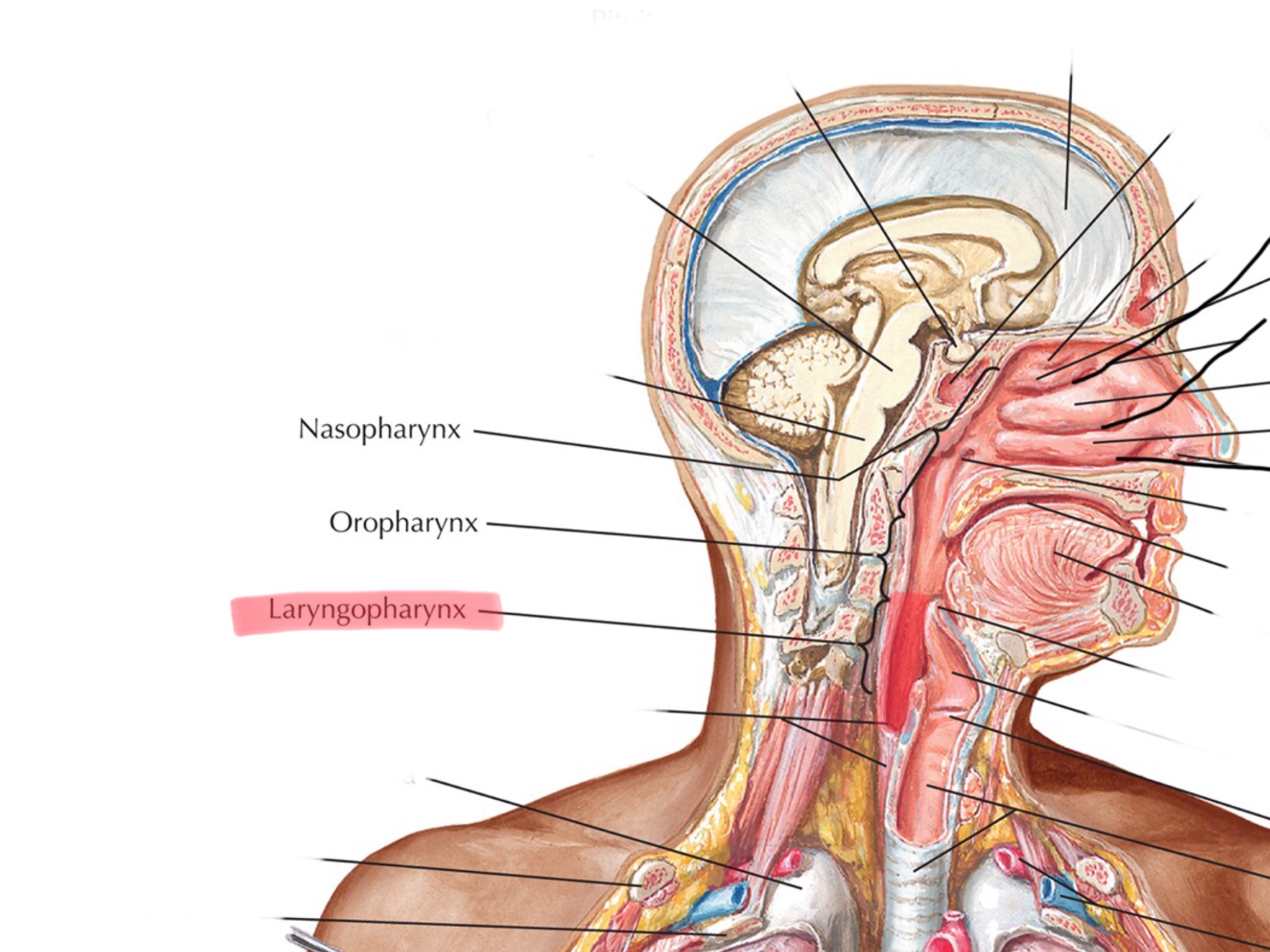
Identify the hard palate.
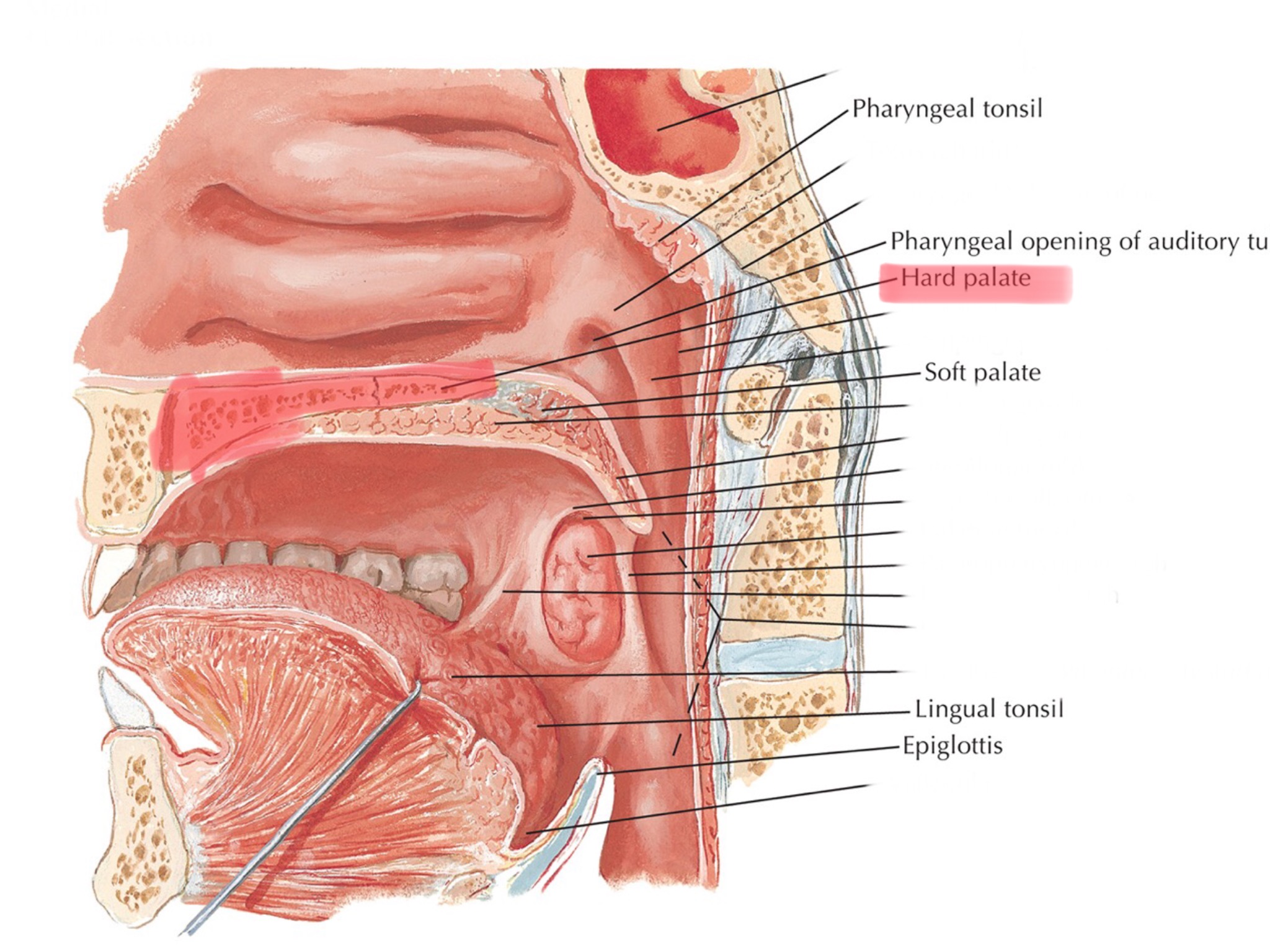
Identify the soft palate.
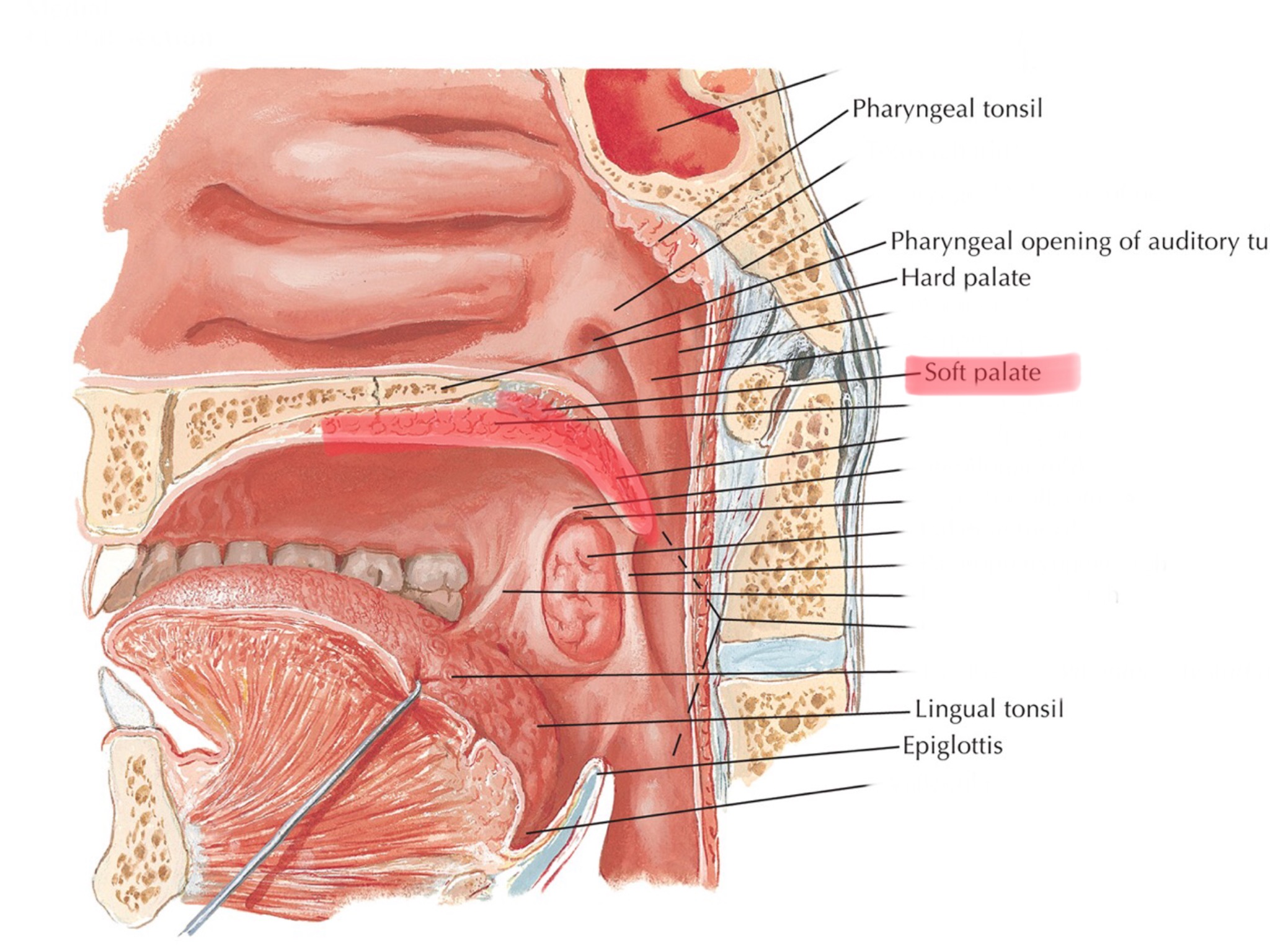
Identify the uvula.
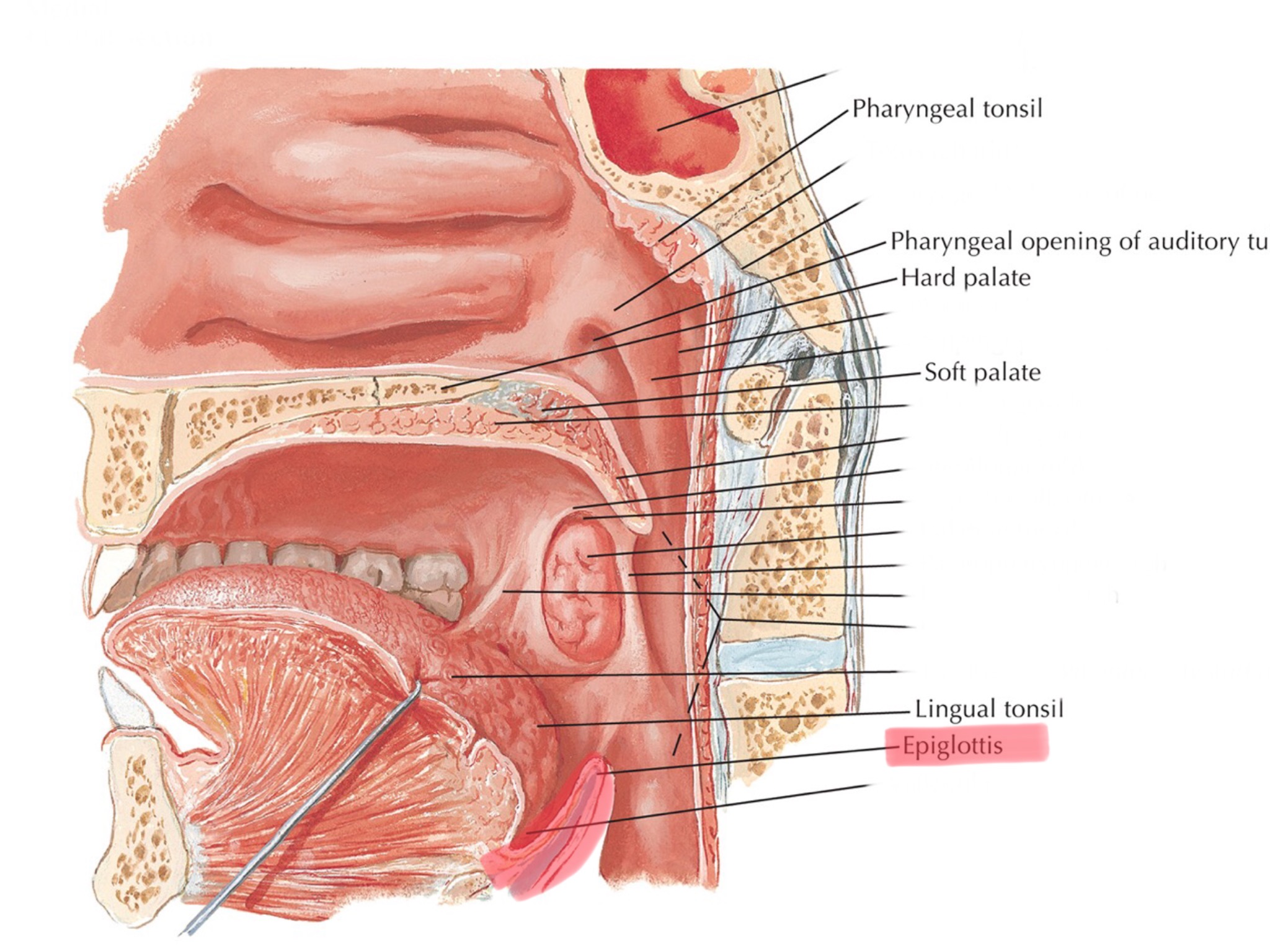
Identify the epiglottis.
Identify the hyoid bone.
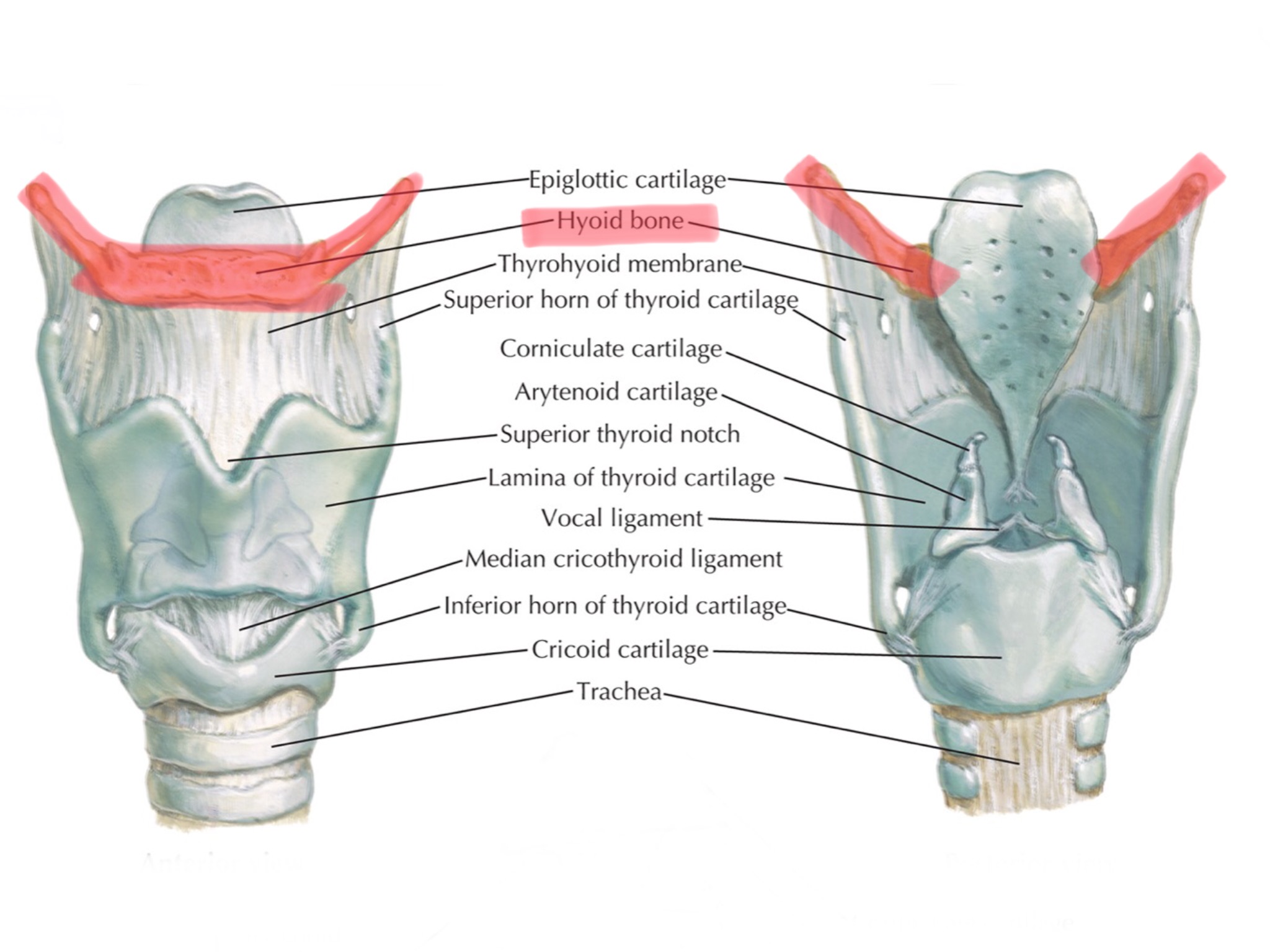
Identify the thyroid cartilage.
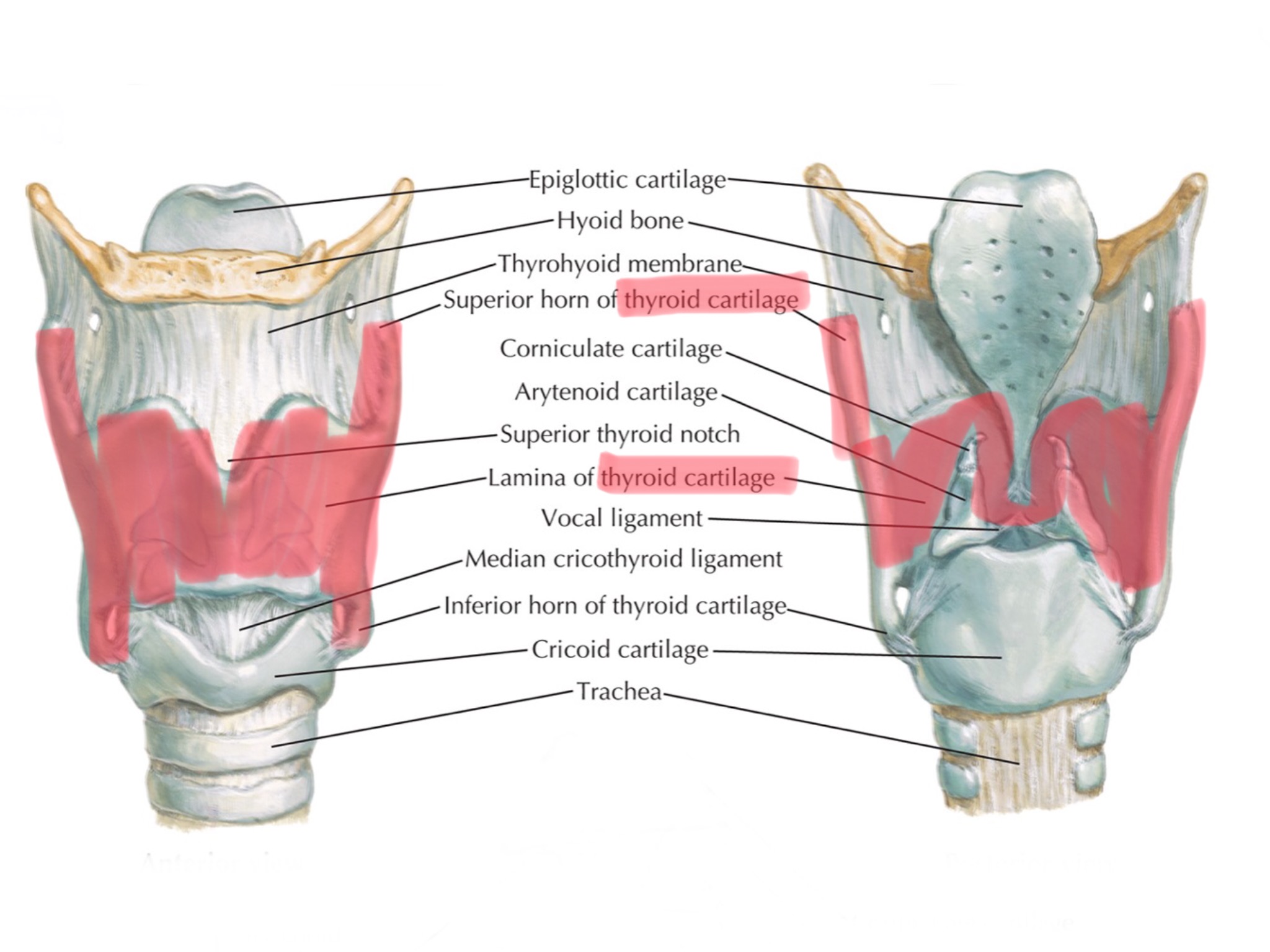
Identify the laryngeal prominence.
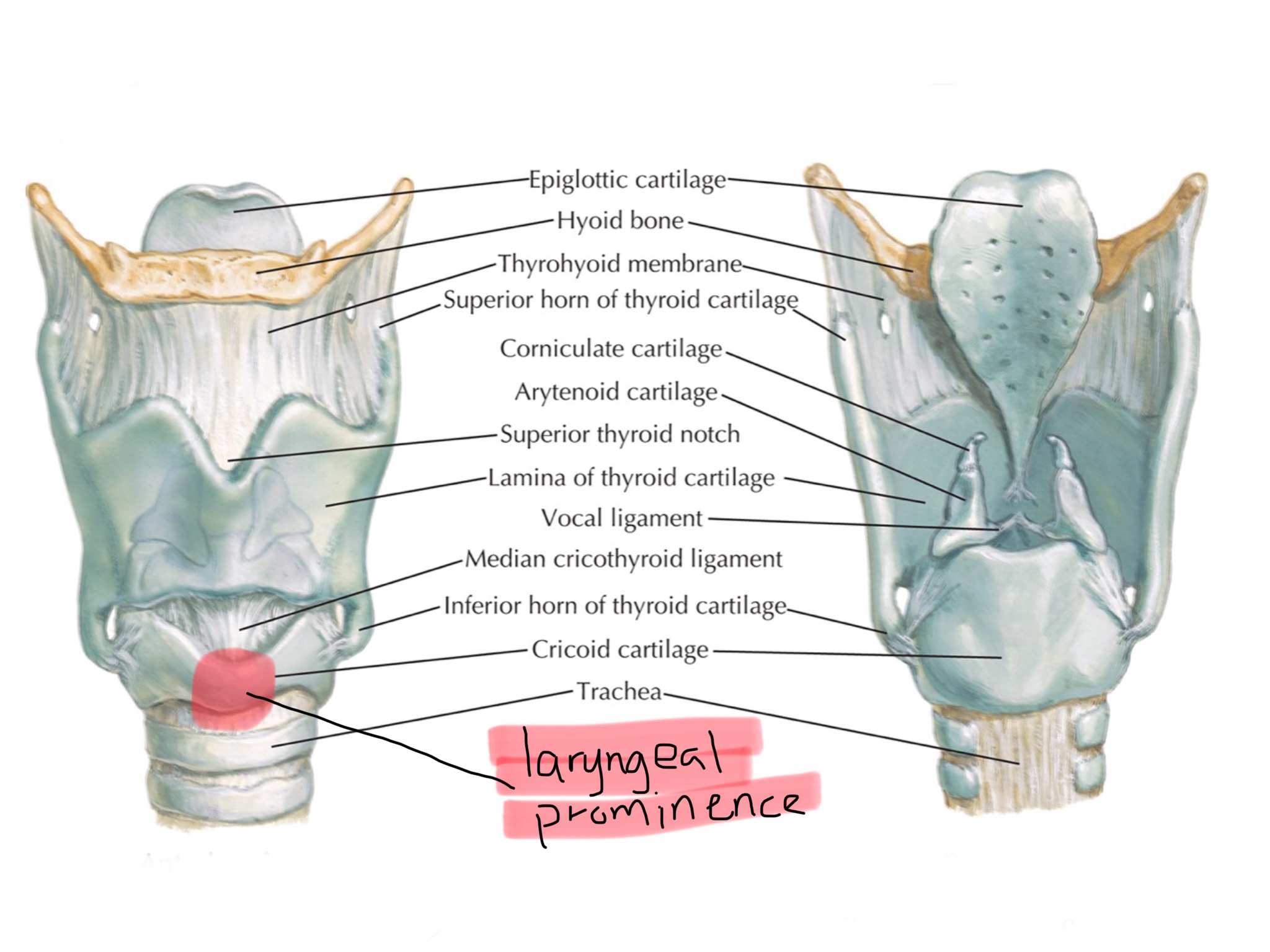
Identify the cricoid cartilage.
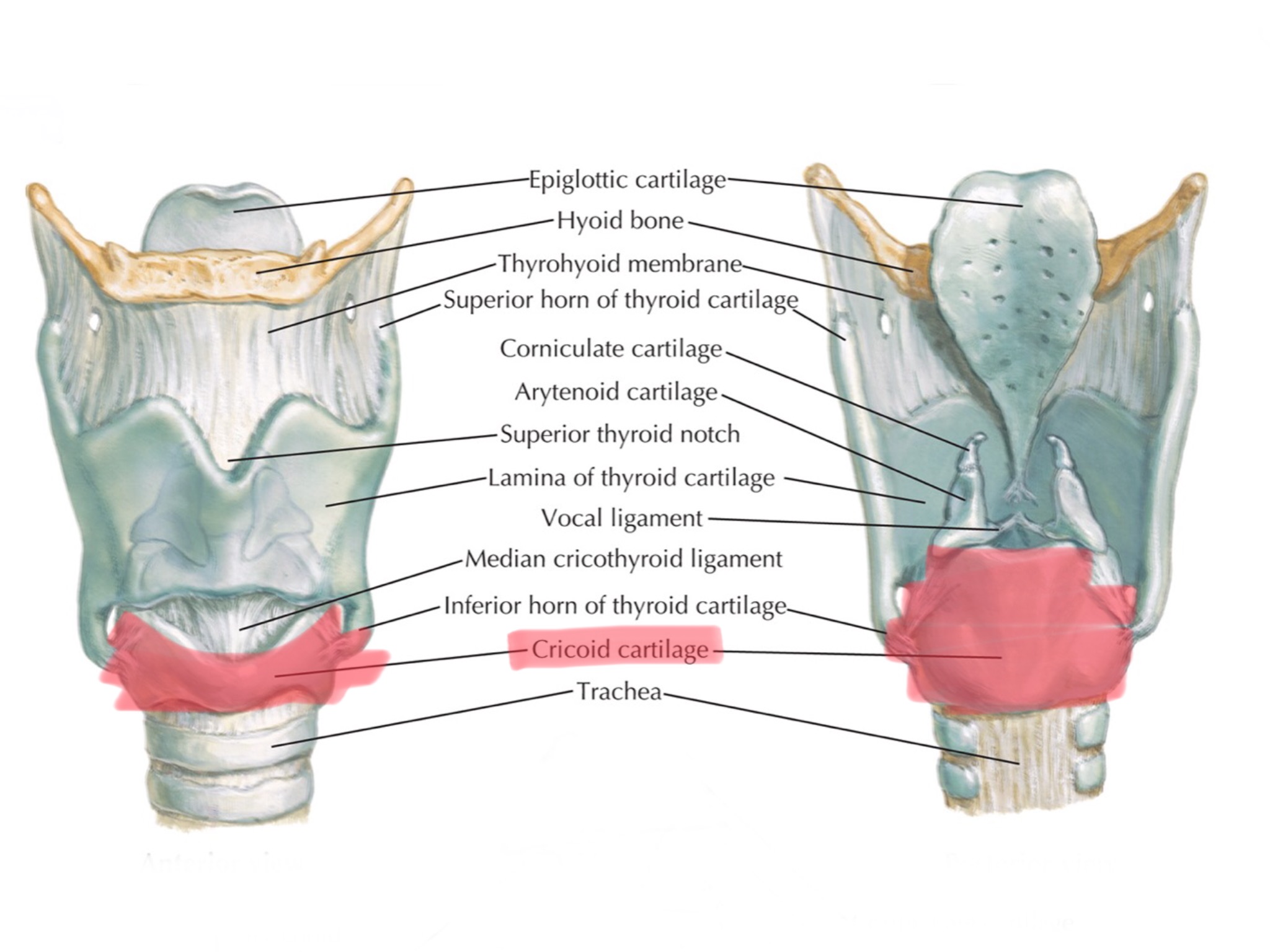
Identify the tracheal rings.
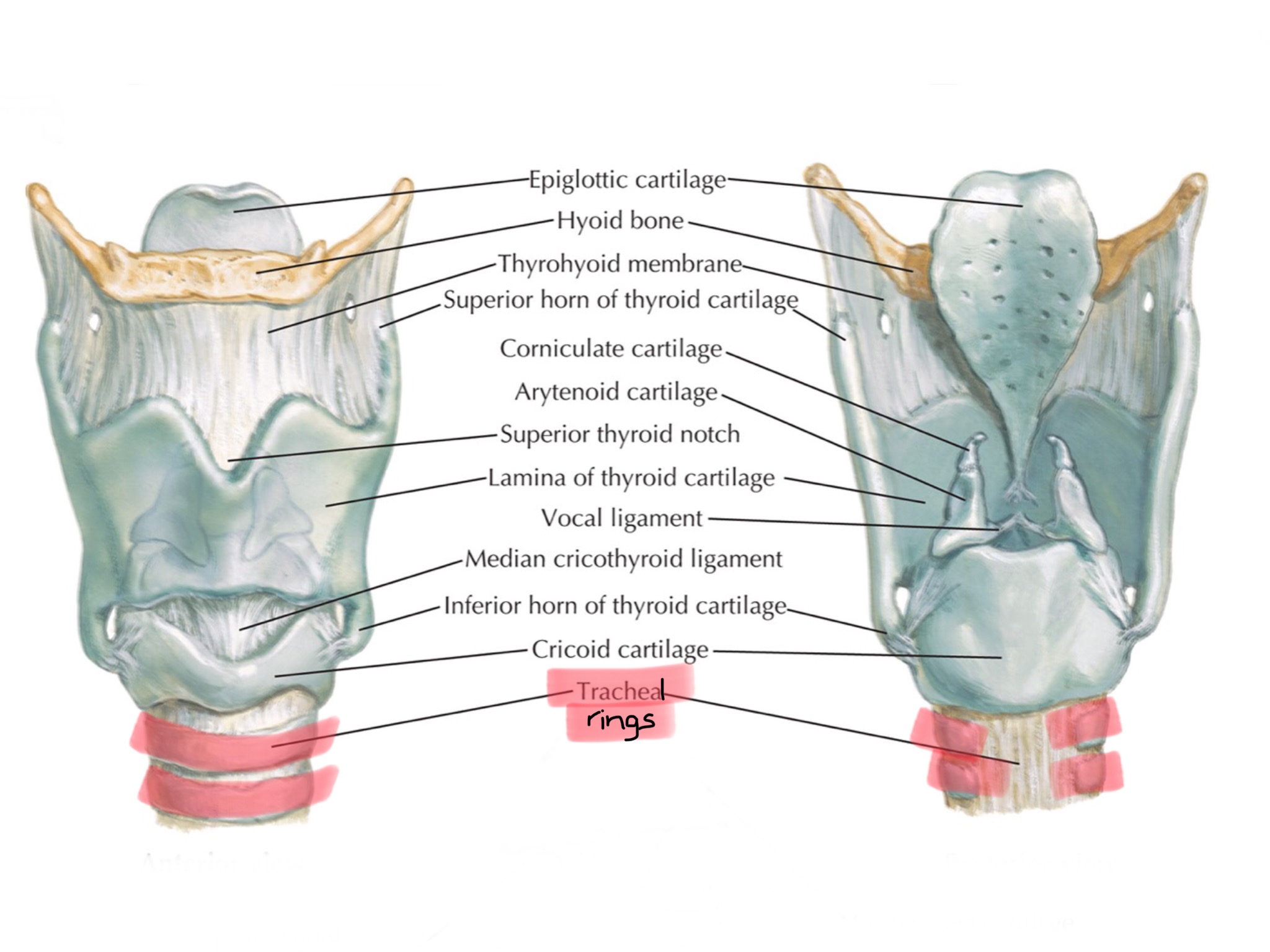
Identify the arytenoid muscles.
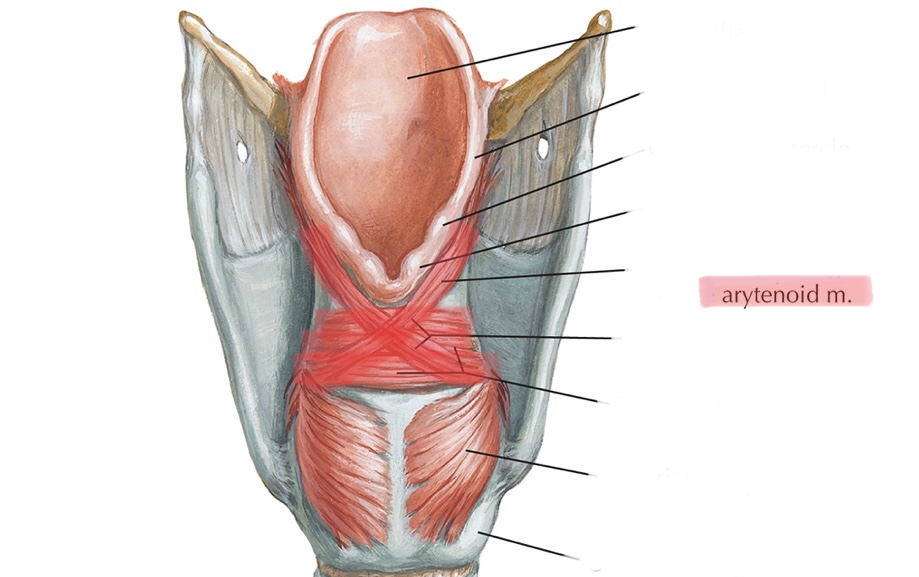
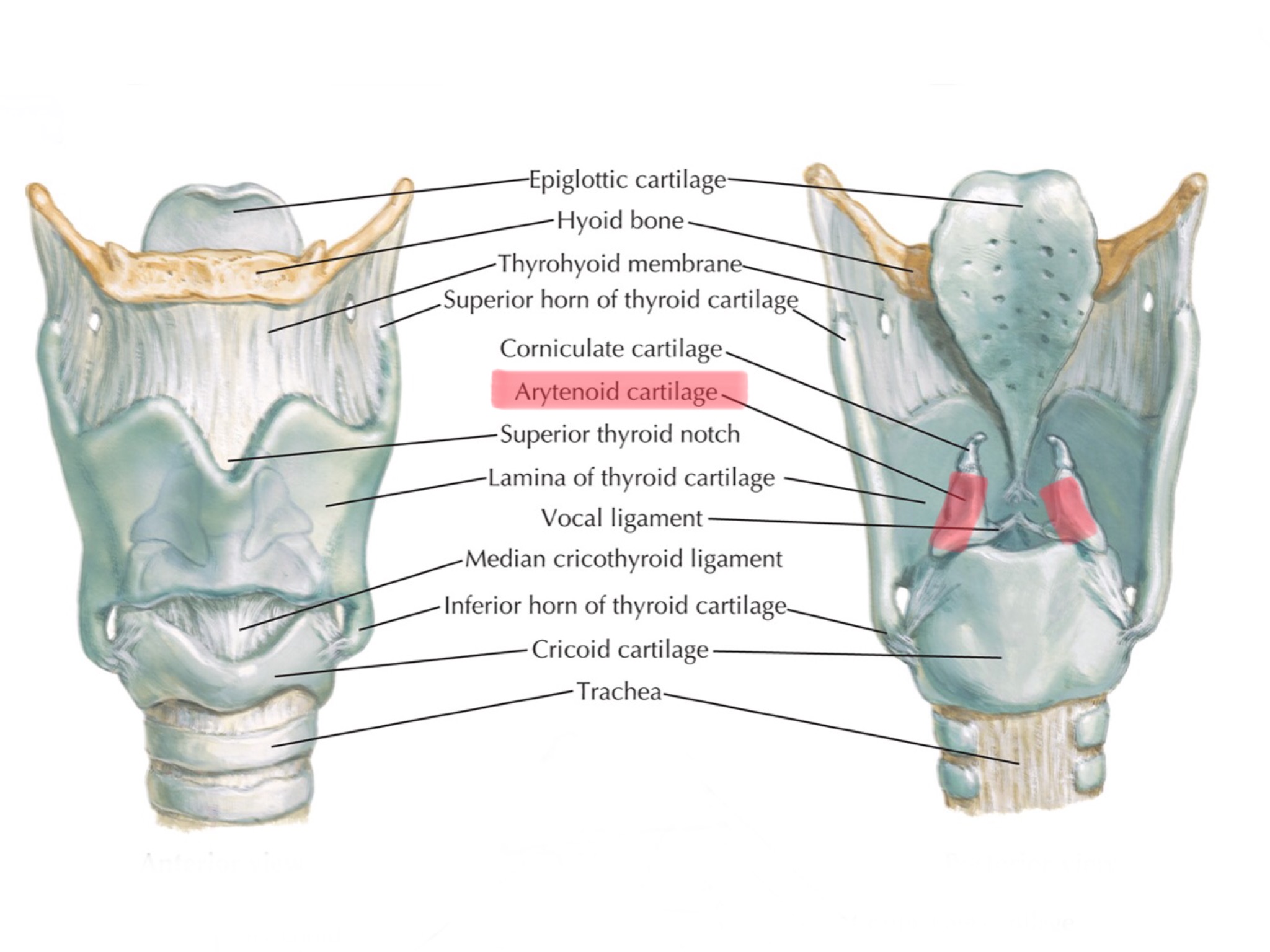
Identify the arytenoid cartilages.
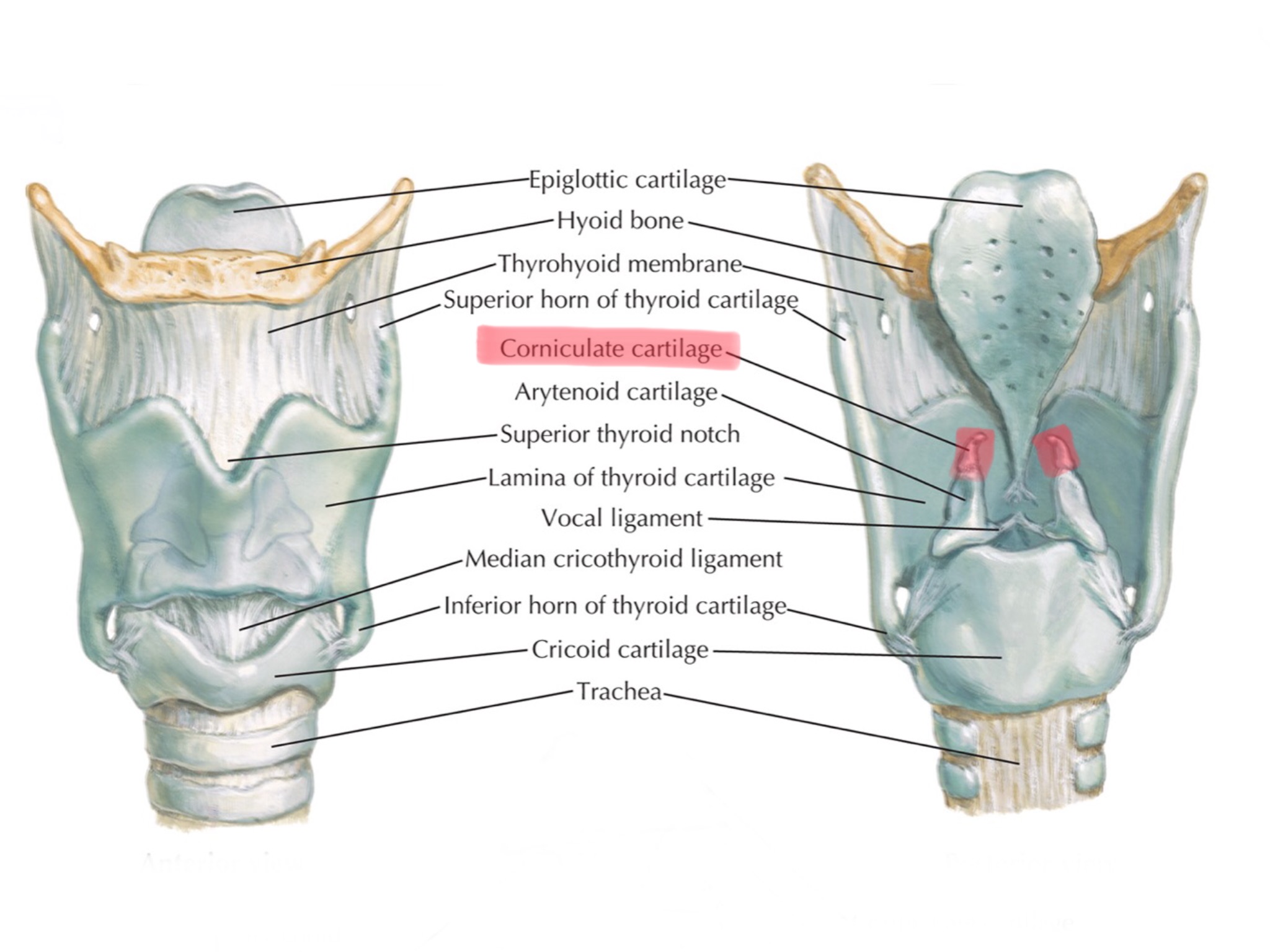
Identify the corniculate cartilages.
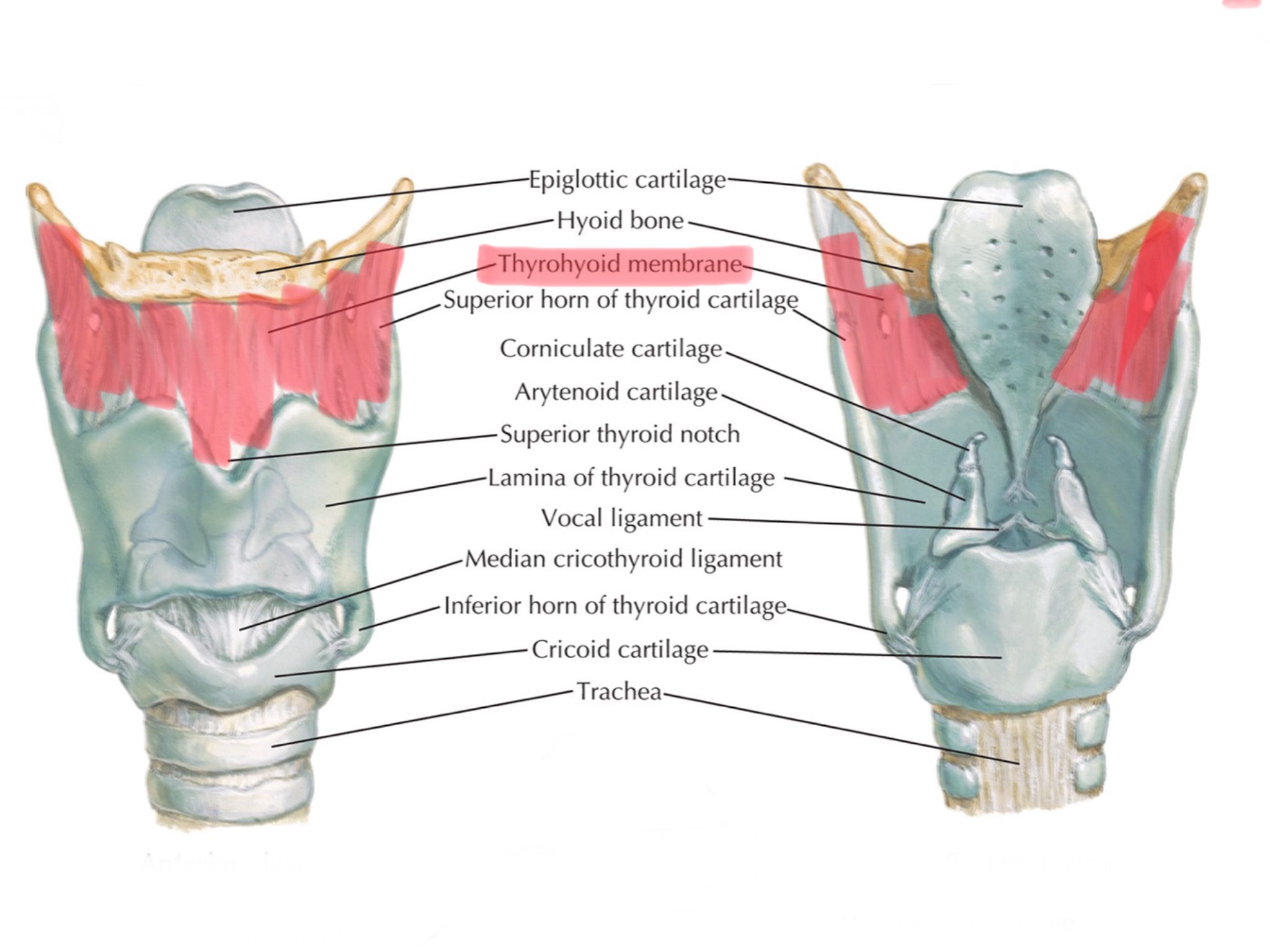
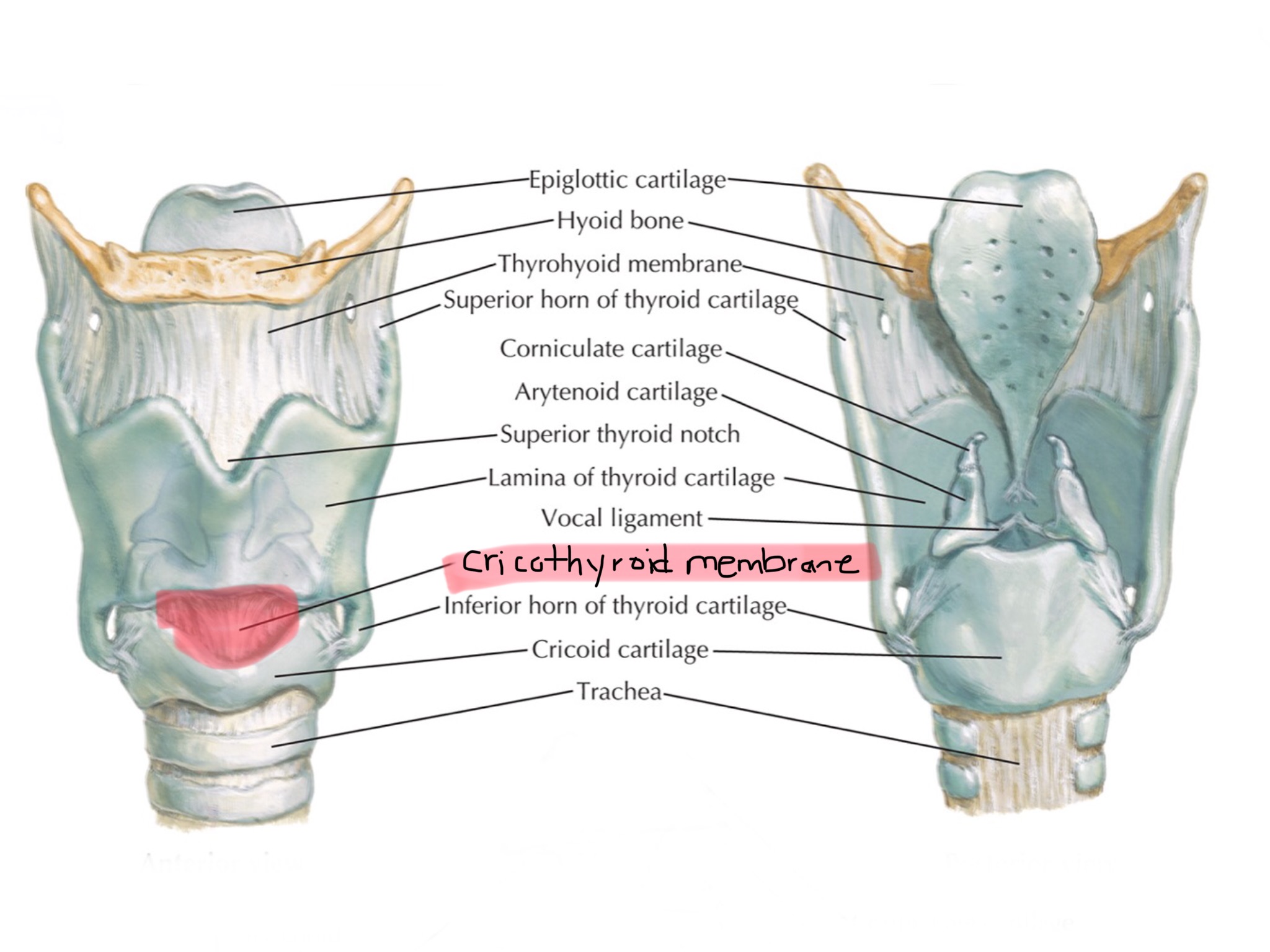
Identify the thyrohyoid membrane.
Identify the cricothyroid membrane.
Identify the glottis.
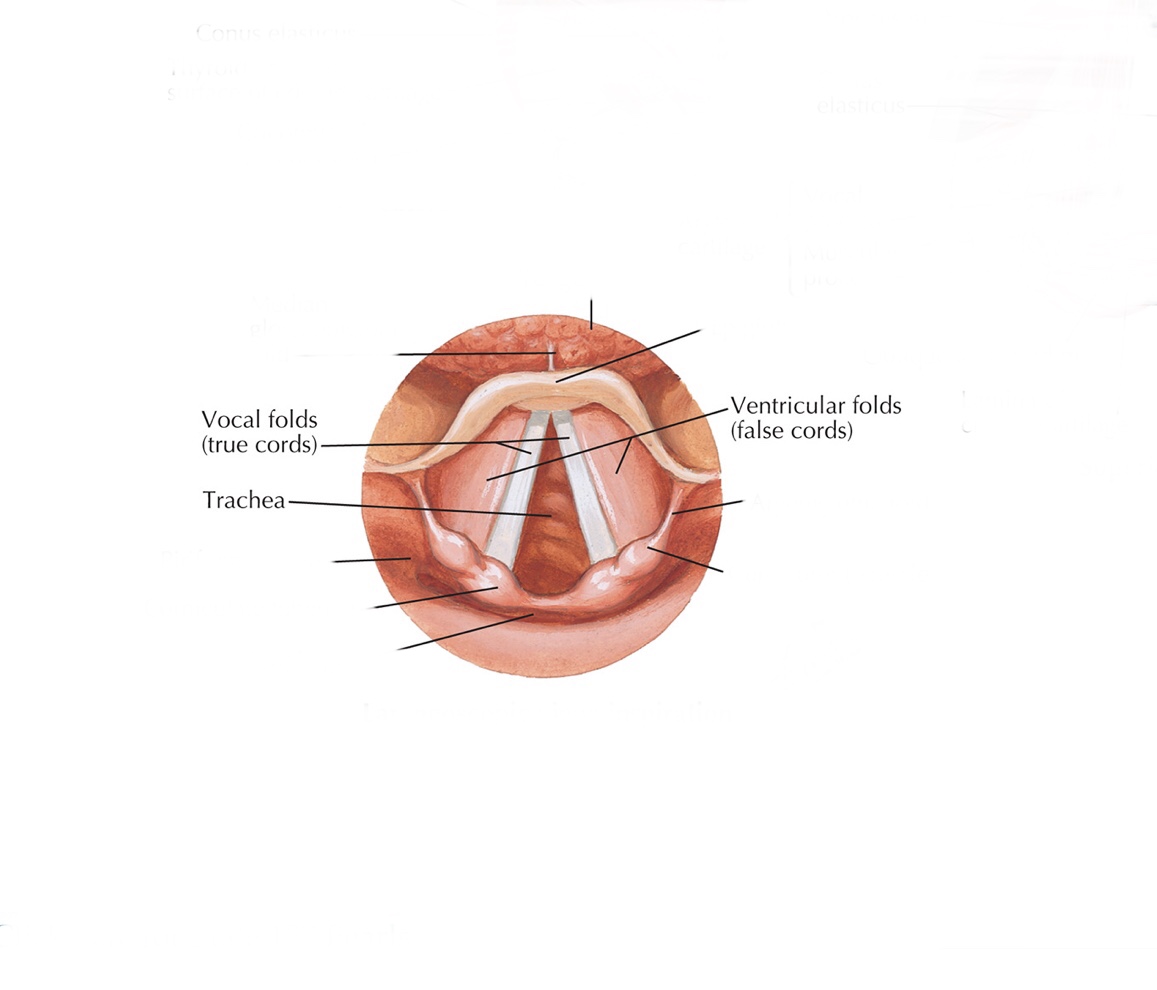
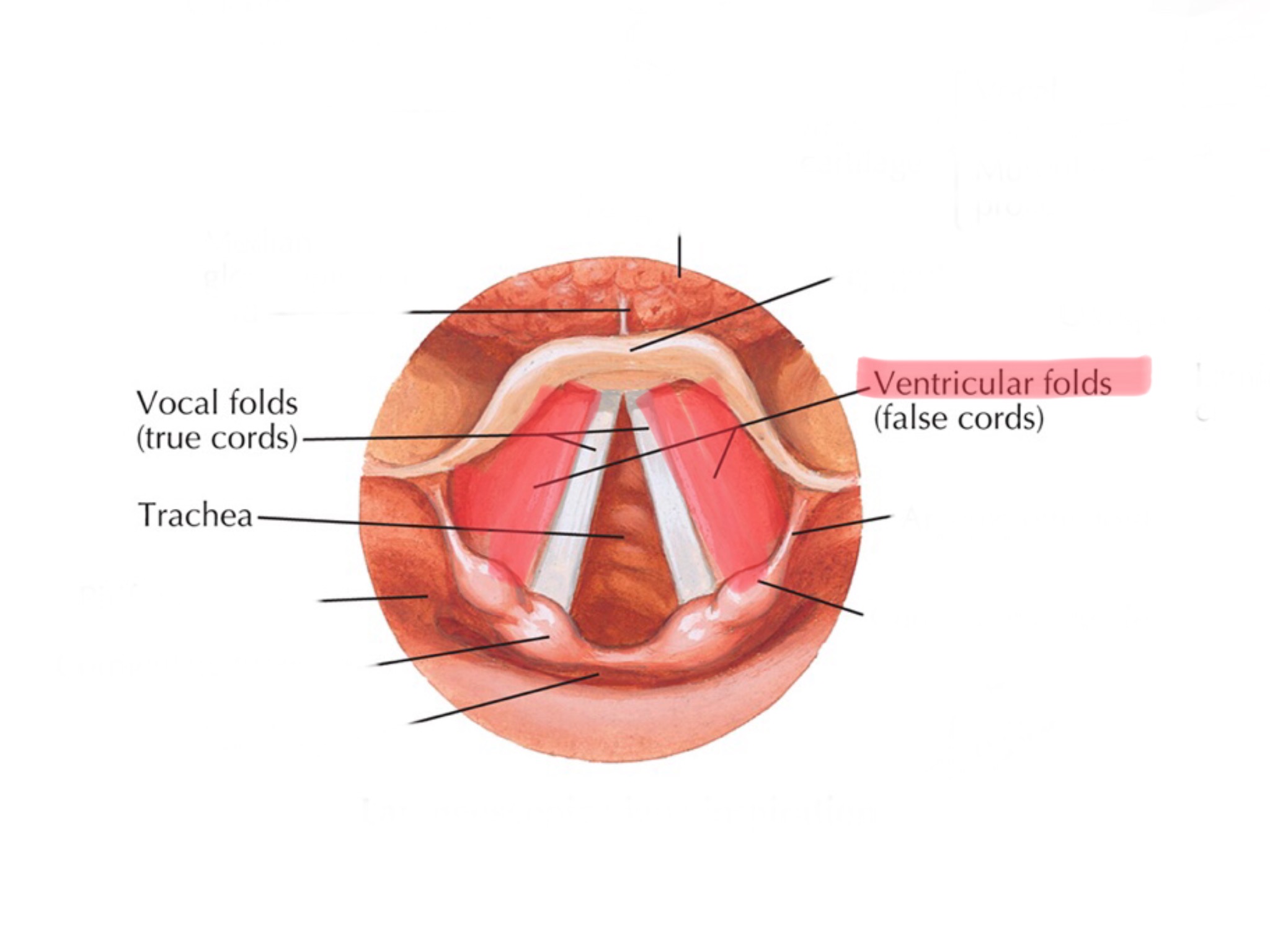
Identify the vestibular folds.
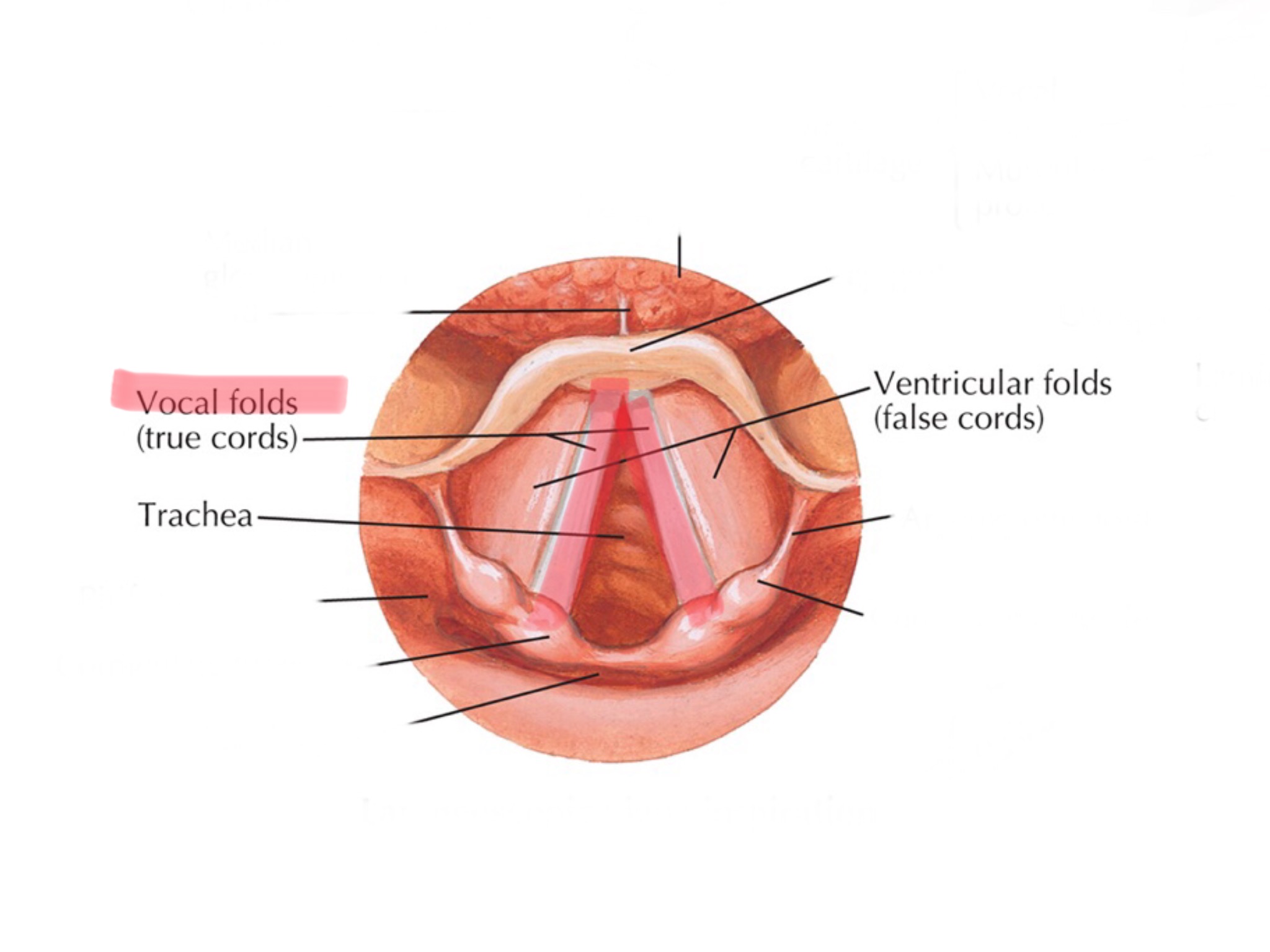
Identify the vocal folds.
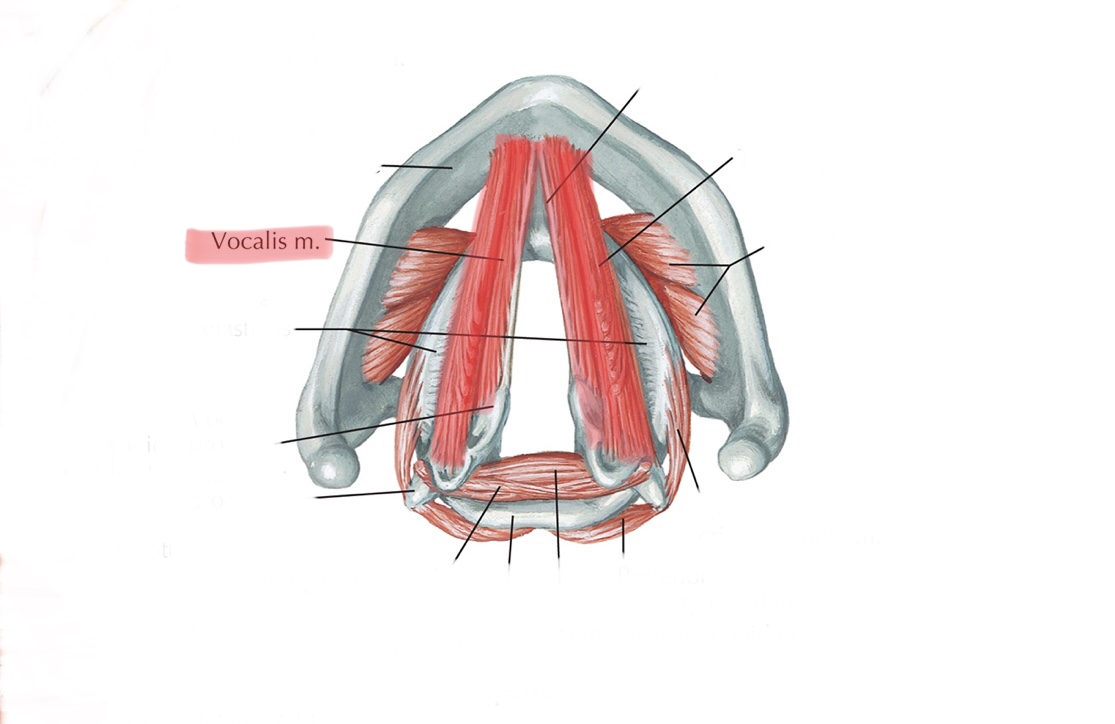
Identify the vocalis muscle.
Identify the trachea.
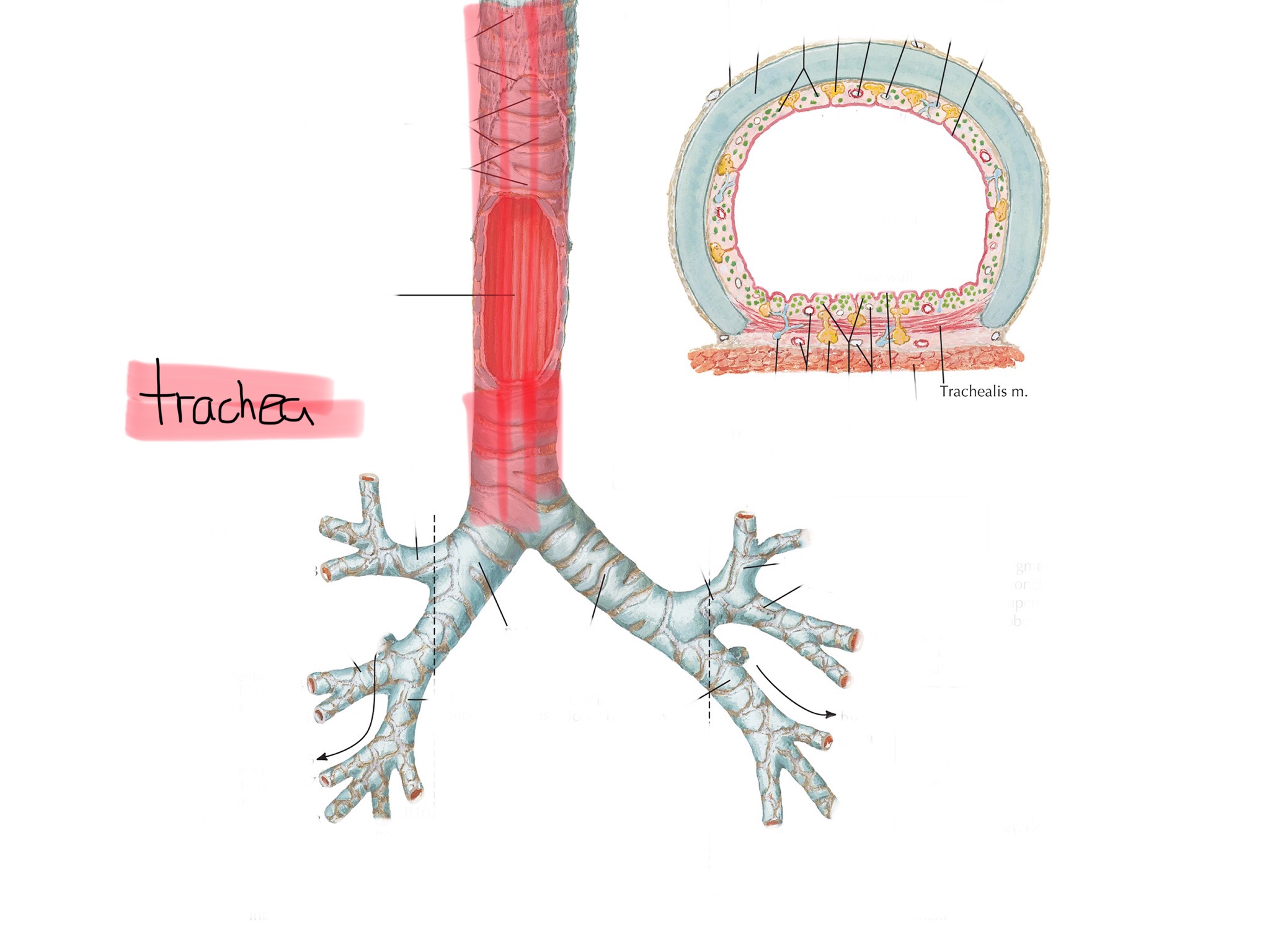
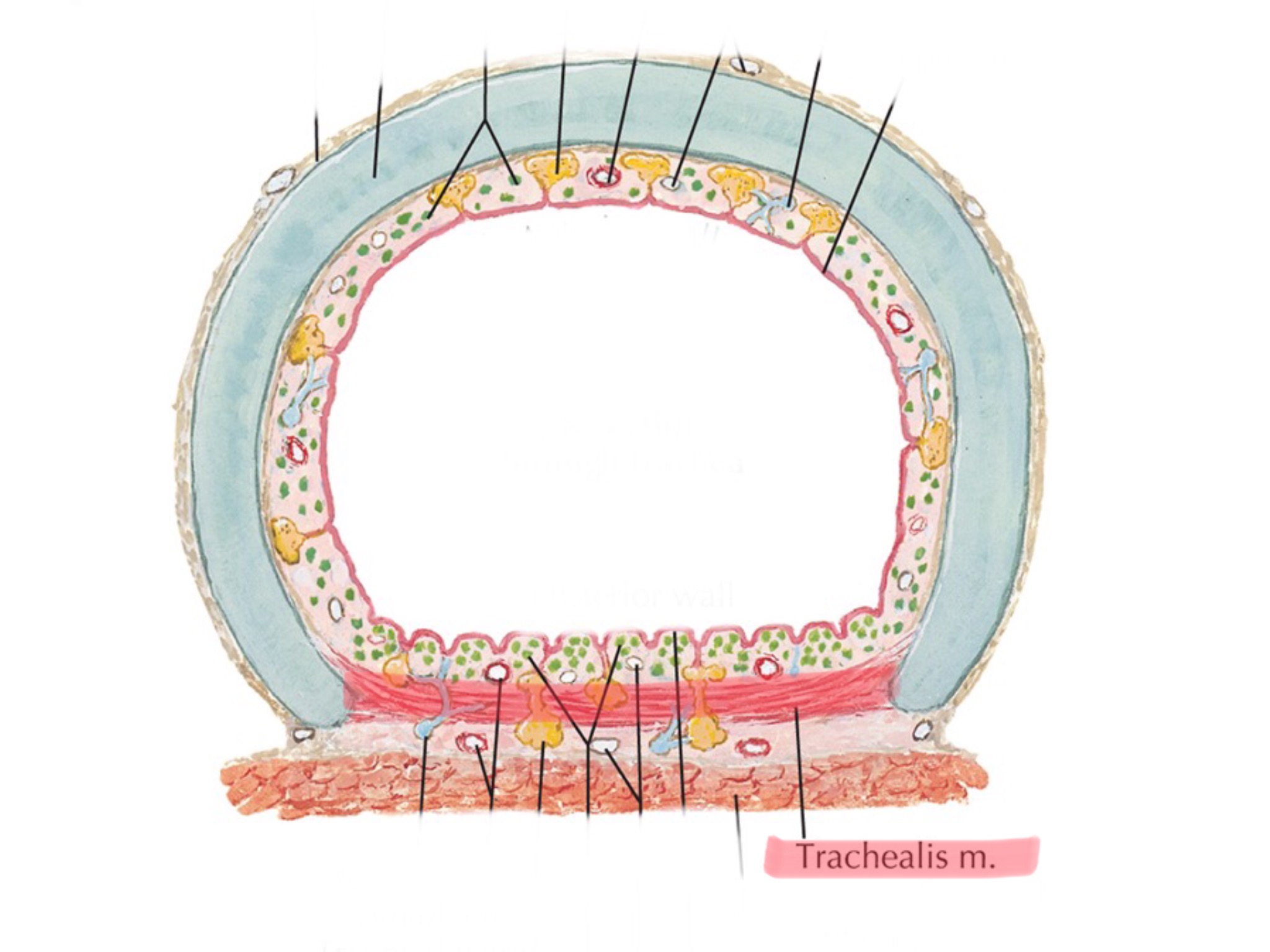
Identify the trachealis muscle.
Identify the carina.
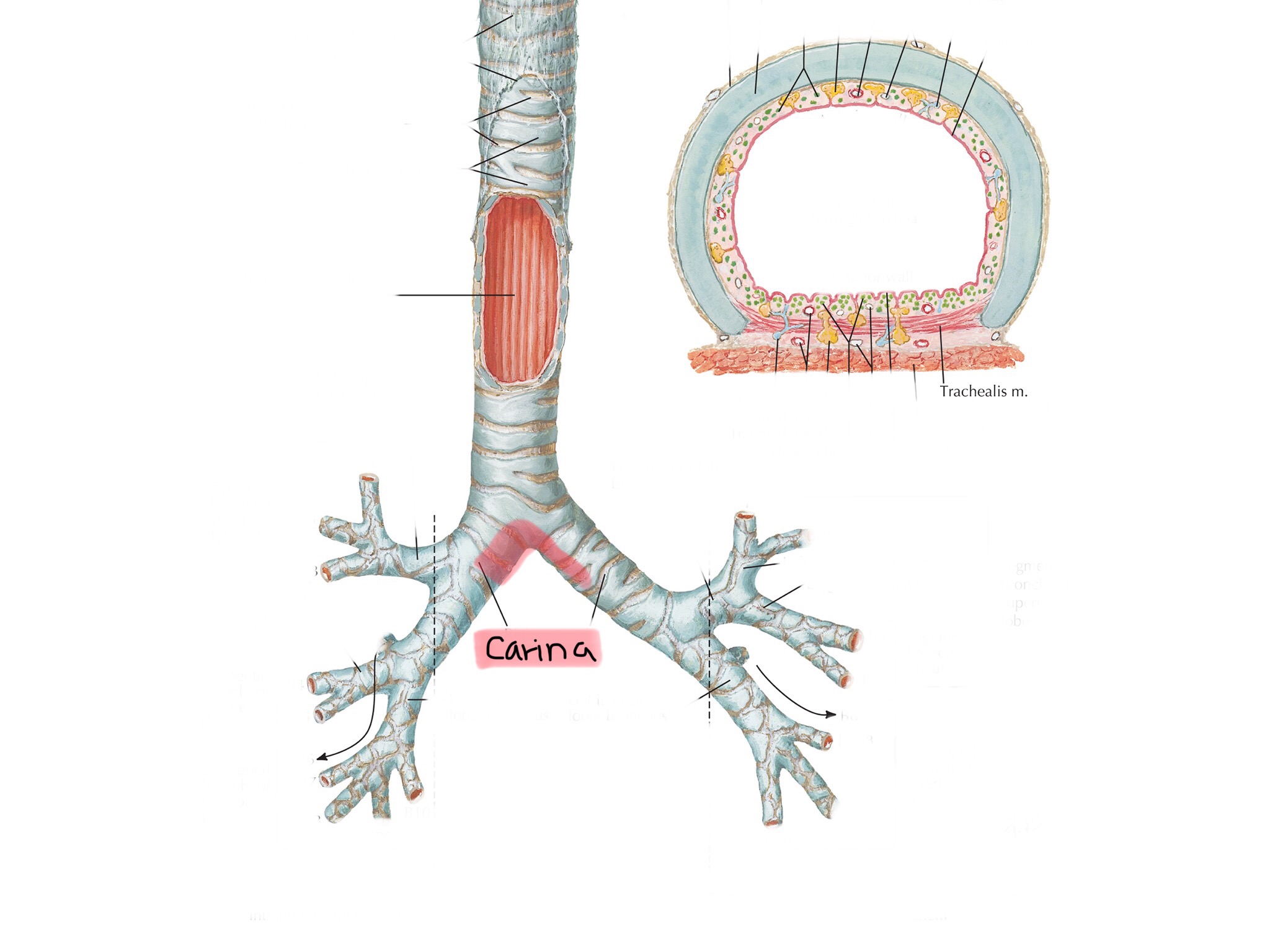
Identify the primary bronchi.
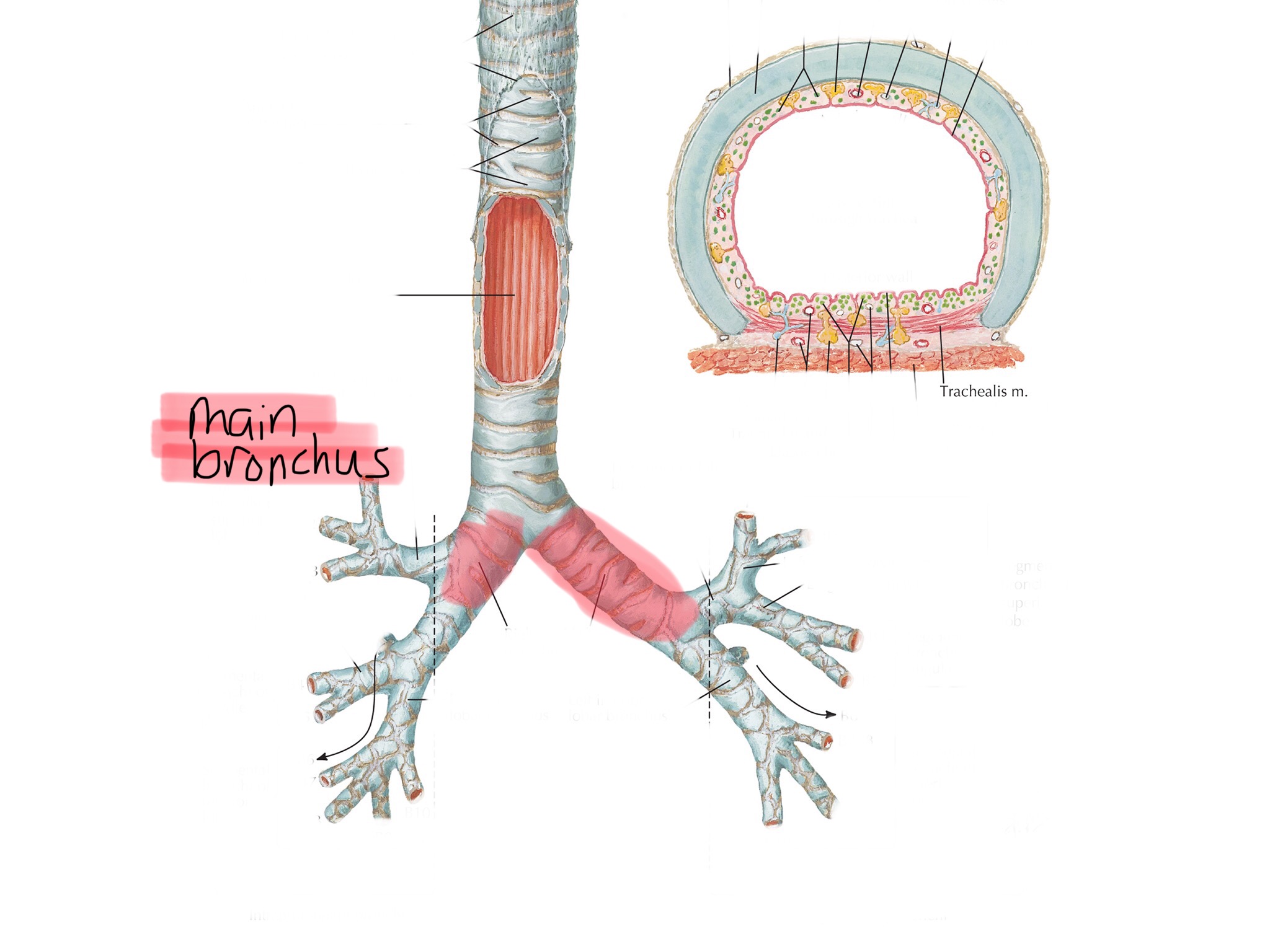
Identify the secondary bronchi.
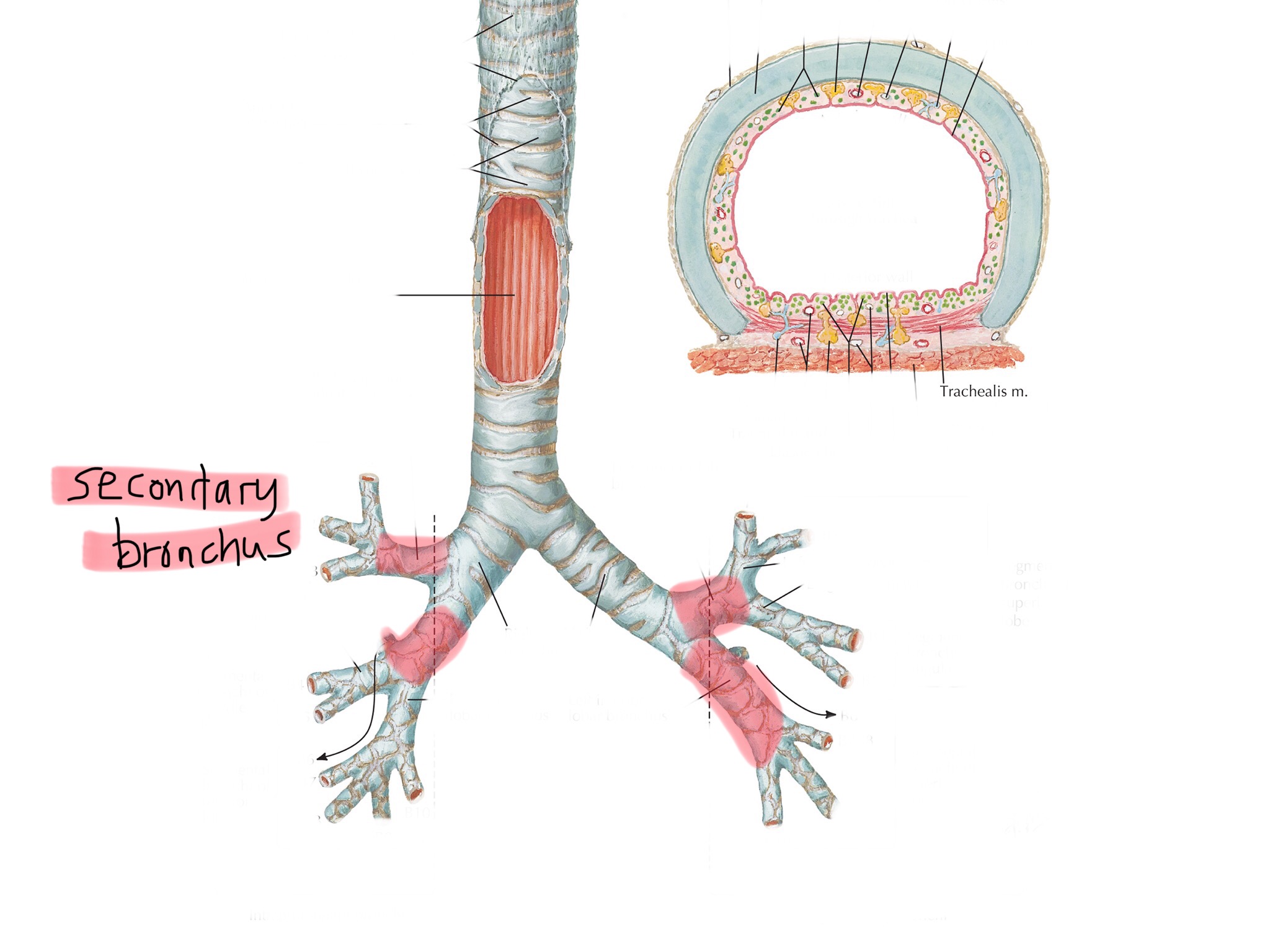
Identify the tertiary bronchi.
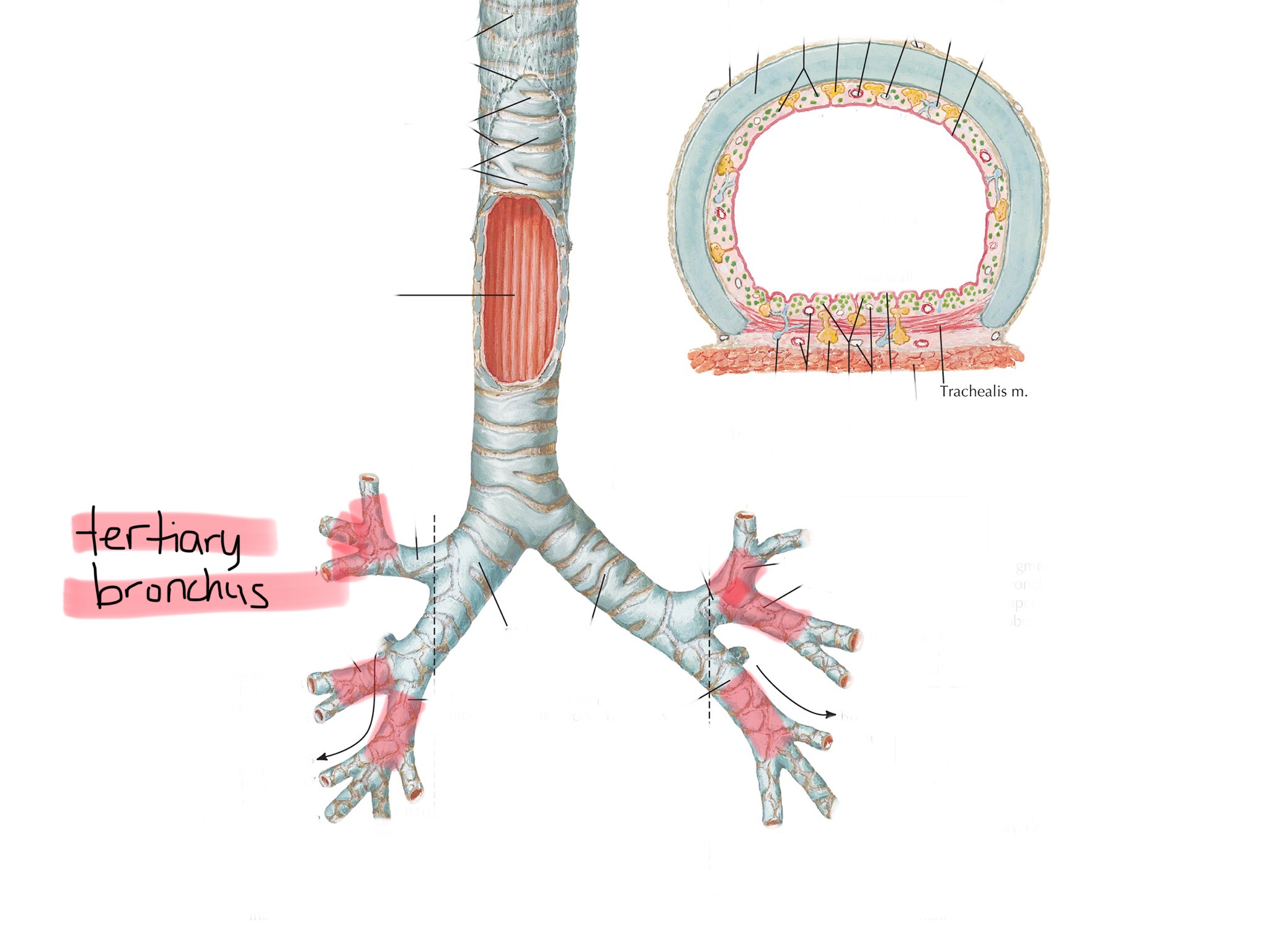
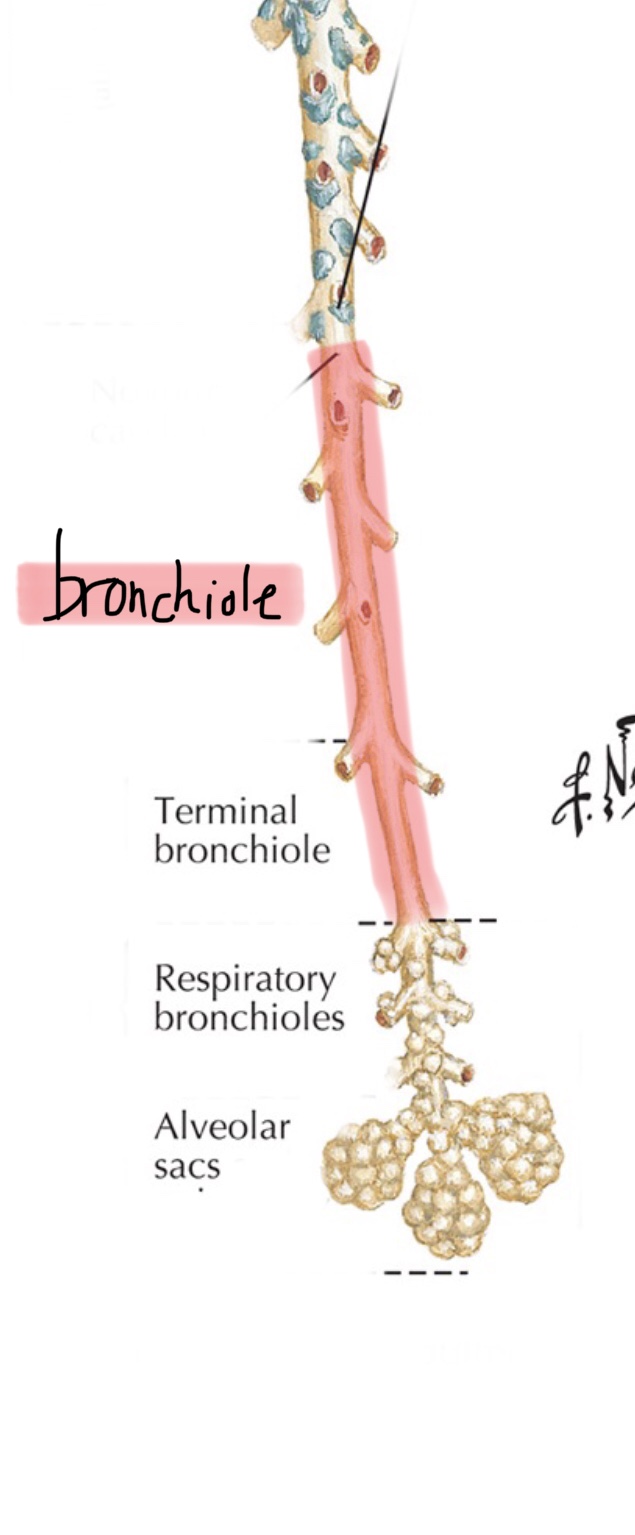
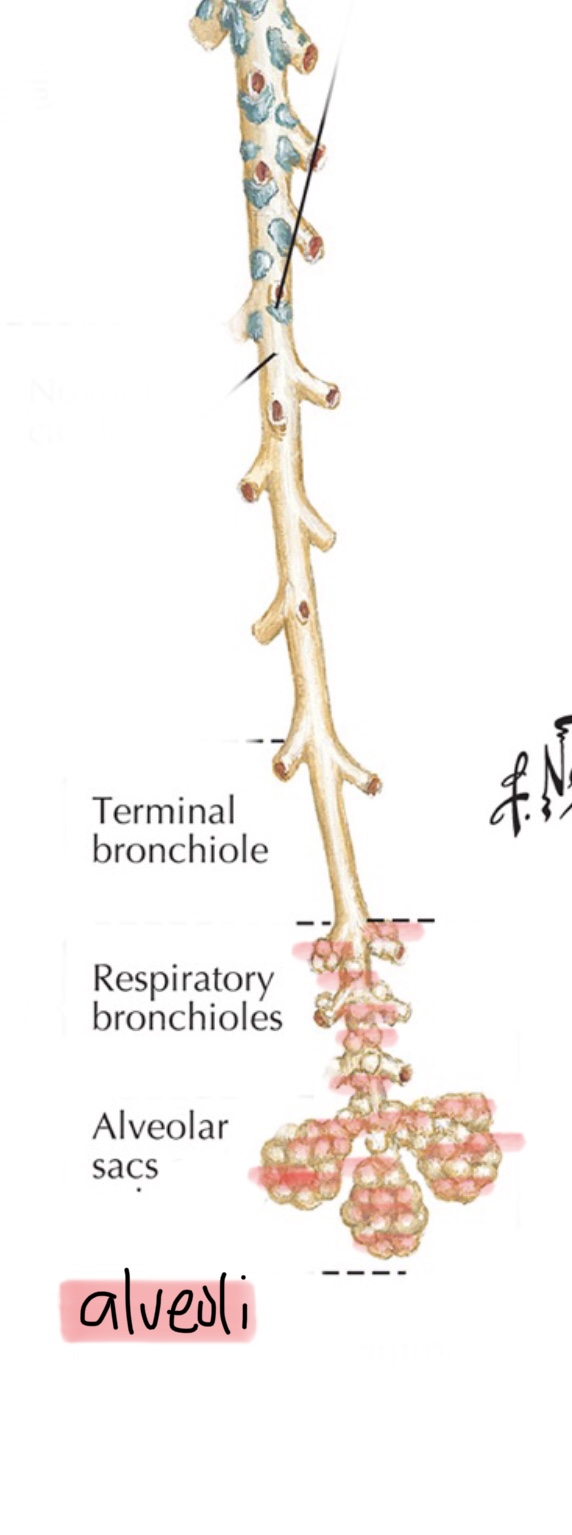
Identify the bronchioles.
Identify the tertiary bronchioles.
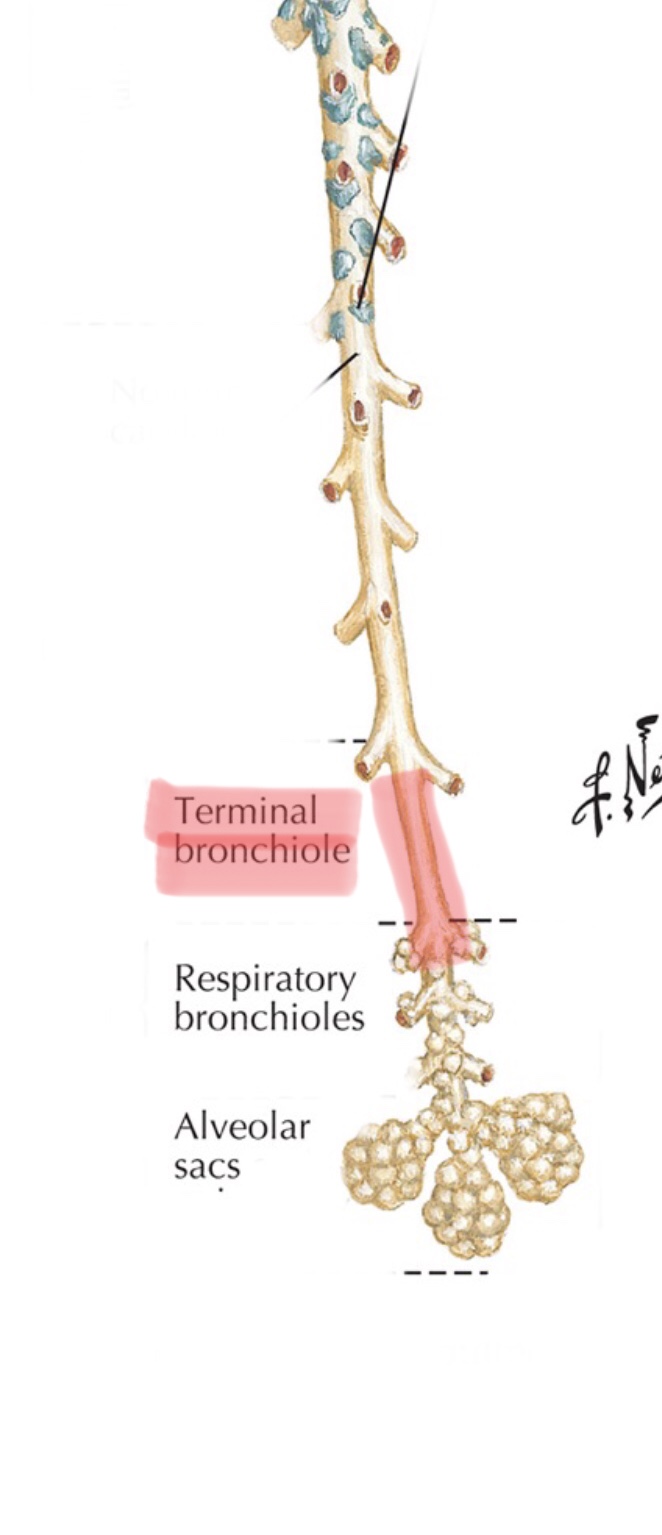
Identify the respiratory bronchioles.
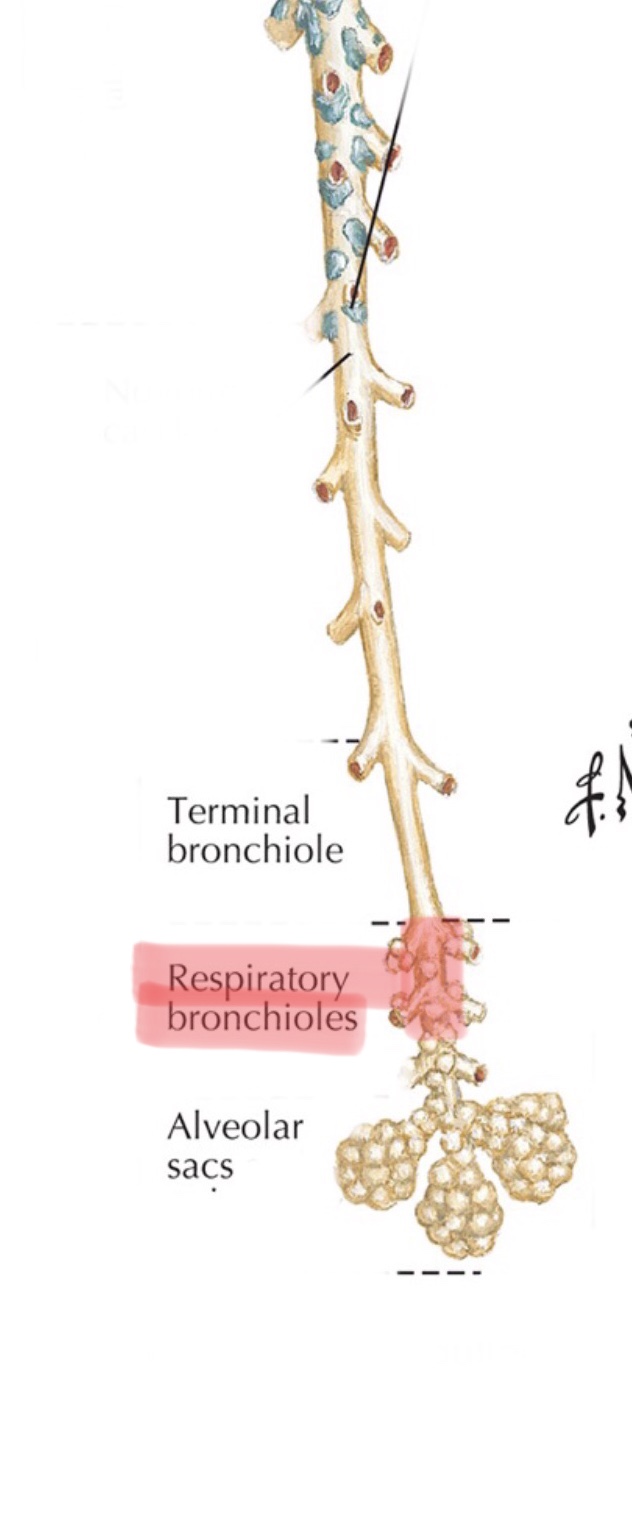
Identify the alveolar ducts.
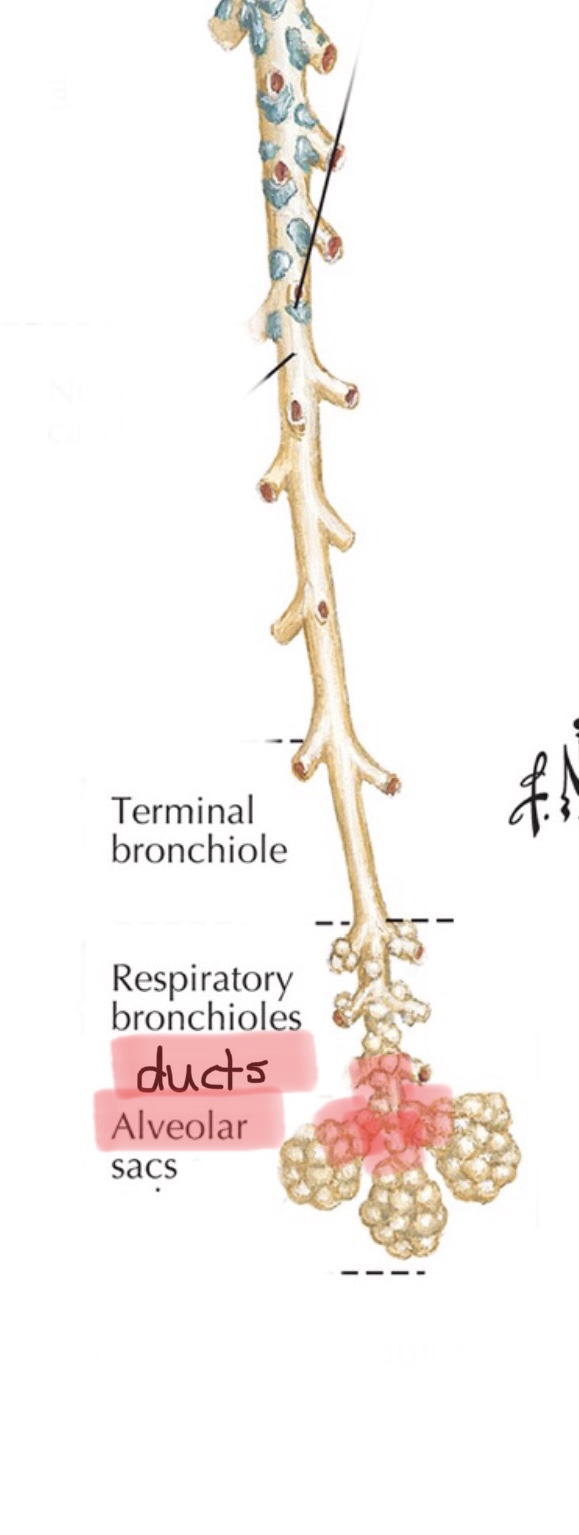
Identify the alveolar sacs.
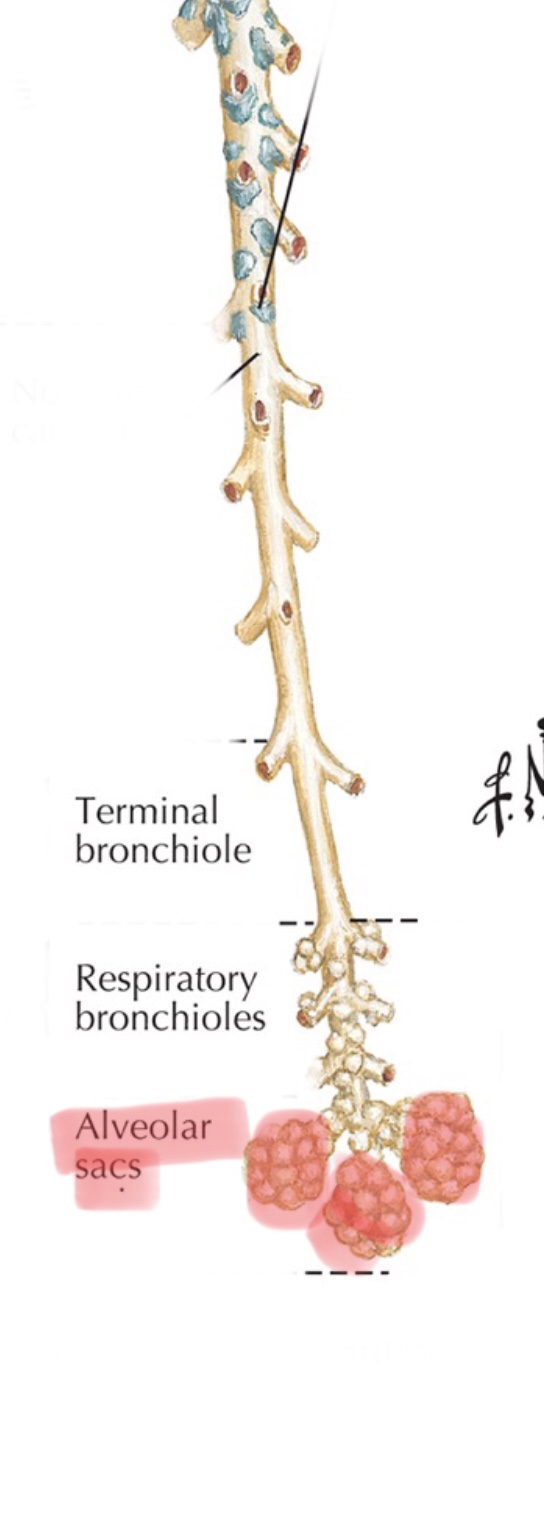
Identify the alveoli.
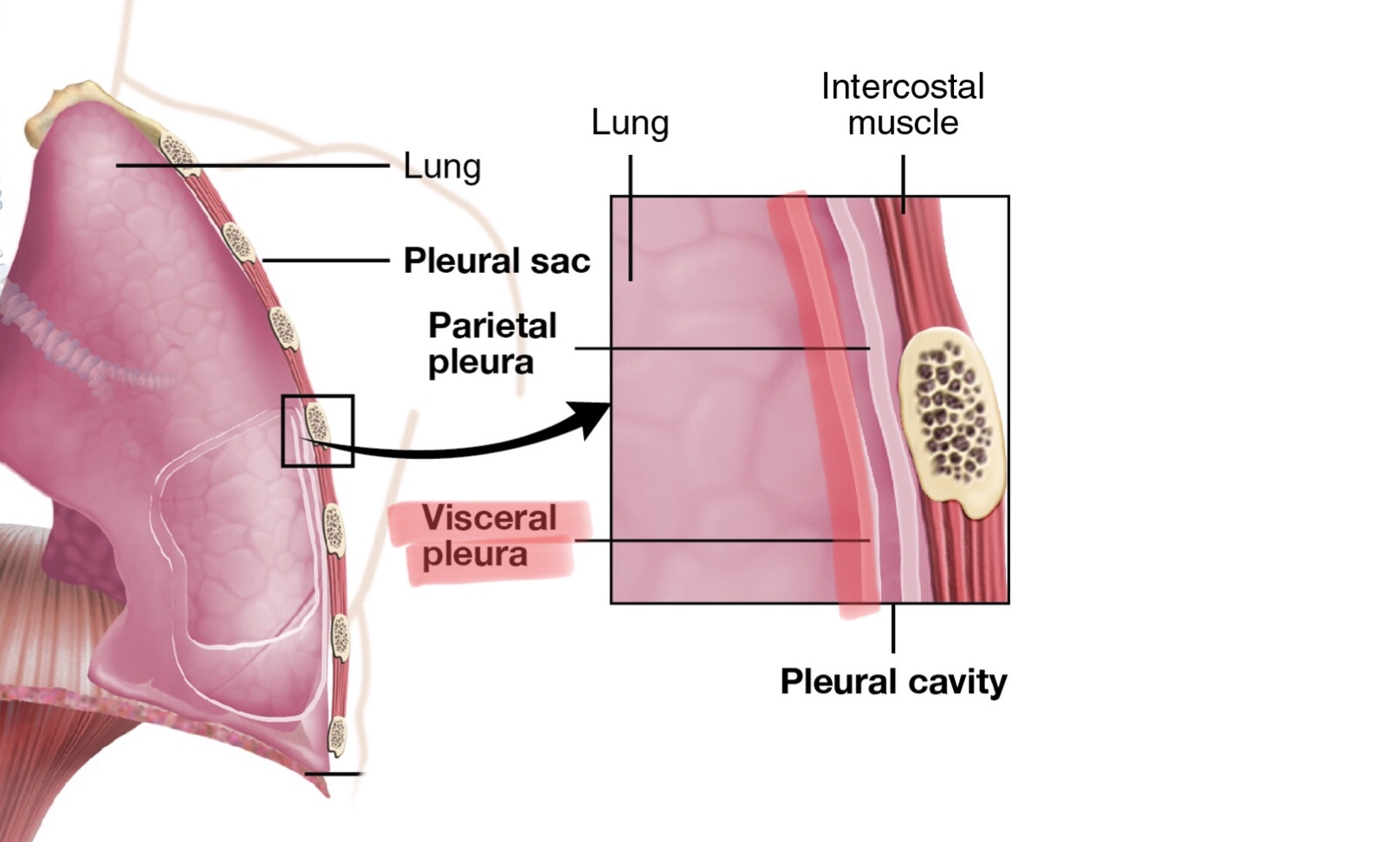
Identify the parietal pleura.
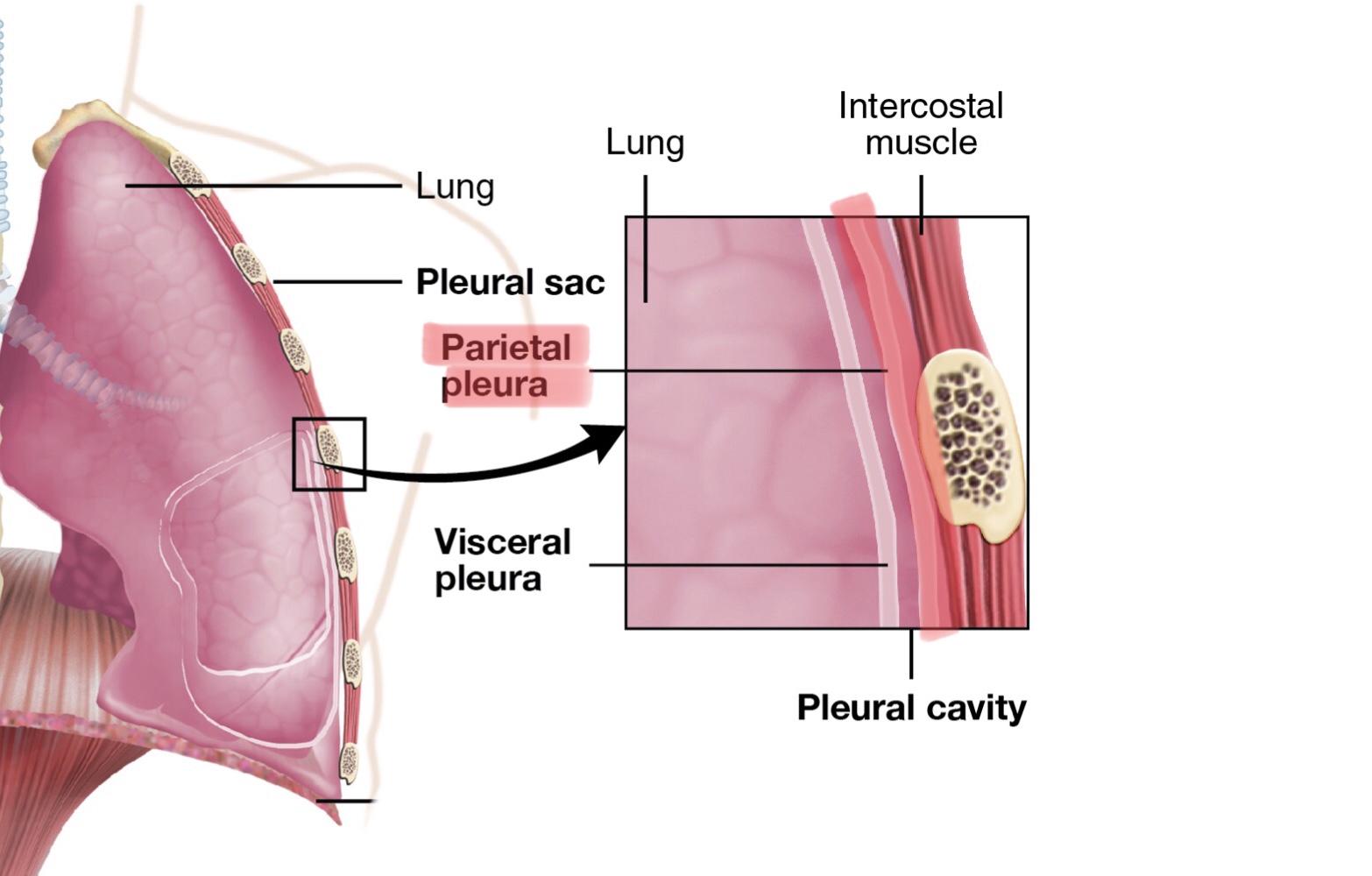
Identify the visceral pleura.
Identify the superior lobe of the right lung.
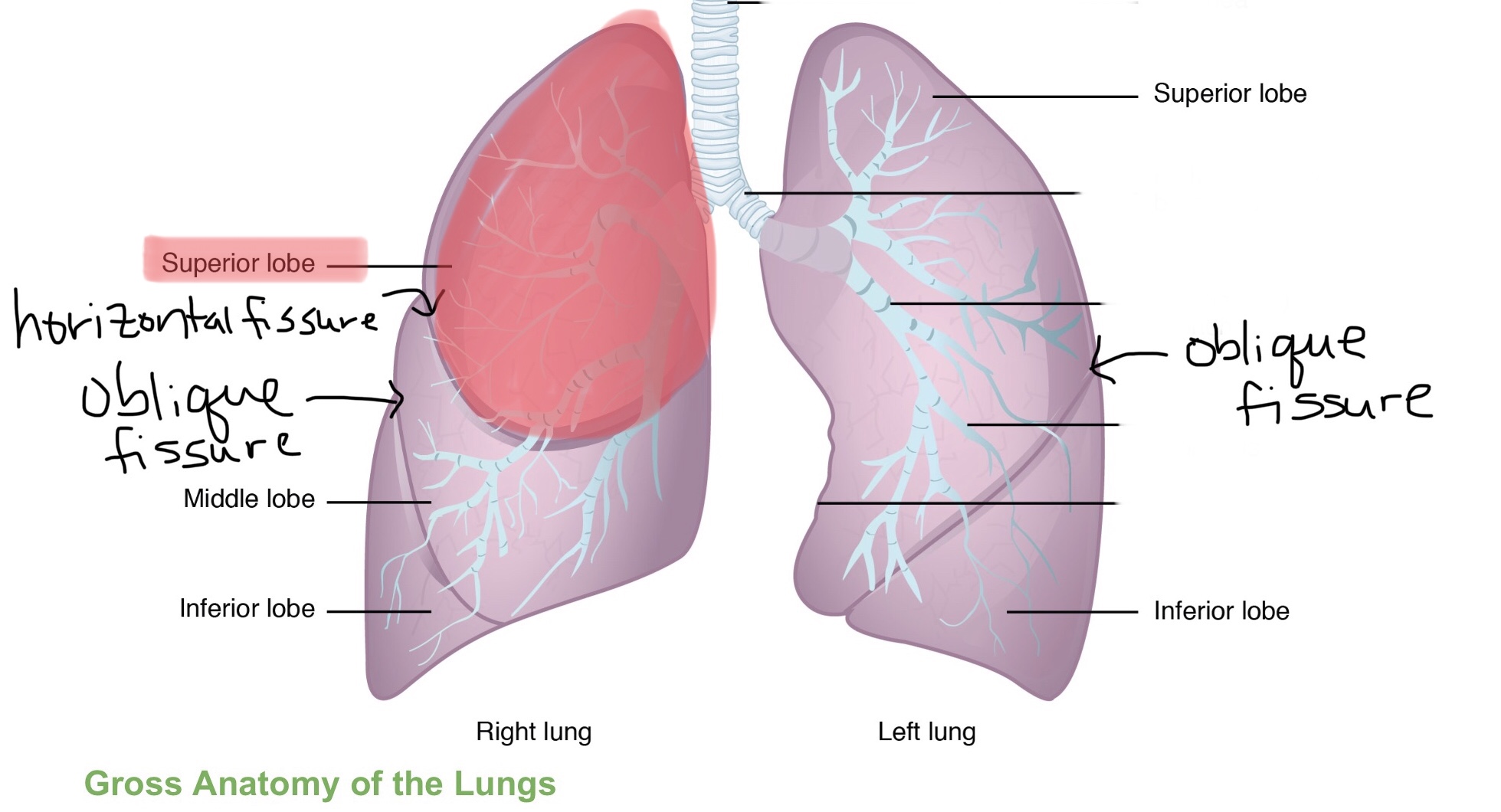
Identify the middle lobe of the right lung.
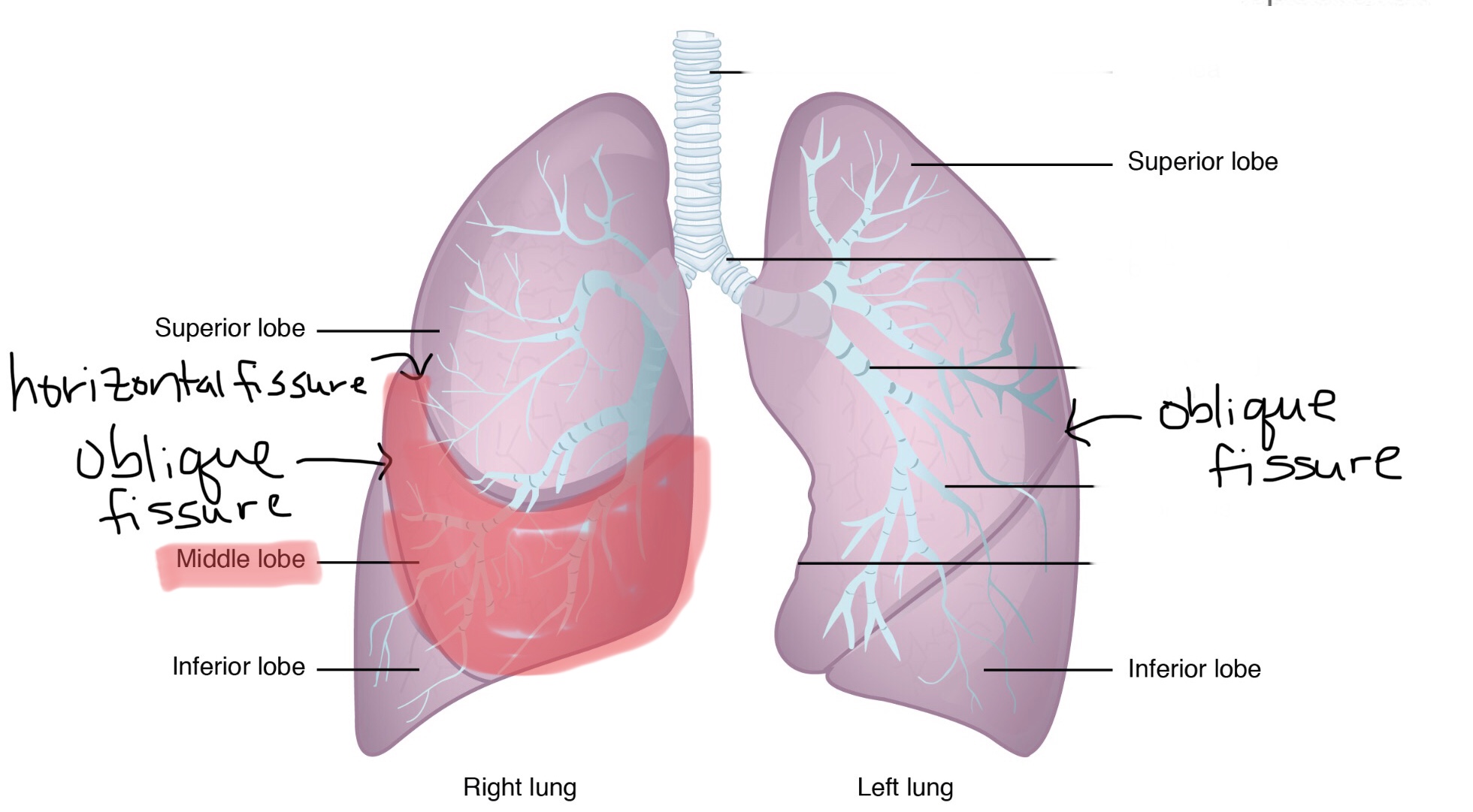
Identify the inferior lobe of the right lung.
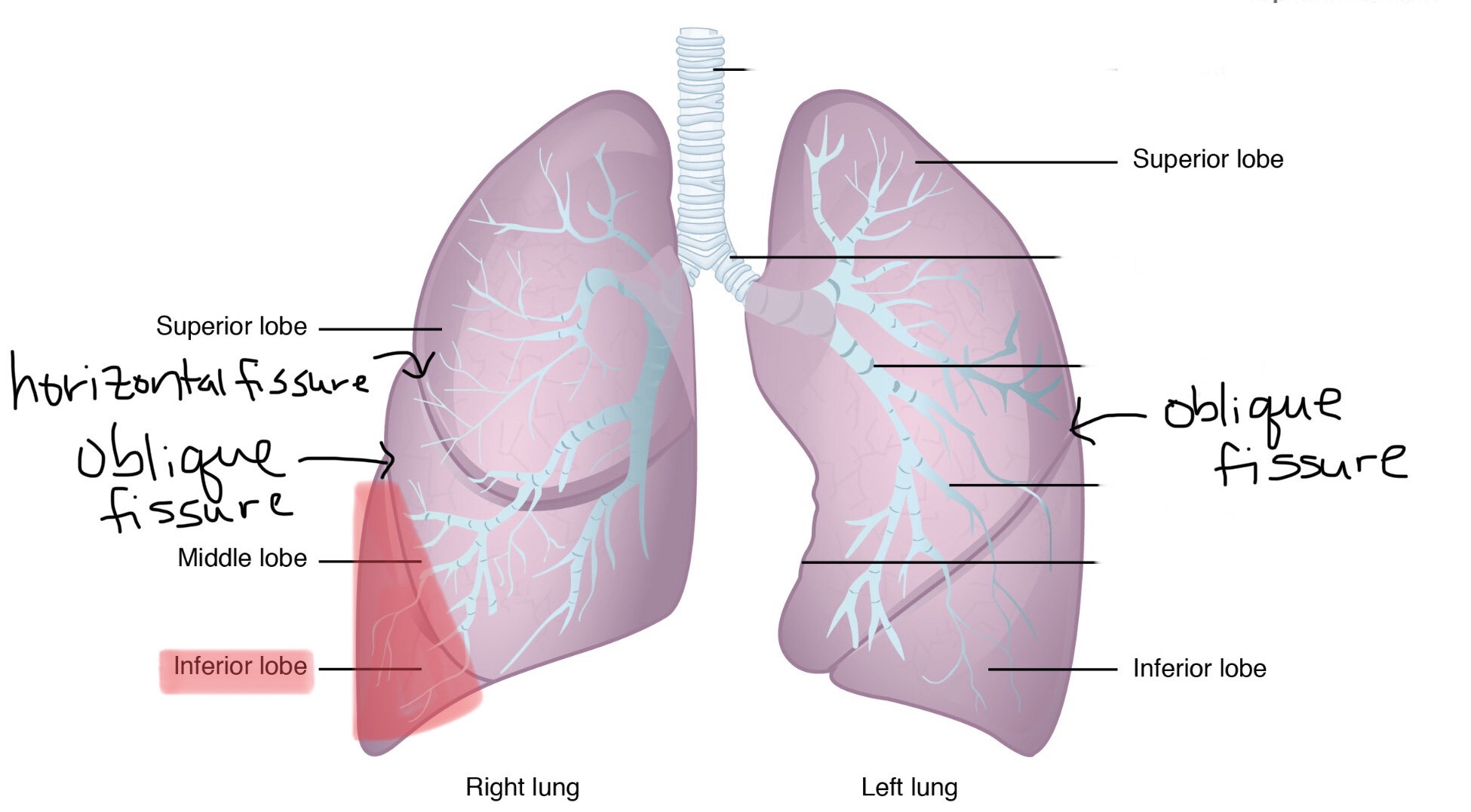
Identify the superior lobe of the left lung.
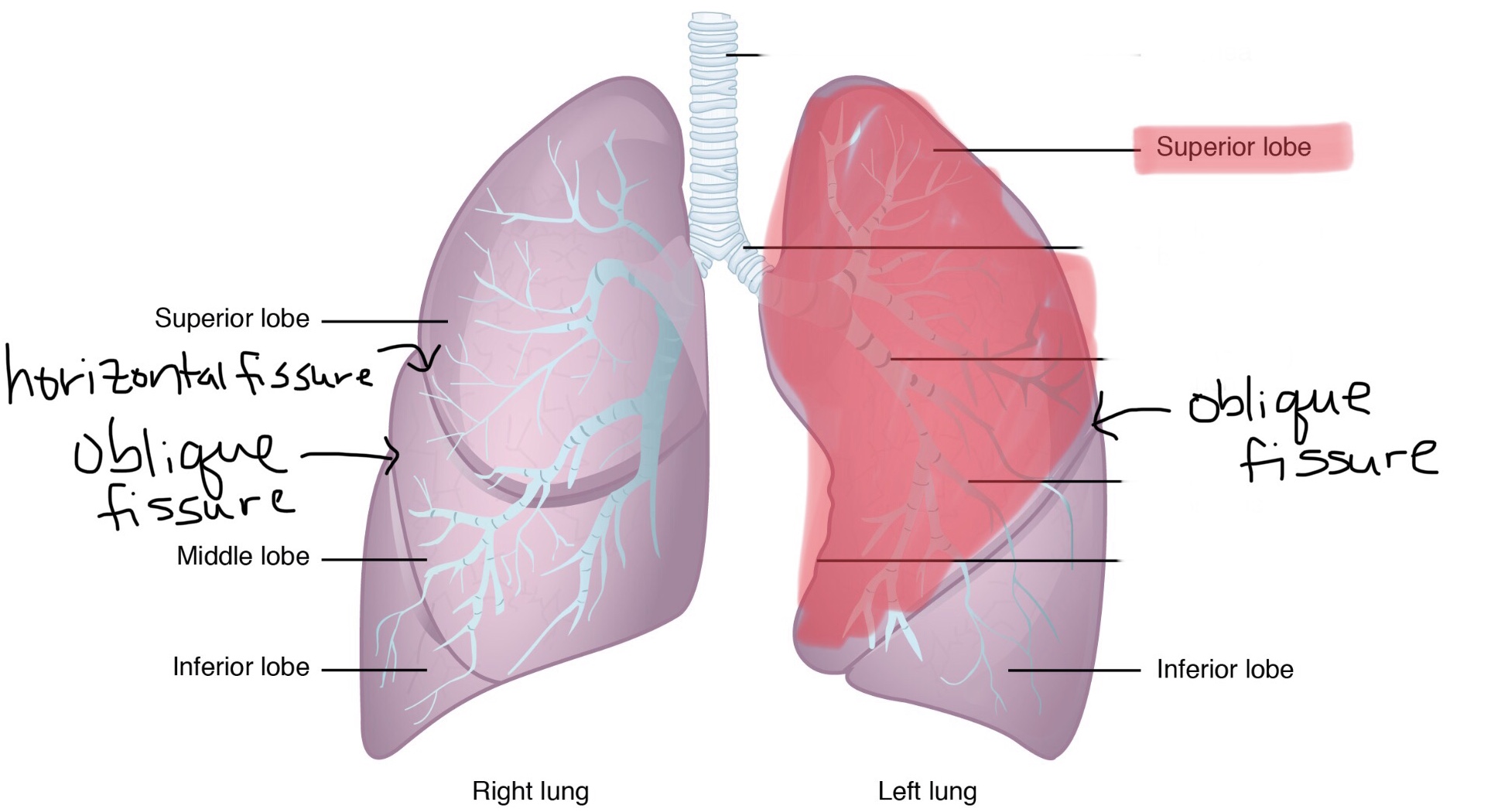
Identify the inferior lobe of the left lung.
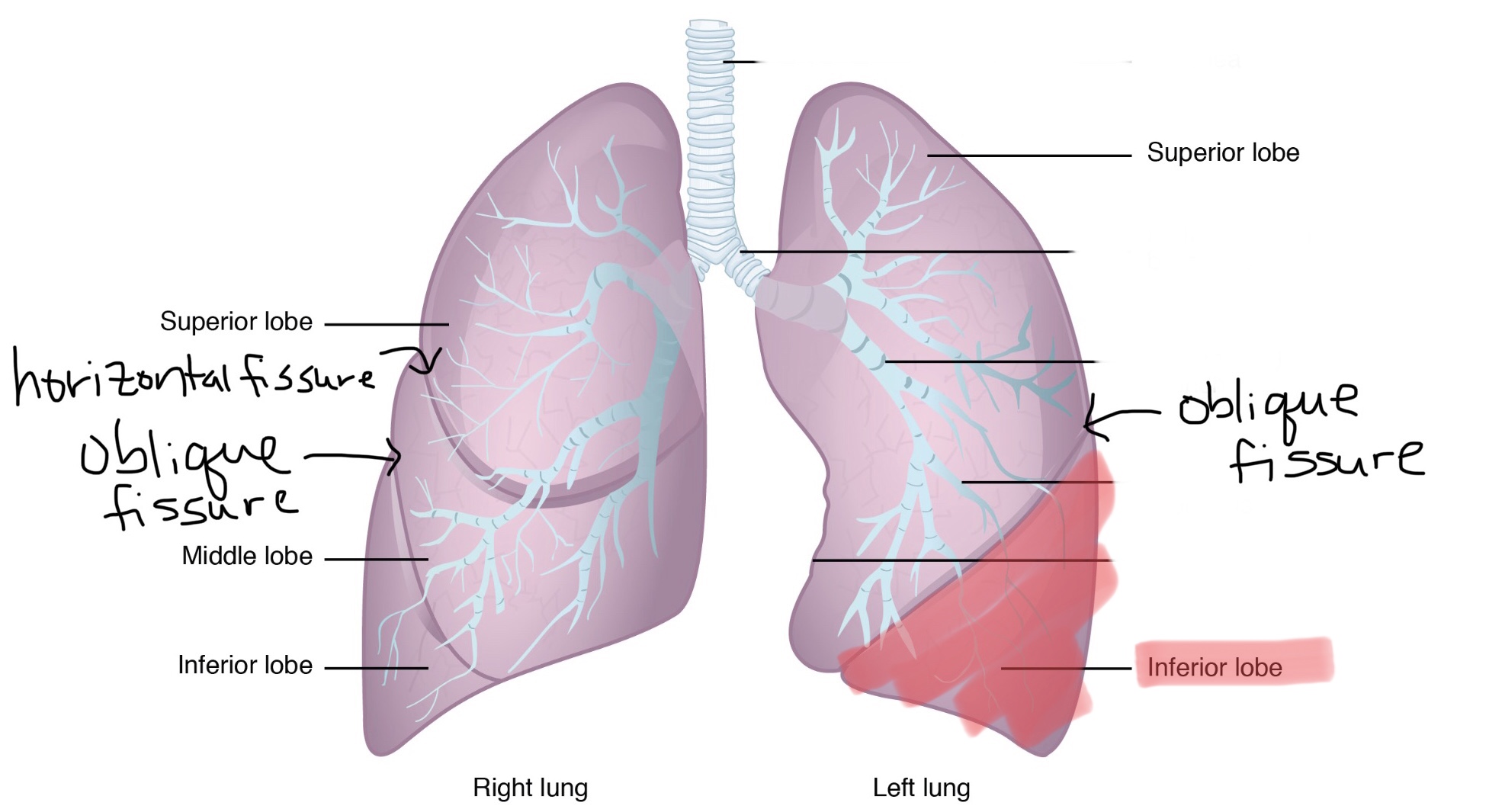
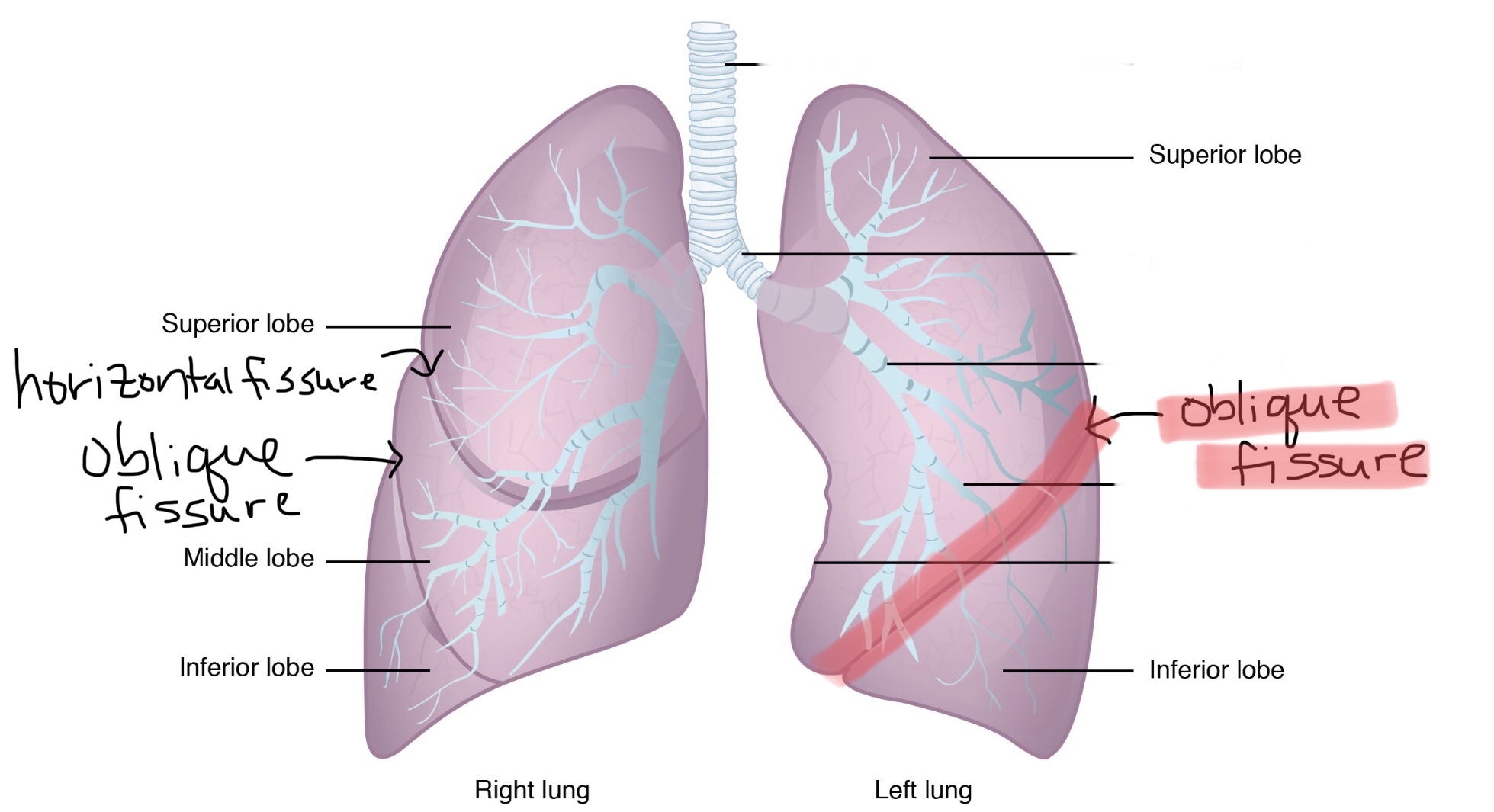
Identify the oblique fissure of the right lung.
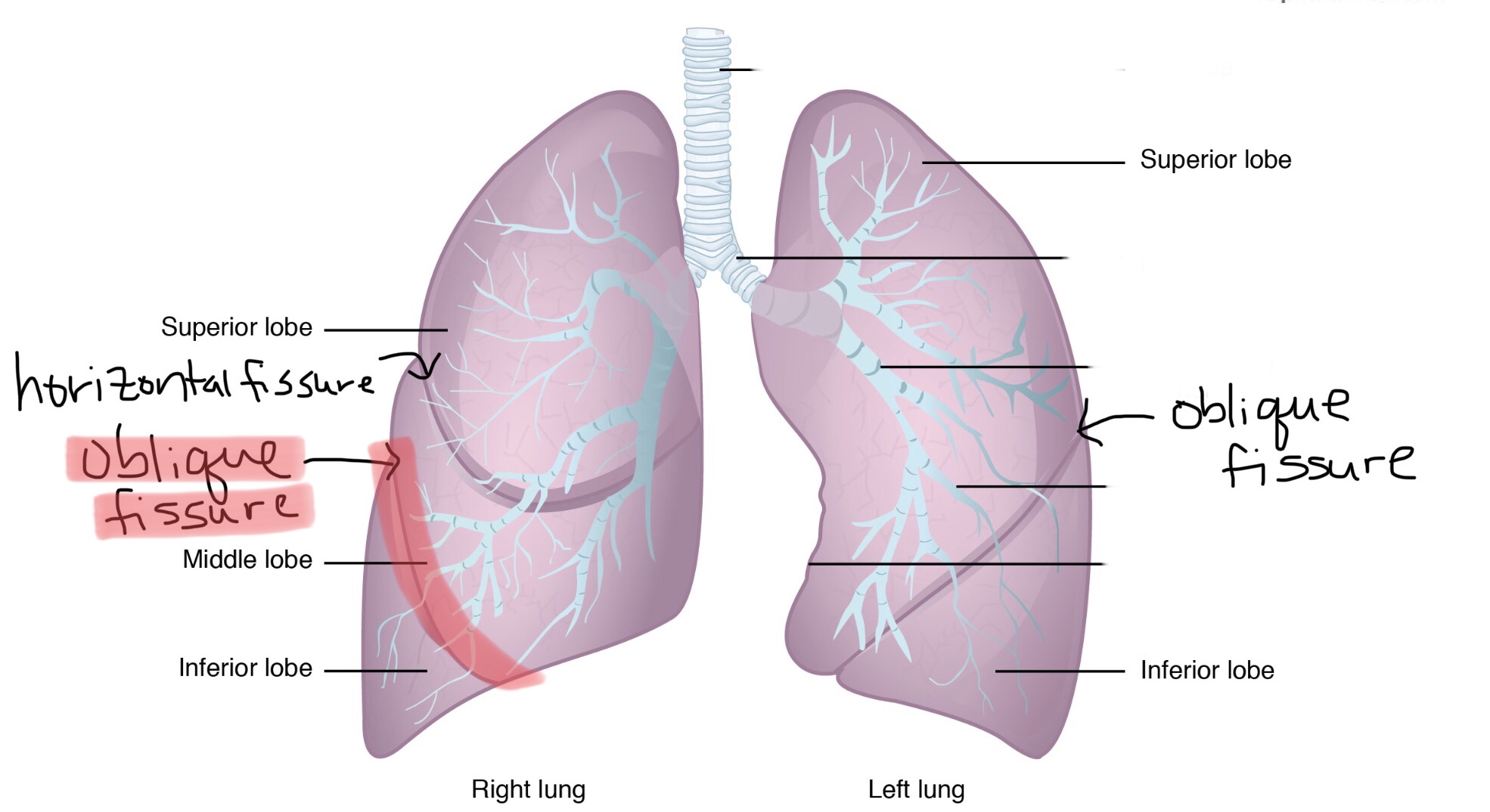
Identify the horizontal fissure of the right lung.
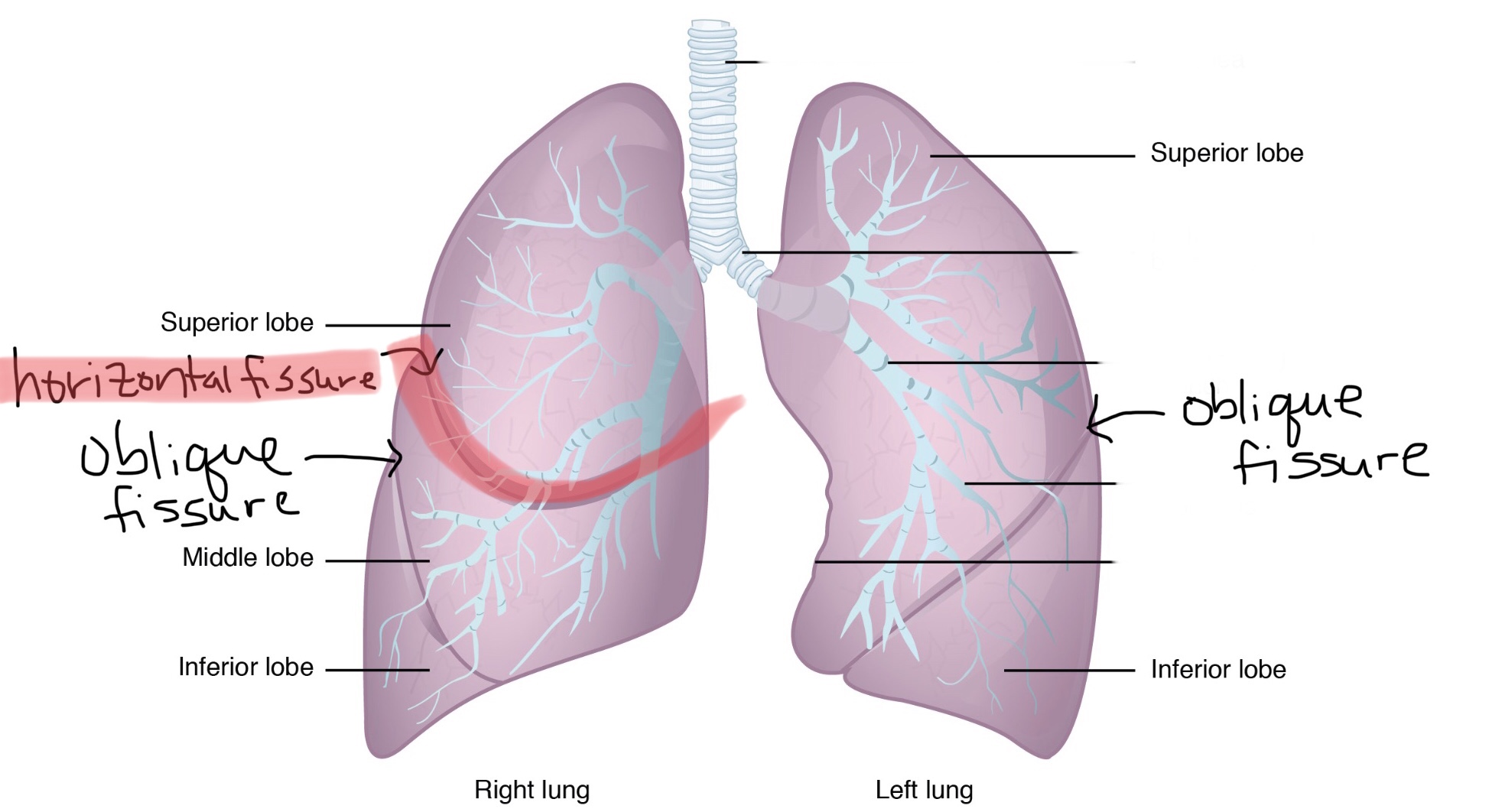
Identify the oblique fissure of the left lung.
Identify the hilum.
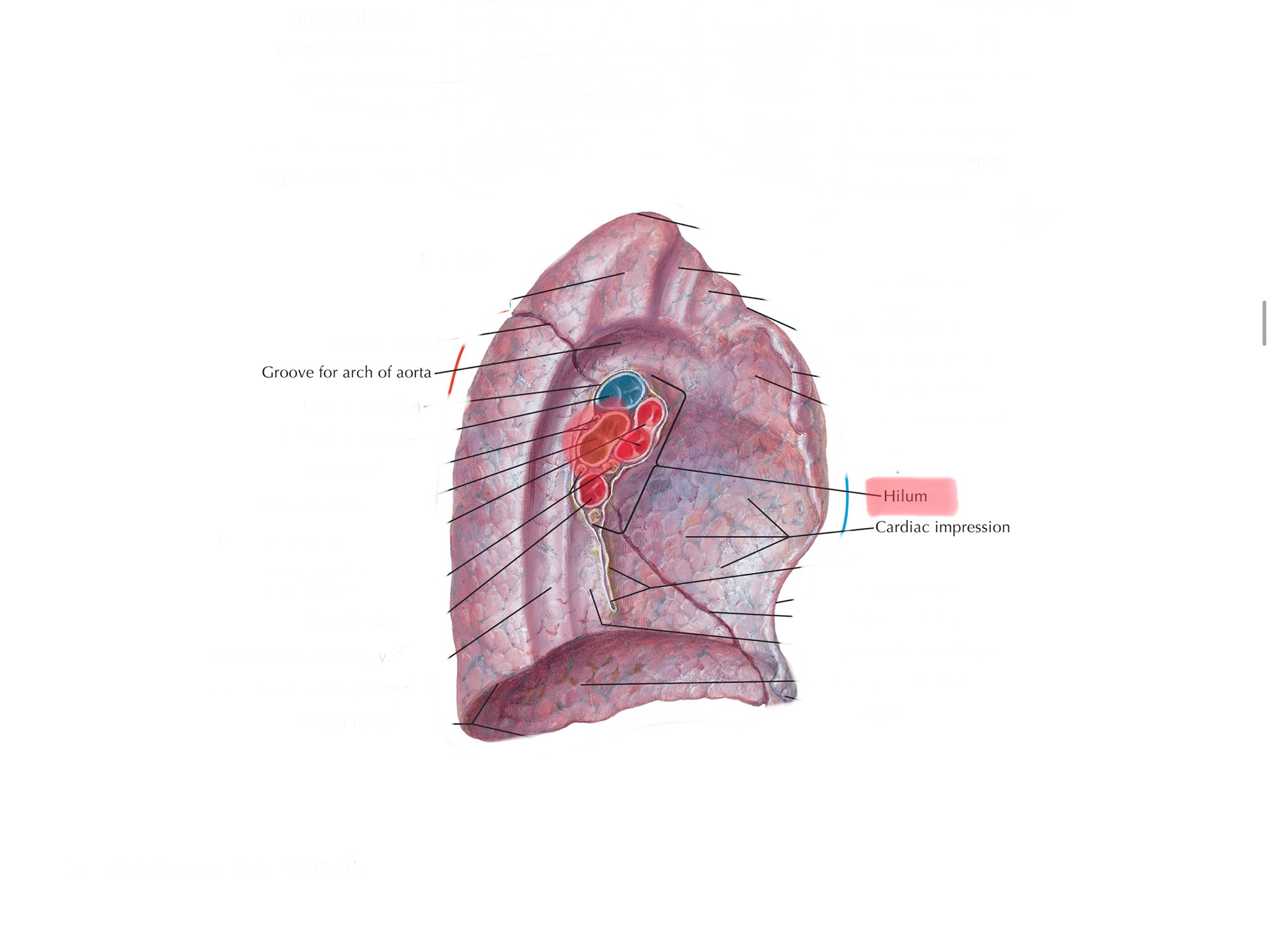
Identify the cardiac impression of the left lung.
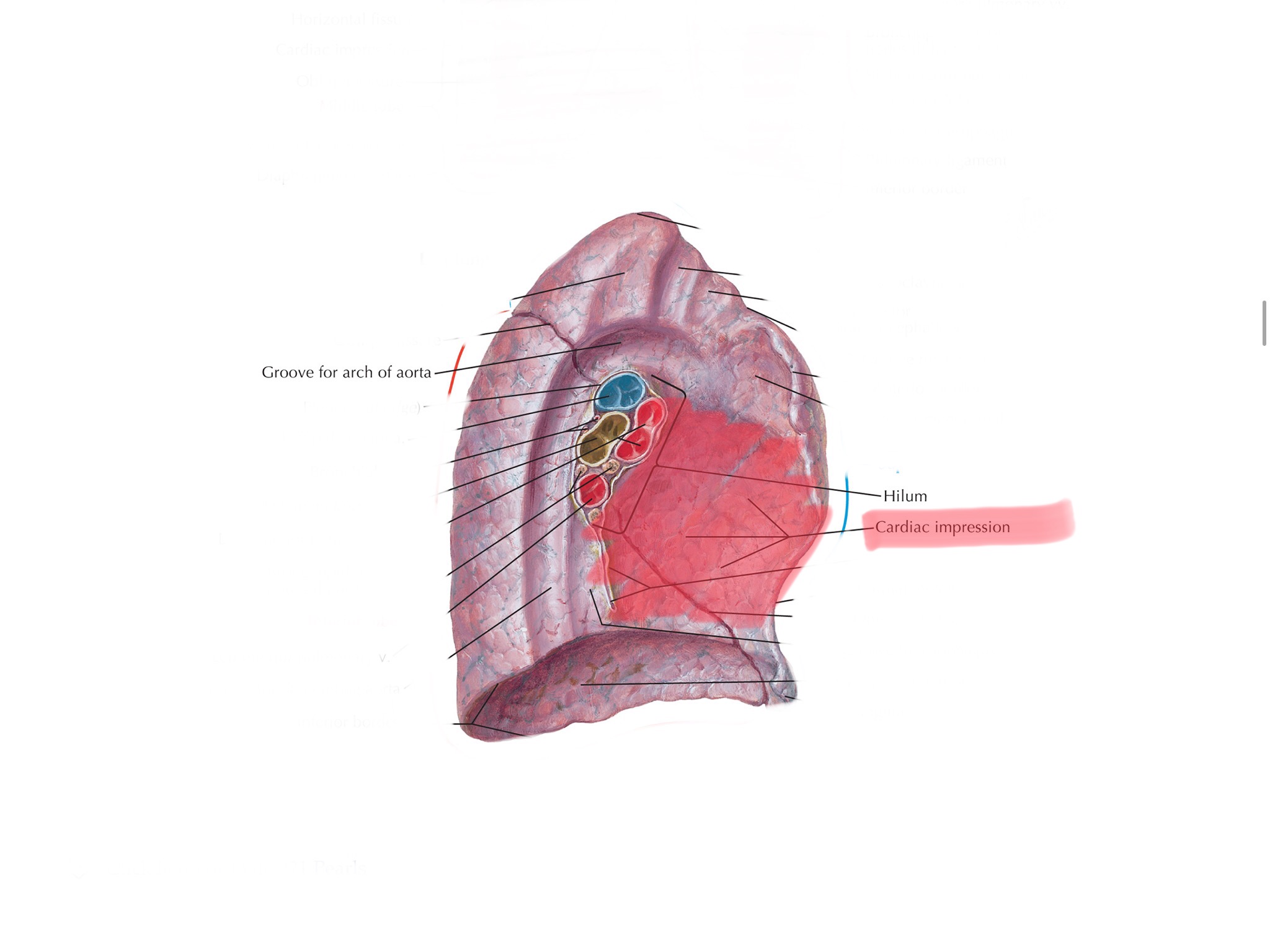
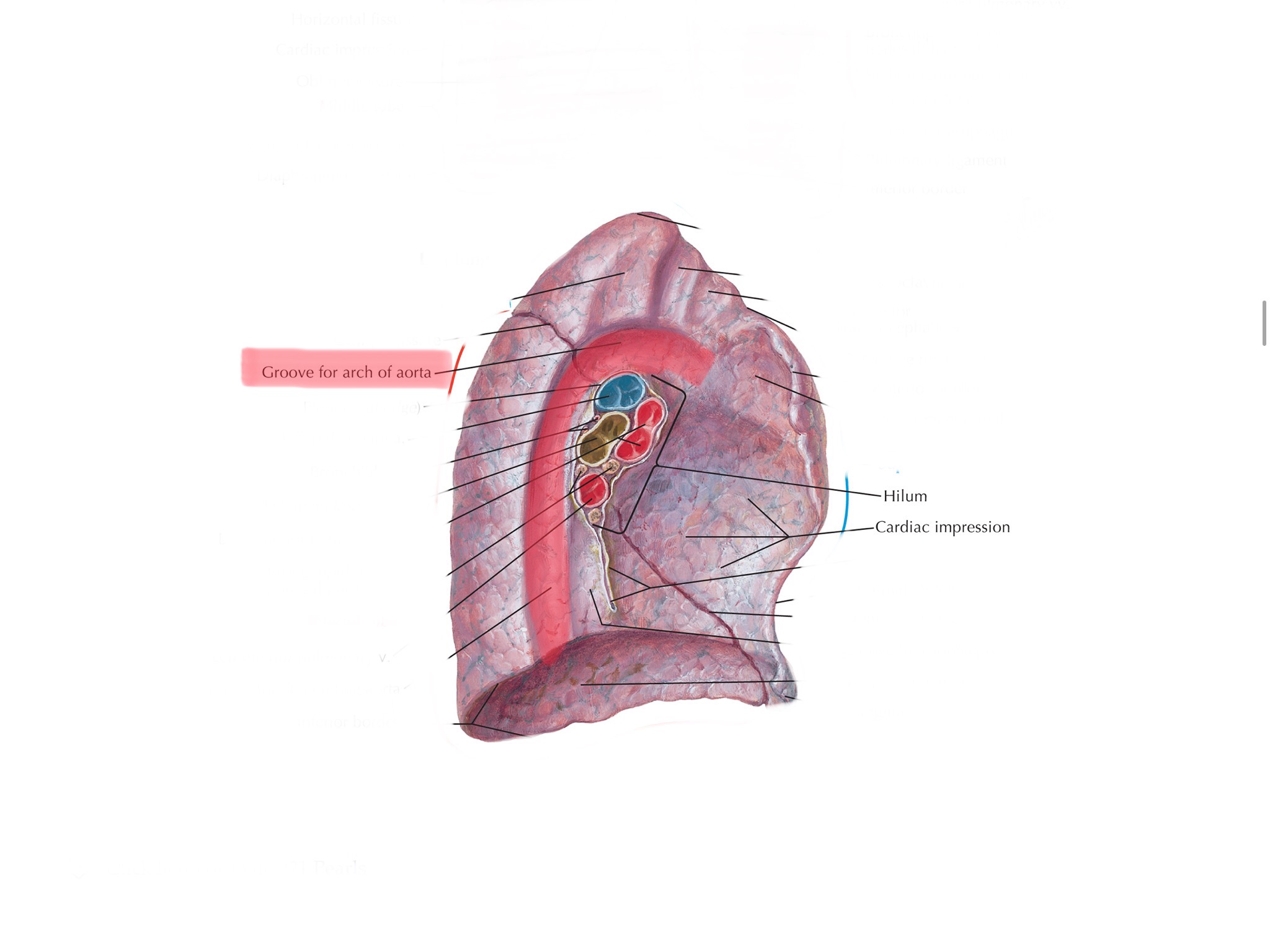
Identify the aortic impressions of the lungs.
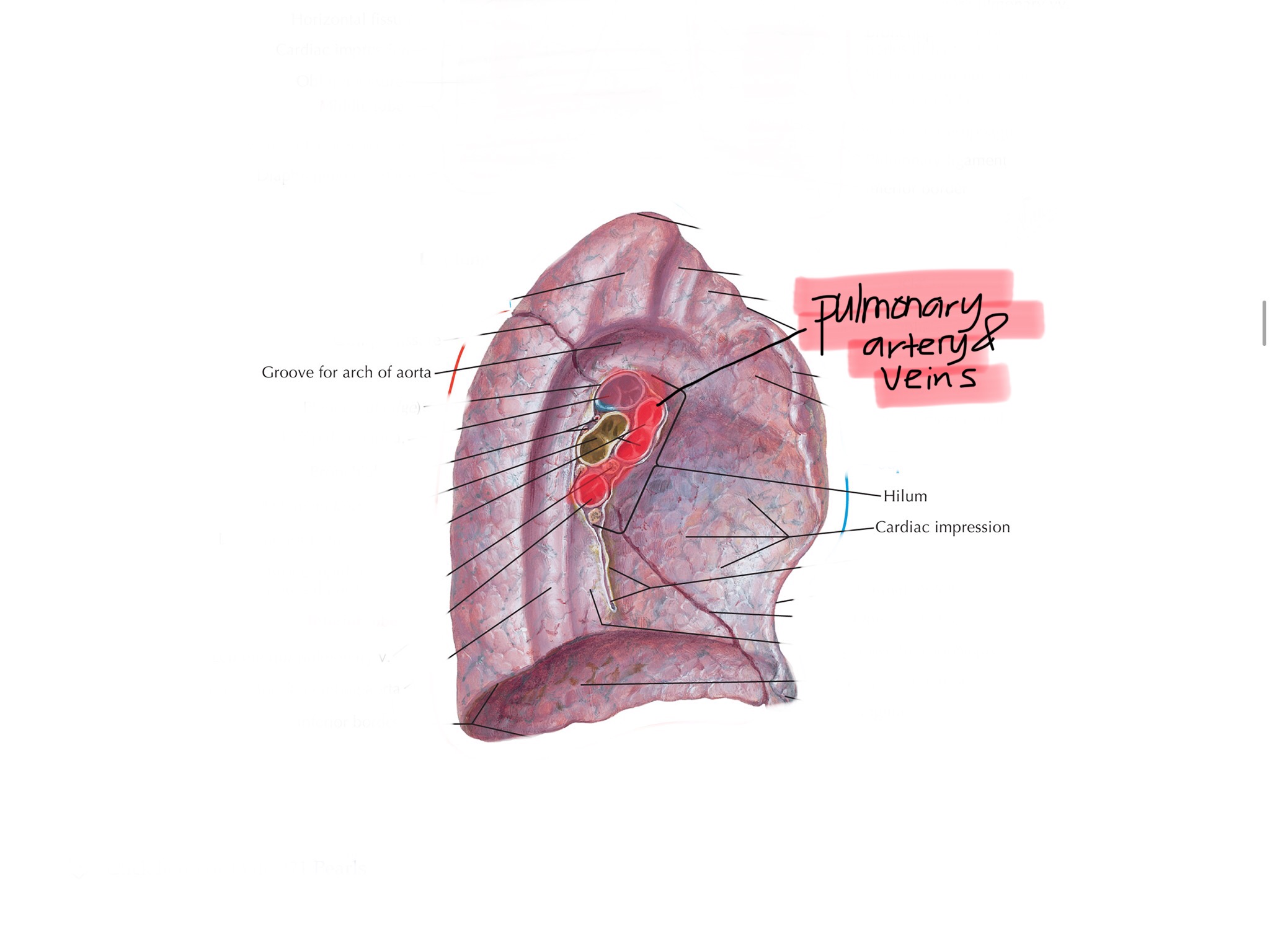
Identify the major vessels of the lungs.
Identify the diaphragm.
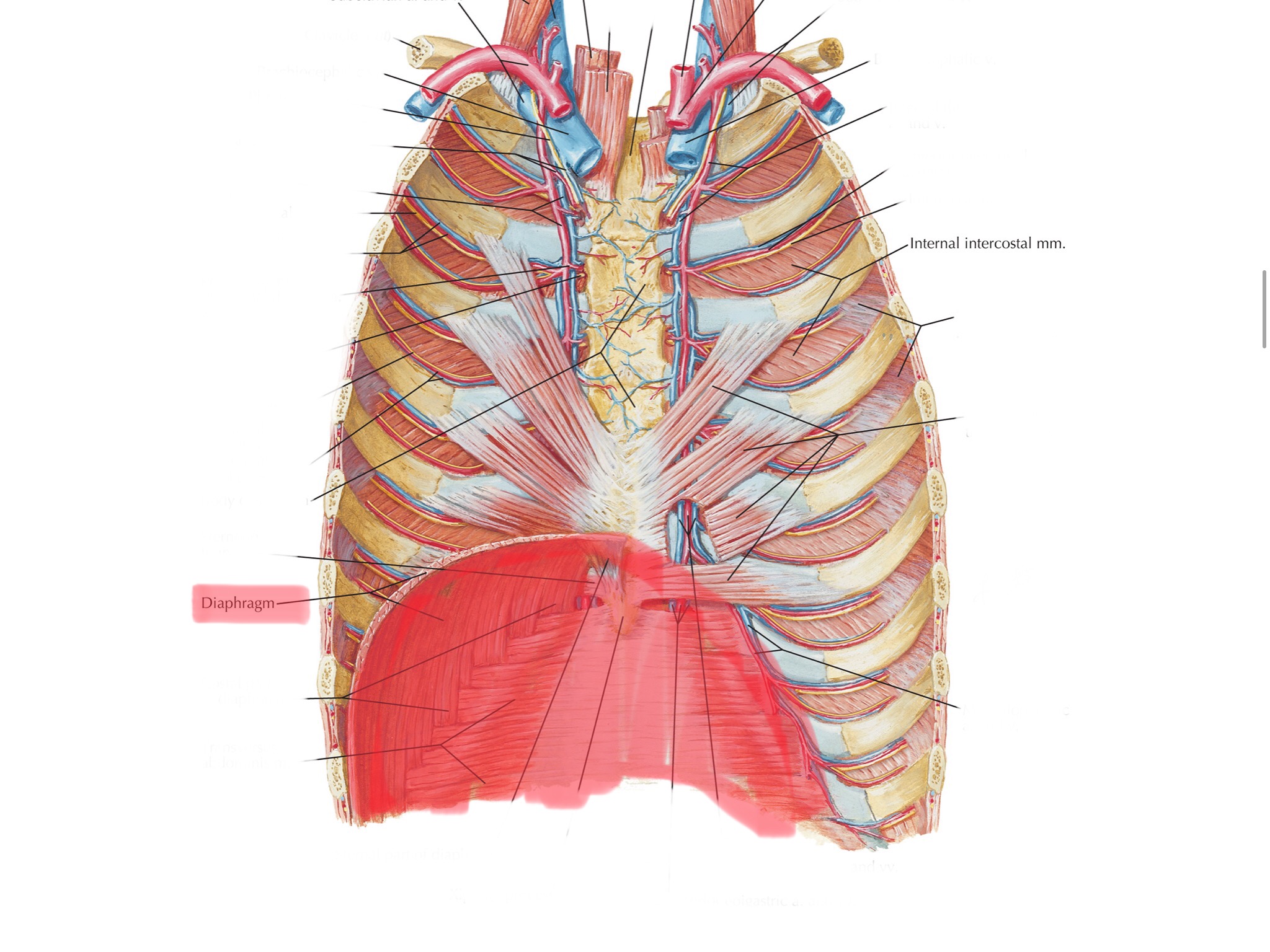
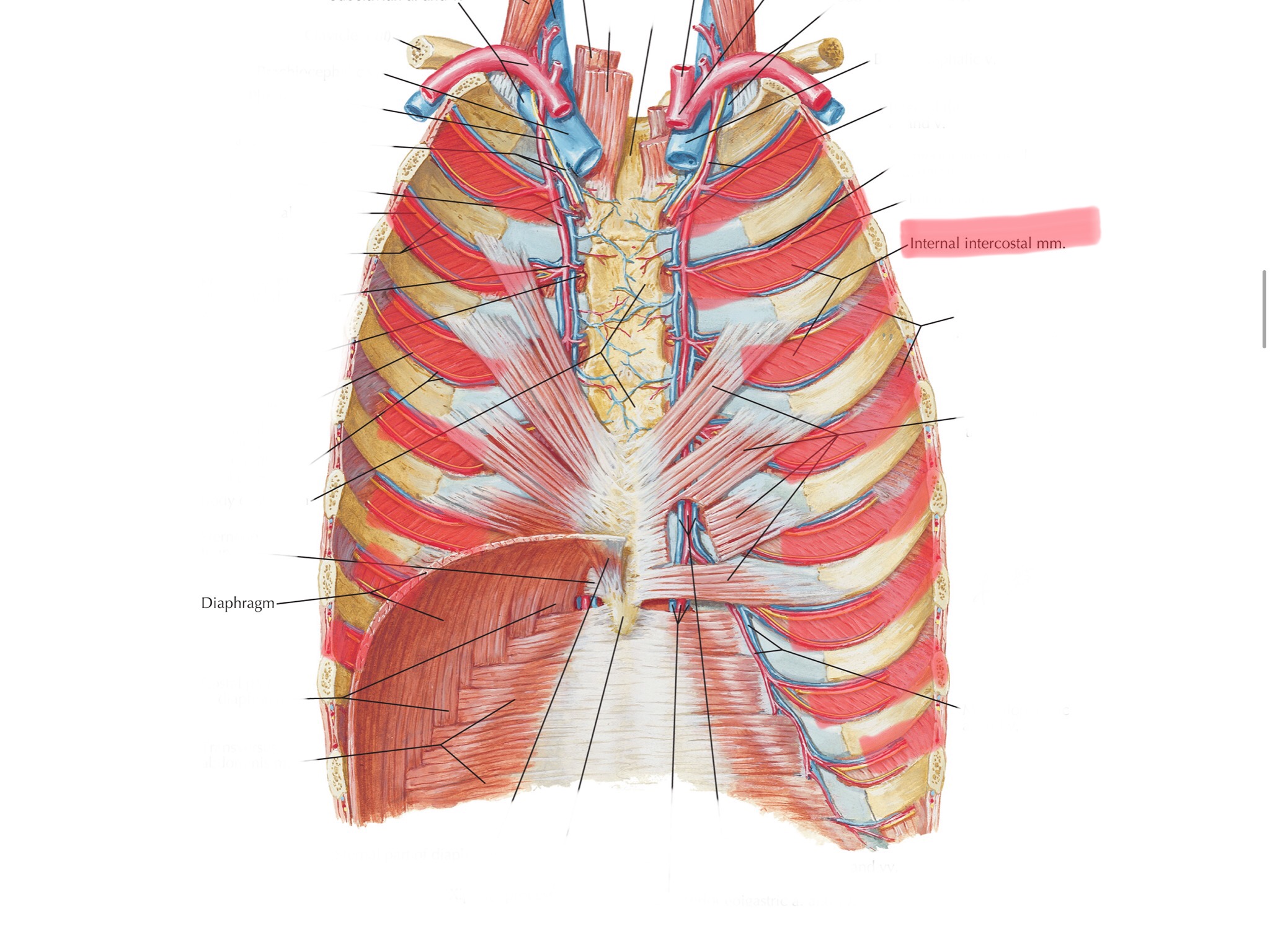
Identify the internal intercostals.
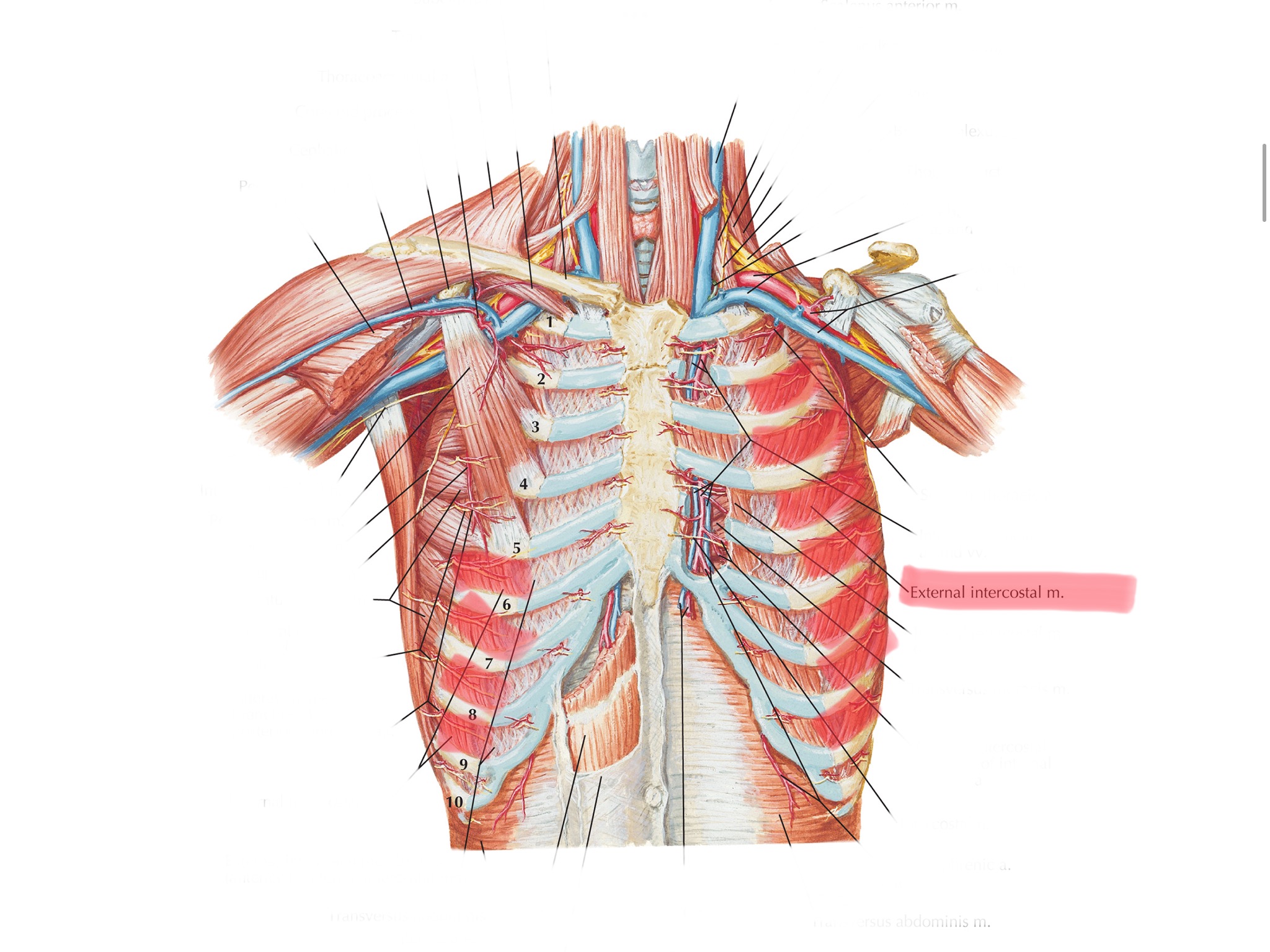
Identify the external intercostals.
Identify lung tissue.
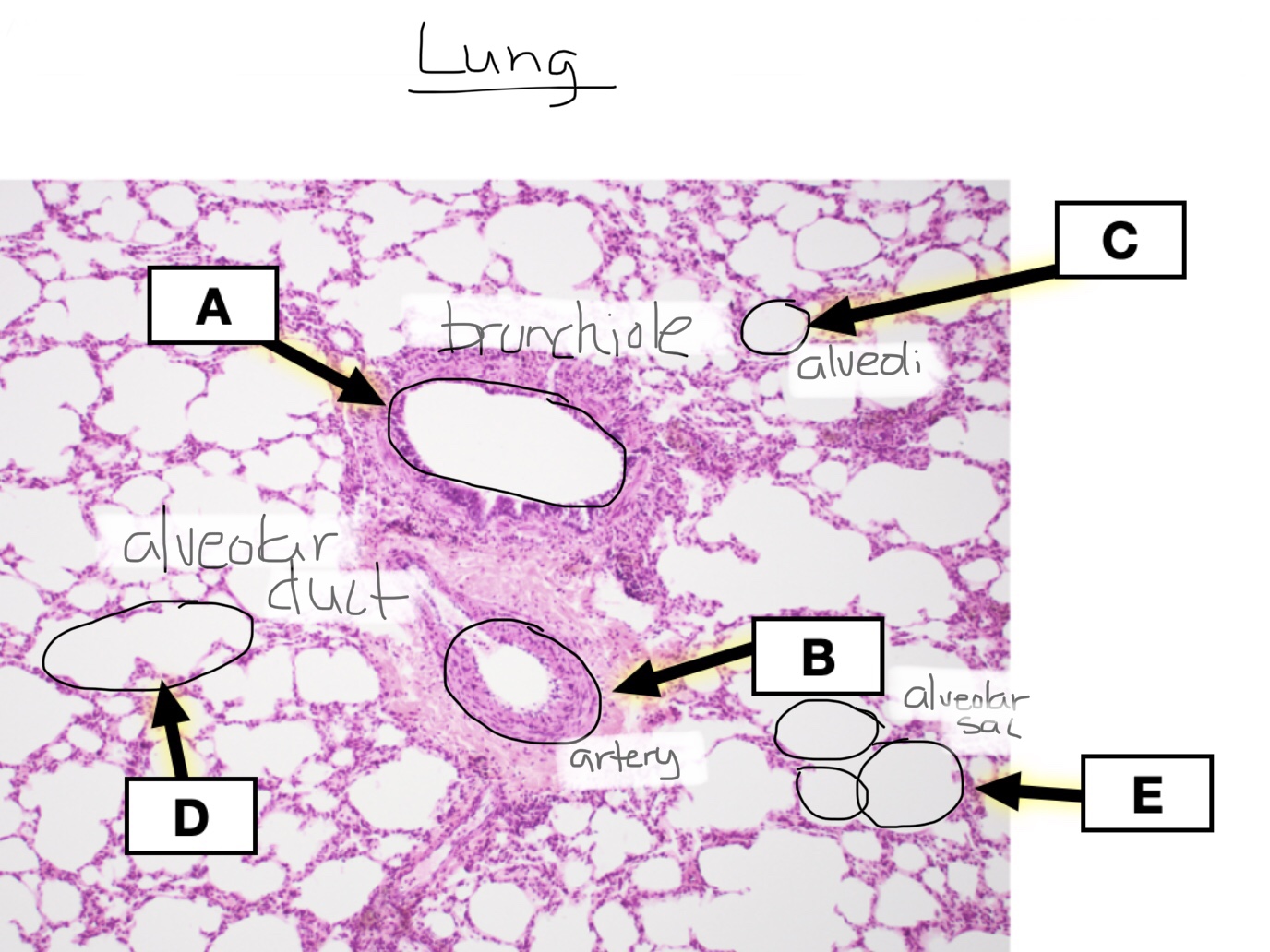
Identify alveoli in lung tissue.
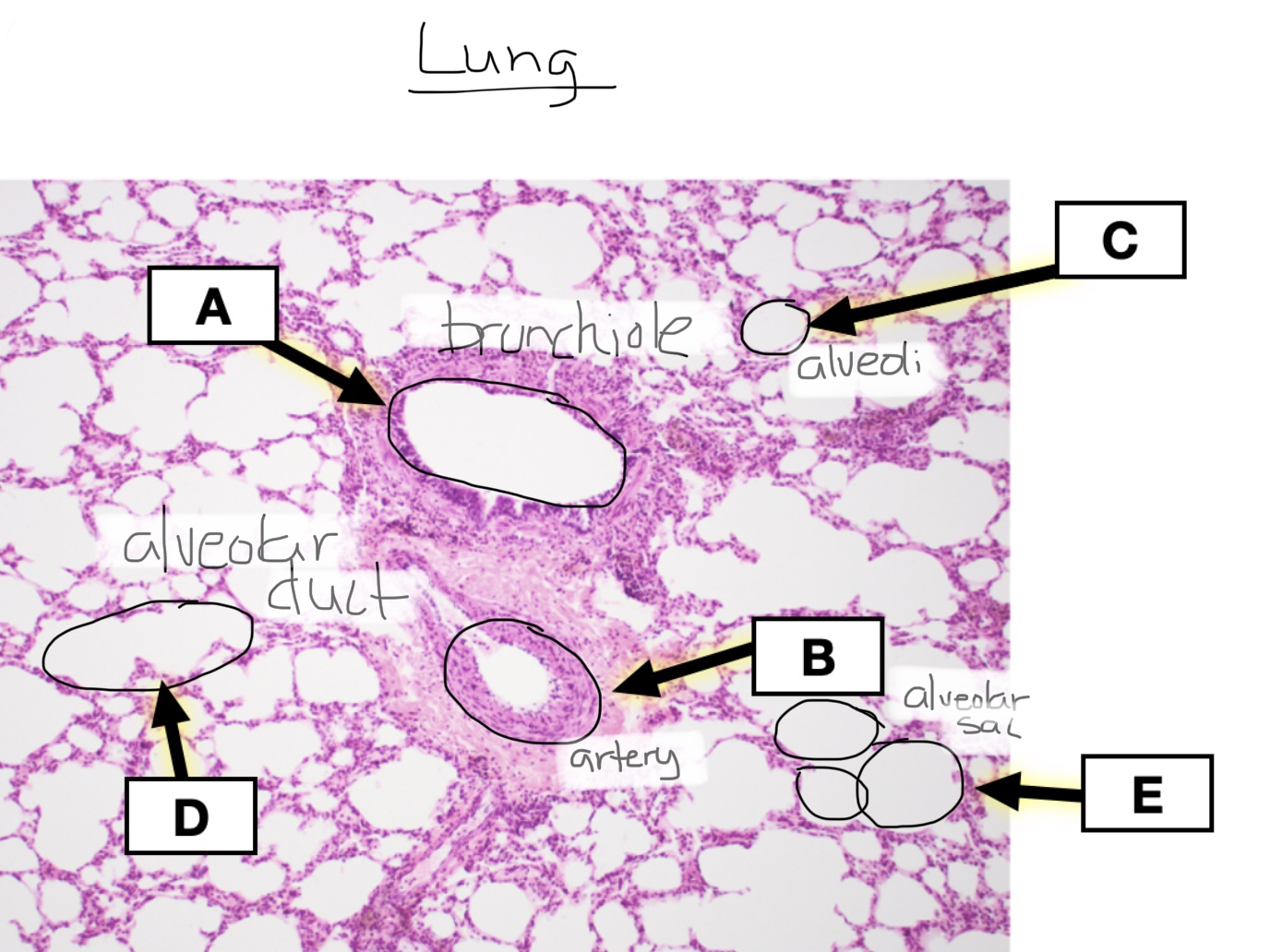
Identify alveolar sacs in lung tissue.
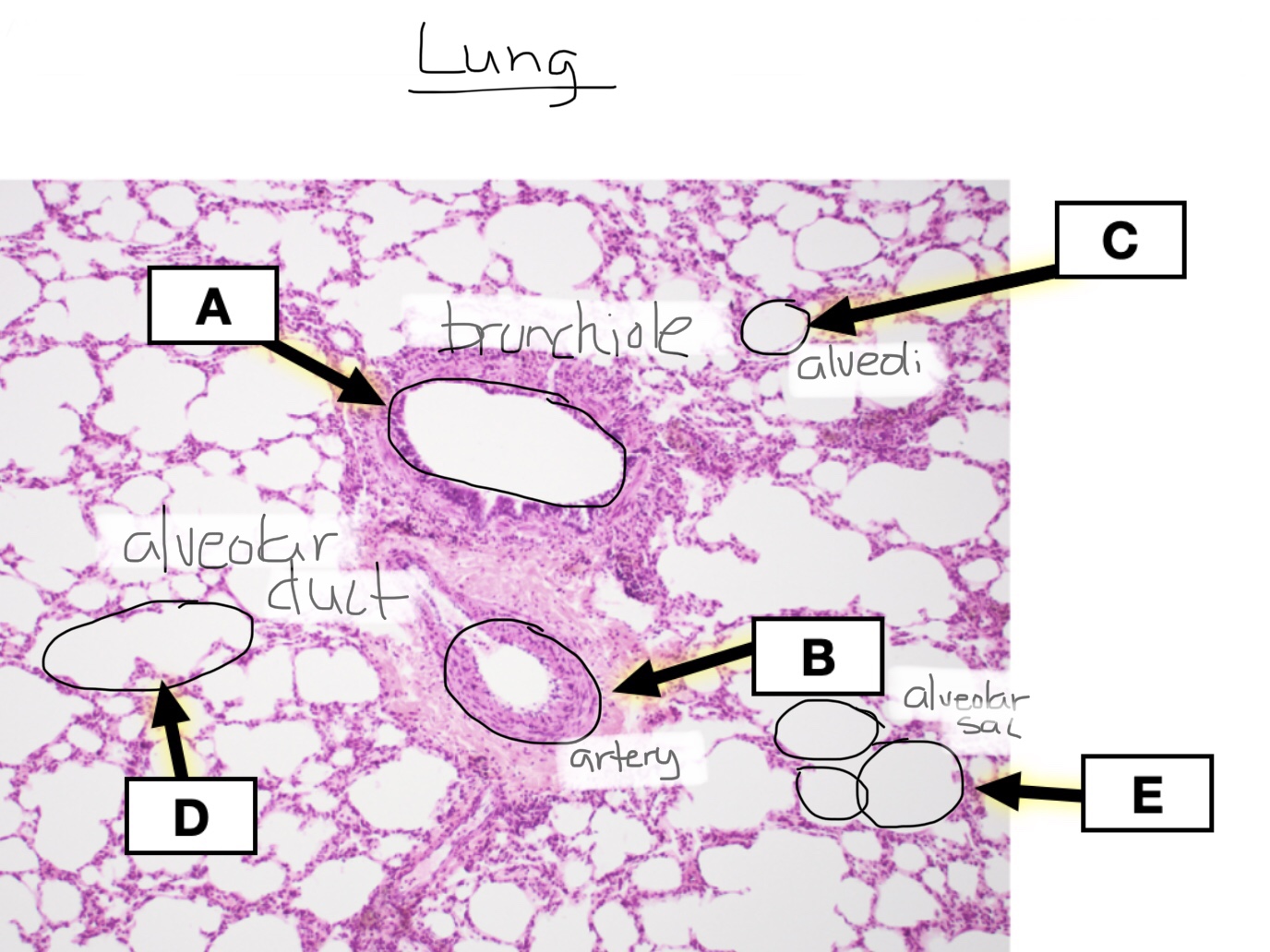
Identify alveolar ducts in lung tissue.
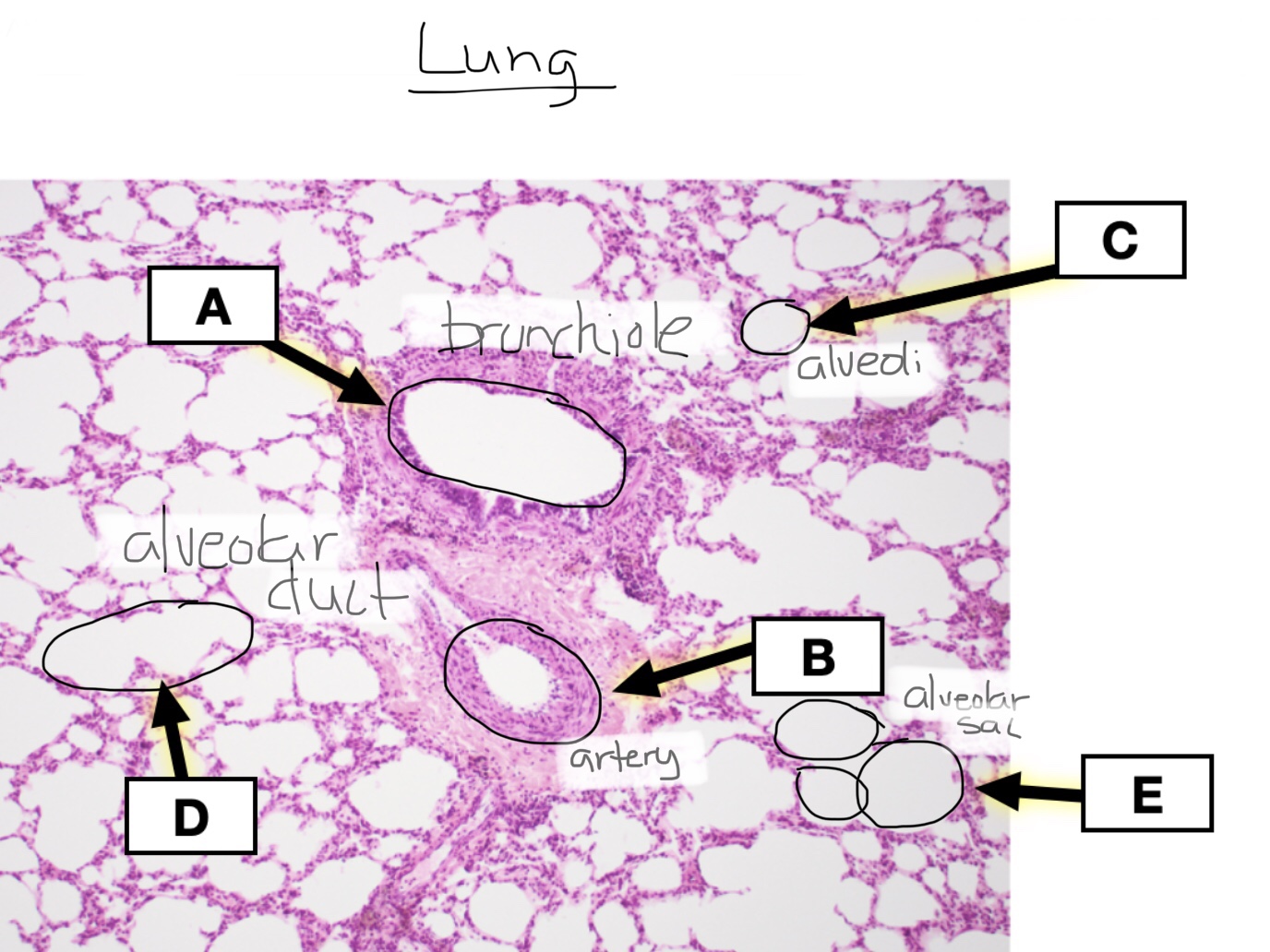
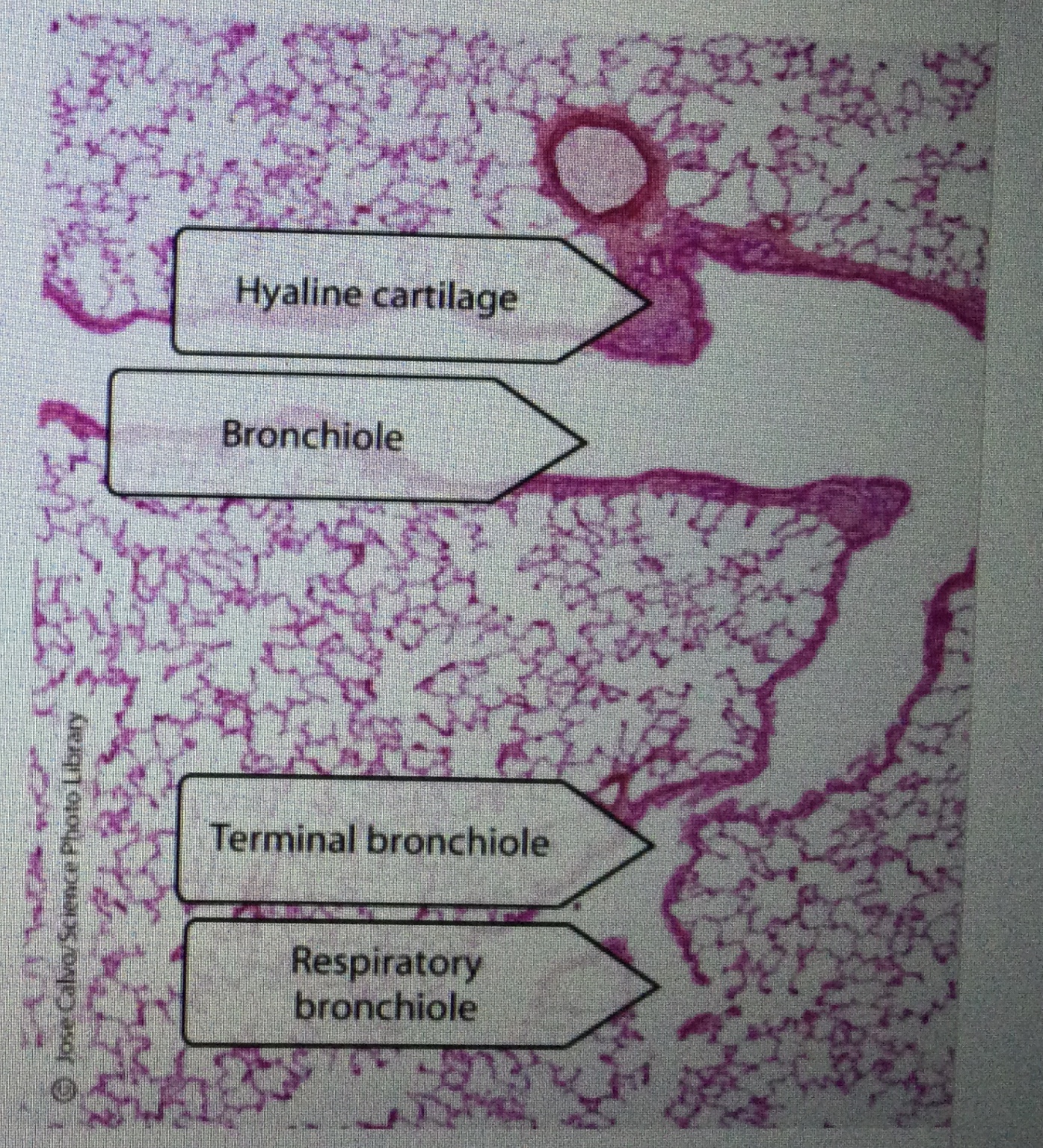
Identify respiratory bronchioles in lung tissue.
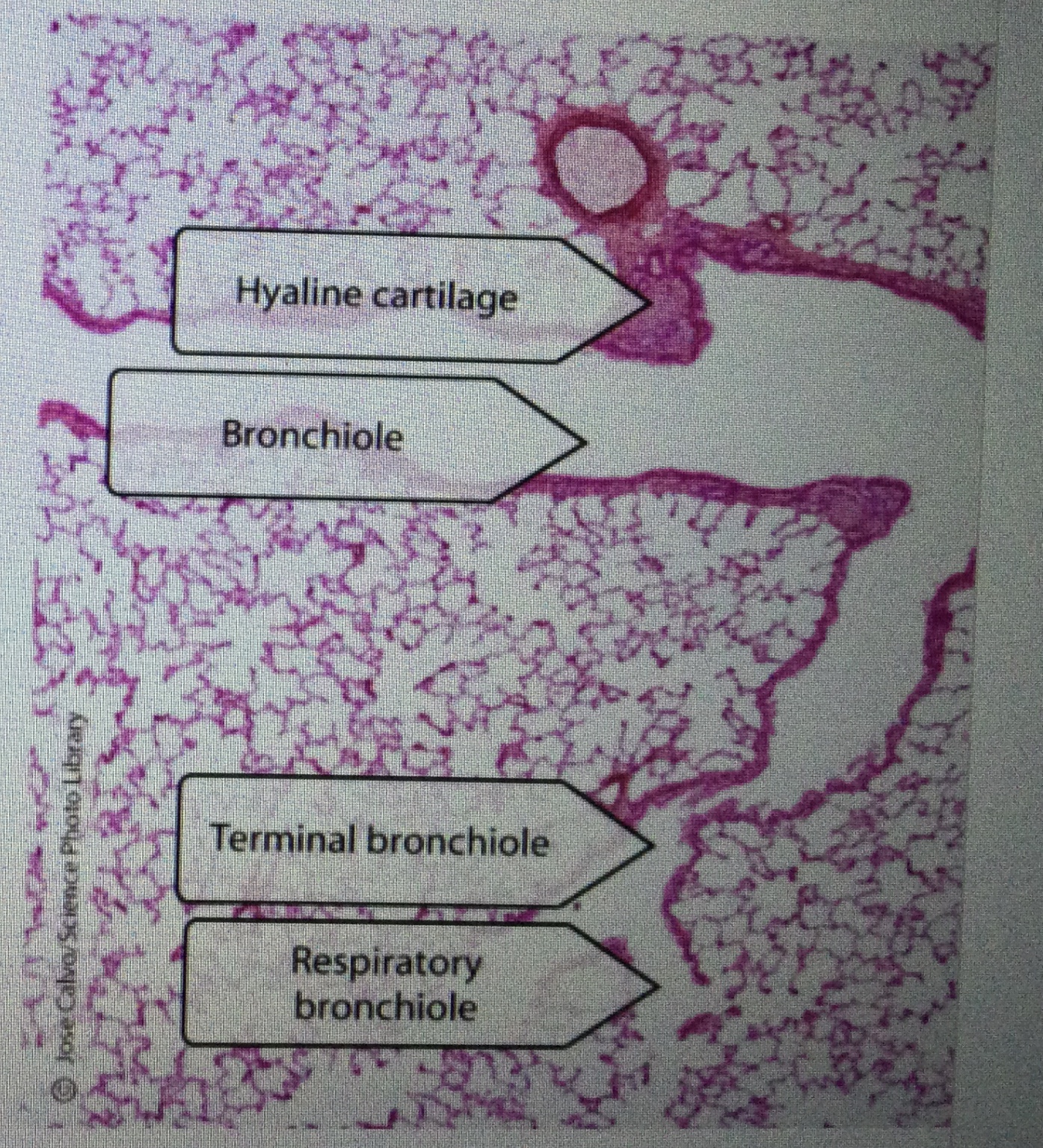
Identify bronchioles in lung tissue.
Identify bronchi in lung tissue.
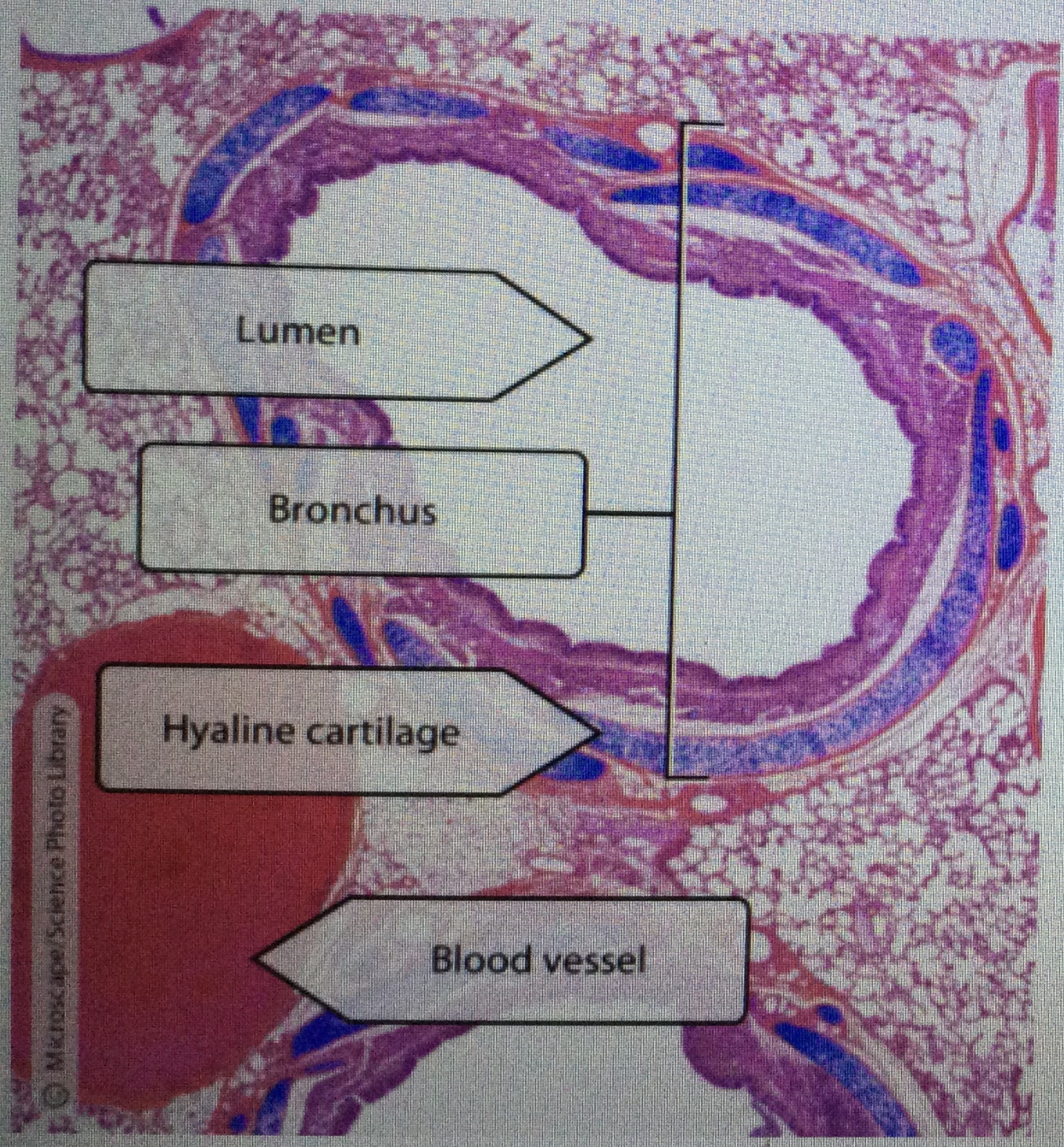
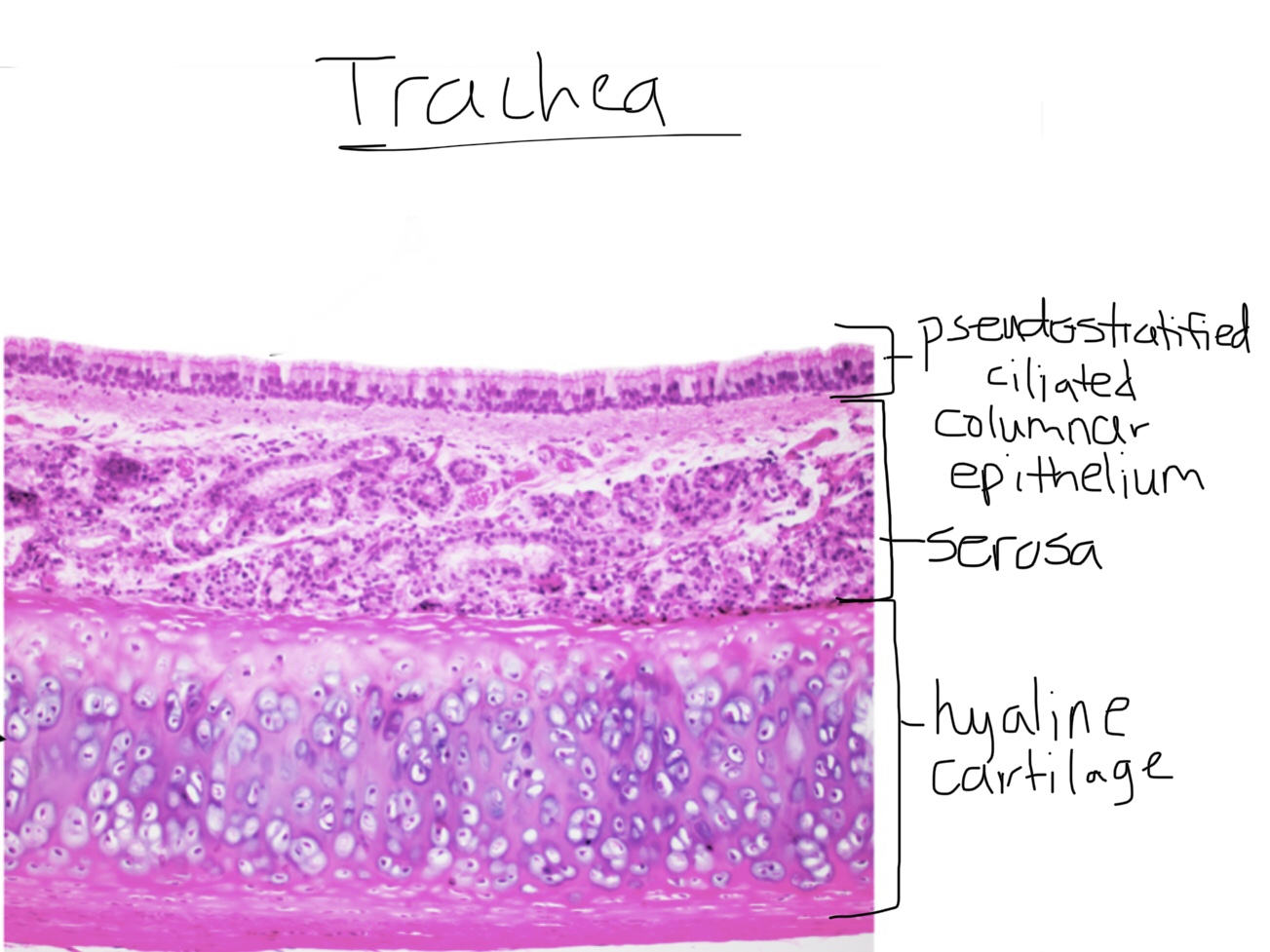
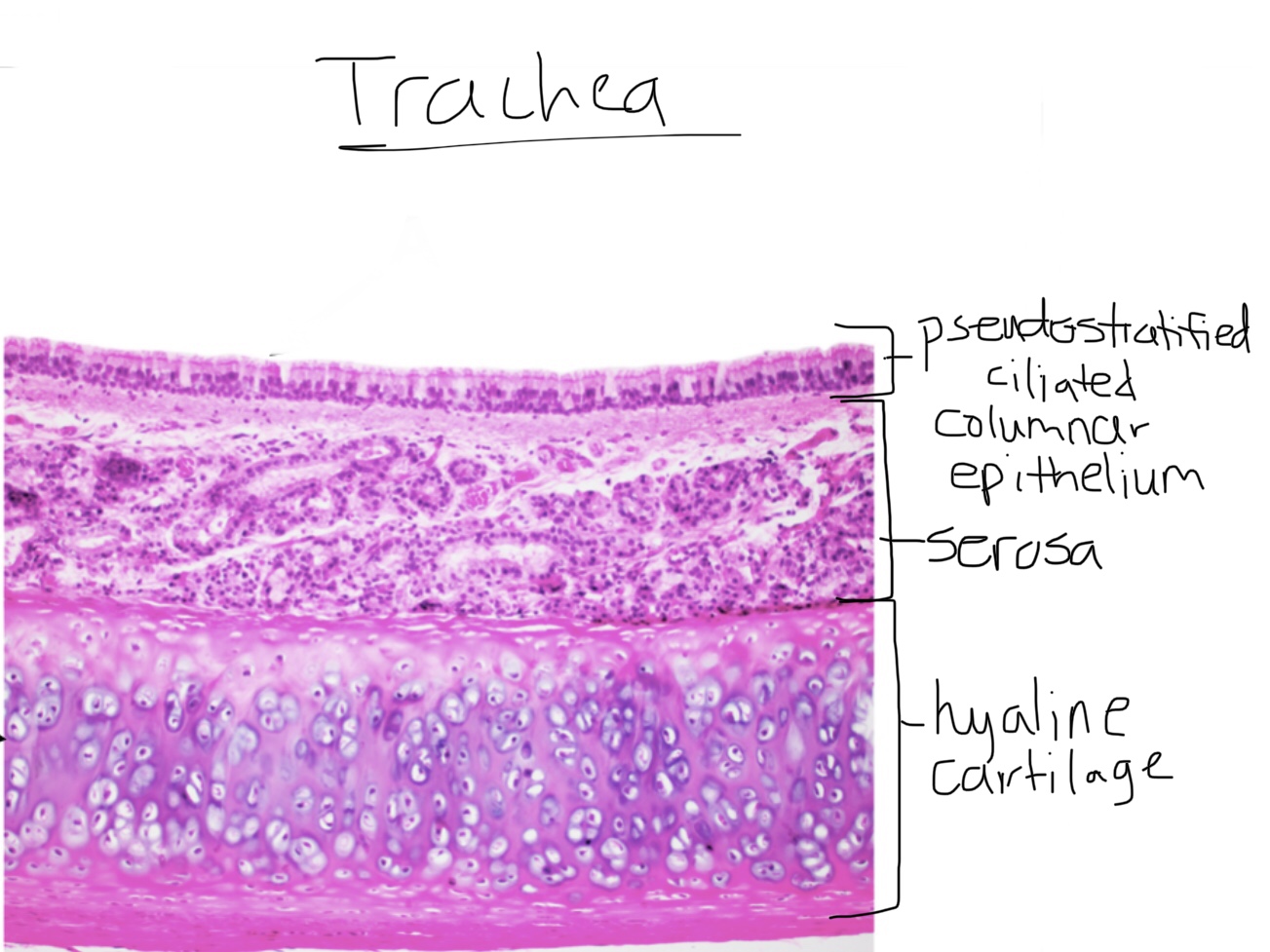
Identify trachea tissue.
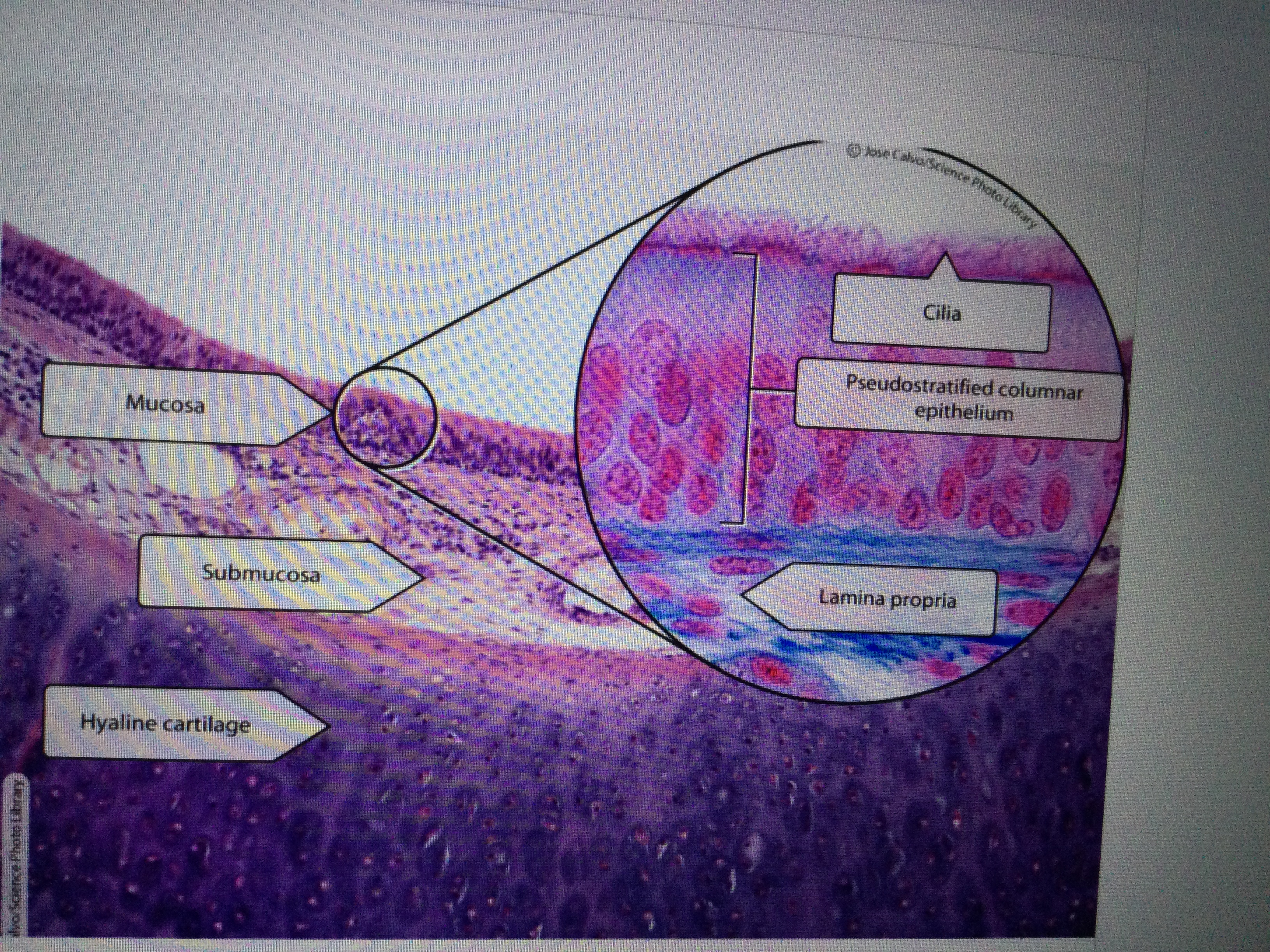
Identify the pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium of trachea tissue.
Identify the submucosal layer in trachea tissue.
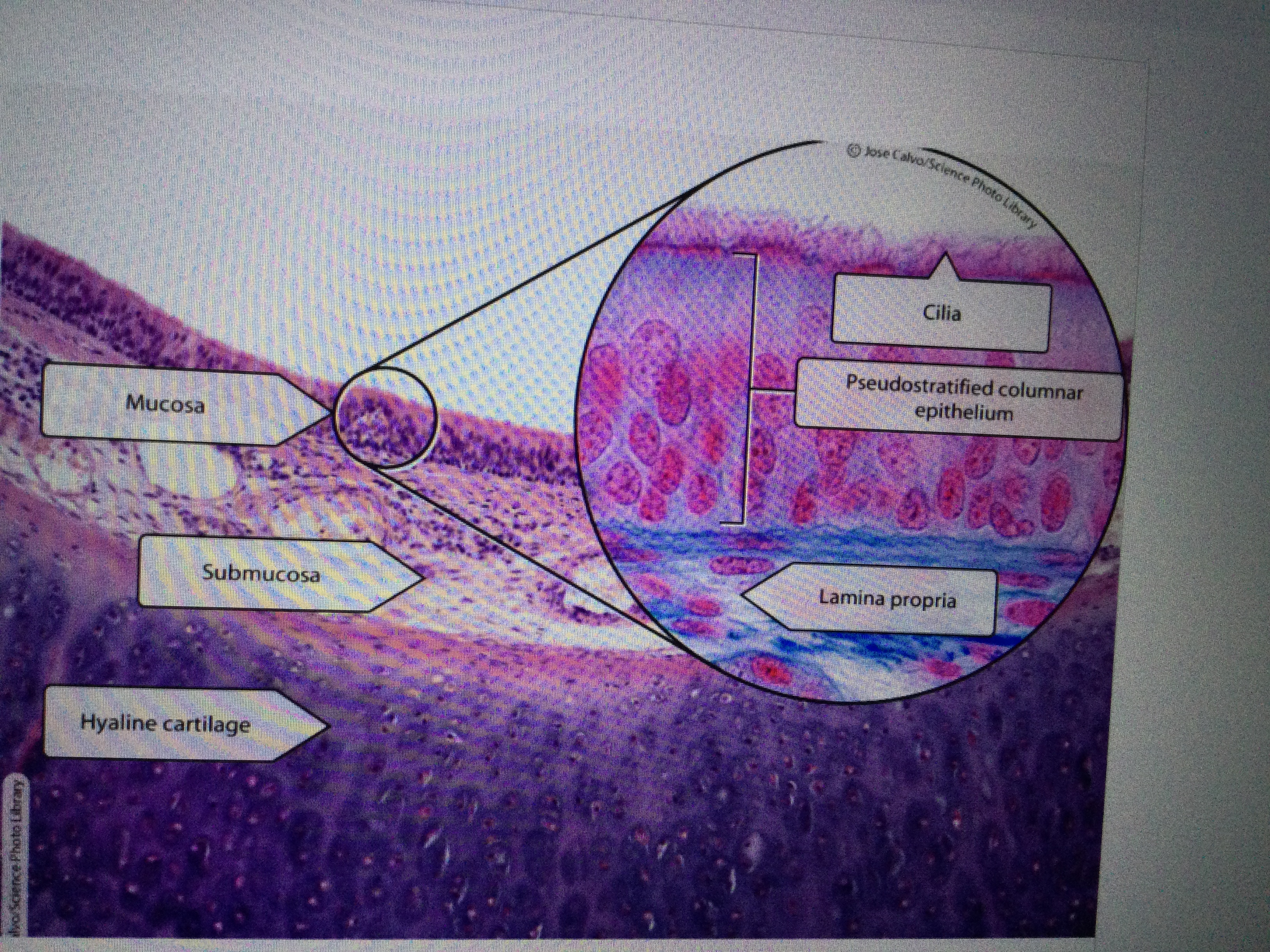
Identify the hyaline cartilage rings in trachea tissue.
What are the two zones of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system is divided into conducting and respiratory zones. The two zones are divided by the respiratory bronchioles.
What is the conducting zone of the respiratory system?
The conducting zone of the respiratory system is responsible for air travel but not gas exchange. It also assists in filtration and humidification.
What is the respiratory zone of the respiratory system?
The respiratory zone of the respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide gas.
What is the root of your nose?
The root of your nose is the region between your eyebrows.
What is the bridge of your nose?
The bridge of your nose connects the nose root to the rest of the nose.
What is the apex of your nose?
The apex of your nose is the tip of your nose.
What are the alae of your nose?
Alae are the lateral cartilaginous structures of your nose.
What is the philtrum?
The philtrum is the concave surface that connects your nose to your upper lip.
What is the septal cartilage of your nose?
Septal cartilage separates your nostrils and nose into left and right.
What is septal cartilage made of?
Septal cartilage is made of hyaline cartilage.
What is alar cartilage?
Alar cartilage makes up the end of your nostrils.
What is alar cartilage made of?
Alar cartilage is made of elastic cartilage.
What is the role of paranasal sinuses?
Paranasal sinuses warm and humidify incoming air and are lined with mucosa to filter our pathogens and debris.
What is the main type of epithelium found in the respiratory system?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is the most prevalent type in the respiratory system.
What is the role of goblet cells?
Goblet cells in the epithelial lining of the respiratory system produce mucus to trap debris.
What is the epiglottis made of?
The epiglottis is made of elastic cartilage and covers the opening of your trachea when you ingest food.
What is the glottis?
The glottis refers to the combination of both your true vocal cords and false vestibular folds.
What is the trachea made of?
The trachea consists for c-shaped hyaline cartilage rings connected by dense connective tissue.
How many lobes make up the right lung?
The right lung consists of three lobes.
How many lobes make up the left lung?
The left lung consists of two lobes.
What constitutes the upper respiratory system?
The upper respiratory system is anything above the trachea.
What constitutes the lower respiratory system?
The lower respiratory system includes the trachea and anything below it.
What is cleft palate/cleft lip?
Cleft palate is caused by the failure of facial arches of the hard palate to fuse during embryonic development and may include the exterior upper lip.
What distinguishes bronchi from bronchioles?
Bronchi has hyaline cartilage whereas bronchioles do not.