3.5 Seed Plants
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Progymnosperms
extinct
first naked seed plants
transitional group
Structures that allowed seed plants to survive on dry land:
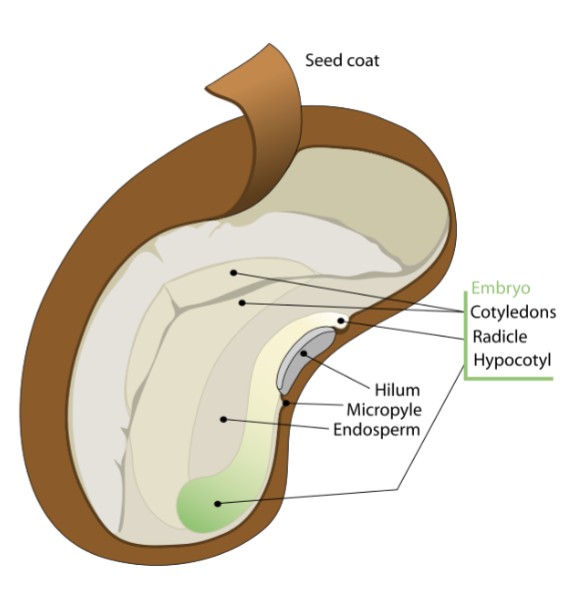
Seed
Pollen
Seed coat
protects embryo
endosperm
stores food for developing embryo
Seed
Micogametophytes
male
pollen grains
dispersed by wind or pollinator
Megagametophyts
develope within ovule
enclosed within diploid sporophyte tissue in angiosperms
Monoecious
male and female on same plant
dioecious
male and female on separate plants
gymnosperms characteristic
dominant sporophyte
gametophyte small and not independent
lack flowers and fruits
unclear monophyletic or paraphyletic
Conifers
dominant, most diverse
monoecious
needle like leaves with thick cuticle
softwood

Cycads
slow growing gymnosperms
resembles palm trees
dioecious
flagellated sperm

Ginkgos
no longer found in the wild
dioecious
pollen with flagellated sperm
fan shaped leaves

Gnetophytes
Three unusual genera: ephedra, gnetum, welwitschia
Dioecious
angiosperm like features most like because of convergent evolution
Female and male cones- conifers
megastrobilus produces megagametophyte
microstrobilus/pollen cone produces microgametophyte

Gamete production in megastrobilus
sporogenesis: diploid megasporocyte divides via miosis, 1 large haploid cell survive and becomes megaspore
Gametogenesis: megaspore divides via mitosis and developes into megagametophyte with egg cell inside (containing archegonium)
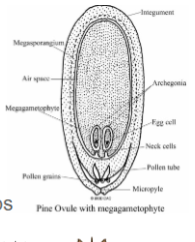
Gamete production in microstroblius
Sporogenesis: diploid microsporocyte divides via meiosis into 4 haploid microspores: tetrad
Gametogenesis: one microspore divides via mitosis to produce generative cell and tube cell. Generative cell divides via mitosis to produce two sperm cell. Tube cell grows into pollen tube that sperm travel down to fertilize
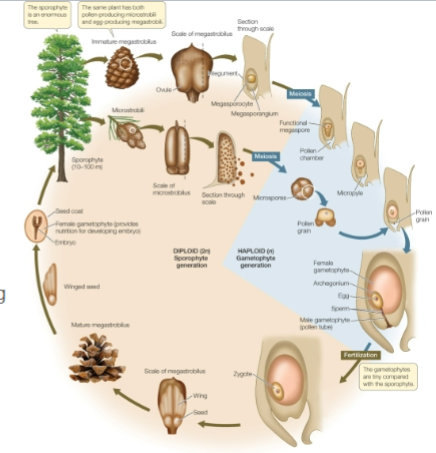
Conifer Life cycle
micro and mega sporocytes undergo meiosis to produce haploid gametes
Archegonium has sticky pollen to trap micropyle to pollinate
pollen tube grows toward gametophyte
one sperm nuclei fertilizes egg → embryo→seed
can take 1-2 years after pollination
Angiosperms
flowering plants
success due to flowers and fruits
sporophyte dominant
monophyletic
monocots dicots
Flowers
modified stems bearing modified leaves
houses gametophytes
have both male and female
Flowers: monoecious
separate male and female flowers on same plants
flowers: dioecious
separate male and female plants
Angiospore female gamete production
meiosis in megasporocyte→ 4 megaspores (1 large)
1 megaspore survives produces 8 nuclei and 7 cells via mitosis
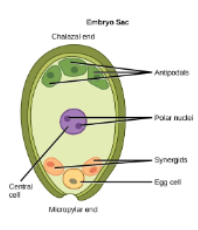
3 cells at each end of embryo sac: antipodal cells, synergids and egg
central cell contains polar nuclei ( cell with 2 nuclei)
Angiospores male gamete production
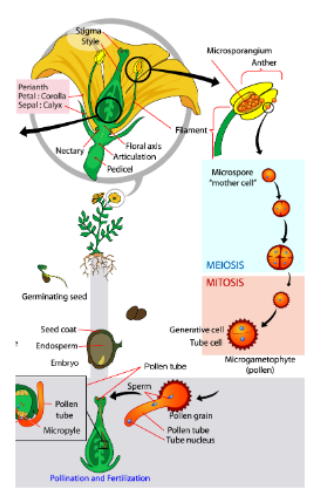
meiosis of mother spore cells in microsporangium produces 4 microspores
each microspore forms pollen grain
pollen contains 2 cells
generative and pollen tube
Double fertilization
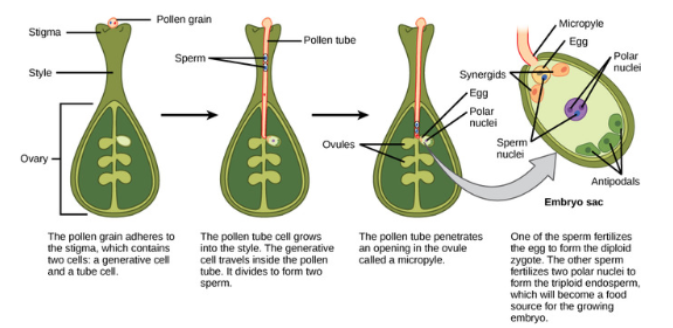
pollen lands on stigma and pollen tube begins to grow
First fertilization: 1 sperm+1 egg= diploid zygote
Second fertilization: other sperm fuses with polar nuclie= triploid cell
zygote develops into embryo with radicle and one or two cotyledons
Basal angiosperms
branched off before monocots and dicots
magnolidae
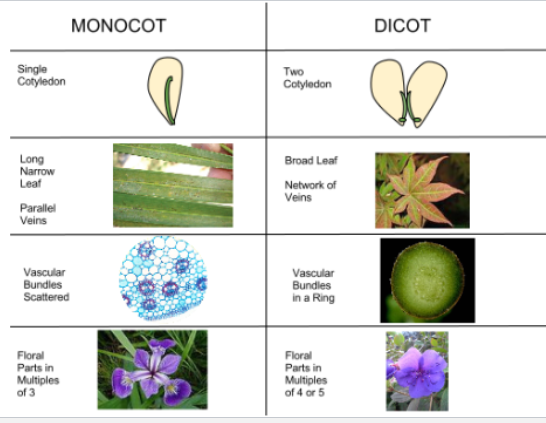
Monocots
do not produce true wood, herbaceous
only primary growth at apical meristems
One cotyledon
parallel veins
scattered vascular tissue
fiberous roots
pollen is monosulcate
flower is three or multiples of three
eudicots
produce true wood
primary and secondary growth
wood is proleferating xylem
two cotyledon
network veins in leaves
vascular tissue in ring pattern
tap rool with lateral roots
pollen is trisulcate
flower parts in 4, 5 or multiples of 4 and 5