BIOL 376 - Unit 4: Synaptic Pruning, Plasticity
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
when does synaptic pruning and apoptosis start?
4 months after birth
( )% of neurons removed during programmed cell death
50
conditions to induce programmed cell death in PNS
TrkA and TrkC expression with absence of NGF and NT3
conditions to induce programmed cell death in CNS
not dependent on neurotrophic factors
pruning
weakening OR complete removal of synaptic connections
3 main mechanisms of pruning
axon retraction, axon degeneration, axon shedding
axon degeneration
axons degenerate from proximal to distal end
Wallerian degeneration
distal axon separates from soma, catastrophic fragmentation
Wallerian degeneration steps 1 and 2
injury, swollen beaded axon
Wallerian degeneration steps 3 and 4
myelin degeneration, axon cytoskeleton breakdown
Wallerian degeneration step 5
glial cells clear debris, promote new axon formation
in development, injury is replaced by cellular signals to induce…
hormonal degeneration, genetic switches
axon retraction
nerve shortens from distal to proximal end
what influences formation of a retraction bulb? (axon retraction)
neurotrophic factors, cell-substrate adhesion, cell activity
what are used to induce axon retraction in HIPPOCAMPAL PROJECTIONS?
semaphorins, neuropilins, plexins
what are used to induce axon retraction in the RETINA?
ephrin, Eph
axon shedding
distal to proximal breakdown of axon branches
synaptic competition
competing synapses occupy similar locations, covered by perisynaptic Schwann cells
losing neuron…
retreats from synapse
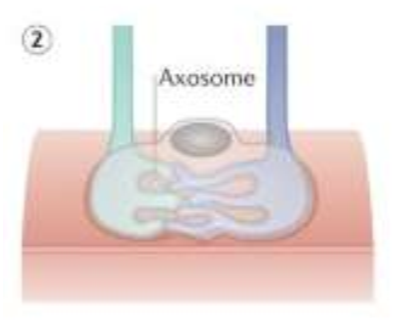
axosome shedding (of synapse and axon)
shedding of axoplasm-containing axosomes
perisynaptic Schwann cell
engulfs axosomes and breaks them down
synaptic rearrangement
occurs due to neural activity and synaptic transmission
synaptic rearrangement triggers…
intracellular Ca2+, influencing cytoskeletal organization and gene expression
critical period
crucial temporal window for synaptic development and pruning
NOTE: Know and be able to describe Hubel and Wiesel’s feline experiment
Hebb’s postulate
neurons that fire together, wire together
if signals from one set of neurons is closely correlated with the output of other, these synapses will be ( ), others are ( )
strengthened, removed
Hebb’s postulate, second part
neurons that fire out of sync, lose their link
synaptic plasticity
ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time in response to change in neuronal activity
short-term plasticity
lasts for a few minutes or less
short-term plasticity mechanisms
facilitation, depression, augmentation, post-tetanic potentiation
facilitation (short-term)
caused by prolonged elevation of presynaptic Ca2+ levels following synaptic activity
depression (short-term)
dependent on progressive depletion of synaptic vesicles in presynaptic terminal
augmentation and post-tetanic potentiation
increases amount of transmitter released from presynaptic terminals
augmentation speed
fast, over a few seconds
augmentation process
Ca2+ enhances action of munc-13 to prime readily-releasable vesicles
post-tetanic potentiation speed
10 seconds to minutes
post-tetanic potentiation process
Ca2+ enhances actions of presynaptic protein kinases to phosphorylate substrates, regulating transmitter release
long-term plasticity most studied in the…
hippocampus
hippocampus functions
formation and retrieval of memories
damage to hippocampus…
results in inability to form certain types of memories
neuronal layers involved in hippocampal long-term potentiation
CA1, CA3
presynaptic pyramidal cells in ( ) region sends synapse to pyramidal cells in ( ) region via ( )
CA3, CA1, Schaffer collaterals
NOTE: Know Lomo and Bliss experiment with rodent hippocampus
long-term potentiation lasts for…
greater than a year
long-term potentiation also found in…
cerebral cortex, amygdala, cerebellum
long-term potentiation is a Hebbian synapse, this means…
stimulus to Schaffer collaterals must be paired with strong depolarization of postsynaptic CA1 cell to undergo long-term potentiation
strong postsynaptic depolarization must occur within ( ) of presynaptic transmitter release for long-term potentiation to occur
100 ms
long-term potentiation, glutamate release, binds to both…
NMDA and AMPA receptors
at normal postsynaptic potential, ( ) receptor pore is blocked by ( ), thus excitatory postsynaptic potential mediated by ( ) signal associated with ( ) receptor (LTP step 1)
NMDA, Mg2+, Na+, AMPA
Mg2+ block on NMDA only opens upon… (LTP step 2)
summation of EPSPs resulting in prolonged depolarization
postsynaptic depolarization removes ( ) from NMDA pore, allowing ( ) to flow through the NMDA receptor (LTP step 3)
Mg2+, Ca2+
long-term potentiation is triggered by… (LTP step 4)
increase in Ca2+ in dendritic spines of postsynaptic cell
NMDA receptor only opens to induce long-term potentiation when there is ( ) bound to the NMDA receptor along with the ( ) block
glutamate, Mg2+
long-term potentiation must be…
specific and associative
Ca2+ entering through NMDA receptors activates ( ) and ( )
CaMKII, PKC
mutation of CaMKII protein at Schaffer collateral synapses…
prevents long-term potentiation
CaMKII can ( ) and prolongs ( ) of long-term potentiation
autophosphorylate, duration
long-term potentiation is maintained from ( ), leads to increase in membrane expression of postsynaptic ( ) receptors
kinase phosphorylation, AMPA
long-term potentiation duration
minutes to hours
long-term sustained long-term potentiation last for more than ( ), involves changes in ( ) and ( ) expression
2 hours, gene, protein
late-phase long term potentiation is due to ( ) activation, leading to phosphorylation and activation of ( ), turning on gene transcription
PKA, CREB
long-term depression
selective weakening of synapses
low stimulation of Schaffer collateral-CA1 path for 10-15 minutes induces…
long-lasting depression of synaptic transmission
long-term depression is also activated by…
Ca2+ entry into postsynaptic NMDA receptor
long-term potentiation activates ( ), long-term depression activates ( )
protein kinases, Ca2+-dependent phosphatases
long-term depression associated with…
internalization of AMPA receptors
internalization of AMPA receptors is via…
clathrin-dependent endocytosis
long-term potentiation and long-term depression both reversibly…
affect synaptic efficacy