Ch. 4 In-Class Notes--Alkenes and Alkynes: The Nature of Organic Reactions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
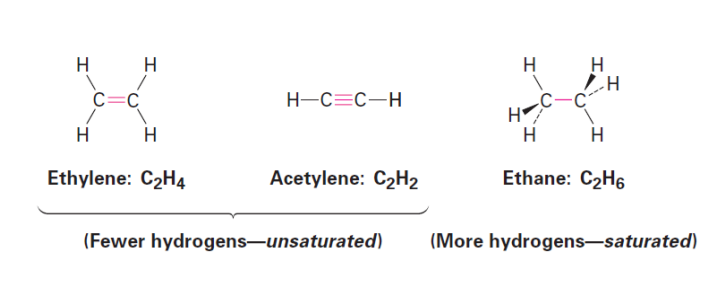
Unsaturated hydrocarbons have ___ hydrogens per carbon due to the presence of multiple bonds between carbons
fewer
Naming Alkenes Rules
Find the longest Carbon chain that includes the double bond. Name the compound using the correct roots with the suffix of -ene instead of -ane.
Number the carbon atoms in the chain, giving the lowest numbering possible to the alkene and numbering through both carbons of the alkene.
Using additional rules learned previously, write the full name
in cycloalkenes, start numbering at the first carbon of alkene. Do not need to specify “1” locant.
If there are 2 alkenes, it gets called “diene,” identifying locant of first carbon in each alkene.
Add an “a” to the name of the longest chain (EX: hepta-1,3-diene)
Naming alkynes rules
Same rules as alkenes, except use “-yne” ending
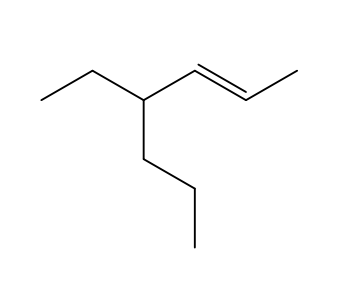
Using your knowledge thus far, what is the name of the following structure?
4-ethylhept-2-ene
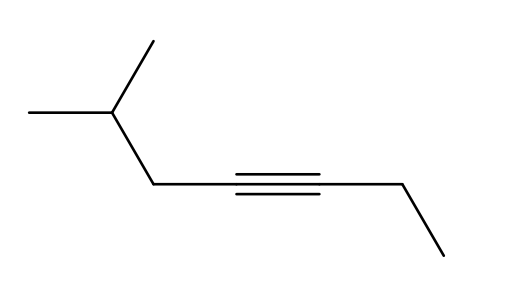
What is the IUPAC name of the following structure?
6-methylhept-3-yne
Electronic Structure of Alkenes
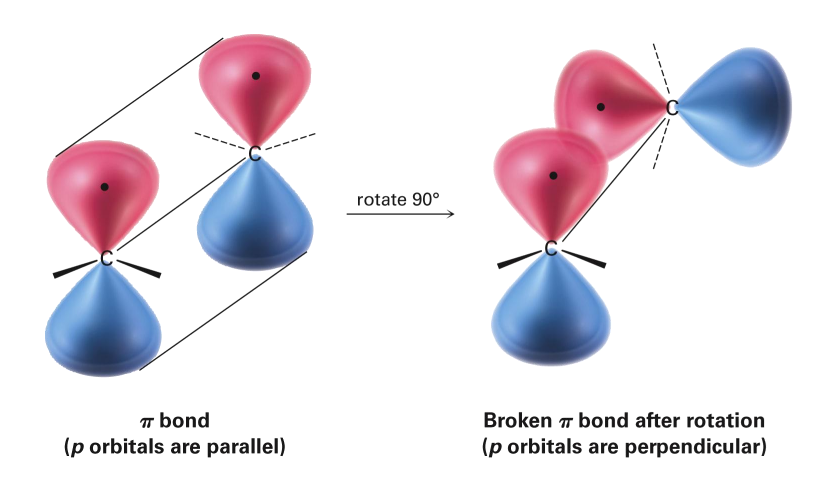
Cis-trans isomers of Alkenes
Possible with disubstituted alkenes, where each carbon of the alkene has one substituent
cis= same side of double bond
trans= opposite sides of double bond
Fatty Acids
triesters of glycerol with 3 long-chain carboxylic acids
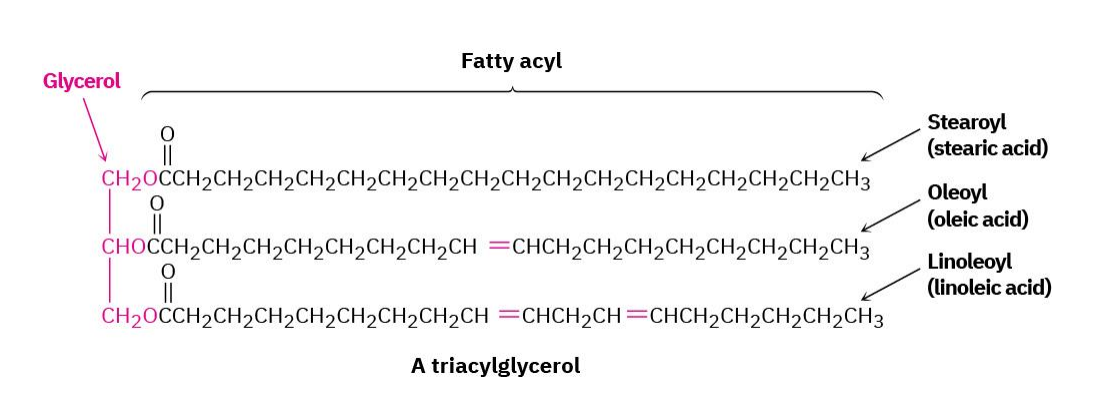
Saturated fatty acids
no C=C double bonds
unsaturated fatty acids
containing C=C double bonds
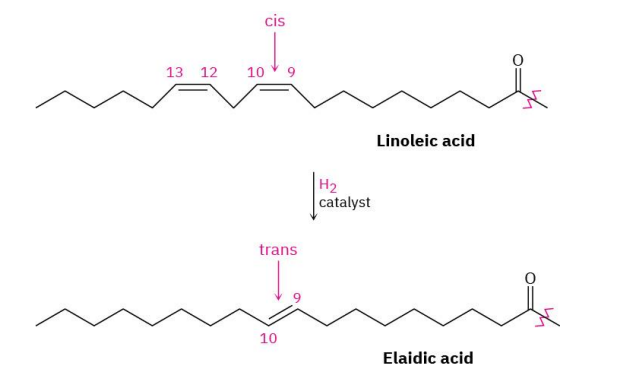
Trans-Fatty Acids
trans far can be produced by catalytic hydrogenation of vegetable oils
trans fats are no longer considered safe by the FDA
increased cholesterol levels in the blood
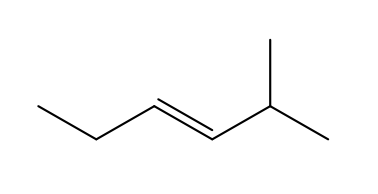
Name the following structure, including stereochemistry.
trans-2-methylhex-3-ene
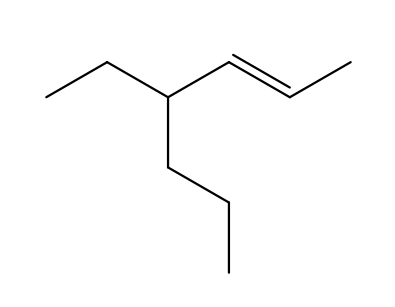
What is the correct way to label the stereochemistry of this alkene?
Trans (opposite side of pi bond)
Sequence Rules: The E/Z Designation
Trisubstituted and tetra substituted alkenes
Sequences rules used to rank each group bonded to each carbon of the alkene
E=higher ranked groups on the opposite sides of the double bond
Z=higher ranked groups on the same side of the double bond
Ranking rules (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog):
1. Consider the double bond carbons separately. Look at the atoms directly attached to each carbon and rank them according to atomic number. The atom with the higher atomic number is higher priority.
2. If a decision cannot be reached by ranking the first atoms in the substituents, look at the second atoms/ third atoms/ fourth atoms (etc.) until the first difference is found.
3. Multiple bonded atoms are equivalent to the same number of single-bonded atoms.
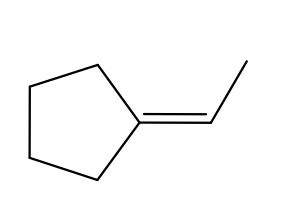
What is the correct way to label the stereochemistry of this alkene?
None of the above (not cis, trans, E or Z)
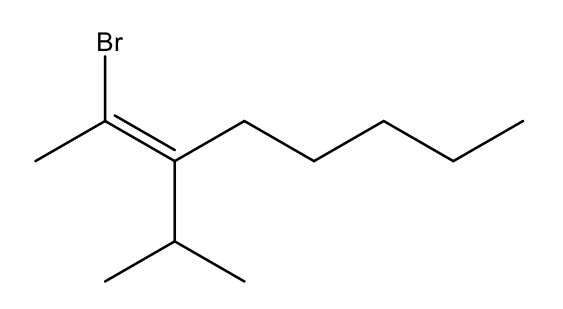
What is the correct way to label the stereochemistry of this alkene?
E
Addition Reaction
two reactants add together to form a single new product, with no atoms left over
Elimination Reaction
one reactant splits into two products
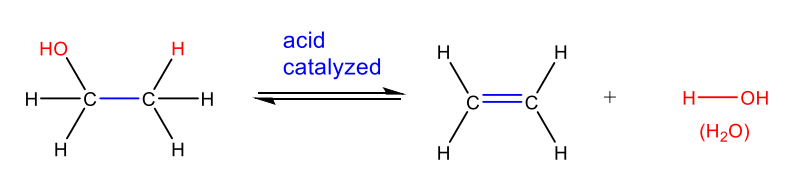
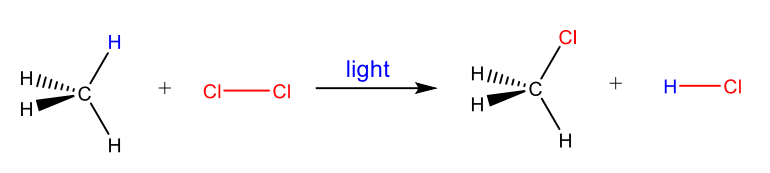
Substitution Reaction
two reactants exchange parts to give two new products
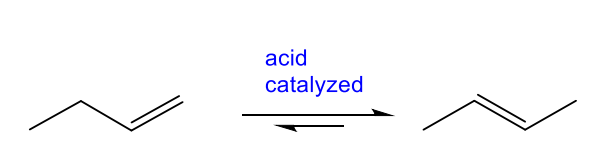
Rearrangement Reaction
a single reactant undergoes reorganization of atoms/bonds to yield a single isomeric product
Reaction mechanism
describes movement of electrons at each state of a chemical transformation
order that bonds are formed and broken
relative rates of steps
Radical reactions (symmetrical, single-headed arrow)
homolytic cleavage
chemical species that includes unpaired electron
Polar reactions (asymmetrical, double-headed arrow)
chemical species that have electron pairs
electron rich sites in one molecule react with electron poor sites on another molecule
Nucleophile
electron rich species (donates electrons, Lewis base)
Electrophile
electron poor species (accepts electrons, Lewis Acid)
Common Electrophiles
(accepting electron)
H3O+, BrC, H2O
Common Nucleophiles
NH3, H2O, OH, X (-)
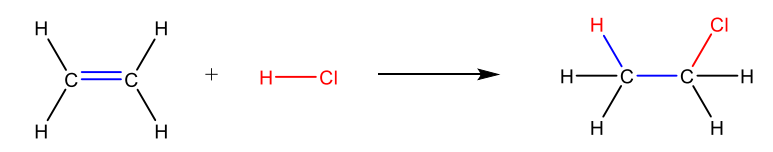
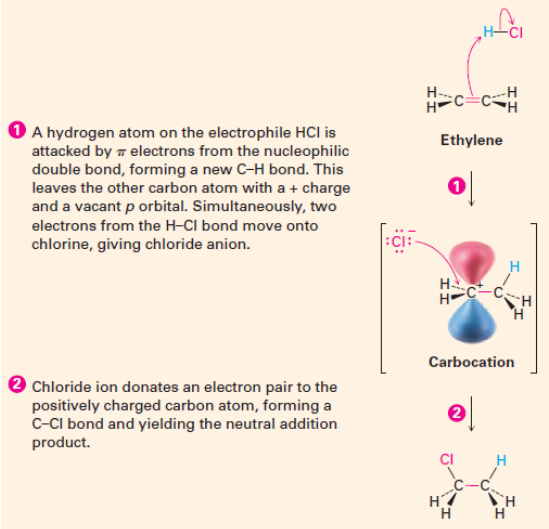
Electrophilic addition reaction of HCl to ethylene (2 step mechanism)
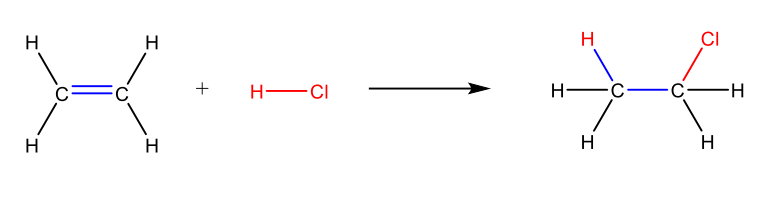
The Mechanism: Addition of HCl to Ethylene cont.
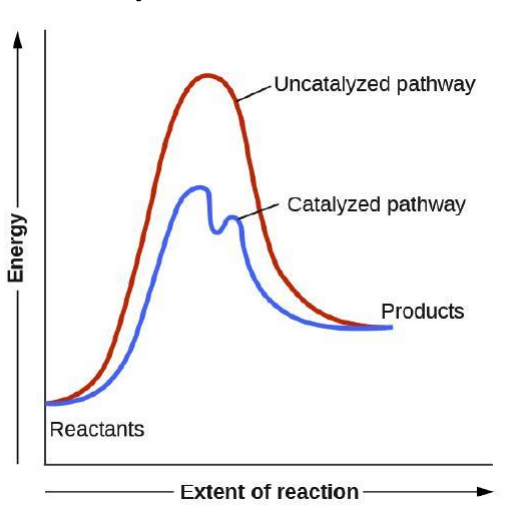
Reaction coordinate diagram
depicts energy changes during the progress of the reaction
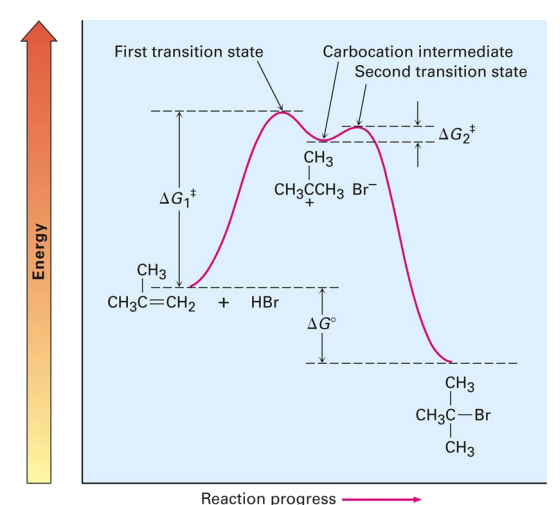
Activation energy (E_act):
energy difference between reactants and transition state
Transition state:
highest energy structure i
Reaction intermediate:
intermediate product formed from one step of a mechanism that is immediately consumed in the next.
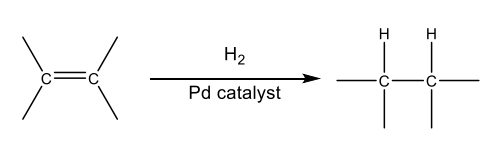
Catalyst
substance that increases the rate of a chemical transformation by providing an alternate mechanism