Plasma Membrane
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Plasma Membrane
- protective barrier that contains the cytoplasm and regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell.
- allows cell recognition of signals from other cells
- binding site for enzymes
- anchoring for filaments for cytoskeleton
Phospholipid
- lipid molecule that consists of a phosphate group attached to a glycerol, and two fatty acid tails
-semi permeable
kink
- located ON the tail of the phospholipid
- prevent tight packing
Hydrophilic
- attracted to water.
- polar head
Hydrophobic
- repel water
- non polar
cholesterol
-acts as a fluidity buffer
- found between phospholipids
- warm temp: decreases membrane fluidity
- cold temp: increases membrane fluidity
integral protein
-structural support (foundation)
-gateways for molecules to enter and exit
peripheral protein
-found on the surface of the cell membrane
- facilitate communication between the cell and the environment
-where cytoskeleton rests
glycoprotein
- maintains membrane stability
- facilitate cellular recognition (receptors)
glycolipid
-lipids with attached carbohydrates
Fluid Mosaic Model
A model that describes the structure of cell membranes as a mosaic of various components that move fluidly within the lipid bilayer.
Seymour Jonathan Singer and Garth L. Nicolson
proposed fluid mosaic model 1972
Diffusion
The process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Simple Diffusion
-no energy
-high to low concentration
-Oxygen diffusing into a cell and CO2 diffusing out
Facilitated Diffusion
A passive transport process that uses transport proteins to move molecules across the cell membrane from high to low concentration.
-H2O, glucose, amino acids
carrier proteins
-change their shape to transfer molecules (active)
- prevents hydrophilic or changed molecules to interact with the nonpolar part of the cell
channel proteins
- have pores (passive)
- create a hydrophilic path through the bilayer
Membrane Proteins
These are short branched chains of fewer than 15 sugar units. They facilitate cell-cell recognition and to a lesser extent, maintain structure.
Active Transport
The movement of molecules across a cell membrane from low to high concentration, requiring energy.
Endocytosis
The process by which cells engulf external substances, fluids, or particles by enclosing them in a vesicle formed from the cell membrane.
Exocytosis
- The process of moving large molecules out of the cell by vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane.
- this is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with one another
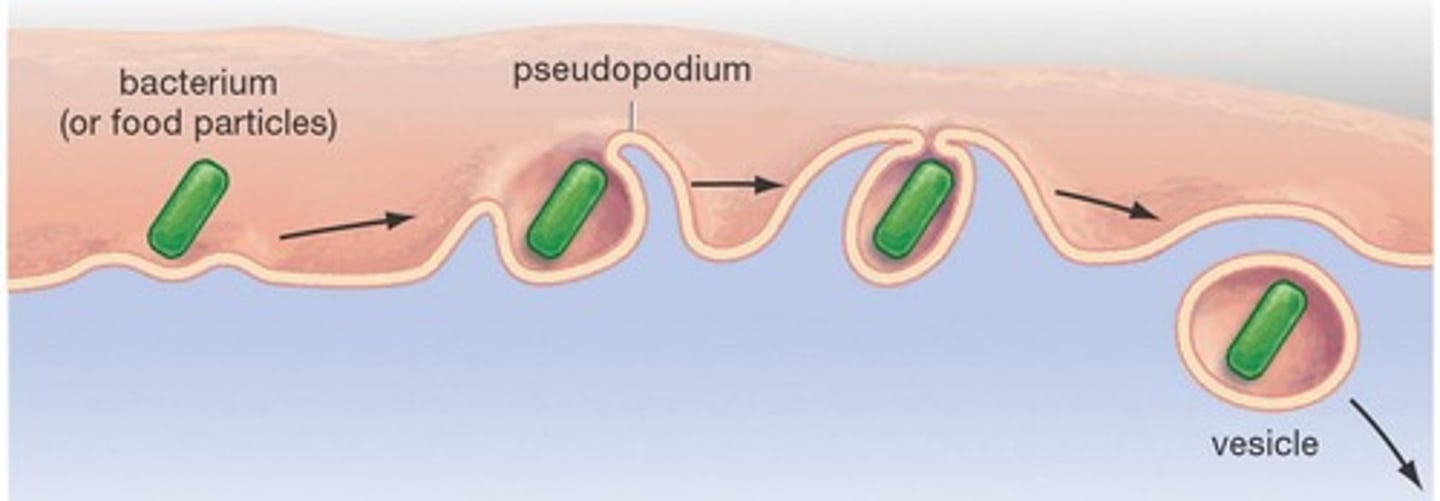
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis where the cell engulfs large particles, such as bacteria or food, often referred to as 'cell eating'.
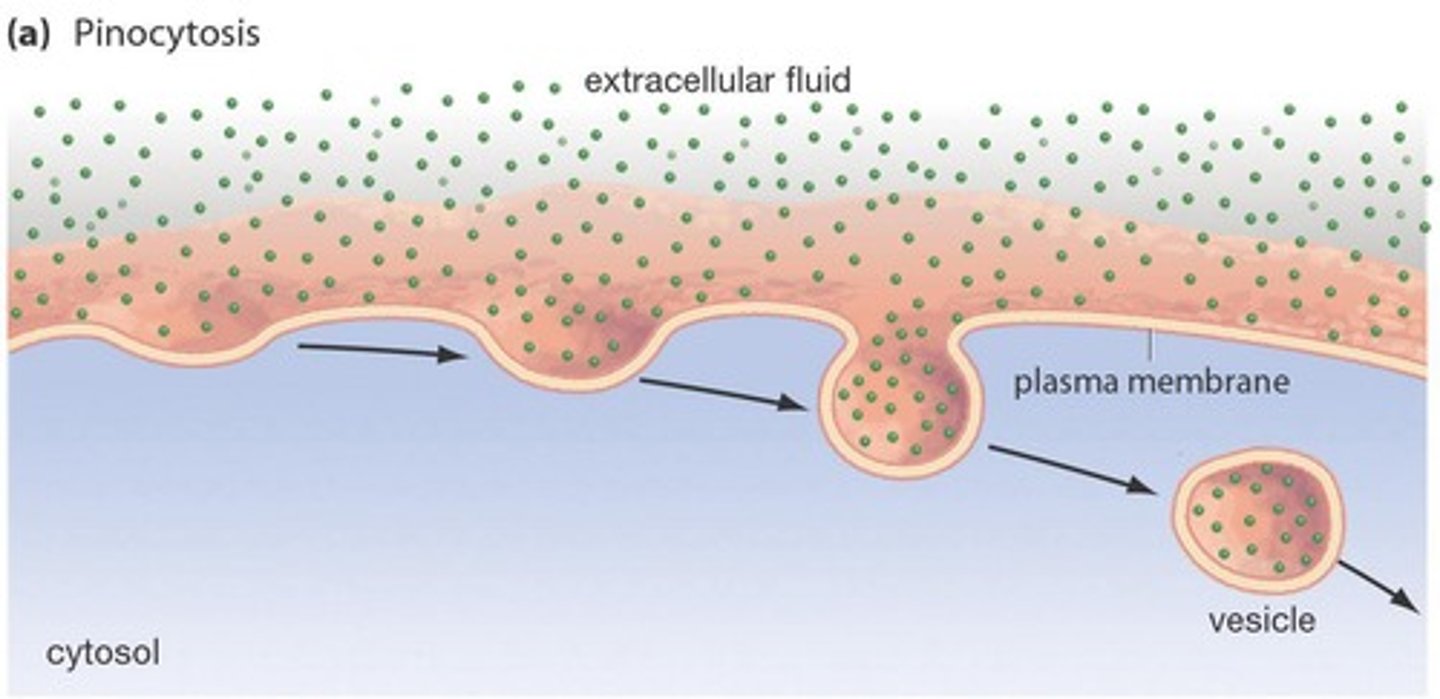
Pinocytosis
A form of endocytosis where the cell takes in dissolved molecules as a vesicle, often referred to as 'cell drinking'.
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
- A process where cells take in specific molecules based on receptor-ligand interactions.
- only allow certain molecules
water potential
- tendency of water to move from one area to another
tonicity
ability of an extracellular solution to make water move into or out of a cell by osmosis
Isotonic Solution
- concentration of solutes is equal inside and outside
- no net movement of H2O
Hypotonic Solution
- lower concentration of solutes
- H2O will enter the cell
- cell will swell then burst
Hypertonic Solution
- higher concentration of solutes
- H2O will exit
- cell will shrink then crenate
Osmosis
- The diffusion of water across membrane
- high (low solute) to low (high solute)
Cytolysis
The bursting of a cell due to excessive water intake in a hypotonic environment.
Plasmolysis
The process where cells lose water in a hypertonic environment, causing the cell membrane to pull away from the cell wall.
Aquaporins
allow for the passage of water in certain cells