orbital floor fractures1
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Types of orbital injuries
Blow out fracture
soft tissue injury
supraorbital fracture
naso-orbital fracture
zygoma fracture
What is a blow out fracture
The orbit is hit & forces soft tissue content backwards without rupturing globe
Rise in IOP fractures orbital walls - medial & orbital wall
Males more than F - assault, road traffic port work related

Types of blow out fracture
Pure
trap door
linear
hanging
hinged bone crack
Depressed
or combination
Impure
Orbital rim is involved
Blow out fracture mechanism
limitation of OM = direct entrapment & damage to EOM - commonly IR
=entrapment of orbital fascia, septum, connective tissue & muscle pulley
CH
Signs inc
Periorbital echhymosis
surgical emphysema
enophathalmos
depression of globe
traumatic mydriasis
sub conjunctival haemorrhage
hyphaema
facial asymmetry
symptoms inc
diplopia - vertical
infraorbital anesthesia - from damage from the infraorbital nerve = loss of sensation of ipsilatral cheek and upper gum
pain on eye movement
VA & AHP
VA - can slightly reduce = hyphaema
AHP - Chin elevation/ depression
Maybe face turn for medial wall fractures
CT
CT with & without AHP
hypotropia - entrapment of tissue anterior = limitation in elevation
hypertropia - entrapment of tissue posterior = limitation of depression
OM
Enophthalmos
limitation in elevation & depression with orbital floor fractures
limited abduction & adduction = medial wall fracture
Retraction of globe position of maximum limitation
Diplopia may swap depending position of gaze
infraorbital anesthesia = damage or bruising to infraorbital nerve = numbing of nerve i.e cheeck, upper lps - side of nose
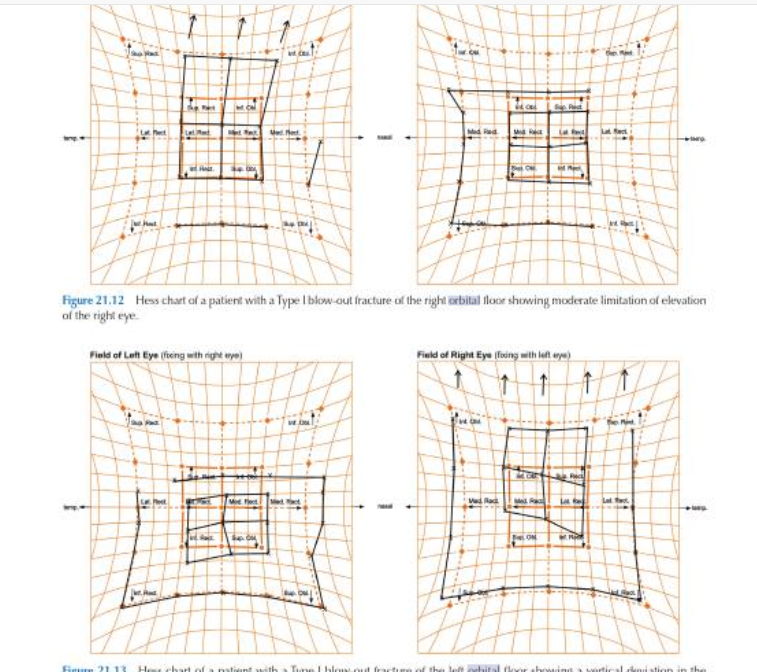
Hess chart
field of binoc single vision
Diplopia reverses w limitations in opposite position of gaze
good binoc in pp w AHP = limitation in opposite direction of gaze
examine fundus & media to check globe has been damaged or retinal detachment, vitreous detachment subluxed lens & optic nerve patency
X-ray, CT, tomography to see point of fracture
measure IOP if hyphaema
FDT - mech/neuro
Enophthalmos - exophthalmos
measure saccadic velocity
mx
wait for recovery wait apprx 14 days
younger pts responded poorly than older pts due to faster formation of fibrous scar tissue in young pts
pts w fractures involving alot of orbital floor be operated early
soft tissue thats damaged when trapped between bone fragment = fibrosis & tethering of globe
antibiotics & prednisolone help ↓ infection & inflammation
treatment options orbital injuries
observation
conventional treatments - prisms, exercises & occlusion
surgical
indications for surgery - dulley & fells
Diplopia not resolving
enophthalmos >3mm
large fracture
incarceration of tissues w globe restriction
IOP increase on upgaze
aims of surgery
free trapped tissue & repair fracture site
correct strabismus
Le fort classification
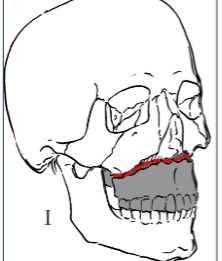
Le Fort type I
Tooth bearing portion separated from upper maxilla
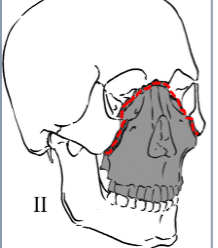
Le Fort type II (pyramidal fracture)
Fracture across orbital floor and nasal bridge (involves medial wall
and floor)
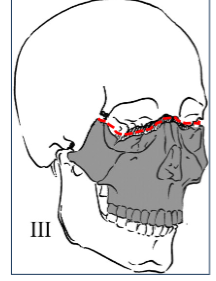
Le Fort type III (craniofacial separation)
Fracture across fronto-zygomatic suture line, entire orbit and nasal
bridge (involves floor, medial and lateral walls

soft tissue injury
due to trauma to orbital area - not causing fracture of any bone = damage to orbital area
muscle damage
lacerations
damage to nerve supply to EOMS
hemorrhage = limitations of movement & proptosis
lid injuries inc
lid lacerations
injuries involving lacrimal canal
swelling & pseudoptosis
levator damage with traumatic ptosis
ocular signs
sub conjunctival haem
corneal abrasions
lens dislocation
damage to iris with traumatic mydriasis
hyphaema
retinal detachment
optic nerve damage
choroidal ruptures
Supraorbital fracture
sharp object going through orbital roof
characteristics
superior periorbital swelling & haem
lid oedema
supraorbital anesthesia
damage to levator and nerve supply
diplopia due to muscle damage
depression of supraorbital rim = globe retraction
CSF fluid discharge
naso orbital fracture
direct trauma to naso orbital area
due to road traffic
charactristics
dish face appareence
oedema & bruising
epistaxis
nasal obstruction
surgical emphysema
damage to tear duct and lacrimal sac
zygoma fracture
bone displaced outwards = traumatic enophthalmos = swelling
bone displaced inward = traumatic proptosis
characteristics
muscle or nerve damage
oedema - impair OM
infra orbital anesthesia
white eye
IR caught in trap door orbital floor fracture
urgent surgical to prevent ischemic muscle damage
Painful restriction of eye movement.
Double vision (diplopia).
Enophthalmos (a sunken appearance of the eye).
Autonomic symptoms like nausea and vomiting
lack of significant soft tissue trauma (like bruising or swelling) around the eye, despite the presence of a fracture and potential muscle entrapment
A: Types of orbital fractures include:
Pure fracture: Only the orbital floor is fractured
Impure fracture: Involves the orbital rim
Other types: Blow-out fractures - orbital floor, medial wall, or both
naso-orbital fractures, orbital roof fractures, and zygomatic fractures
Q: What types of fractures are common in pediatrics?
Depressed fractures: A detached bone piece
Trapdoor fractures: A fracture where bone swings but doesn't fully detach
Linear fractures: Bone breaks and closes, trapping tissue (greenstick fractures)
What is the hydraulic mechanism in blow-out fractures?
buckling
hydraulic mechanism= increase IOP = Blunt trauma pushes the globe back, causing the orbital floor or medial wall to fracture.
buckling
They're a compression fracture, which means the break is caused by sudden pressure on a bone.
Blow-out (Smith & Regan 1957) - hydraulic
Q: What are common causes of blow-out fractures?
: Common causes include blunt trauma from sports, road traffic accidents, and assaults. These are most common in males in their 20s/30s.
Q: What are the eye symptoms associated with orbital fractures?
Diplopia (double vision)
Restriction in eye movement (due to muscle entrapment)
Enophthalmos (sunken eye)
Infraorbital anesthesia (tingling or loss of sensation)
Q: What deviations can occur with orbital fractures?
: Deviations can include hypotropia (downward deviation) or hypertropia (upward deviation) depending on the fracture.
Q: What are the periorbital signs of orbital fractures?
Periorbital signs include:
Bruising
Black eye (ecchymosis)
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
Crepitus (crackling sound)
Epistaxis (nosebleed)

Q: What is the Oculocardiac Reflex (OCR) in relation to orbital fractures?
: The Oculocardiac Reflex (OCR) is triggered by EOM traction, leading to bradycardia (decreased heart rate).
Q: When is immediate surgery indicated for orbital fractures?
Immediate surgery is indicated for severe cases such as:
Non-resolving OCR
Significant enophthalmos
Pediatric "white-eyed" fractures with muscle entrapment
Q: Why might late surgery be preferred for orbital fractures?
Late surgery may be preferred to:
Reduce risks of infection
Reduce risk of blindness
Assess late enophthalmos after edema has reduced
Q: What surgical techniques are used for orbital fractures?
FDT (Forced Duction Test) to assess mechanical restriction
Approaches: Trans-eyelid, trans-conjunctival, Caldwell-Luc (via the maxilla),
endoscopic
Medial wall exposure: incision can be used to expose the medial wall.
Periosteum incision: The periosteum is incised and elevated to expose the fracture borders.
Q: What conservative management options are available for orbital fractures?
: Conservative management options include observation, prisms for small deviations, or no immediate surgery for mild cases.
what are the feature of a white eye fracture?
a linear trapdoor blowout fracture - orbital wall fracture - in adults & children. Features:
Limited eye movement: Patients may avoid opening their eyes or looking up due to pain or nausea.
diplopia
Nausea and vomiting: This can be caused by the oculocardiac reflex.
Pain: Patients may experience pain during eye movement.
Lack of bruising: The name "white-eyed" refers to the lack of periorbital bruising and swelling that's often present.
No subconjunctival hemorrhage: This is a characteristic feature of a white-eye fracture.
White-eye fractures are considered a surgical emergency and require urgent surgery within 24–48 hours.
infection travels through sinuses = bruising
bone breaks and snap back = eyes look normal
ocular cardiac reflex - A triad of symptoms that includes bradycardia, nausea, and syncope. It's a rare but serious complication
check elevation - IR
white eye fracture + OCR = emergency
medial wall = thin = more susceptible to fracture = eso
inferior wall - hypo
spinchter restrict
radial dilate
Orthoptic investigation
diplopia - not always as can be too swollen to see
numbness - 5th CN damage - trauma to floor infraorbital anesthesia
ask about ocular cardiac reflex = IR trapped + SR
increase pressure to eye = faint
CHP = chin elevation - eyes move down = mechanical deviation
CT scan
pupil = traumatic mydriasis = pupil dilated slightly = mid dilated pupil
haematoma - bruising anywhere
conjunctiva bruising
if blood in anterior orbit = hyphaema
measure eye using exophthalmometer
CT w/ CHP = BSV
Common dev - hypo = pseudoptosis
pulling sensation
trap door fracture
scan looks normal
broken but goes back to where it was
severe
floor is gone = inset plate
completely breaks - eyes sink in - look lower
medial wall and lr can break - IR = trapped anywhere
measurement & tests
BSV
w/ CHP = normal BSV unless sublex lens - cornea scratch
PCT - 5 position of gaze
synoptophore
if obliques were affected = no torsion
MRI - soft tissue scan
CT scan look at bones
Hess chart - 2 stages of ms - affected = squashed
field of unioc fixation - mechanical restriction
field of BSV - surgery to stretch field of BSV
treatment
white eye
immediate emergency + ocular cardiac reflex
surgery release muscle - bc floor + wall provide no support - medial wall or sig wall entrapment = facial asymmetry
Diplopia
no muscle entrapment - just looks swollen - observe and occlusion
sig dip - surgery
cold compression
severe accident
wait till medically stable
late surgery
little to no opthalmus
sm diplopia
Criteria for orbital fracture repair
10- 14 days after onset
-sig diplopia
herination
incareraion/retraction
significant enophthalmos >3mm
Timing - immediate vs early vs late - burnstein 2002
immediate
Non-resolving oculocardiac reflex (e.g., bradycardia).
Significant enophthalmos (>3mm) or facial asymmetry.
White-eyed blow-out fracture (<18 yrs): minimal edema, marked restriction, tissue/muscle entrapment.
Early vs Late
Early: After edema/hemorrhage reduction; assess enophthalmos.
Late: Risk fibrosis; complications include blindness, infection, implant migration, diplopia.
Evidence
Simon et al. 2009: Minimal motility outcome differences between early and late surgery (limited data).
Management: Surgical and Conservative
FDT
Trans-eyelid
Trans-conj
Caldwell-Luc
Endoscopic
Conservative
Suspect soft tissue
Small deviation (elevation)
Prisms
Record progress prior to any surgical
intervention