Exam 1
1/238
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Human Reproduction and Sexual Behavior (Lectures 1-11) IMPORTANT: Idk if the first topic (history aspects) super relivant for the exam but it's there just in case !!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
239 Terms
True or false?: Is there a huge variation in sex and reproductive strategies across animals?
True
Sex for procreation (SFP)
historically common idea was that reproduction is only legitimate and moral reason for sex
Sex became synonymous with penile-vaginal intercourse
True of false: Oral and anal sex was illegal in 10 states until 2003
True (sodomy laws)
Rigid male and female gender roles
based on concept of gender binary - two genders
How did SFP develop?
Christians associated sex with sin —> celibacy & spirituality linked, superior to marriage (New Testament: included anger, selfishness, and… non-martial sex
Celibacy (old times)
unmarried, no intercourse
Celibacy (modern day)
simply no intercourse (marital status isn’t a factor)
Who declared that the original sin of Adam and Eve was lust?
Augustine
Who claimed homosexual acts, anal intercourse, and oral sex were against God’s will?
Thomas Aquinas
also believed that sex organs were solely for reproduction
(18th Century) Who were proponents of the value of sex in marriage and eased restrictions? (Hint: Reformers)
Martin Luther & John Calvin
How did the Victorian era define the roles of men and women? (Hint: step back from Reformation)
Encouraged self-restraints on all aspects of life including sex, however, prostitution flourished
Believed women didn’t experience sexual desire, enjoyment, or orgasm
Sigmund Fraud Contributions (20th Century)
The Interpretation of Dreams (1900) said sexuality innate in both men and women
Physician Havelock Ellis (20th Century)
Wrote Life and Sex: emphasized love rights of women
oral sex, homosexuality, and masturbation are okay if nobody is harmed
WWI (1914-18)
Gender roles expanded as thousands of women took paying jobs for first time
Great Depression (1929-39) - RGR
Went back to strict gender roles
Women’s suffrage
began late 19th C
goal was giving women right to vote
19th amendment in 1920 gave right to vote to women
WW II (1941-45)
gender roles expanded
postwar retreat to traditional gender roles
Sexual revolution (1960s-70s)
Numerous contraceptives introduced: pill, IUD
Kinsey studies
Masters and Johnson studies

Media and Sexuality
Sex sells!
sexual images, both blatant and subtle designed to attract attention to and sell products
1981 most music videos included sexual content (more overt & explicit)
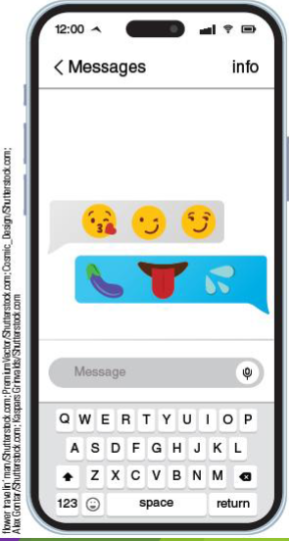
What does this image mean? (Research verified)
most common emojis people send and receive in sexually suggestive messages
Sexology
Study of sexuality
goals —> understand and predict sexual behavior
Population
group of individuals being studies
Sample
subset of individuals in population
Random sample
randomly chosen subset of a population
Representative sample
limited sample that provides an accurate representation of the larger target population
Convenience sample (ie. students in class)
selected based on convenience and accessibility
Volunteer bias
tendency for those who volunteer for research to be different in some way from those that refuse
ie) more sexually experienced or positive attitudes toward sexuality are more likely to volunteer
Demographic bias
tendency for some members of population to be over-represented and others to be excluded
Qualitative Study
examines small group (6-10) of people in depth
pros: in-depth explorations of behaviors thoughts, and feelings
cons: limited generalization of findings; possibility of inaccurate info
Survey
data gathered from relatively large groups of people by means of questionnaires or interviews
pros: relatively cheap and quick method for obtaining large amounts of data; more practical
cons: non-response bias, demographic bias, possibly inaccurate
Direct observation
researchers observe and record responses of participants
pros: eliminates the possibility of data falsification
cons: a person’s behavior can be influenced by presence of observers(s) or artificial nature of environment where observations are made
Experimental method
researcher manipulates a set of conditions, or variables, and observes the effect of this manipulation on participants’ behavior
pros: provides controlled environment for testing relevant variables; can determine casual relationships b/w variables
cons: artificiality of lab settings can change or bias participants’ responses
Spontaneous Orgasms
case studies revealed association b/w various antidepressant drugs and orgasm w/o sexual stimuli
Non-response
refusal to participate in a study
Demographic bias
sampling bias in which certain segments of society are disproportionately represented
Kinsey Reports (Most famous Survey Study)
1938 Kinsey began collecting sex histories (through marriage and fam course for married people) & 3 years later gathered nearly 2000 Findings: American men and women masturbated, had premarital sex, same sex interactions, adultery, oral, anal, etc; hetero and homosexuality are not binary
Demographics of Kinsey Reports
broad spectrum of Americans (ages, marital status, occupations, education, religion, etc)
BUT only white people were sampled AND educated urban protestants, volunteered
NHSLS = National Health and Social Life Survey
(representative sample) survey 4,369 Americans from ages 18-59
79% respondent rate
Conclusion: most content with erotic lives and more sexually conservative than believed
Masters and Johnson
most famous observers
studied physiological changes during sexual arousal
book: Human Sexual Response (1966)
developed 4 stage model (Human Sexual Response 1996)
discovered that people could have multiple orgasms
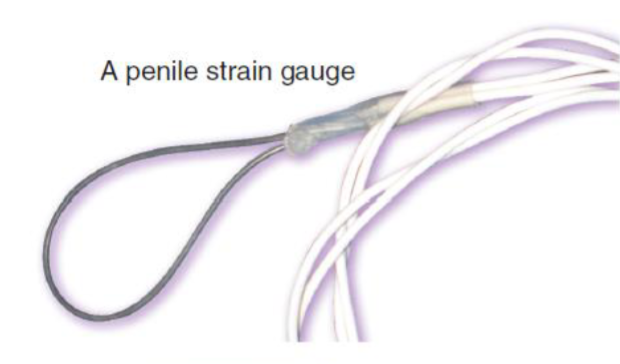
Penile plethysmograph
looped around base of penis
measures changes in blood flow to penis (increase in circumfrence)
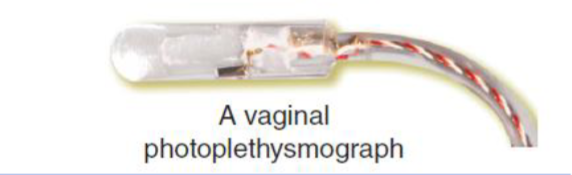
Vaginal photoplethysmograph
light sources and detector
measures increased vaginal blood volume bc of arousal via light backscattered to device
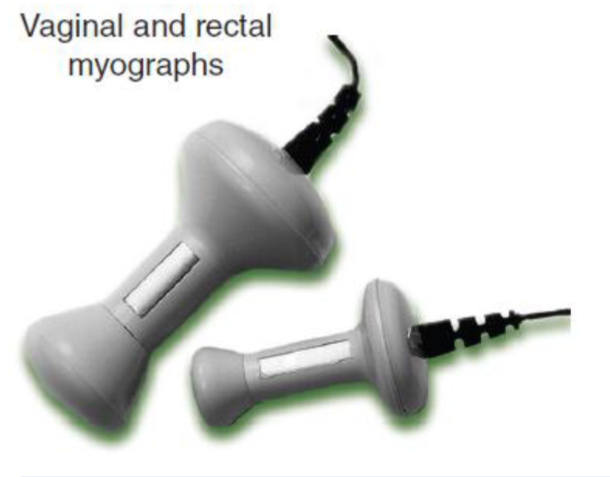
Vaginal and rectal myographs
measure muscular activity in pelvic area
Functional MRI
imaging tool that creates detailed, cross-sectional pictures of inside the body using radiofrequency waves, powerful magnets and a computer
Variable
anything that can vary or change
Experimental group
is exposed to some variable
Control group
not exposed to variable
Placebo
inactive substance that resembles treatment you are testing (fake treatment)
Independent variable (IV)
variable that is manipulated by researcher (possible cause)
(ie.) shown R rated movies with or w/o violence to test for violent media consumption leading to desensitisation of violence)
Dependent variable
what is measured by researcher (effect)
(ie.) questionnaire few days later about attitudes of violent films
Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in Black Americans
group of 399 Black men with syphilis given periodic exams and told they being treated for syphilis but were not
victims of study were all Black and many died of syphilis, 40 spouses who contracted the disease and 19 children born with congenitalssphillis
Homology
derived from the same primodial tissue; develop from the same stem cells (ie. penis and clitoris)
Gamete (23 chromosomes)
haploid cell capable of reproduction by fusing with another haploid gamete (fertilization)
Sperm
gamete produced by testes in a process called spermatogenesis
Ova
gamete produced by the ovaries in a process called oogenesis
Penis
internally made up of nerves, blood vessels, and cylinders of erectile tissue and urethera
Scrotum
pouch of skin that holds testicles
can rise and fall depending on temprature
can sweat to cause cooling
What are the primary functions of the Penis?
conduit urine to leave the body
conduit semen (has sperm) to leave body
organ of sexual pleasure
Identify the 3 sections of the penis:
glans: head of penis
shaft: body of penis
root: base of penis (not external)
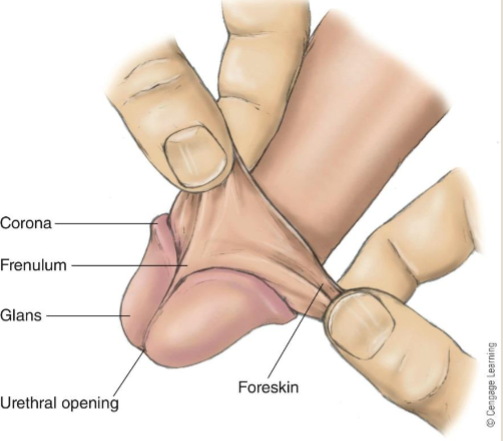
Glans
made up of:
corona (rim)
meatus (urethral opening)
frenulum (most sensitive)
foreskin (prepuce)
Smegma
build-up underneath foreskin; cheesy material —> wash to prevent infections
Circumcision
removal of foreskin; more common in US
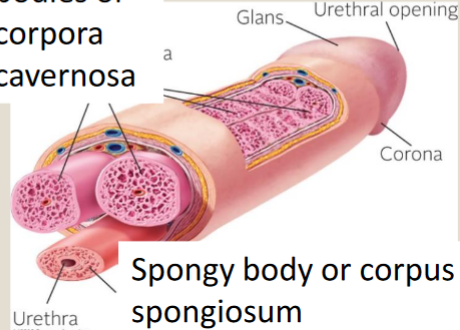
Two Cavernous bodies (corpora cavernosa)
run dorsally along upper portion of penis
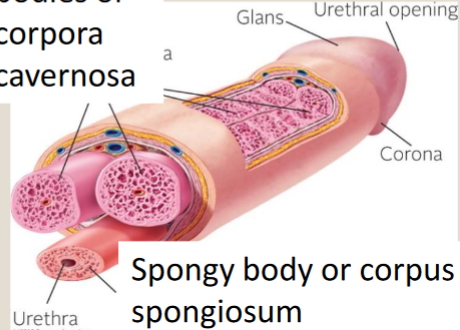
Spongy body (corpus spongiosum)
erectile tissue that are on the underside of the penis and surrounds urethra
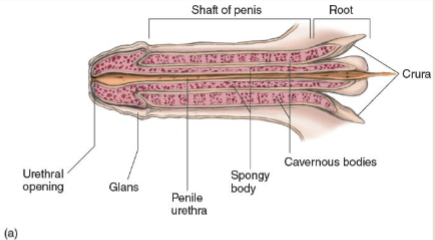
Root
extensive network of muscles to control unrination and ejaculation
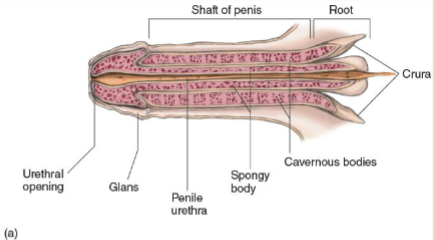
Cruca
attached to pubic bone through ligaments
muscles help control urnination and ejaculation
Kegel
may get stronger orgasms and ejaculatory control
stopping and starting urination (for males)
What is the optimal temprature for sperm production?
93 F
Tunica dartos
smooth muscles and connective tissue raising and lowering testicles when warm or cold
Perineum (taint)
sensitive area b/w genitals and anus
can ehance pleasure and orgasm
supports urogental muscles important in defecation
Pubic hair
act as cushion during sexual contact and traps scents that are attractive
Internal spermatogenic reproductive anatomy includes:
penis
testes (gonads)
ejaculatory pathway
seminal vesicles
prostate gland
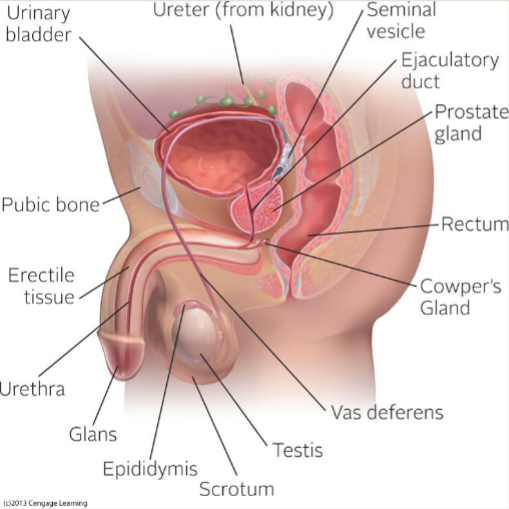
Testes (gonads)
main functions are to produce gametes and testosterone
Ejaculatory pathway
sperm have to take to leave body
epididymis
vas deferens
ejaculatory ducts
seminal vesicles
behind bladder; make 2/3 volume of semen, alkaline, fructose (giver sperm energy), vitamins
prostate gland
doughnut shaped and walnut sized
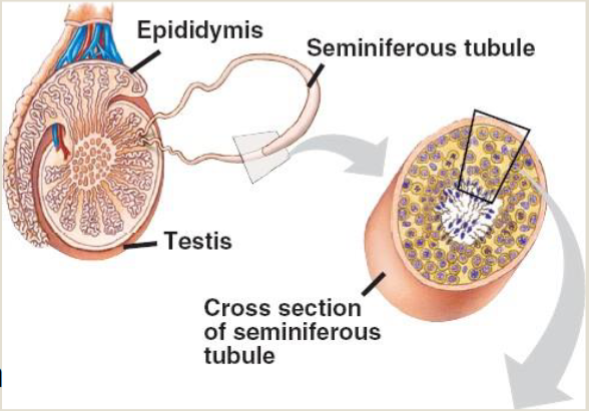
Seminiferous tubules
sperm are produces
each testicle has 250-1000 and each 1-3ft long
lined with two types of cells: Sertoli cells and spermatogonia
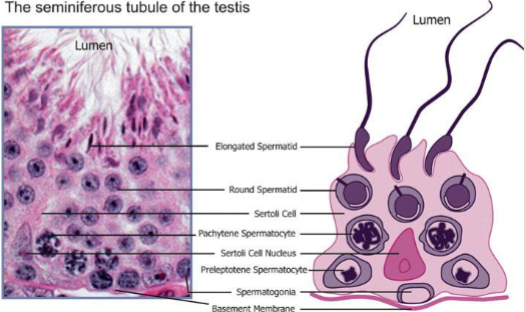
Sertoli cells
nurture and facilitate spermatogenesis (process of making sperm
secrete anti-mullerian hormone involved in prenatal sexual differentiation
Spermatongia
primordial germ cell that goes through meiosis to produce mature sperm cells
Scrotum and Testes
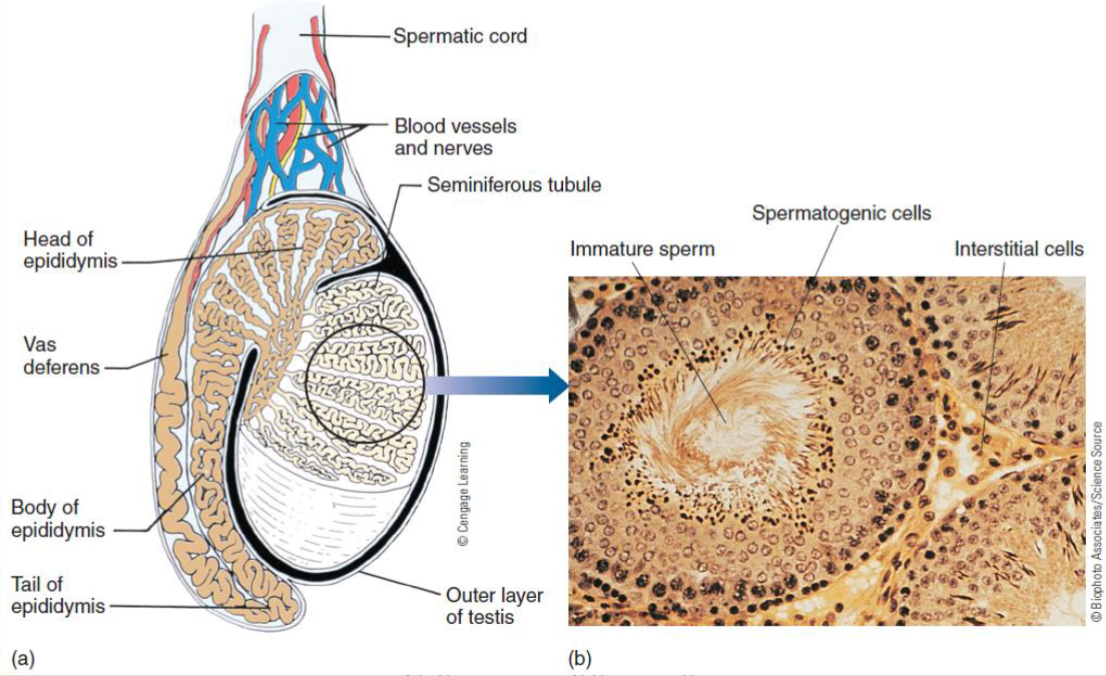
Interstitial cells of Leydig
cells b/w seminiferous tubules that secrete testosterone and other androgens
List the 3 regions of Sperm:
head (acrosome contains enzymes)
body (mitochondria provides energy needed for tail)
tail (flagellum)
What is the tail of sperm called?
flagellum
How many chromosomes do ova and sperm contain?
23
Autosomes
genes that produce other traits (not sex chromosomes)
Sex chromosomes:
X or Y
Which chromosomes induce formation of spermatogenic structures?
XY
Which chromosomes induce formation of oogenic structures?
XX
How many gametes are produced at a time in spermatogenisis?
Hundreds of millions of sperm
How many gametes are produced at a time in oogenesis?
one egg
How long does it take for spermatogenesis formation?
sperm produced every 100 days; from puberty onward
How long does it take for oogenesis formation?
female is born with all the primary oocytes she will ever have (born will all eggs)
What is the number of functional gametes from one stem cell in spermatogenesis?
4
What is the number of functional gametes from one stem cell in oogenesis?
1
True or false: Sperm are among the largest cells in the body
False
(they are the smallest !)
True or false: The egg is one of the largest cells in the body
True
Spermatogenesis
Sperm production
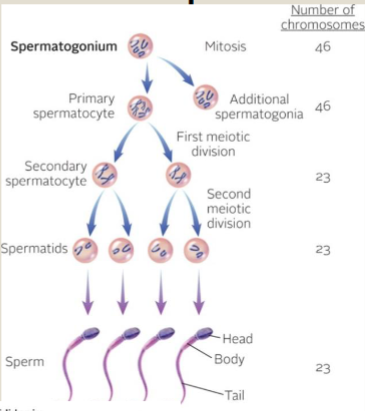
This is for the spermatogonium, make sure to know this
What happens to sperm through meiosis 1 division?
primary spermatocytes become secondary spermatocytes
What happens to sperm through meiosis 2 division?
Secondary spermatocytes become spermatids
What do spermatids mature to?
Sperm !