Orgo 2 Exam 1
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
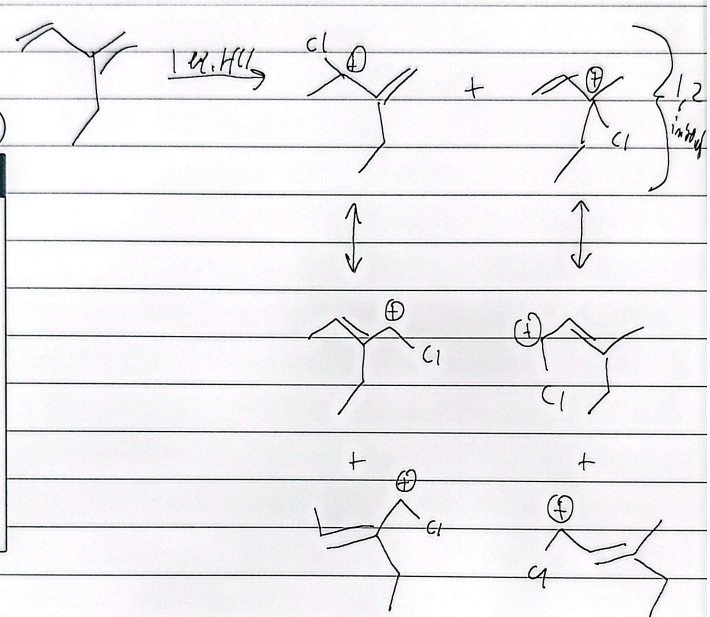
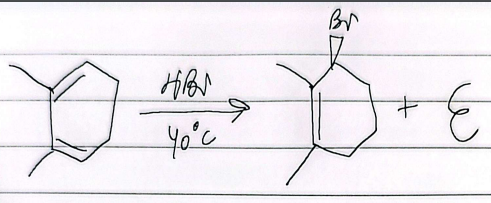
hydrohalogenation
mark

hydrohalogenation
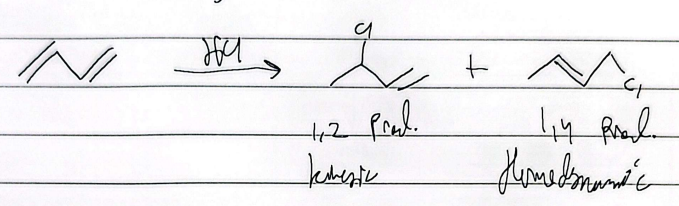
hydrohalogenation
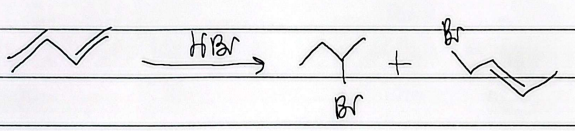
hydrohalogenation
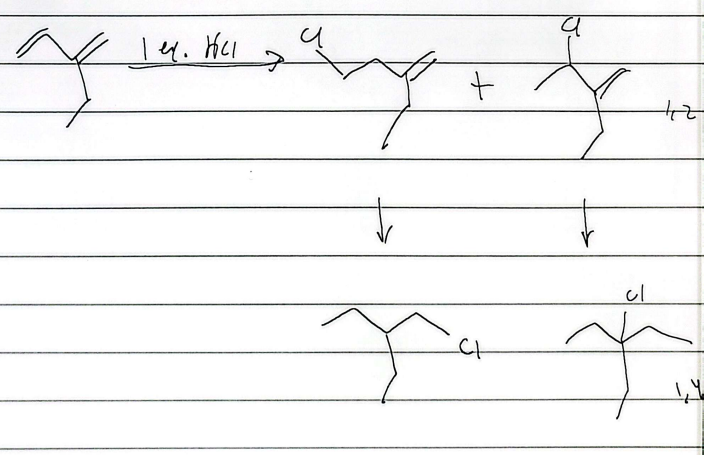
hydrohalogenation
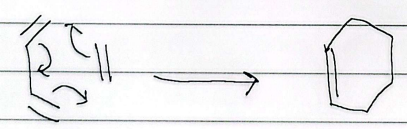
diels alder
s-cis
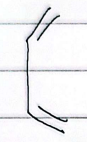
s-trans

diels alder
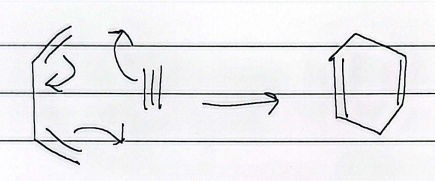
diels alder
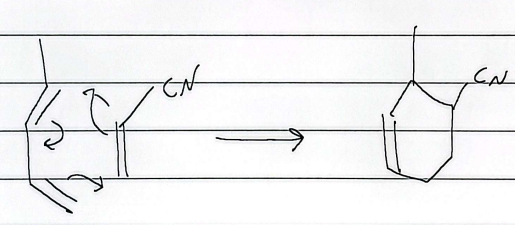
diels alder
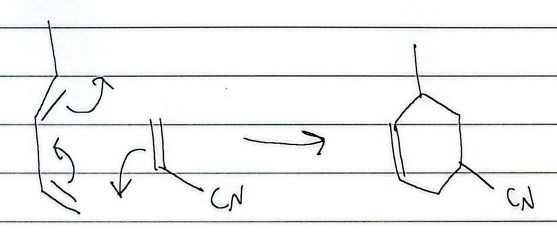
endo rule
substituents must be endo while the hydrogens must be exo
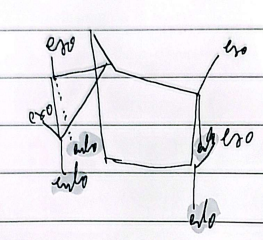
bicyclic diels alder
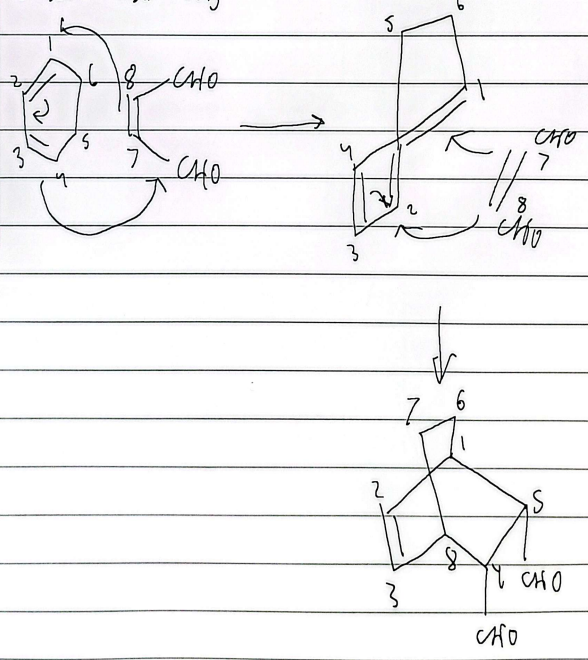
bicyclic diels alder
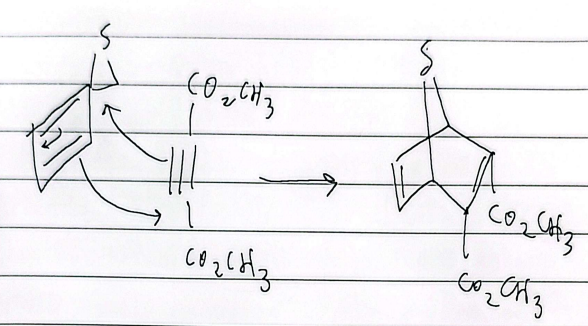
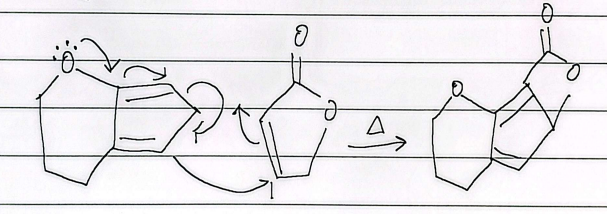
retro diels alder
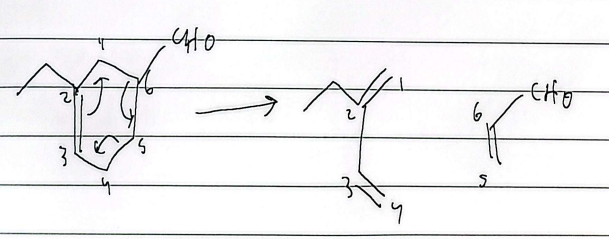
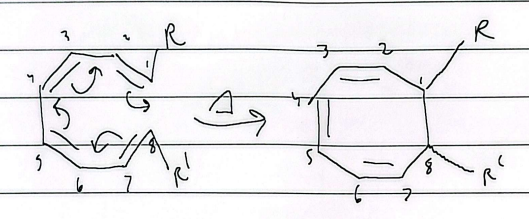
electrocyclic
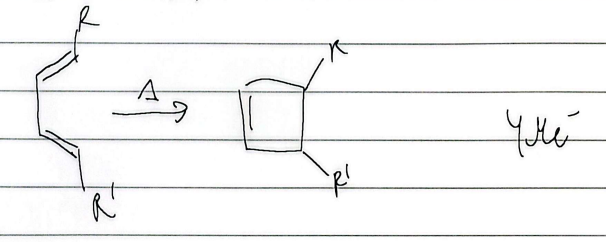
electrocyclic
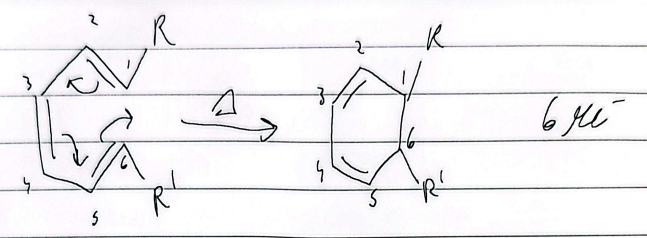
electrocyclic
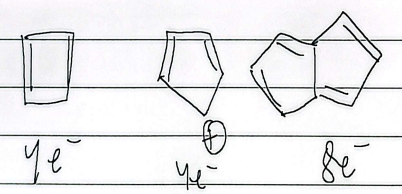
4e-
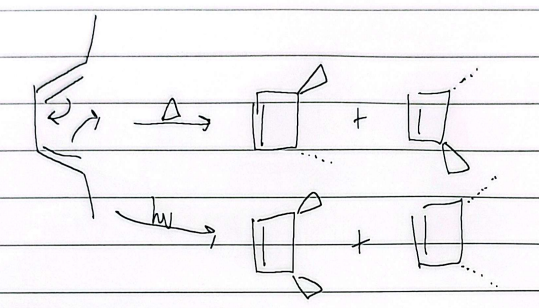
heat trans, light cis
4e-
heat trans, light cis
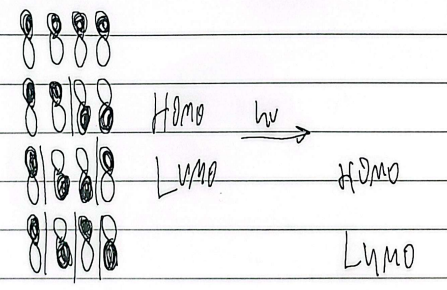
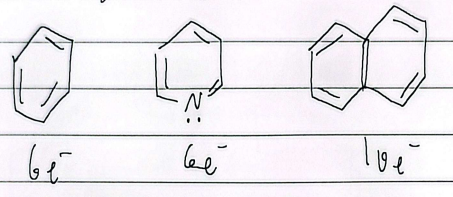
6e-
heat cis, light trans
6e-
heat cis, light trans
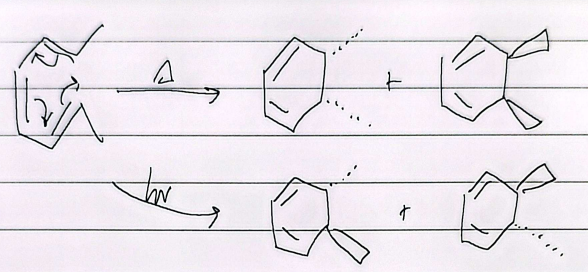
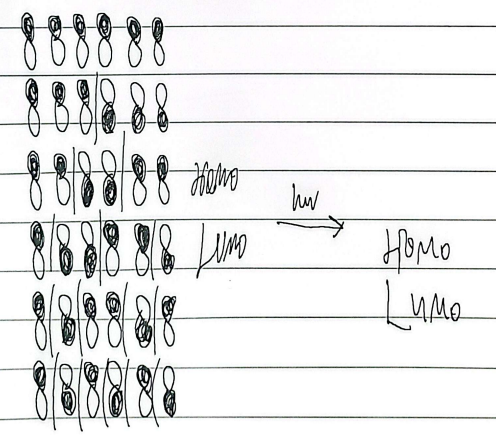
8e-
heat trans, light cis
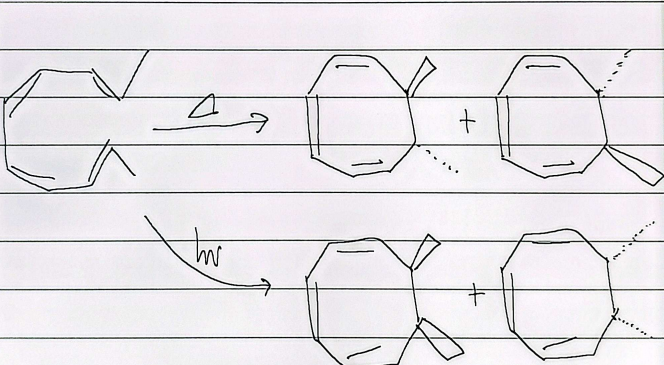
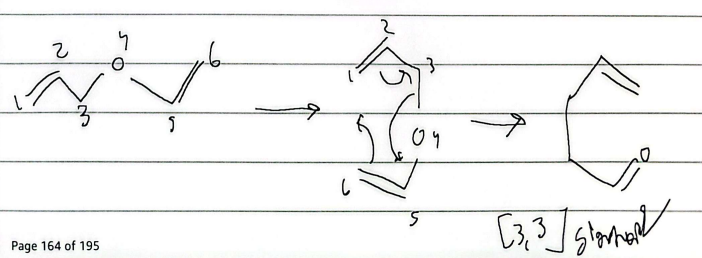
sigmatropic rearrangement
when symmetrical, 3-3 is formed
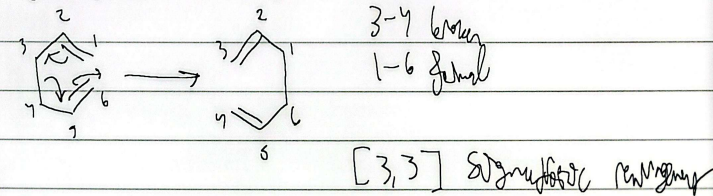
sigmatropic rearrangement

sigmatropic rearrangement
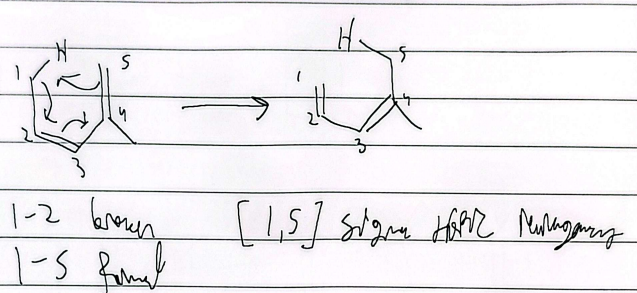
allyl vinyl ether
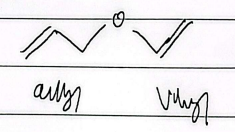
aryl vinyl ether
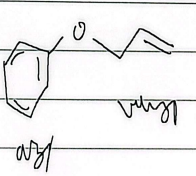
sigmatropic rearrangement
hydrohalogenation
diels alder
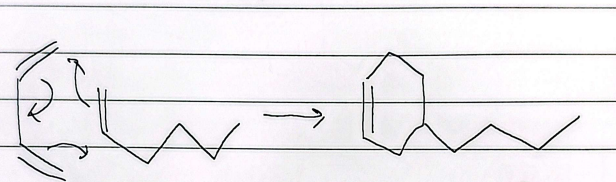
bicyclic diels alder
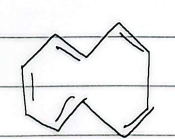
10 annulene
non-aromatic
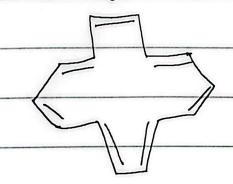
14 annulene
aromatic
2 annulene
antiaromatic
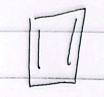
6 annulene
aromatic
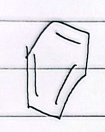
8 annulene
nonaromatic
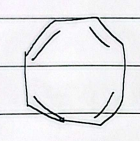
12 annulene
antiaromatic
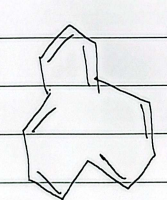
antiaromatic
a ring is ________ if it’s aromatic in every way except it’s number of pi e- is a multiple of 4 (4n; 4, 8, 12, 16..)
aromatic
planar, fully conjugated, delocalized e-, 4n+2 pi e-, all carbons must be sp2 to be planar
ortho
1,2
meta
1,3
para
1,4
priority
aldehyde > ketone > alcohol > amine > alkyl
phenol
aniline
anisole
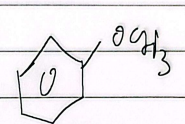
toluene

benzoic acid
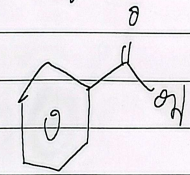
benzaldehyde
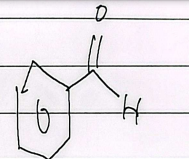
o-xylene
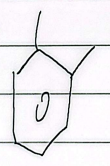
m-xylene
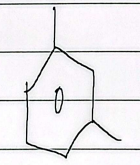
p-xylene
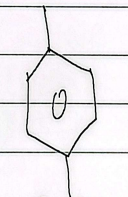
acetophenone
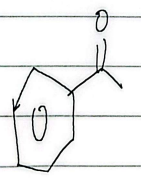
benzophenone
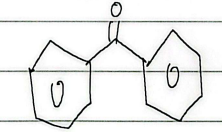
styrene
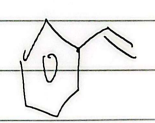
oxidation
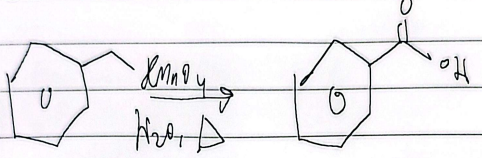
oxidation
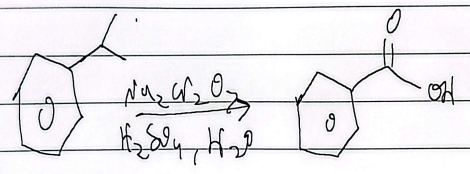
oxidation
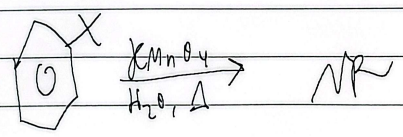
free-radical halogenation
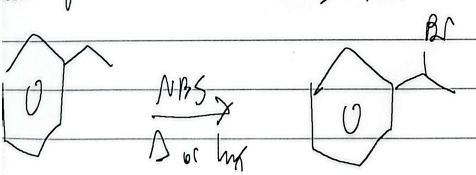
substitution

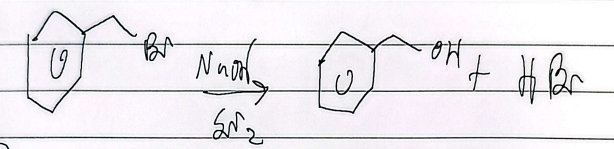
substitution
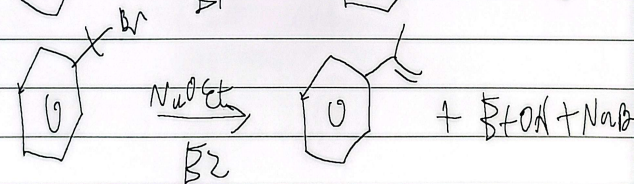
elimination

ellimination
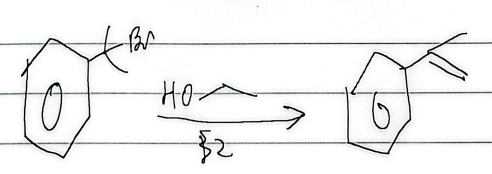
elimination
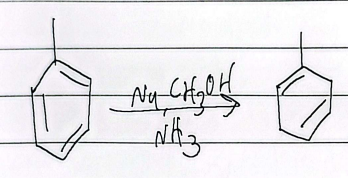
birch reduction
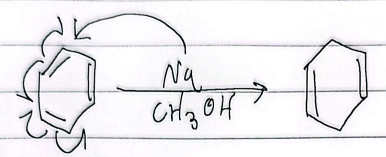
birch reduction
halogenation
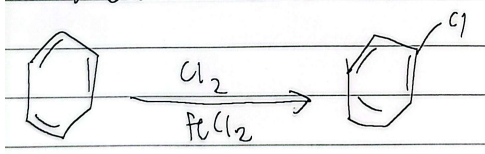
halogenation

EAS mechanism
E = Cl or Br
B: = FeCl4 or FeBr4
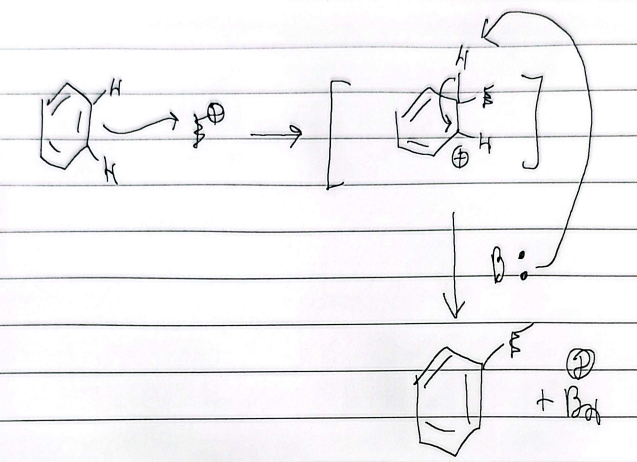
halogenation
selefluor is used

halogenation
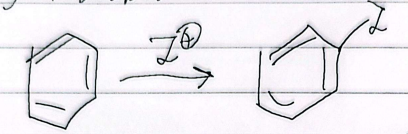
nitration
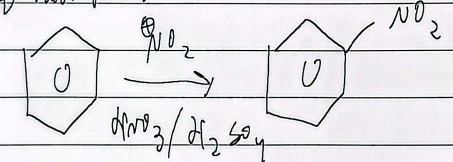
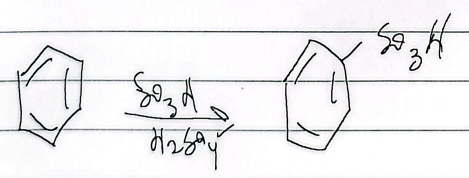
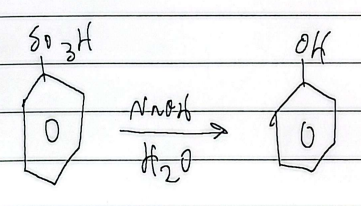
hydrosulfonation
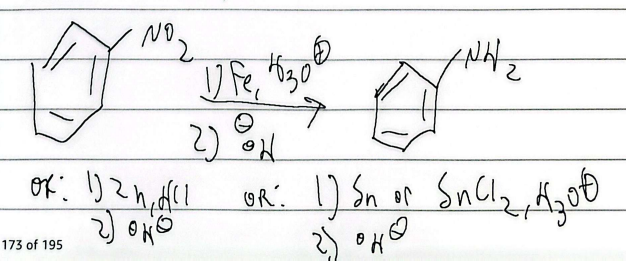
reduction
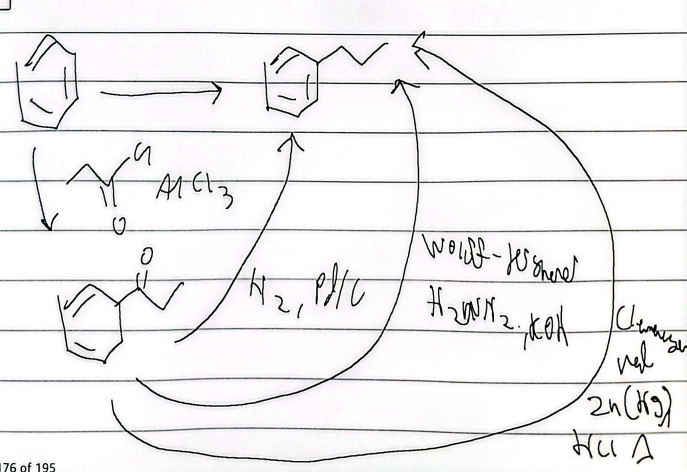
friedel-craffs alkylation
limitations
any alkyl halide can be used (single bonds only)
impossible to stop at mono-alkylation (multiple substitutions)
wont react if theres a strong deactivator
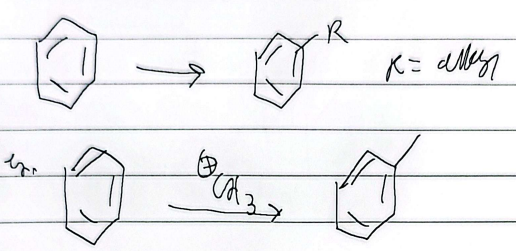
rearrangement
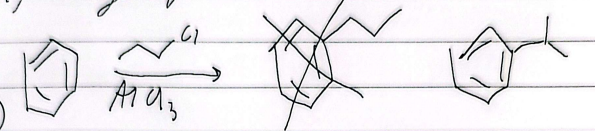
rearrangement
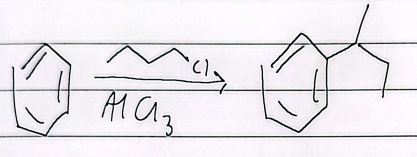
friedel-acylation
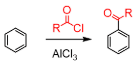
friedel-acylation
sandmeyer
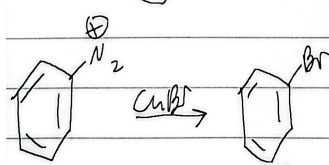
sandmeyer
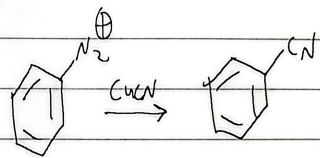
sandmeyer

rearrangement
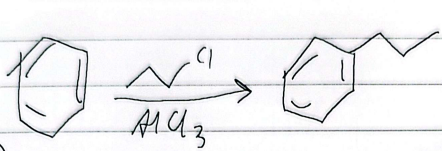
friedel acylation
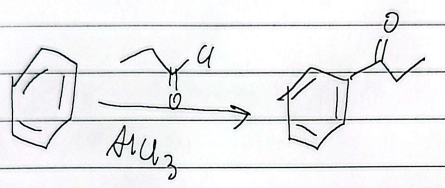
reduction
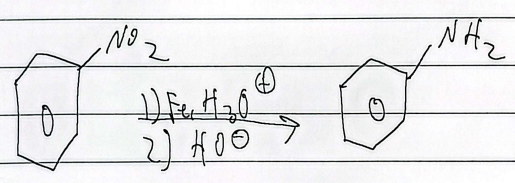
nh2 to n2+
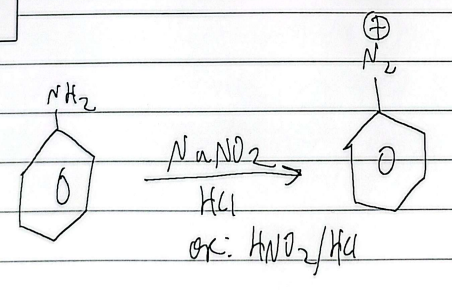
aromatic rxns
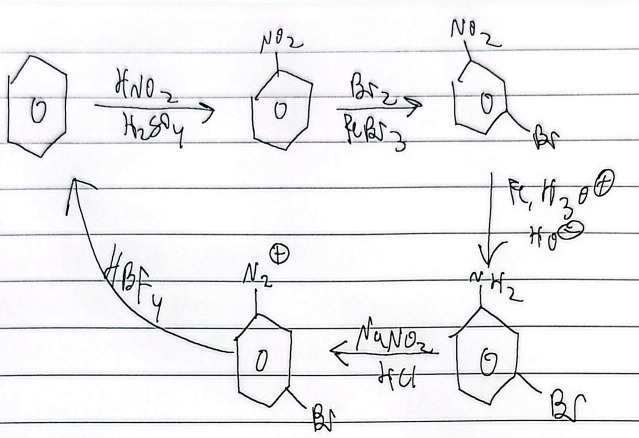
hydrolysis
activating groups
faster rxn, lone pair e- directly connected to benzene, neg or partial neg charge
ortho/para director
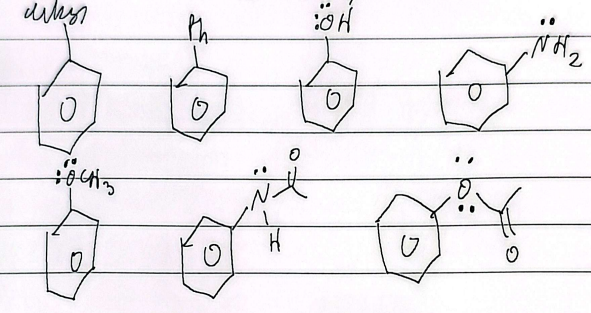
deactivating groups
slower rxn, pos or partiall pos charge
meta director
exception: halogens ortho/para deactivators
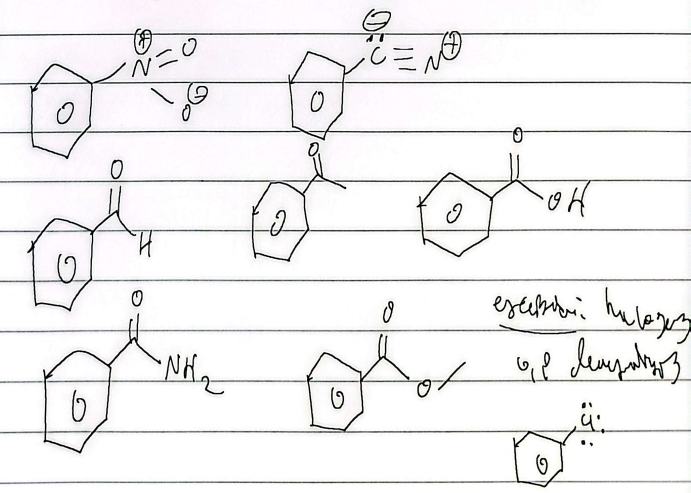
halogenation
sulfonation and halogenation
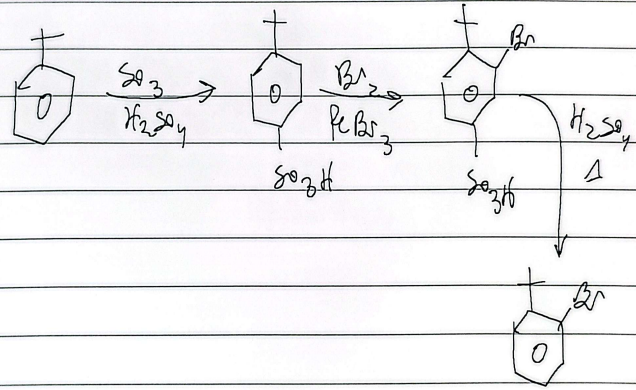
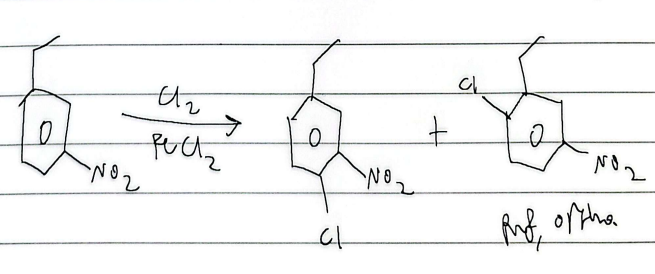
chlorination
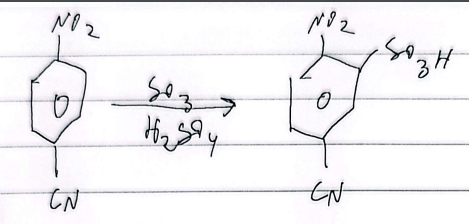
sulfonation
ring priority
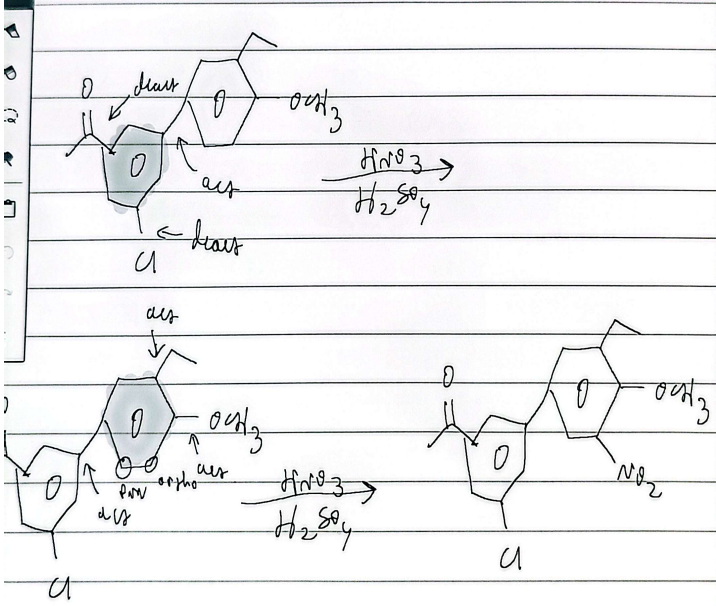
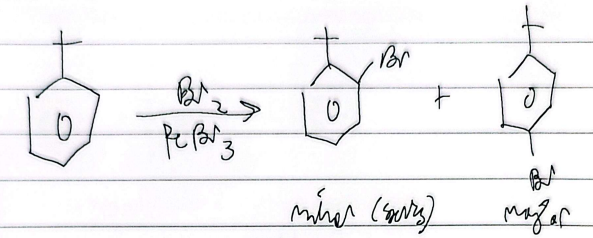
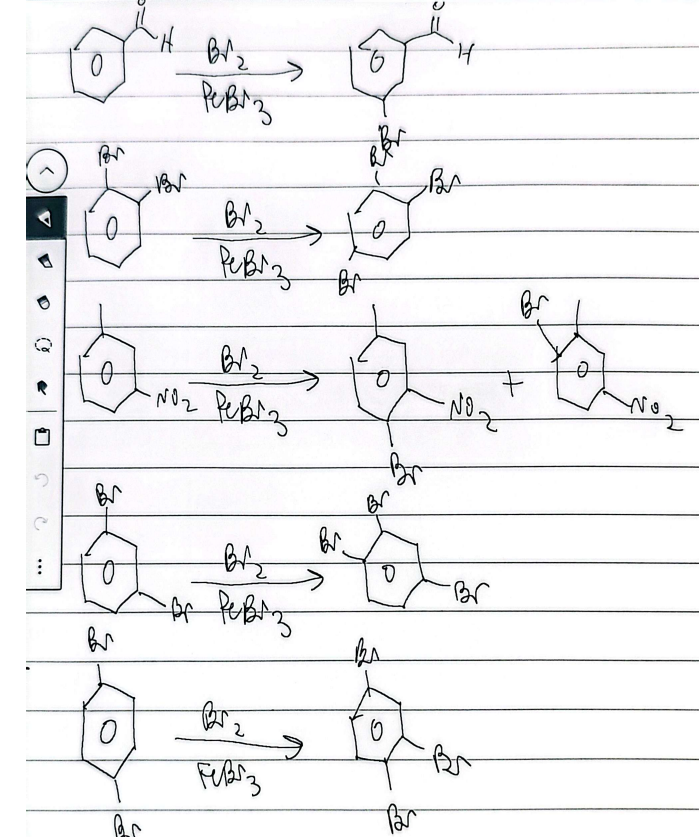
bromination
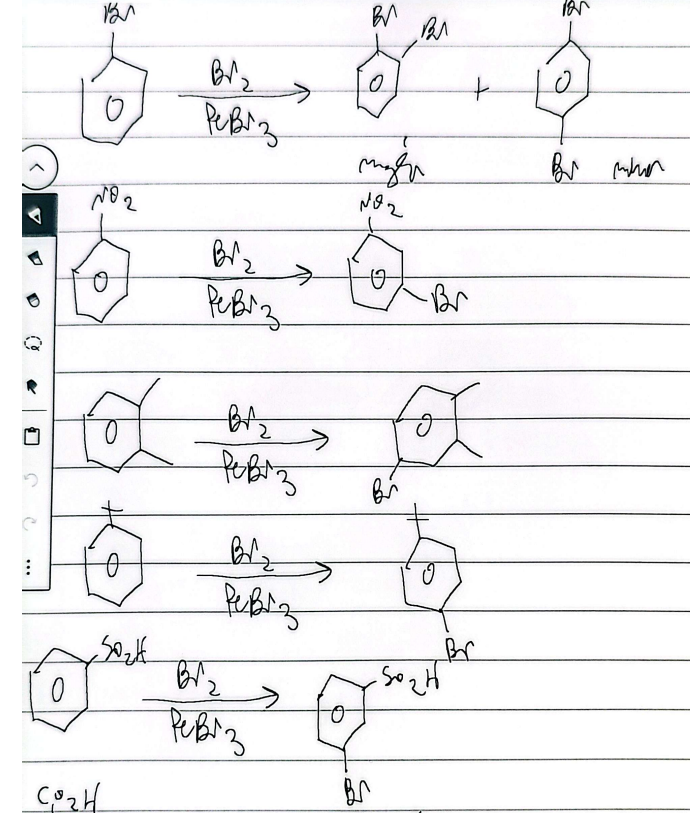
bromination
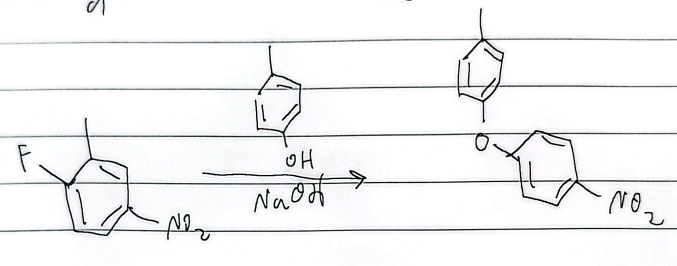
NAS (nucleophilic aromatic substitution)
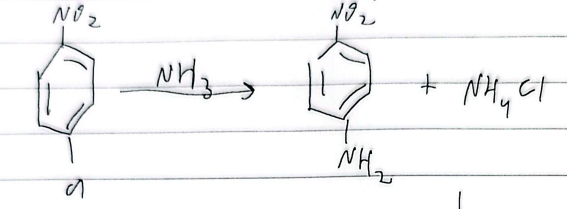
NAS