6/7/8) Igenous tectonic settings & Classification & Textures
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
igneous rocks basic
form by crystallization from magma, magma comes to surface gradually cools, crystals start to form
diff minerals crystallize at diff temp
magmas have many different compositions, which influences the rocks you form
what are the types of plate boundaries
transform: igneous don’t form here
divergent: crust is created
convergent: crust is recycled
ocean ocean convergence vs ocean continent convergence
ocean ocean: cooler older ocean plate subducts underneath island arcs (creating deep sea trench)
ocean continent: ocean almost always subducts under continental
explain continent continent convergence
results in extremely high topography
neither plate wants to subduct, so they both go up
lots of folding and stacking of rocks on each other
volcanoes not commone
explain hot spot
volcanoes forms in pacific ocean as crust passes over hot spots
increasing temp not decreasing pressure
hot spot stays stationary, plate moves over, creating hawaiian islands
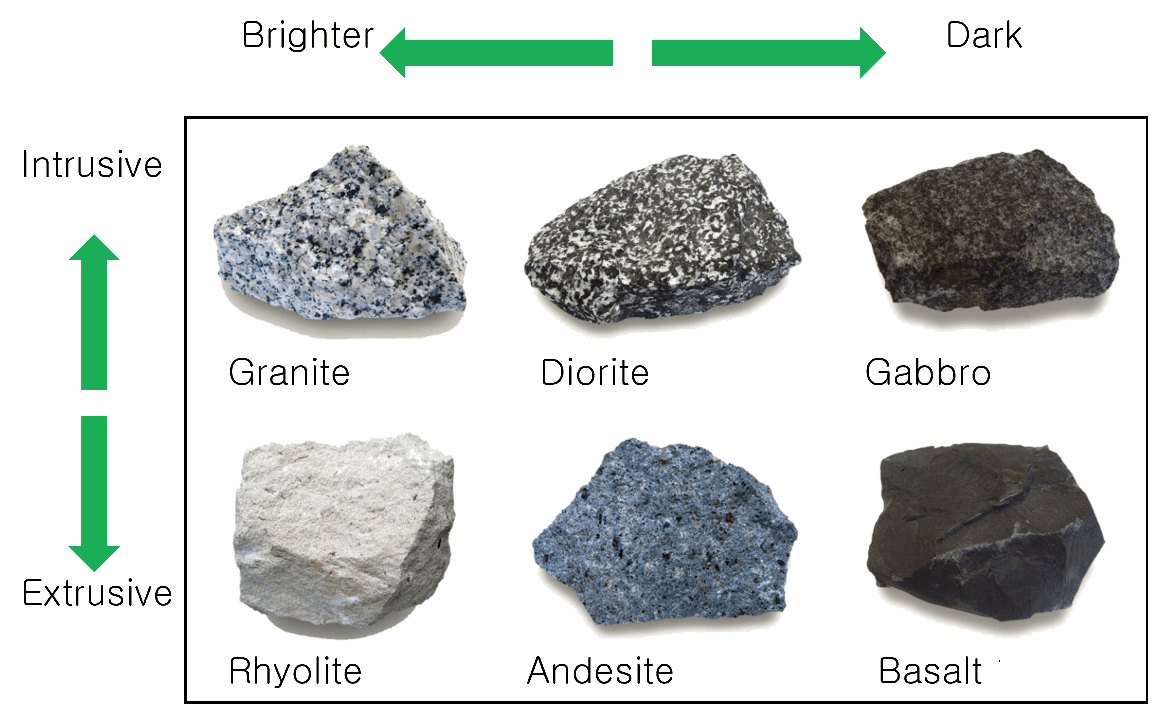
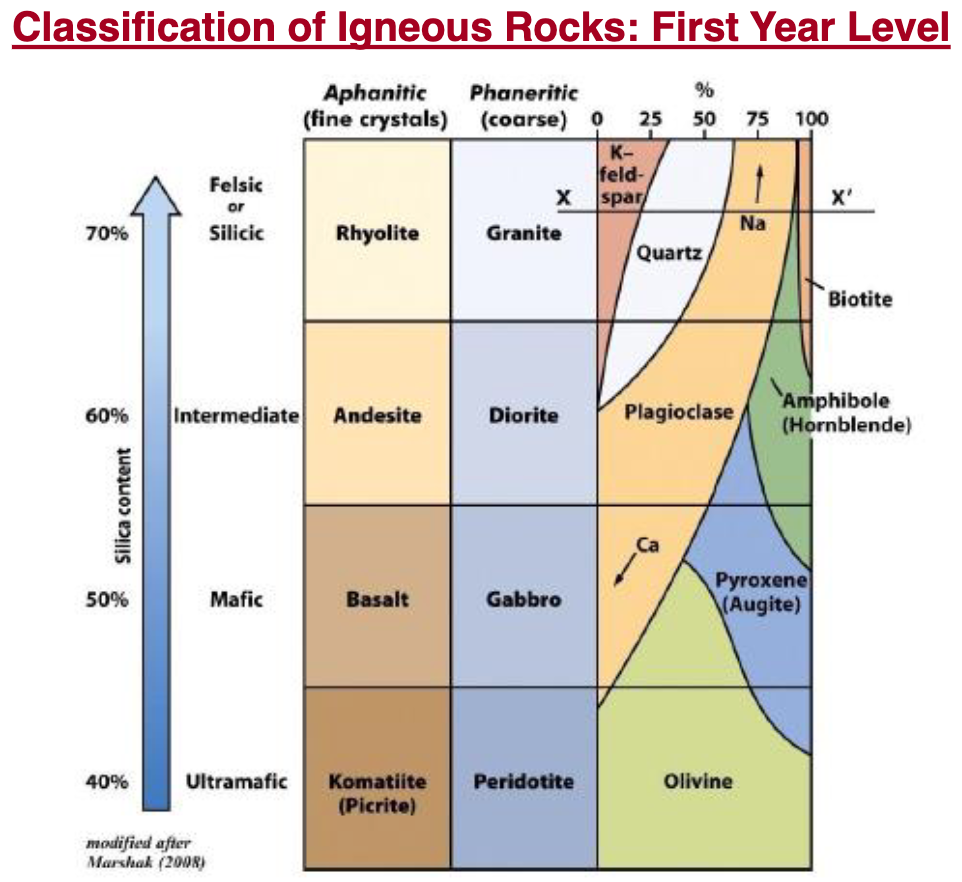
intrusive vs extrusive
intrusive: plutonic, magma cools within earth’s crust, large interlocking crystals due to slow cooling, granite
extrusive: volcanic, lava erupts at surface through volcanoes or fissues, very fine-grained or glassy texture due to rapid cooling, basalt
plutonic light to dark
volcanic light to dark
granite, diorite, gabbro
rhyolite, andesite, basalt

notes on this
aphanitic fine crystals
phanertic: coarse crystals
ultramafic: komatiite = not common, peridotite
quartz will not be in mafic rocks
pyroxene and olivine will not be in felsic rocks
quartz and pyroxene or olivine will not form together
ultramafics have >75% olivine
explain lava for felsic vs mafic
felsic has lots of silica, making its lava not flow easily
mafic has less silica, lava flows easier
explain pyroclastic rocks, types of pyroclasts
clastic rock composed solely of fragmented volcanic debris (pyroclasts)
felsic to intermediate
bomb (large >64mm, ball shape
block: large >64mm, block shape
lapilli: between 2-64mm, any shape
ash: less than 2mm
tephra: loose pyroclastic material not compacted into rock yet, unconsolidated general term
pyroclastic deposit must be >75% pyroclasts
what is the main factor that determines the texture of igneous rock?
what are related factors
cooling rate
diffusion: rate at which atoms or molecules can move through the liquid (viscosity)
nucleation: rate at which enough of the chemical constituents of crystals can come together in one place without dissolving
growth: rate at which new constituents can arrive at the surface of the growing crystal. depends largely on the diffusion rate of the molecules of concern
list phaneritic rock textures
granular
hypidiomorphic granular
pegamtitic
graphic
mymekitic
poikilitic
corona
porphyritic
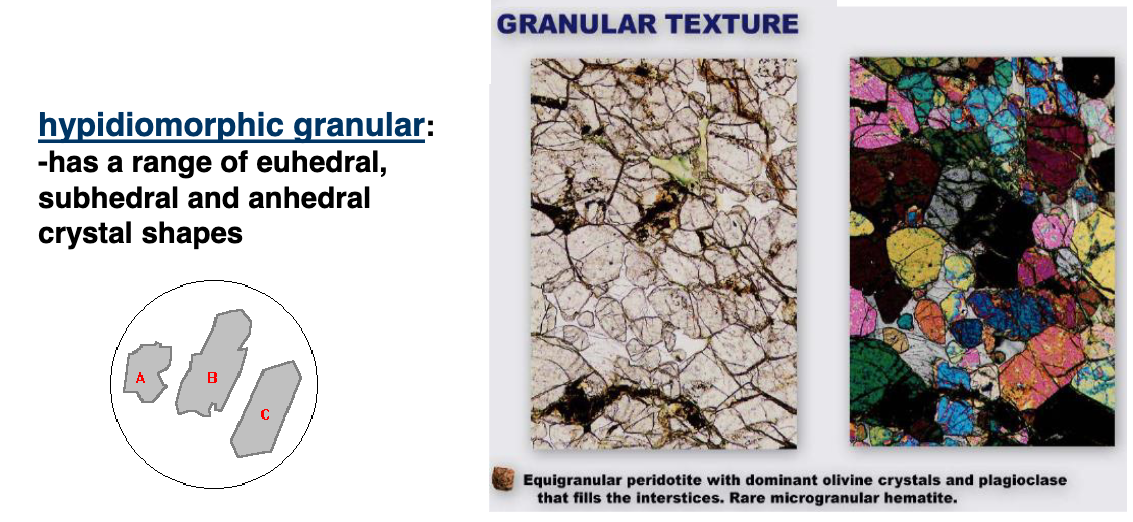
what are granular and hypidiomorphic granular textures
granular: sugary, roughly same size crystals, rounded, looking like grains
hypidiomorphic granular: range of euhedral to anhedral grains (euhedral generally form first)
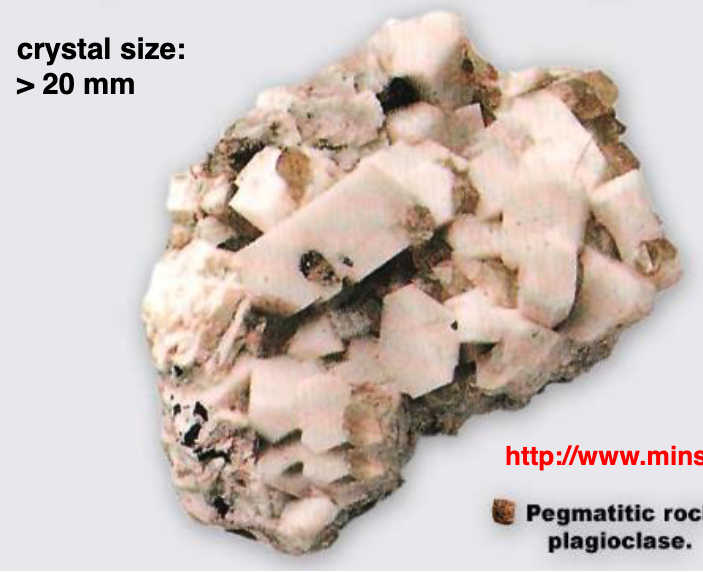
what is pegmatitic texture
crystal size greater than 20mm, very coarse grained, off-shoots of cooling magma granite, filling fractures, last stage of crystallization
pegmatite can contain gemstones and REE, higher prop of water in magma, water lowered viscosity, made it easy for elements to diffuse into magma, resulting in large crystals, not cooling slow (abnormal)

what is graphic texture
intergrowths of quartz and alkali feldspar where the orientation of quartz grains resembles cuneiform writing
commonly observed in pegmatites

what is myrmekitic texture
intergrowth of quartz and plagioclase that shows small worm-like bodies of quartz enclosed in plag
found in granites, late stages of crystallization
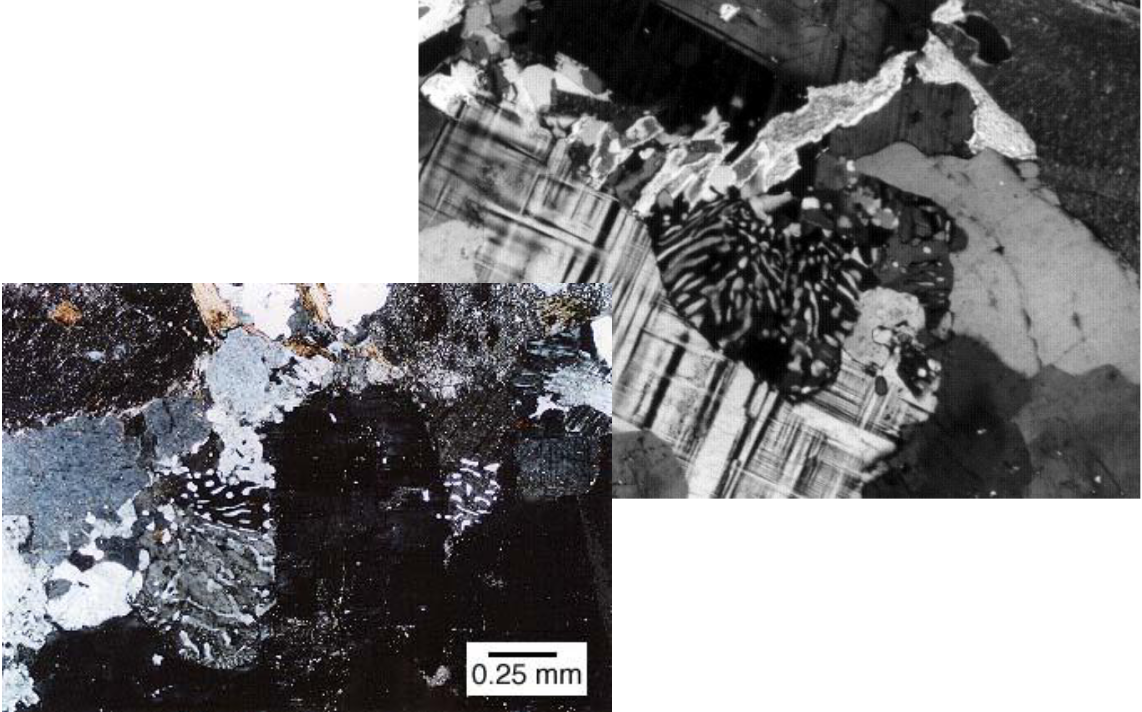

what is poikilitic texture
presence of a crystal that has totally growth around other crystals (includes them)
small crystal had to be first, then larger after (enclosed it)
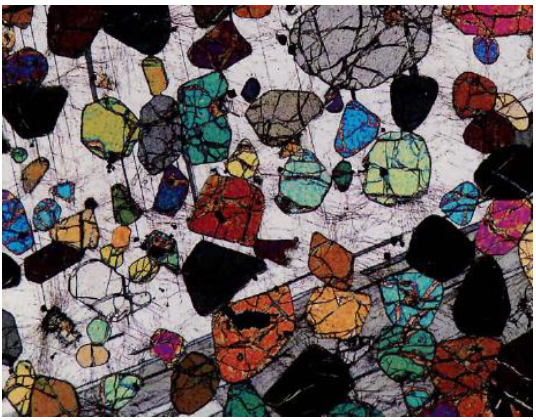

what is corona texture
presence of a rim of one or more crystals of a mineral around another mineral
effect of incomplete reactions between inner mineral and surrounding melt or fluid, to produce another mineral species
Ex: incomplete reaction like hornblende wants to form, but pyroxene doesn’t
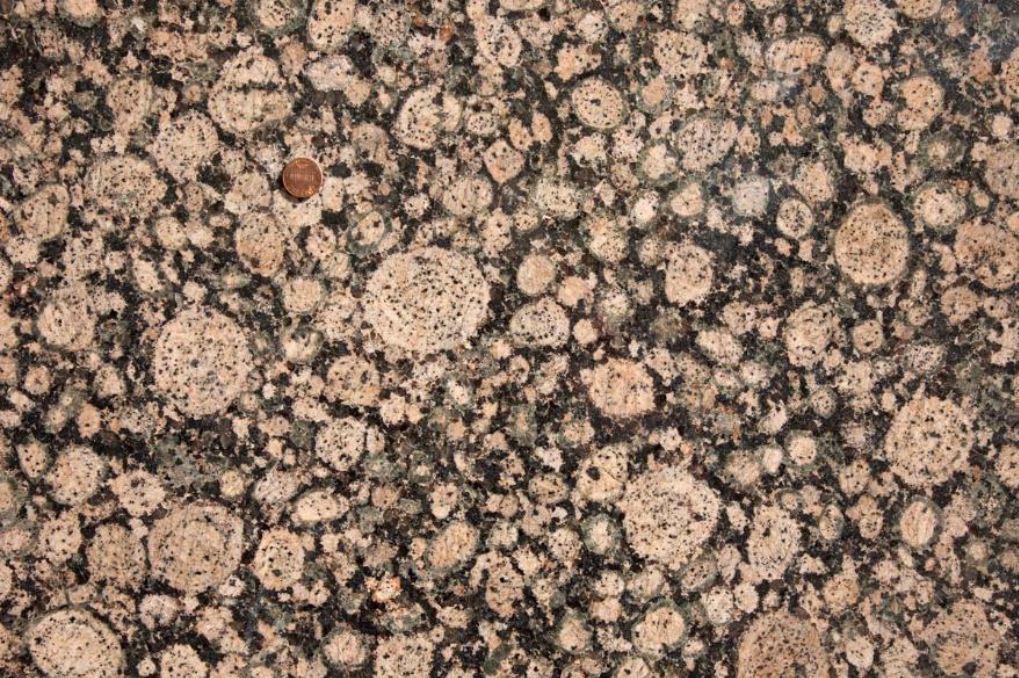

what is porphyritic texture
large euhedral phenocrysts and small-sized crystals, which form the ground mass
different stages of cooling, larger crystals started underground in a magma chamber, then possibly the whole thing got erupted and the ground mass formed quickly
glomeroporphyritic: phenocrysts are found to occur as clusters of crystals

list some other textures
trachytic: oriented crystals from a flow
sieve: plag crystals show an abundance of holes
vesicular: rock contains numerous holes that were air bubbles
amygdular: vesicles filled with material after the rock has cooled (secondary), usually calcite or quartz, refilled vesicle
glassy: crystallized very rapidly, no time for elements to arrange themselves, obsidian is metastable
xenolith vs autolith
xenolith: inclusions are unlike the host rock, foreign rock
autolith: inclusions are of the same composition or directly related to host rock, same rock