Anatomy & Physiology I: Skin and Body Membranes
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Body Membranes
Multicellular sheets of epithelia and connective tissue.
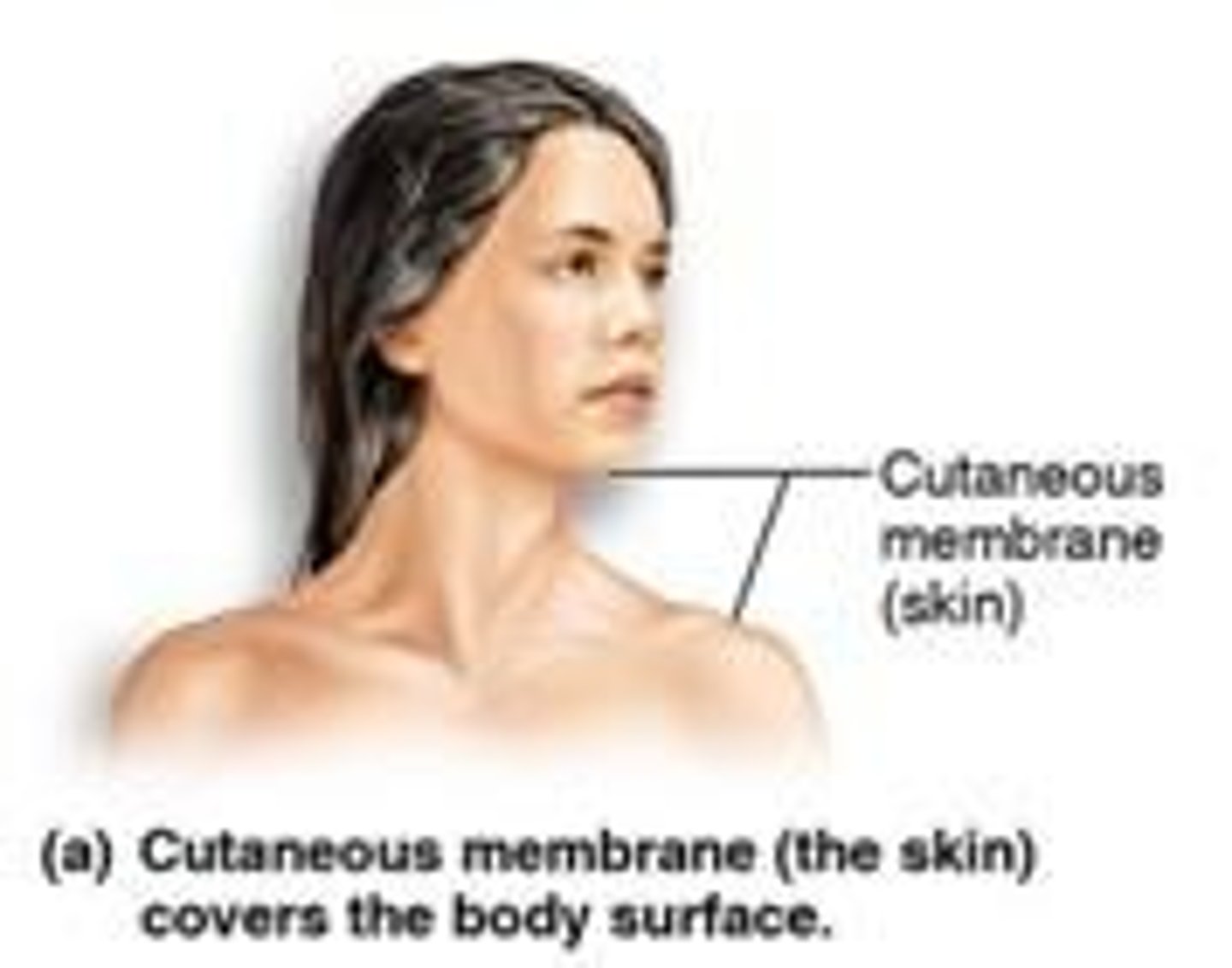
Cutaneous Membrane
Skin; covers external body surfaces.
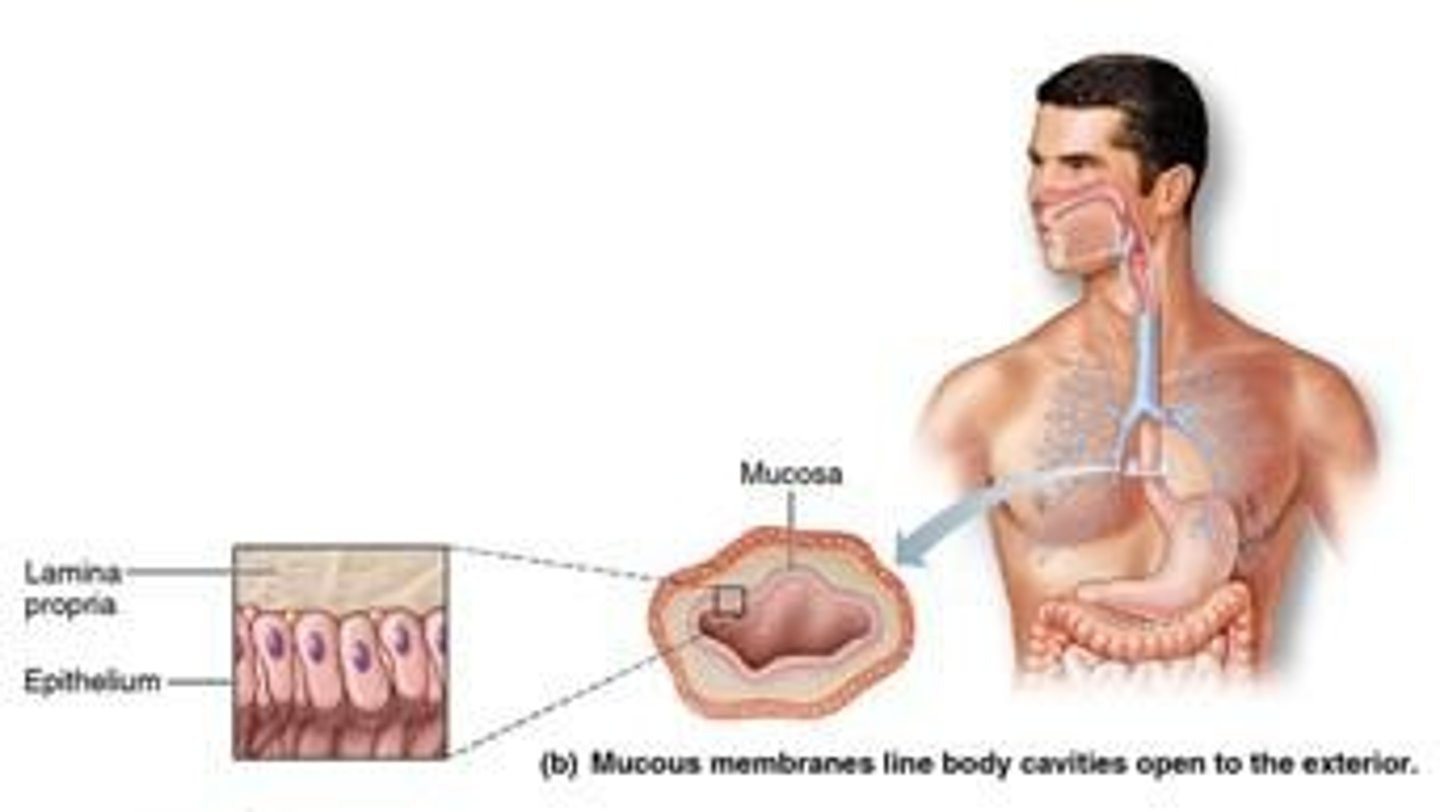
Mucous Membrane
Lines open body cavities; moist surface.
Serous Membrane
Lines closed body cavities; reduces friction.
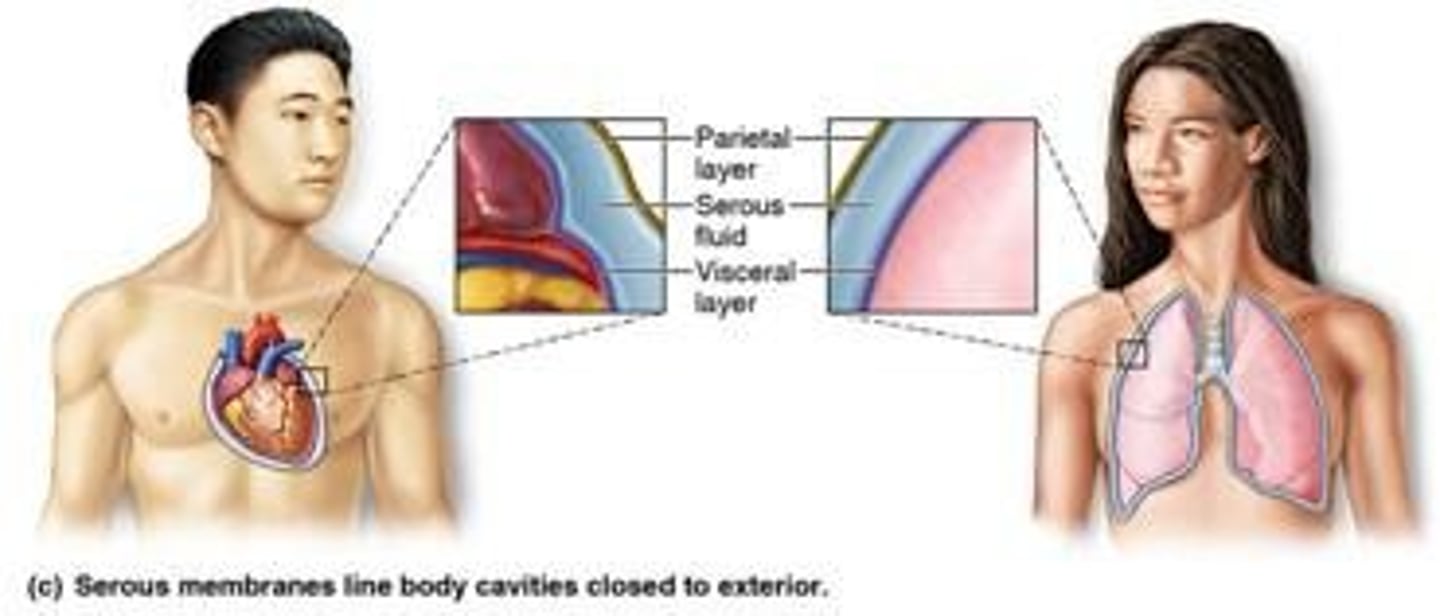
Parietal Serosa
Lining layer of serous membrane cavity.
Visceral Serosa
Covers organs within serous membrane cavity.
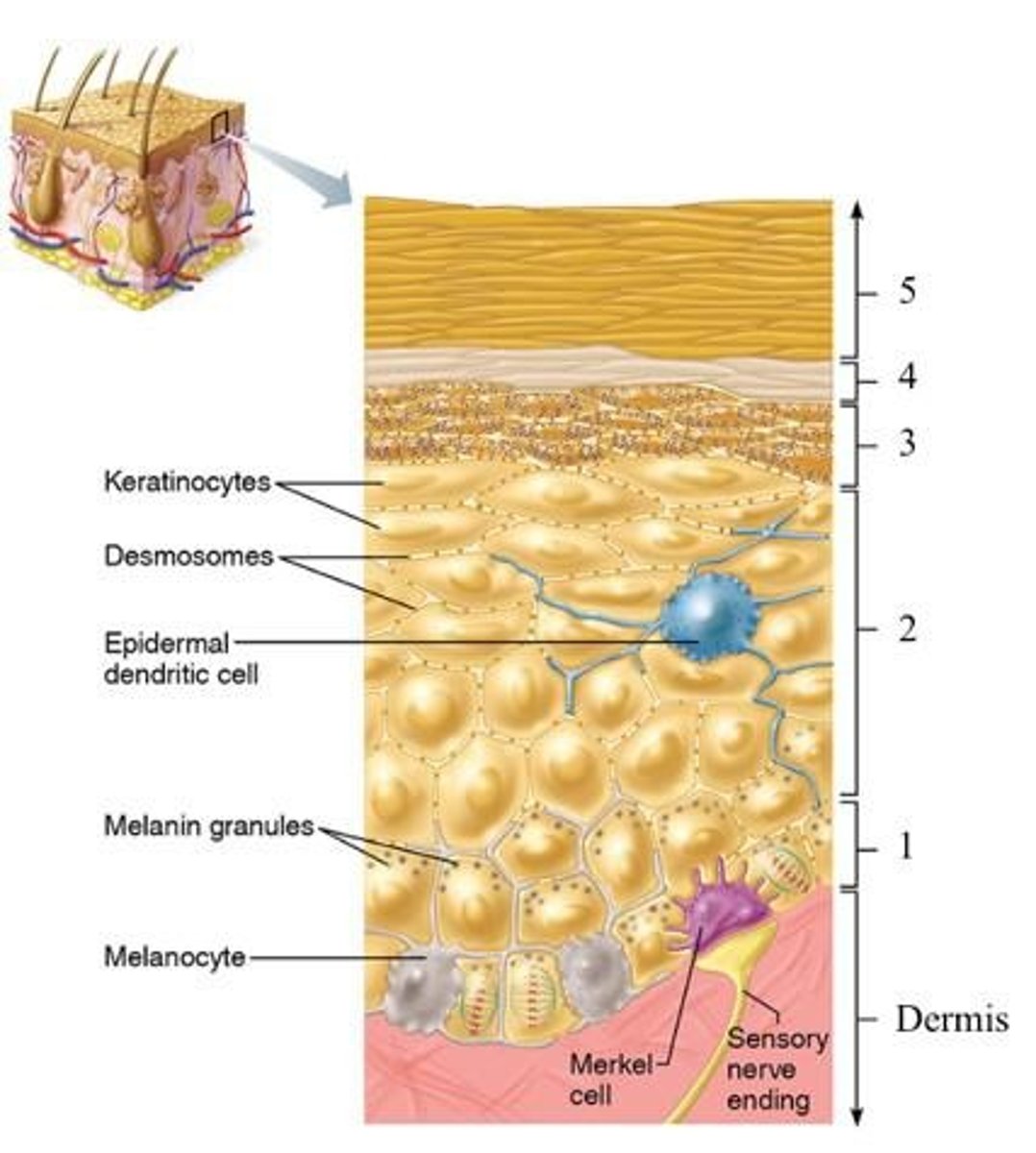
Epidermis
Superficial region of the skin.
Dermis
Middle region of the skin.
Hypodermis
Deepest region of the skin.
Keratinocytes
Produce keratin, a fibrous protein.
Melanocytes
Produce melanin, skin pigment.
Dendritic Cells
Macrophages activating the immune system.
Tactile Cells
Touch receptors in the skin.
Stratum Basale
Deepest epidermal layer; stem cells present.
Stratum Spinosum
Prickly layer with intermediate filaments.
Insensible Perspiration
Routine sweat loss; ~500 ml/day.
Sensible Perspiration
Increased sweating during elevated body temperature.
Acid Mantle
Low pH secretions retarding bacterial activity.
Biological Barriers
Dendritic cells and macrophages protect skin.
Blood Reservoir
Skin can hold up to 5% blood volume.
Excretion
Sweat contains nitrogenous wastes and salts.
Cutaneous Sensations
Includes temperature, touch, and pain perception.
Stratum granulosum
Thin layer with three to five flat cells.
Keratohyaline granules
Protein aggregates aiding in keratinization.
Stratum lucidum
Clear layer found only in thick skin.
Stratum corneum
Outer layer with 20-30 rows of dead cells.
Epidermal thickness
Stratum corneum accounts for three-quarters.
Skin protection
Prevents abrasion, penetration, and water loss.
Papillary layer
Upper dermis with areolar connective tissue.
Dermal papillae
Contain capillary loops and free nerve endings.
Reticular layer
80% of dermis, provides strength and resiliency.
Collagen fibers
Provide structural strength to the skin.
Elastic fibers
Allow skin to stretch and recoil.
Epidermal ridges
Form friction ridges for grip and fingerprints.
Cleavage lines
Collagen bundles dictate skin tension and healing.
Melanin
Pigment responsible for dark skin colors.
Carotene
Yellow-orange pigment visible in palms and soles.
Hemoglobin
Pigment giving skin a pinkish hue.
Cyanosis
Bluish skin due to poor oxygenation.
Sweat glands
Epidermal derivatives for thermoregulation.
Oil glands
Sebaceous glands that lubricate skin and hair.
Hair follicles
Structures from which hair grows.
Skin appendages
Derivatives of the epidermis including glands and hair.
Exocrine glands
Glands that secrete substances through ducts.
Sweat glands
Glands producing sweat for thermoregulation.
Apocrine glands
Sweat glands in axillary and anogenital areas.
Eccrine glands
Sweat glands abundant on palms and forehead.
Sebum
Oily secretion from sebaceous glands.
Ceruminous glands
Glands in ear canal secreting cerumen.
Mammary glands
Glands producing milk in females.
Sebaceous glands
Oil glands that secrete sebum.
Holocrine secretion
Entire cell disintegrates to release secretion.
Keratinized cells
Dead cells containing keratin for protection.
Melanins
Pigments responsible for hair color.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Least malignant skin cancer, slow-growing.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Involves keratinocytes, more aggressive than basal.
Melanoma
Most dangerous skin cancer, involves melanocytes.
Nevus
A mole, small dark skin growth.
Dysplastic nevus
Atypical mole with potential to become cancerous.
ABCDE rule
Mnemonic for melanoma risk factors.
First degree burn
Epidermal damage with redness and pain.
Second degree burn
Epidermal and dermal damage with blisters.
Third degree burn
Full thickness skin damage, no pain initially.
Fluid loss estimation
Critical if >25% body has second degree burns.
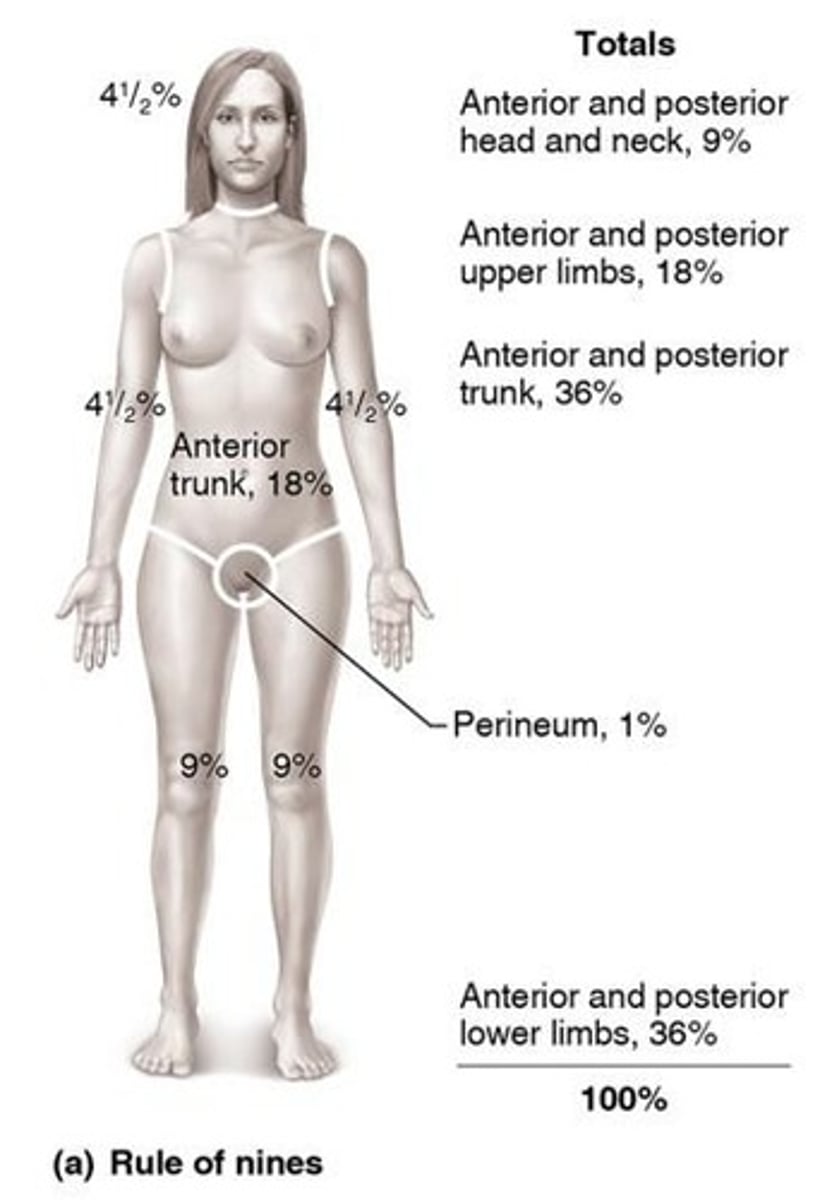
Infection risk
Main threat after burns, post 24-36 hours.
Risk factors for skin cancer
UV exposure and frequent skin irritation.