StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.1.6 ATP
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What type of molecule is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)? (1)
Nucleotide derivative (a modified nucleotide)
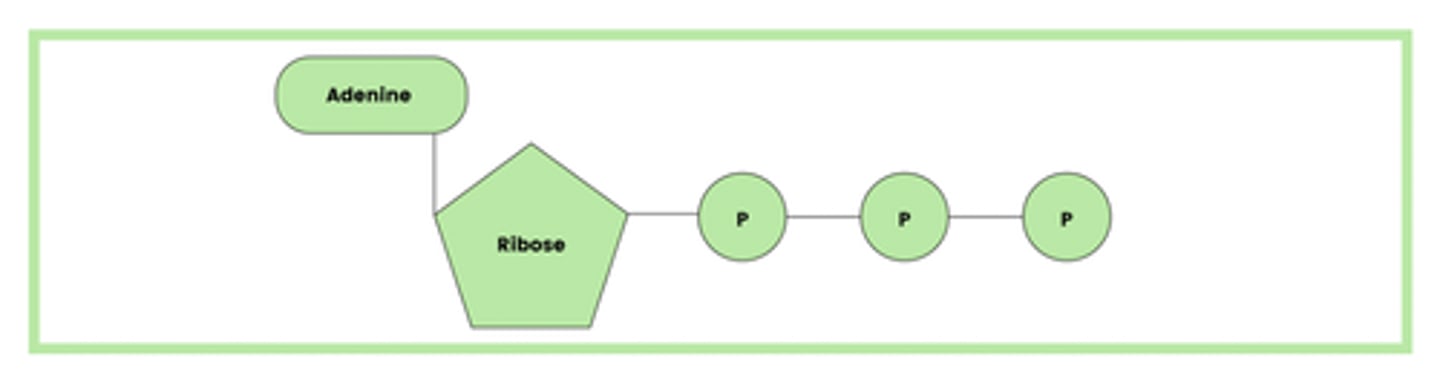
Draw and label the structure of ATP (1)
- Adenosine
- Ribose
- Three phosphate group
Write out the equations of the hydrolysis and resynthesis of ATP (2)
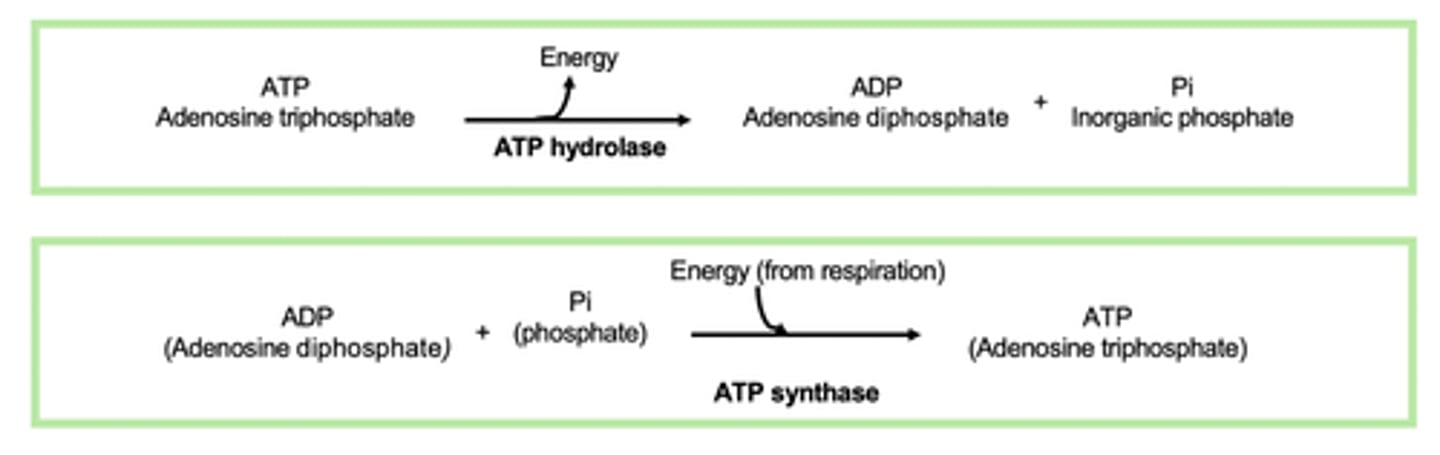
Describe how ATP is resynthesised in cells (3)
- From ADP and Pi
- By ATP synthase
- During respiration / photosynthesis
Describe how ATP is hydrolysed in cells (2)
- Into ADP and Pi
- By ATP hydrolase
What can the hydrolysis of ATP be coupled to? (2)
- Energy requiring reactions
- E.g. protein synthesis, muscle contraction, ion transport etc
What can the inorganic phosphate released during the hydrolysis of ATP be used for? (2)
- To phosphorylate other compounds
- Making them more reactive
Why do humans have to synthesise a large amount of ATP? (2)
- ATP cannot be stored as it is an immediate source of energy
- Only a small amount of energy is released at a time
Explain why ATP is useful in many biological processes (4)
- ATP releases energy in small manageable amounts
- ATP is broken down in a one step reaction
- It phosphorylates other compounds to make them more reactive
- Reformed / remade / resyntesised easily