Membrane Bound Organelles and Eukaryotic Cell Features
1/405
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
406 Terms
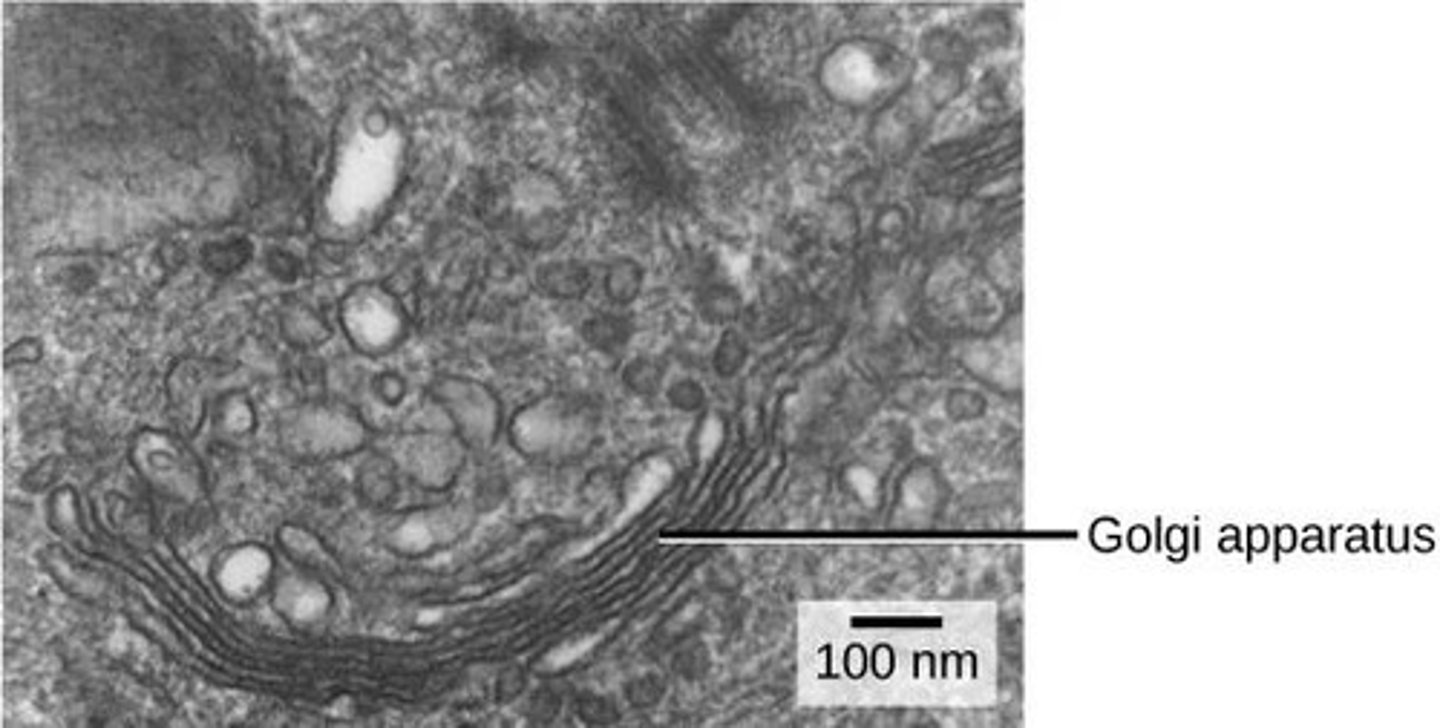
Golgi apparatus
a series of flattened membranes that sorts and packages materials before they leave the cell
Vesicle
a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer and transport of materials within the plasma membrane
Lumen
the cavity or channel within a tube or tubular organ
Plasma membrane
separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment
Intercellular junctions
regions of contact between the plasma membranes of two or more adjacent cells
Gap junctions
channels between neighboring cells that allow for the transport of ions, water, and other substances between cells
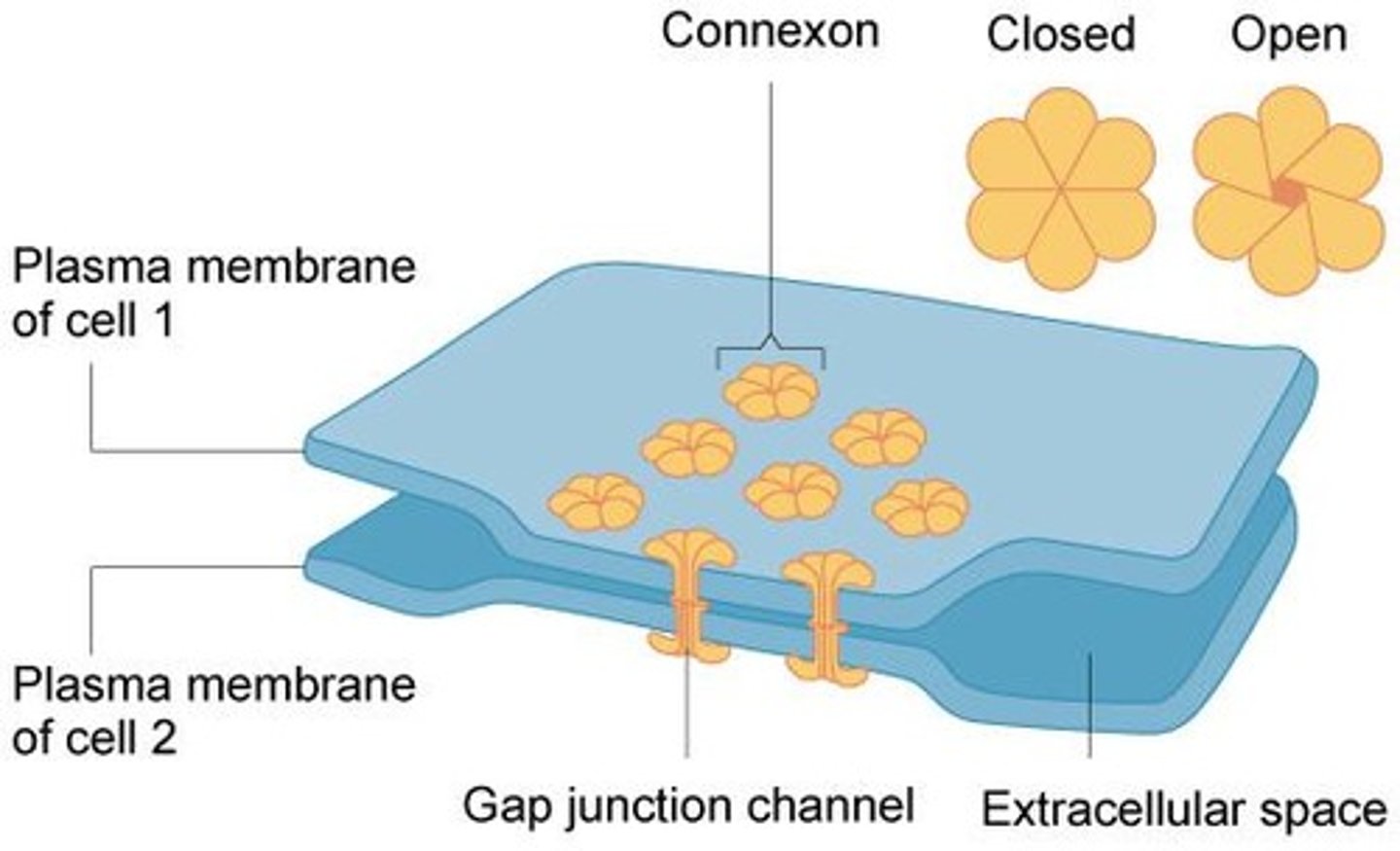
Connexins
a set of six membrane proteins that form an elongated, donut-like structure called a connexon
Connexon
an elongated, donut-like structure formed by connexins that allows for the formation of channels between cells
Tight junctions
create a watertight seal between two adjacent animal cells
Desmosomes
a type of intercellular junction that provides mechanical stability to tissues
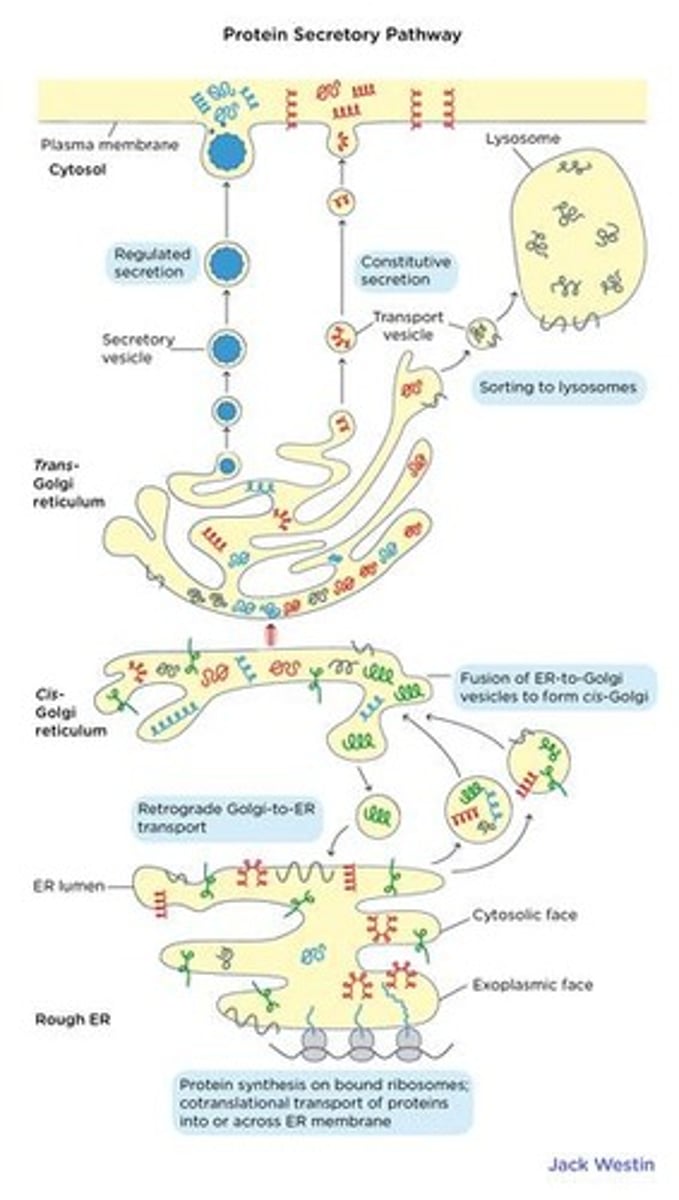
Cis face
the receiving side of the Golgi apparatus where transport vesicles from the ER fuse
Trans face
the opposite side of the Golgi apparatus that secretes materials into vesicles
Endomembrane system
a system within the cell that includes the Golgi apparatus and is involved in the sorting and packaging of materials
Secretory vesicles
vesicles that bud from the trans face of the Golgi apparatus to transport materials
Phosphate groups
small molecules that tag modified proteins and lipids for routing to their destinations
Multicellular organism
an organism composed of multiple cells that interact and adhere to each other
Cytoplasmic connections
connections between cells that allow for the exchange of materials
Watertight seal
a type of connection that prevents the passage of water and solutes between adjacent cells
Transport vesicles
vesicles that carry materials from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus
Short chains of sugar molecules
the most frequent modification added to proteins and lipids as they travel through the Golgi
Proper destination
the specific location within or outside the cell where materials are needed
Cellular materials
various substances produced or utilized by cells, including proteins and lipids
Adjacent cells
cells that are next to each other and can form intercellular junctions
Tight junctions
watertight seal between two adjacent animal cells
Claudins
proteins that make up tight junctions
Desmosomes
small spot connections between epithelial cells
Cadherins
specialized adhesion proteins that interact between cells
Gap junction
channels between neighboring cells that allow for the transport of ions, water, and other substances
Connexin
membrane protein that makes up a gap junction
Epithelial
the outer layer of a cell surface
Adhesion proteins
glycoproteins that mediate cell-cell connections
Intermediate filaments
protein fibers that contribute to cellular structural elements and are often crucial in holding together tissues
Keratin
a fibrous protein found in hair, nails, and skin
Intermediate filaments size
varying sizes that range between 8-12 nm
Cytoplasmic plaque
structure that cadherins attach to inside the cell
Tight junction purpose
to keep liquid from escaping between cells, allowing a layer of cells to act as an impermeable barrier
Desmosome function
pin adjacent cells together, ensuring that cells in organs and tissues that stretch remain connected in an unbroken sheet
Intermediate filaments role
absorb tension and support cellular shape
Tight junction structure
formed by many individual groups of tight junction proteins called claudins
Desmosome structure
involves a complex of proteins that extend across the membrane and anchor the junction within the cell
Tight junction strands
arranged into strands that form a branching network
Desmosome proteins
some extend across the membrane, while others anchor the junction within the cell
Intermediate filaments stability
do not form and disassemble quickly, playing no role in movement or transport
Intermediate filaments network
maintains the cell shape and makes a cage where the nucleus sits
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein fibers that help with cellular movement and maintaining its structure/shape.
Microtubule
Hollow, protein-based tubes that exist in eukaryotic cells and help cells move material around itself and resist compression.
Microfilaments
Thin protein fibers made up of actin proteins; their fundamental role is to absorb tension.
Lysosome
Found in animal cells, is the 'garbage disposal', breaks down molecules and old organelles.
Hydrolytic enzyme
Enzyme needing water to break chemical bonds of large molecules.
Organelles
Membrane-bound compartments with specialized functions.
Polysaccharides
A carbohydrate whose molecules consist of several sugar molecules bonded together.
Cytoplasm
A thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane.
Channel proteins
Span the membrane and make hydrophilic tunnels across it, allowing their target molecules to pass through by diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion
The diffusion process used for those substances that cannot cross the phospholipid bilayer due to their size and/or polarity.
Aquaporins
Channel proteins that allow water to cross the membrane very quickly, playing important roles in plant cells, red blood cells, and certain parts of the kidney.
channel proteins
span the membrane and make hydrophilic tunnels across it, allowing molecules to move through by diffusion
aquaporins
channel proteins that allow water to cross the membrane very quickly
diffusion
substance moves from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
gated ion channels
a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger
hydrophilic
water-loving, usually in contact with aqueous environments
facilitated diffusion
proteins move polar molecules in or out of the cell depending on its concentration gradient
plasma membrane
separates the interior of a cell from its outside environment and can be best represented by the fluid mosaic model
fluid mosaic model
describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components that are fluid and dynamic
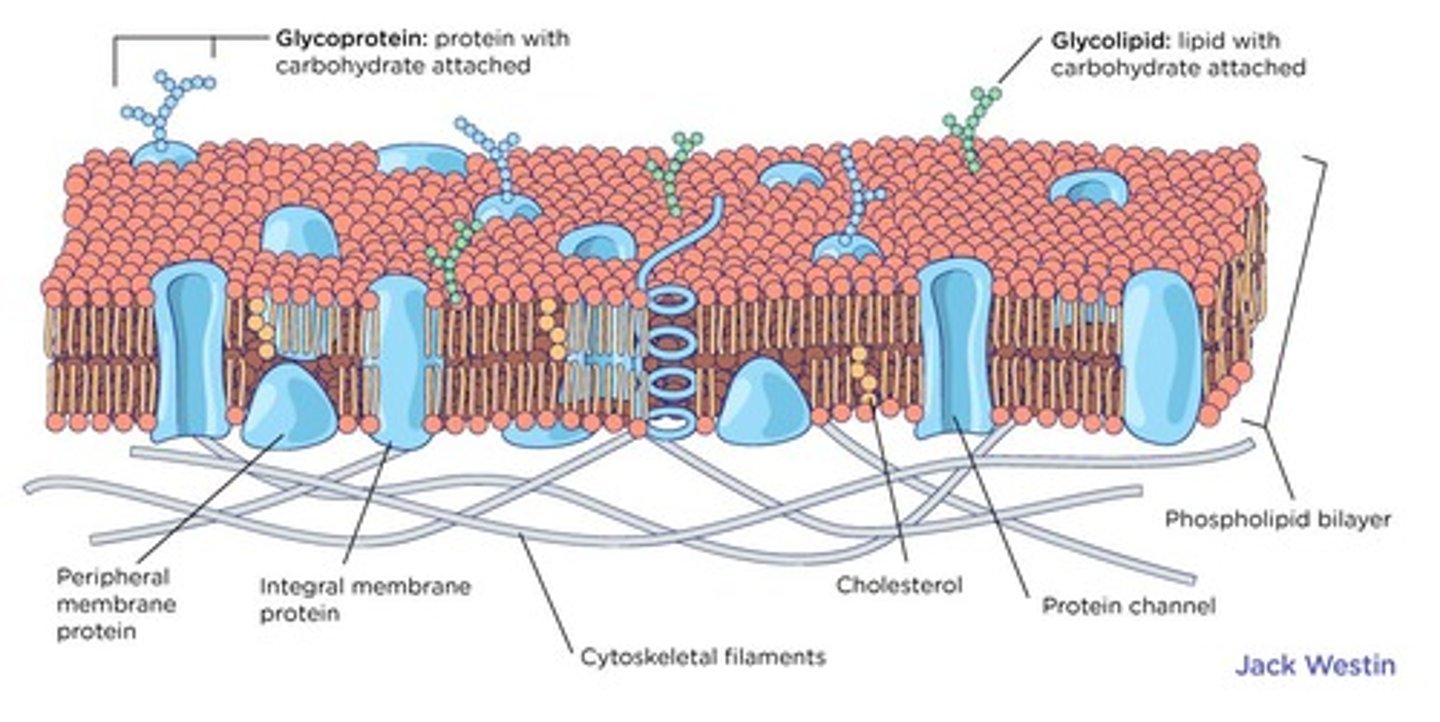
phospholipid bilayer
composed of phospholipid molecules that can move around within the plasma membrane
transbilayer diffusion
the process where a phospholipid can 'flip-flop' to the opposite layer, which is very slow
lateral diffusion
the process when a phospholipid moves side to side within its layer, which is very fast
flippase
a protein that brings a phospholipid from the outer leaflet to the inner leaflet and requires ATP
floppase
a protein that brings a phospholipid from the inner leaflet to the outer leaflet and requires ATP
scramblase
a protein that brings a phospholipid from the outer leaflet to the inner leaflet AND a phospholipid from the inner leaflet to the outer leaflet, and does not require ATP
transbilayer diffusion
a phospholipid can "flip-flop" to the opposite layer, is very slow
lateral diffusion
phospholipid moves side to side within its layer, is very fast
flippase
brings a phospholipid from the outer leaflet to the inner leaflet
floppase
brings a phospholipid from the inner leaflet to the outer leaflet
scramblase
brings a phospholipid from the outer leaflet to the inner leaflet AND a phospholipid from the inner leaflet to the outer leaflet
fluid mosaic model
describes the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins
plasma membrane
the semipermeable barrier that surrounds the cytoplasm (inside contents) of a cell
phospholipids
a major component of cell membranes consisting of two hydrophobic fatty acid tails and a hydrophilic head consisting of a phosphate group
membrane potential
a cell's membrane potential is negatively charged when it is resting and non-signalling and is determined by the concentrations of ions across the membrane
resting membrane potential
non-signalling neuron has a voltage of about -30 to 90 mV
depolarized
membrane potential is more positive than it is at the resting potential
hyperpolarized
membrane potential is more negative than it is at the resting potential
membrane potential
a measurement of the potential gradient that forces ions to passively move in one direction across a membrane
neurons
nerve cells
polarized
the electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative
potential difference
the difference in voltage across the membrane, typically about 30 to 90 mV in resting neurons
ion distribution
the uneven distribution of ions (charged particles) between the inside and the outside of the cell
membrane permeability
the different permeability of the membrane to different types of ions
depolarization
the process by which the membrane potential becomes less negative or more positive
action potentials
the electrical signals that neurons use to transmit information
ligands
external molecules that bind to membrane receptors and cause an internal cellular response
Membrane receptors
Proteins that facilitate the transport of molecules, change a cell's internal environment, or communicate between cells.
Cell-surface receptors
Transmembrane receptors that bind to external ligand molecules and span the plasma membrane to perform signal transduction.
Signal transduction
The process of converting an extracellular signal into an intracellular signal.
Ion channel-linked receptors
Receptors that bind a ligand and open a channel through the membrane, allowing specific ions to pass through.
G-protein-linked receptors
Receptors that bind a ligand and activate a G-protein, which interacts with either an ion channel or an enzyme in the membrane.
Enzyme-linked receptors
Cell-surface receptors with intracellular domains associated with an enzyme that activate a signal chain within the cell.
Gated ion channels
Pores that open when a signaling molecule binds, allowing ions to flow into or out of the cell.
Hydrophobic amino acids
Amino acids in the membrane-spanning region that interact with the phospholipid fatty acid tails of the plasma membrane.
Hydrophilic amino acids
Amino acids that line the inside of the ion channel, allowing for the passage of water or ions.
Conformational change
A structural change in a protein that occurs when a ligand binds to the extracellular region of the channel.