Cholinergic Antagonists
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Muscarinic Receptor Antagonists
Used for
Atropine
Cardiovascular, GI
Benztropin (Congentin) and Trihexyphenidyl (Artane)
Parkinson Disease
Scopolamine (Transderm cop)
Motion sickness, take before, causes dry mouth and sedation
Cyclopentolate (Cyclogyl), Tropicamide (Mydriacyl) and Tropicamide + hydroxyamphetamine (Paremyd)
Mydriasis EYE
Ipratropium (Atrovent), Ipratropium + albuterol (Combivent), Tiotropium (Spiriva), Aclidinium (Tumorza)
For COPD and las 2 for LAMA
Glycopyrrolate (Robinul)
GI, respiratory, peripheral
Dicyclomine (Bentyl) L-Hyoscyamine (Anaspaz)
antispasmodic for IBS
Oxybutynin (Ditropan XL), Tolterodine (Detrol)
Bladder
Darifenacin (Enablex), Solifenacin (Vesicare)
M3 selective for bladder
Contraindications for muscarinic antagonists
Toxicity synmptoms
Narrow/closed glaucoma or prostatic hyperplasia (urinary retention)
Tox symptoms:
Blind as a bat
Dry as a bone
Red as a beet
Mad as a hatter
Hot as a hare
Can’t see can’t pee
Ganglionic Blockers (Cholinergic Antagonists)
Define
Only one drug does this
Effects
Agents that block nicotinic receptors at all autonomic ganglia, pre-synaptic and post synaptic
Results in the Dominant tone being lost with ganglia blockage
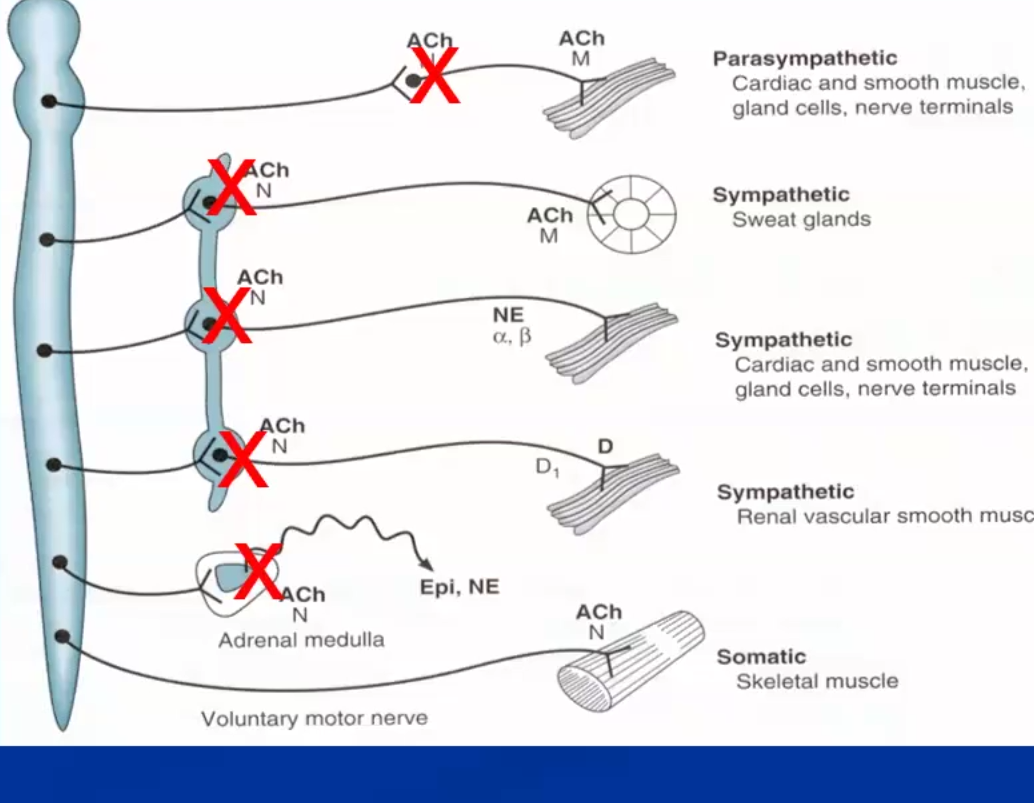
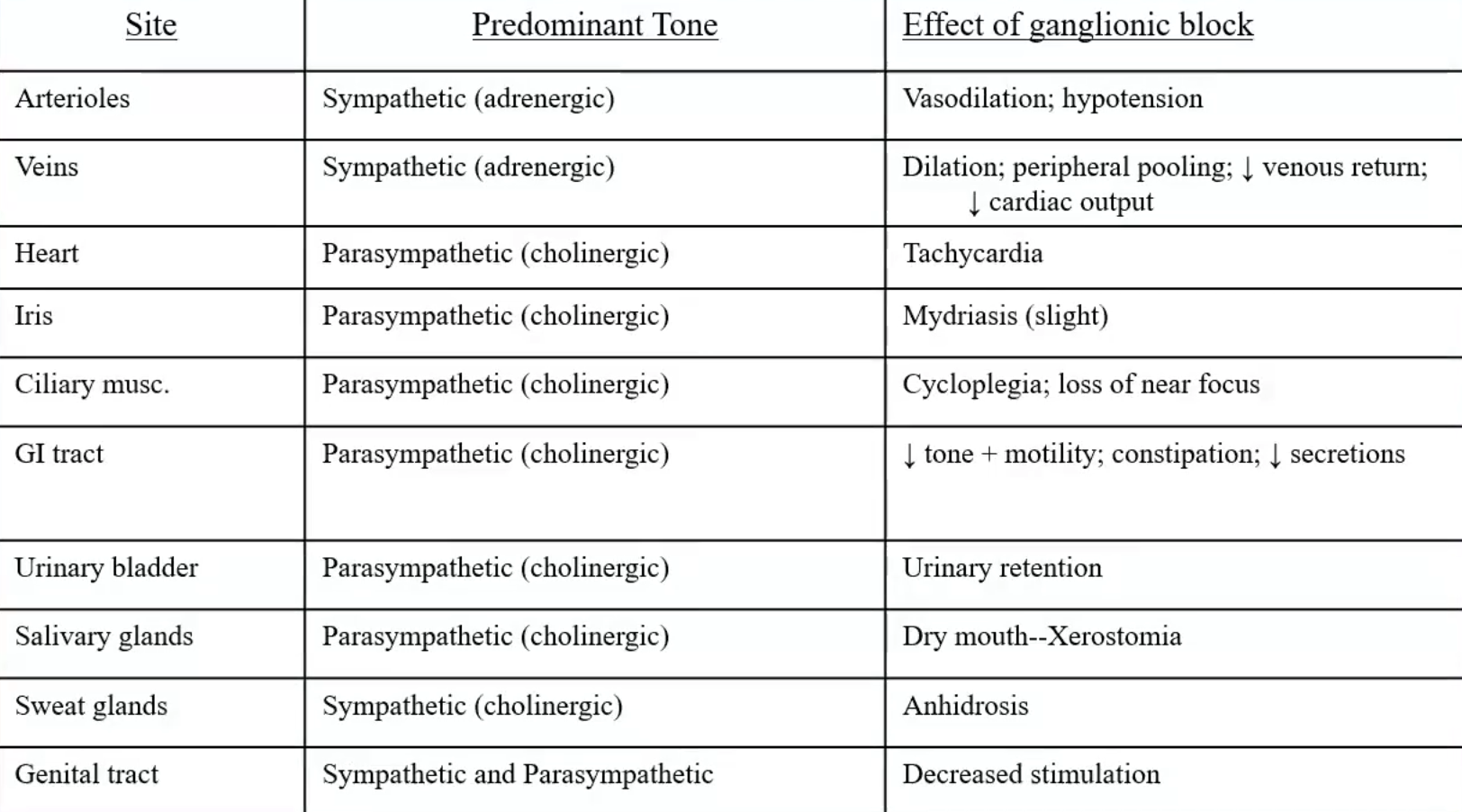
Mecamylamine: rarely used but can reduce bleeding by controlled hypotension

NMJ Blocking Agents (Cholinergic Antagonists)
Define
Types
Drugs
Produce paralysis by blocking muscle contraction
Non-depolarizing: block pre-junctional Na+ channels; causes muscle weakness leading to flaccid paralysis, cannot respond to pain
All reversed by cholinesterase inhibitors such as Neostigmine and Pyridostigmine
Atracurium (Tracrium)
Cistracurium (Nimbex): more potent, no seizures and less histaminic response
Rocuronium (Zemuron)
fastest
Vecuronium (Norcurom)
Depolarizing: P1. activates and keeps channel open and does not allow muscle to recover. P2. membrane repolarizes but receptor is desensitized
Succinylcholine (Anectine): extremely rapid onset and ultra short acting
Dantrolene: use to reverse effects
Hyperkalemia, Arrhytmias, Bradychardia, Fasciculations, Malignant Hyperthemia