Macro - Topic A
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Which market is IS
Goods market
Which market is LM
Money market
Consumption (C)
the goods and services purchased by consumer
Investment (I)
the purchase of capital goods. It is the sum of non-residential and residential investment.
Government spending (G)
the purchases of goods and services by the federal, state and local governments.
It does not include government transfers (benefits), nor interest payments on the government debt.
Imports (IM)
the purchases of foreign goods and services by consumers, business firms and the domestic government.
Exports (X)
the purchases of domestic goods and services by foreigners.
Output (Y)
GDP
How to measure Y
output, income and expenditure
Disposable income, (YD)
the income that remains once consumers have paid taxes and received transfers from the government
• YD = Y – T
Consumption function
C = C(YD)
OR
C = c0 + c1(YD)
c0
intercept of consumption function
c1
marginal propensity to consume
Savings = 1 – c1
What determines I / Investment function
Investments are endogenous
I = I(Y, i)
Are G & T exogenous
Yes
Fixed unless we choose to change it
Equilibrium condition in goods market
Y = C(Y – T) + I(T, i) + G
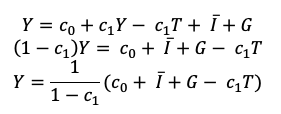
Multiplier formula
1/1-C1
Autonomous spending (intercept in K cross)
c0 + ̅I + G - c1*T
Demand Income graph
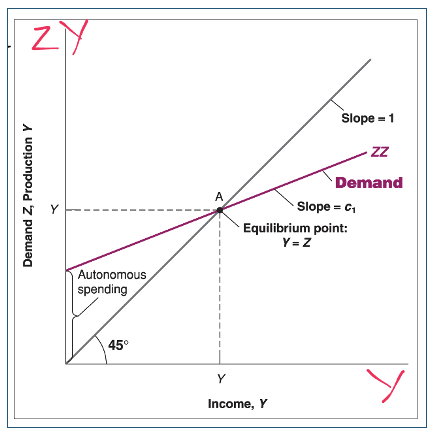
Income = production = demand at the 45 degree line
Equilibrium point where 2 lines intersect
Demand for goods = income = production
If nothing else changes, the economy stays at this point
DY graph with fall in Consumer confidence
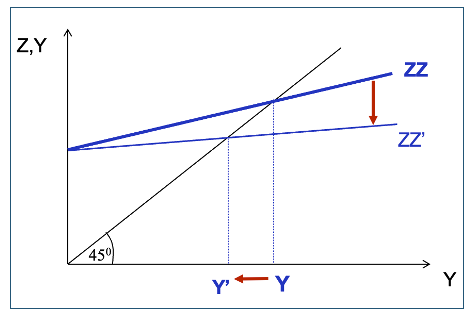
If there is a fall in consumer confidence (like 2008) the MPC (c1) will fall (slope gets shallower)
IS Curve
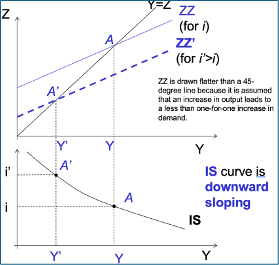
i and Y as axes
If i increases then I decreases
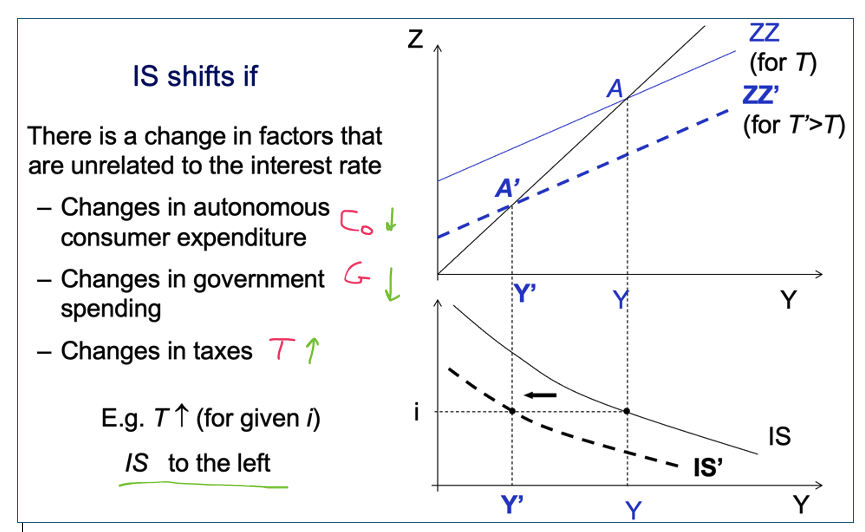
What causes IS to shift
Demand for money
Financial wealth can be held either as cash or as bonds
Bonds pay interest but money can be used for transactions
M^D = L(PY, i)
Your level of transactions - PY
Demand for Money moving proportionally to PY
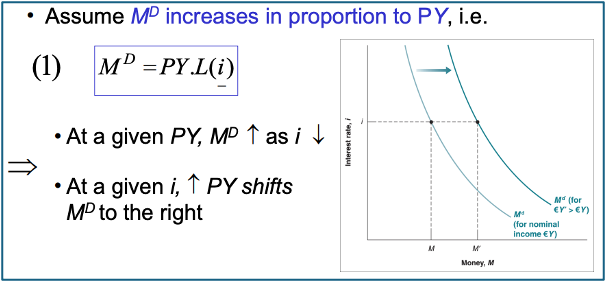
If we assume M^D increases proportionally to PY then M^D = PY * L(i)

Money Supply
CB control Ss but not i using OMOS (buying and selling bonds)
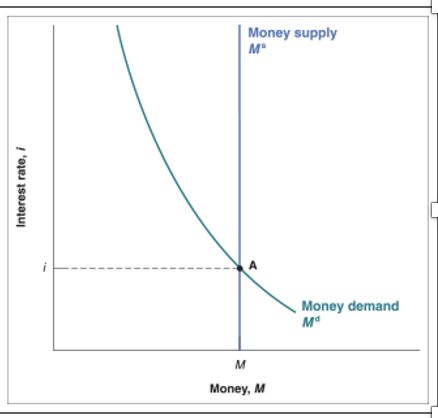
LM function
shows combinations of i & Y where the money market is in equilibrium
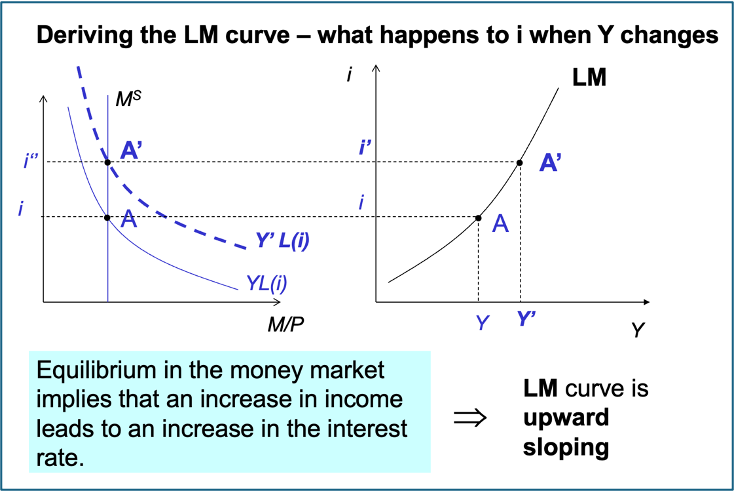
What affects Money market equilibrium
PY and MS changes
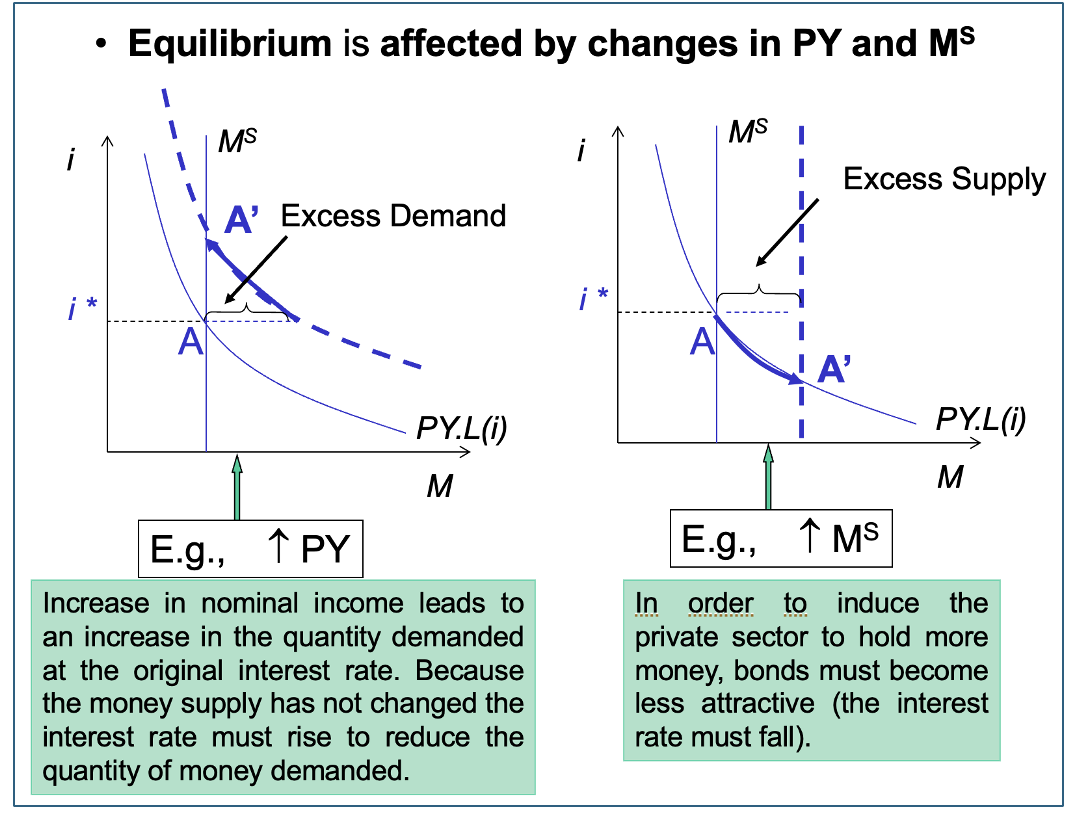
IS-LM model assumptions
that L supply is perfectly elastic – always spare people (unemployed) in the economy willing to work at whatever the wage rate provides
output supply function is perfectly horizontal - Price level fixed
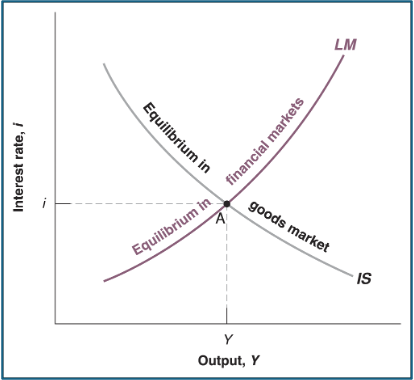
IS-LM equilibrium
IS & LM must be satisfied simultaneously (IS = LM)
How an increase in G affects IS-LM
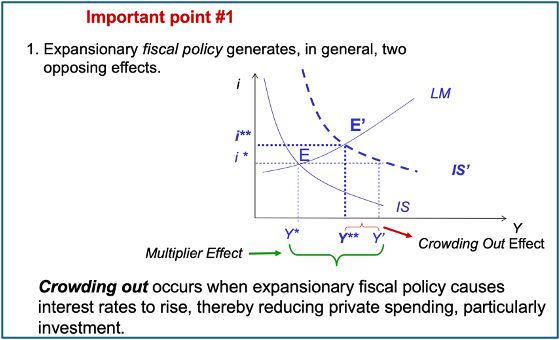
In the short run, the effect of fiscal policy on investment is ambiguous due to crowding out
G UP shifts IS out so Y & i increase (opposite reactions in I)
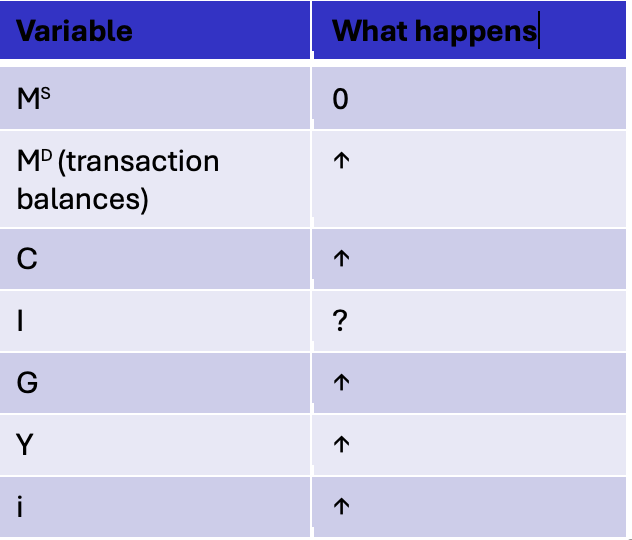
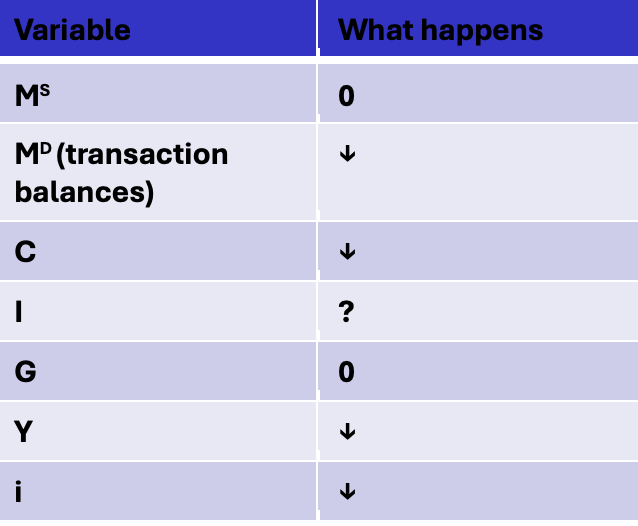
How loss of consumer confidence affects IS-lm
Expansionary MP
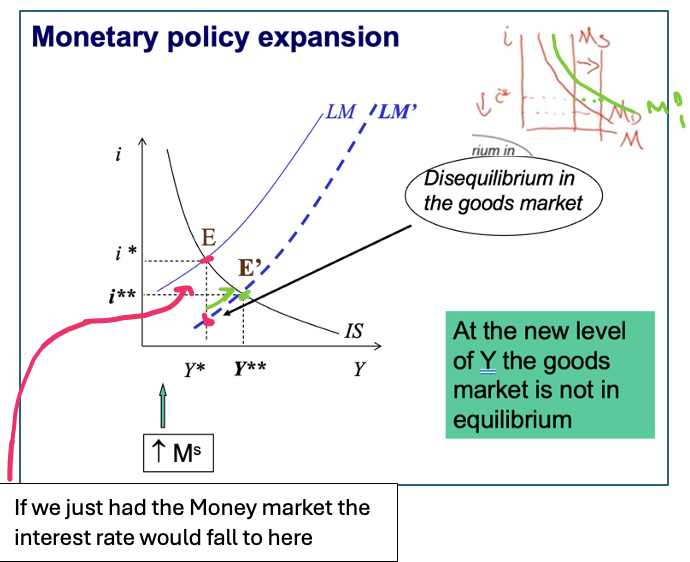
Ms increases - shifts out to the right
o This creates an excess supply of money - i falls
o I & C rise → (Y) rises
The excess supply of money is eliminated as i rises until IS = LM
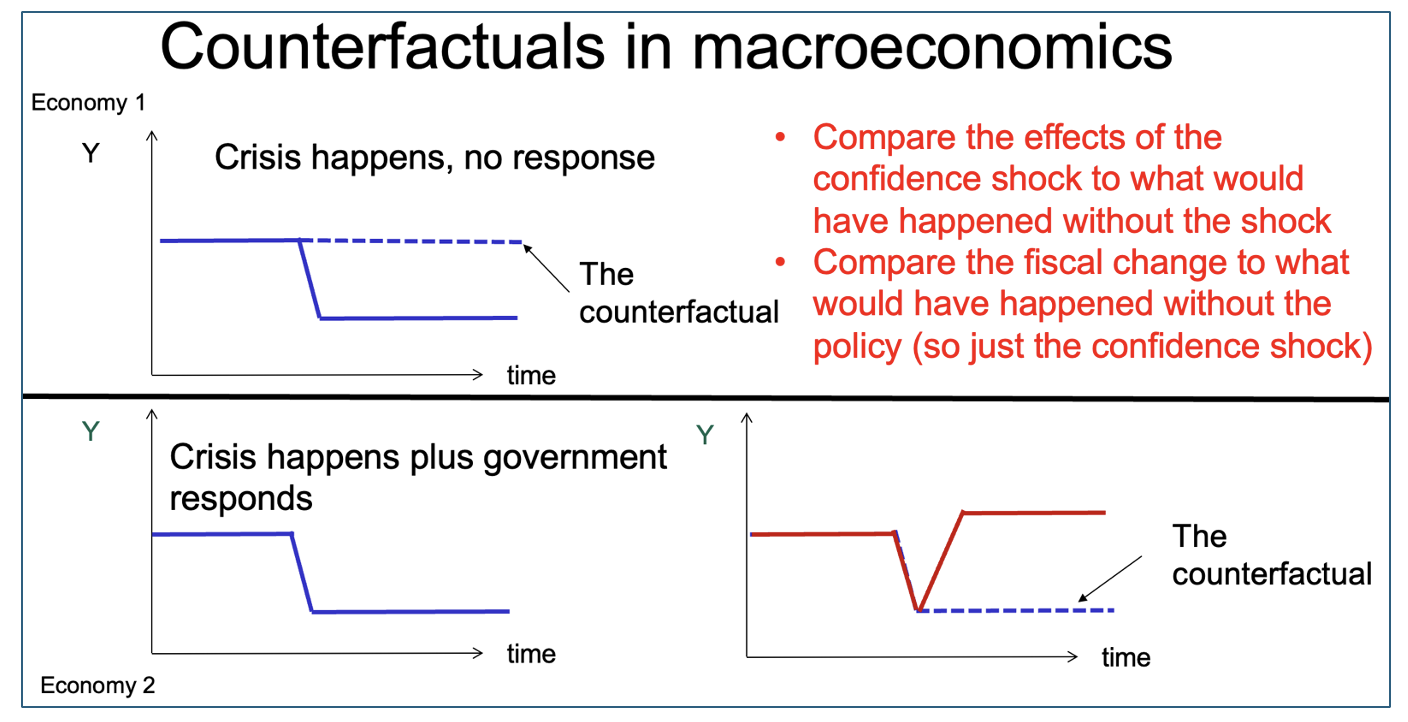
Counterfactuals
When is MP more effective
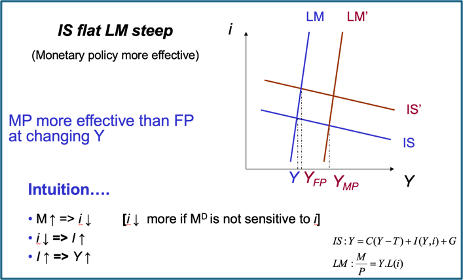
Investment really sensitive to changes in i
When is FP more effective
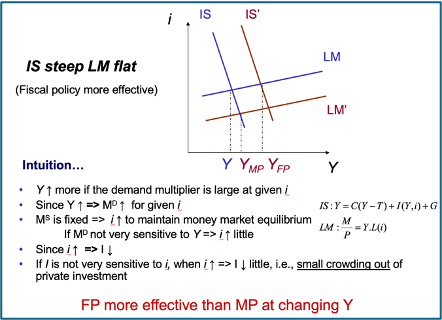
Keynsian vs Monetarist
Keynesian view
- MD is unstable and highly elastic
- Investments are not very sensitive to interest rates
Monetary policy not very effective
Fiscal policy very effective
Monetarist view
- MD stable and dependent on P and Y => highly rigid
- Investments are sensitive to interest rates
Monetary policy is very effective
Fiscal policy not very effective
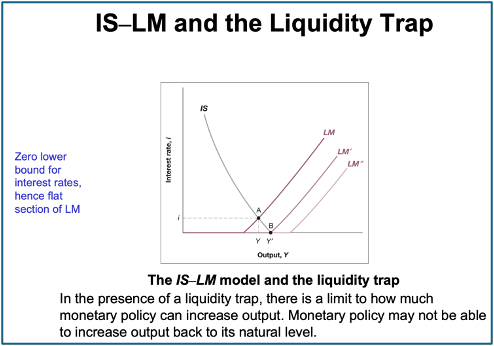
Liquidity trap
• The elasticity of money demand w.r.t. the interest rate is infinite – MP doesn’t have much more room to go
o Given i, any change in MS is absorbed by demand
LM flat
Investment trap
• The elasticity of investment w.r.t. the interest rate is zero
o Investments are unaffected by changes in i
o IS vertical
Limitations of IS-LM model
• Effects of policy depend on slopes of IS & LM
• Assume fixed prices
• Consumption depends ONLY on Current disposable income
• Closed economy assumed