PSYC Exam 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
3 stages of brain evolution - Reptilian
Brainstem, cerebellum
Basic life requirements like breathing, temp regulation, motor processes
EX: being reactive to avoid hazards
3 stages of brain evolution - Mammalian or Paleomammalian
Limbic system (amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus)
”Common denominator” of all mammals
Helps animals navigate more complex environments and form emotional connections
EX: Memory, emotion, social behavior
3 stages of brain evolution - Human or neomammalian
Massive cerebral cortex
More influenced by socio-culture processes
Handles higher-order thinking
EX: language, logic, planning, creativity
Stress Response Order (Apples Hang Around As Elephants Charge)
amygdala → hypothalamus → autonomic nervous system → adrenal glands → epinephrine and cortisol
What are the negative consequences for prolonged stress?
A lot of release epinephrine can damage the blood vessels and arteries which can lead to high blood pressure
High cortisol levels could cause an increased build up of fat tissue
Flight or Flight
Heightens our attention to threat
Epinephrine improves breathing by stimulating the heart in order to raise a dropping blood pressure
Cortisol helps control blood sugar levels, regulate metabolism, help reduce inflammation, and assist with memory formulation
Neuropsychologist
Psychologist who specializes in understanding the relationship between the brain and behavior.
EX: How injuries, illnesses, or disorders of the brain affect cognitive functions and behaviors
Clinical Neuropsychologists
Specialized type of neuropsychologist who focus on assessing/treating patients with brain-based conditions that affect behavior and cognition
EX: Traumatic brain injury or dementia
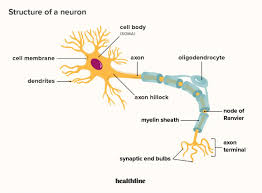
Neuron
Nerve cell that is the basic building block of the nervous system
Sends and receives electrical and chemical signals throughout the body
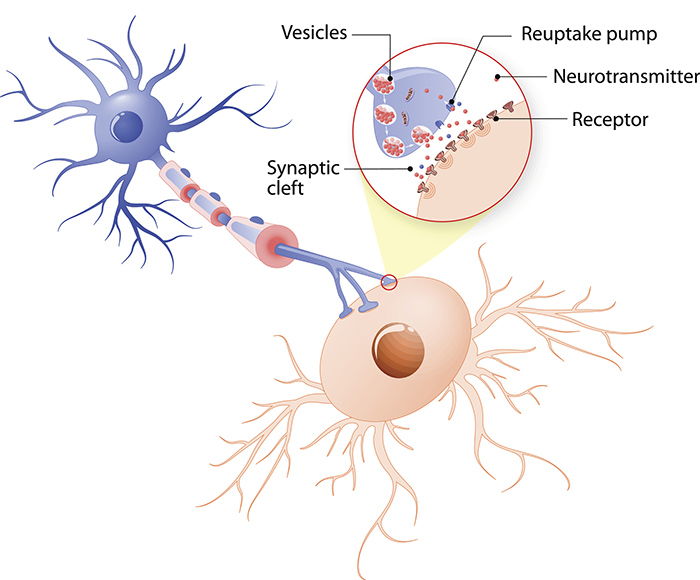
Neurotransmitters
The brains chemical messengers and they’re released by neurons
Sensory neurons (afferent neurons)
They carry information from your senses to your brain and spinal cord.
Motor neurons (efferent neurons)
They carry neural impulses away from the central nervous system/brain and towards muscles to cause movement.
Interneurons
Located in the central nervous system/brain. Between the sensory and motor neurons and they help transmit signals back and forth.
fMRI’s
When neurons activate, there is change in blood flow and the change can be mapped on the brain through fMRI’s
Addiction
Dopamine (chemical) is released.
Moral panic
When a group or behavior is perceived as a major threat to society’s values or safety (could be exaggerated)
EX: Violent video games
Neurological perspective
Anything fun results in the release of dopamine. So dopamine is about learning that rewards feel good. so we can do them again.
EX: Having sex and riding roller coasters
Bad > Good
We feel fear and helplessness stronger than excitement or joy. Bad info carries more weight than good info.
Loss aversion
People have a tendency to prefer avoiding losses over the pleasure of acquiring equivalent gains. Basically losing something feels worse than the feeling of gaining something of the same value
EX: Loosing $100 feels worse than gain $100
Risk aversion
Tendency of people to prefer certainty over uncertainty especially when it comes to making decisions involving potential losses.
EX - Option A: you are guaranteed $100 Option B: you have a 50% chance to win $200 but a 50% chance to win nothing.
Many people would choose Option A because they’re risk-averse
Proximity
People are more likely to form relationships with others who are physically close to them
EX: forming connections with classmates cause you see them everyday
Functional distance
Tendency of an architectural layout to encourage or inhibit certain activities, including contact between people.
Mere Exposure Effect
Finding that repeated exposure to a stimulus leads to greater liking of the stimulus’ images of others
EX: People prefer mirror-image image of themselves, but “true
Physical Attractiveness
Often leads to biases
Halo effect: good looking people are overall better
Facial Beauty
Physical features of the face influence people’s perceptions, judgments, and interactions
EX: symmetry
Self-Disclosing Different Types of Personal Information - Stimulus Stage
First meeting, superficial conversations. Attractions is based on visible attributes such as age/physical appearance.
Self-Disclosing Different Types of Personal Information - Value Stage
Share attitude and beliefs. Decide whether compatible.
Self-Disclosing Different Types of Personal Information - Role Stage
Communicate major life plans, attitudes toward major life tasks (e.g. parenting, career)
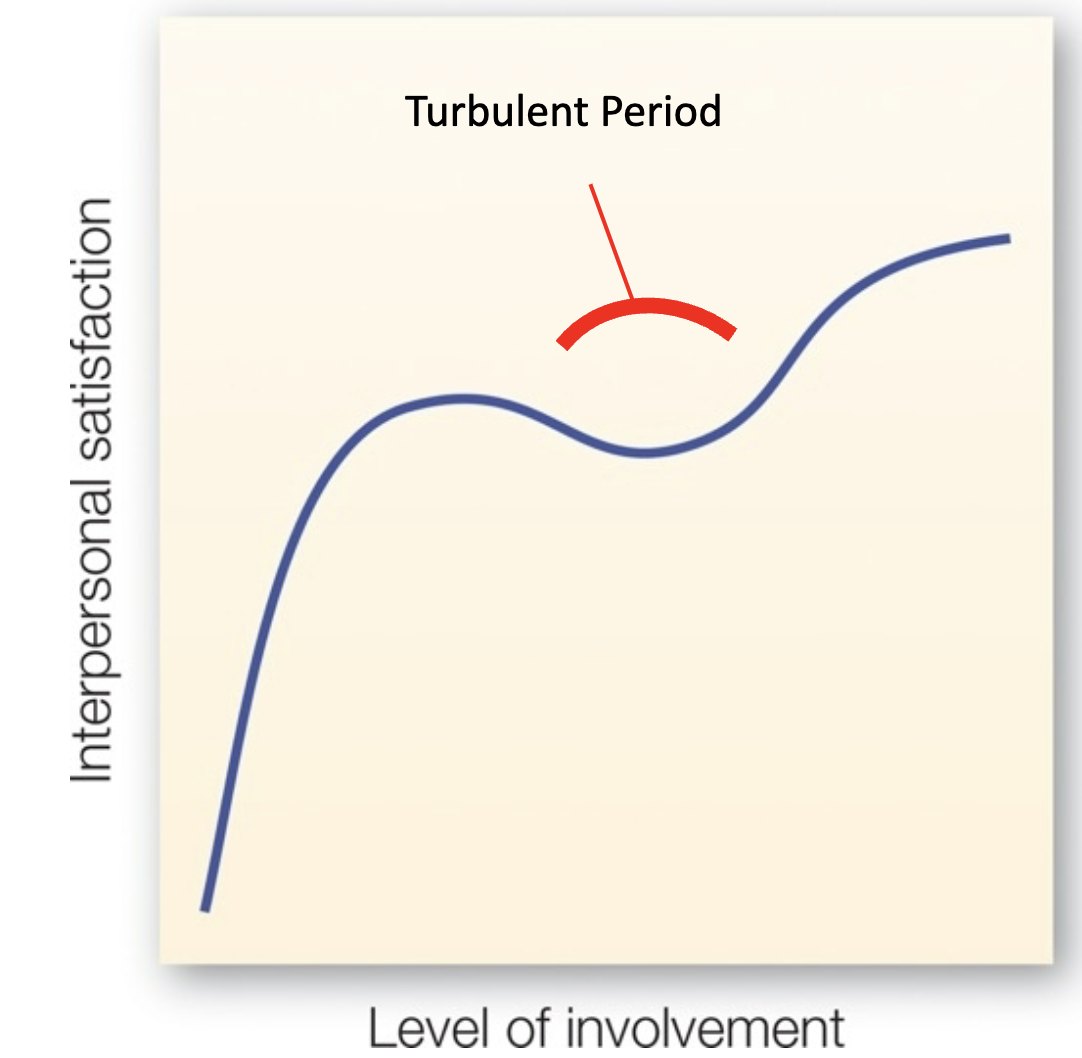
Adjusting to interdependency
The process of adapting to the idea that individuals often rely on and influence other in relationships
Relationship satisfaction changes with level of involvement
If the relationship survives this turbulent period and the partners accommodate to each other’s needs and lives, the couple enjoys even more satisfaction
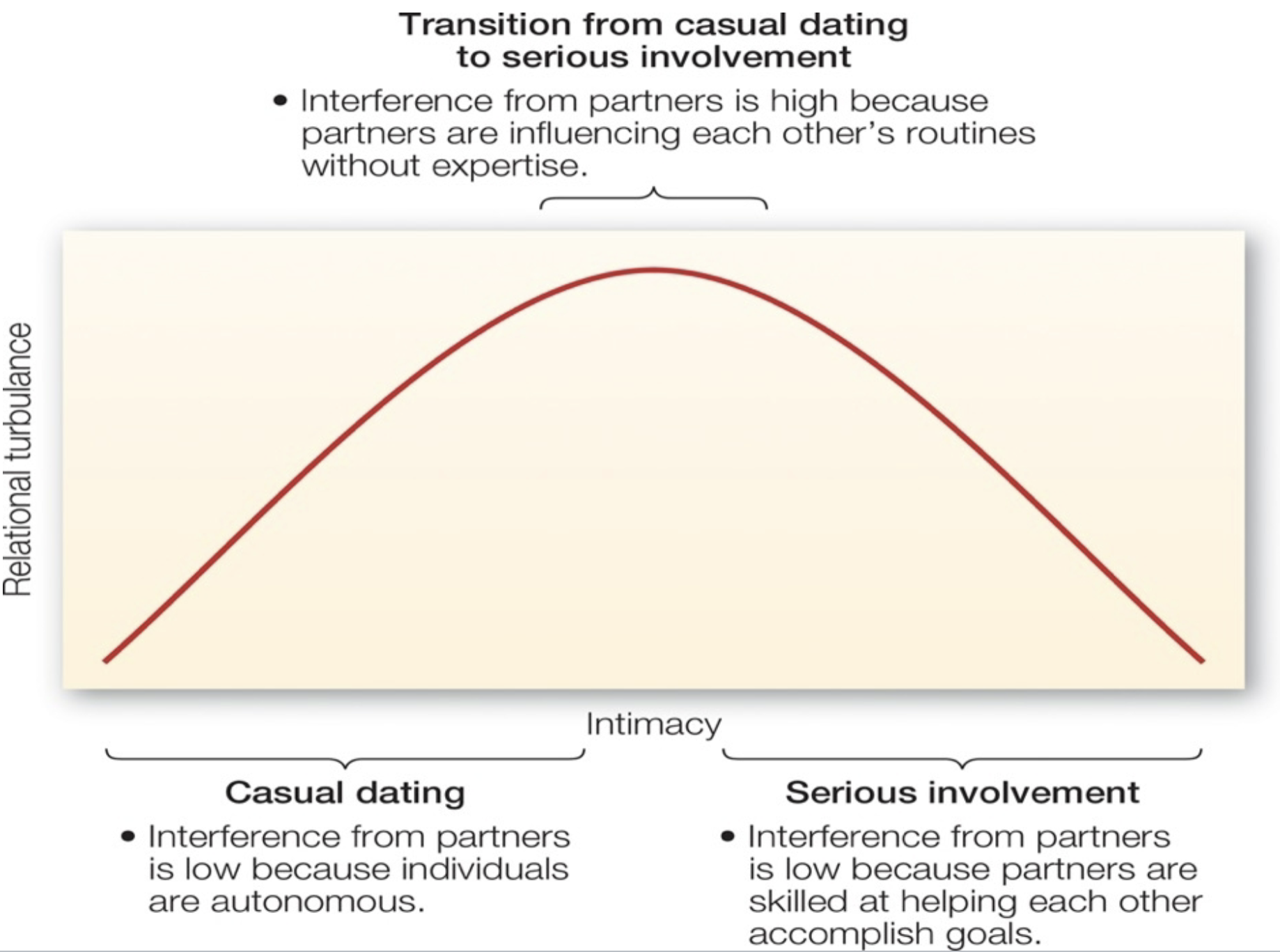
Relationship Turbulence Model
Explains how relationship transitions can cause uncertainty and emotional upheavel thus causing turbulence.
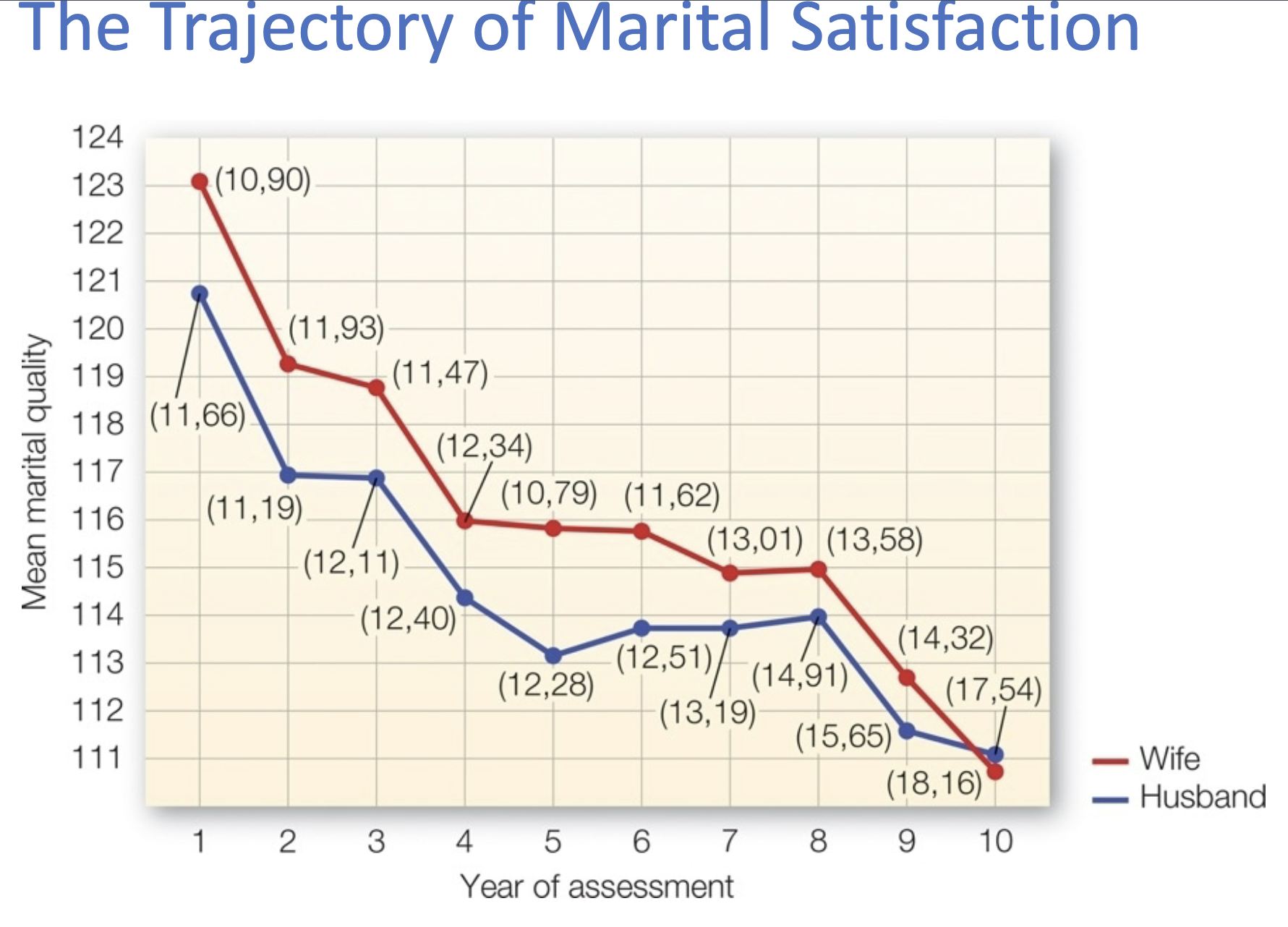
The Trajectory of Marital Satisfaction
Refers to how satisfaction in a marriage change over time. It often follows certain patterns or trajectories depending on life.
Early years: High satisfaction due to excitement and novelty
Middle years: Dip in satisfaction and communication may decline
Late years: Rising satisfaction because after children leave home or careers settle, couples often reconnect
LGBTQ relationships
Self-Identification as LGBT has increased amongst the new generation.
Long-Term Relationships
About 40-50% of people get divorce and it increases for second marriages
Stable and fulfilling marriages are associated with better physical and mental health and economic achievement
Divorced people are at higher risk of early death
Gottman’s 4 Horsemen (Patterns of communication that are lethal to long-term relationships)
Criticism
Contempt (single best predictor of divorce)
Defensiveness
Stonewalling (emotionally shutting down)
Infidelity dilemma
For men sexual infidelity is worse but for women emotional infidelity is worse.
Short term mating
Behaviors that guide people toward casual, non-committed sexual encouters.
Sexual Double Standard
Men are often praise or seen as “studs” for being sexually active while women are often shamed or called “slut” for the same behavior.
Industrial Organizational Psychology
The study of human behavior in the workplace. It blends psychology and business to help organizations work better by improving things like hiring, motivation, performance, leadership, and overall employee well-being.
Areas of Study for IO Psych
Training
Selection
DEI work/Culture Development
Teams
Leadership
Knowledge (KSAO’s)
What you know.
Information that can be applied
EX: knowledge of foreign languages or computer programming languages
Skils (KSAO’s)
What can you do.
Capabilities required to perform tasks accurately
EX: analyzing data or giving presentations
Abilities (KSAO’s)
Capabilities that influence performance, often more long-term or stable than skills
EX: problem-solving ability, physical strength, verbal reasoning, memory capacity.
Other characterisitics (KSAO’s)
Traits that do not fit into the other categories
EX: values, work styler, personality and degrees/certifications
ABC’s of Teamwork
Team’s overall success is not just about how skilled or talented each individual is on their own
Affective States - how members feel
Behavioral Processes - how members behave
Cognitive Processes - thought processes of members
Team Cohesion
Forces exerted on a group or team that push its members closer together
Group pride is more important than thought
Communication Patterns
Who talks to who within a network
Does communication quality or frequency matter more? .36 quality, .19 frequency
Coordination and Back up Behaviors
Using systematic structures/processes to store knowledge
EX: emails, notepads, texts
Shared Mental Model
Knowledge that is held in common with team members
Transactive Memory System
Knowledge of the distribution of information within teams
EX: We know who to go to in order to get certain knowledge
Multi-team Systems (MTS)
A system of teams in which there are present overarching “superordinate” goals that require coordinated efforts of multiple specialized teams to address the goal
Subordinate Team Goals
Goals that are less important than the main goal but still contribute to the overall success
EX: marketing team that creates an advertising campaign
Superordinate MTS Goals
Big, overarching goal that drives a Multi-Team System
Ingroup Prototypicality
Refers to the degree to which an individual is seen representing the typical characteristics of their in group (the group the belong to) compared to other members of that group
EX: If you are apart of a soccer team and you always practice and follow the team so you are a prototypical member. But if you don’t practice and don’t care about the teams values you are seen as less prototypical.
How to increases your prototypicality within a group
Identify and act on norms within the group
Establish relationship with highs status members
Bolster support from subgroup followers
Differentiate yourself from out group members
Take the lead in uncertain situations
How to be an effective leader
Be able to anticipate change in your area and not by myopic
Be comfortable developing relationships with others that are different from you
Be okay with being in uncomfortable situations in the short-term if it means being successful in the long-term.
Team Efficacy
Feeling that the team can accomplish the given task
Related to goal setting
The more team members rely on each other to succeed, the more important it is that they believe in the teams ability to succeed together
Amygdala
Processing emotions like especially fear, anger, and pleasure
Hypothalamus
Acts as the control center for many autonomic functions like maintaining homeostasis