Ultrasound Physics Ch 6 (interaction of Sound and Media)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What happens to sound as it travels through the body?
It weakens, or attenuates
The sound wave a transducer receives during reception is converted into what type of signal?
electrical
What happens to the electrical signal?
It is sent to the ultrasound system where it is strengthened or amplified.
What does the following describe?
. a relative measurement / change
. a comparison
. a ratio
. logarithmic
Decibel Notation
what are the 2 intensities decibels (dB) require?
. the reference (starting level)
. the actual level at the time of measurement
Decibels are a ratio; the.....
measured level divided by the starting level
positive decibels report signals as they are.......
increasing in strength or getting larger
ex. stronger, louder sound
+ 3dB is
orig value doubled
ex. 1x2= 2
+ 6dB is
orig value doubled 2x
ex. 1x2=2 x 2 = 4
+ 9dB is
orig value doubled 3x
ex. 1x2= 2x2= 4x2= 8
+ 10dB is
orig value 10x larger
increases ten-fold
ex. 1 x 10= 10 or 4x10=40
negative decibels (dB) describe signals that are......
decreasing in strength or getting smaller
. weaker, softer
- 3dB is
orig value halved
ex. 1x 1/2 = 1/2
- 6dB is
orig value halved 2x
ex. 1x 1/2= 1/2x 1/2= 1/4
- 9dB is
orig value halved 3x
ex. 1x1/2= 1/2x1/2= 1/4x1/2= 1/8
- 10dB is
orig value 1/10x
one-tenth
ex. 1 x 1/10 = 1/10
What are the 2 factors attenuation is determined by?
. path length
. frequency of sound
Distance and attenuation are
directly related
attenuation is ______ in higher frequency sound than lower frequency sound
greater
How are frequency and attenuation related?
they are directly related
What do the following 2 factors describe?
. longer distances
. higher frequencies
more attenuation
What do the following 2 factors describe?
. shorter distances
. lower frequencies
What 3 processes contribute to attenuation?
-Refection
-Scattering
-Absorption
What is reflection?
the redirection of sound from where it came from, back to the sound source
Reflection is likely to occur when the dimension of the boundary is ______.
large, that is, more than a few wavelength of sound
What 2 forms of reflection are created in soft tissue?
specular and diffuse
What is specular reflection?
When a wave is reflected in a single direction by a smooth surface
E.g. when light is reflected by a mirror, you get a nice, clear reflection
What happens once the wave is slightly off-axis in specular reflection?
the reflection doesn't return to the transducer.

What is diffuse reflection (backscatter)?
Reflection in irregular/ more than one directions from an irregular surface
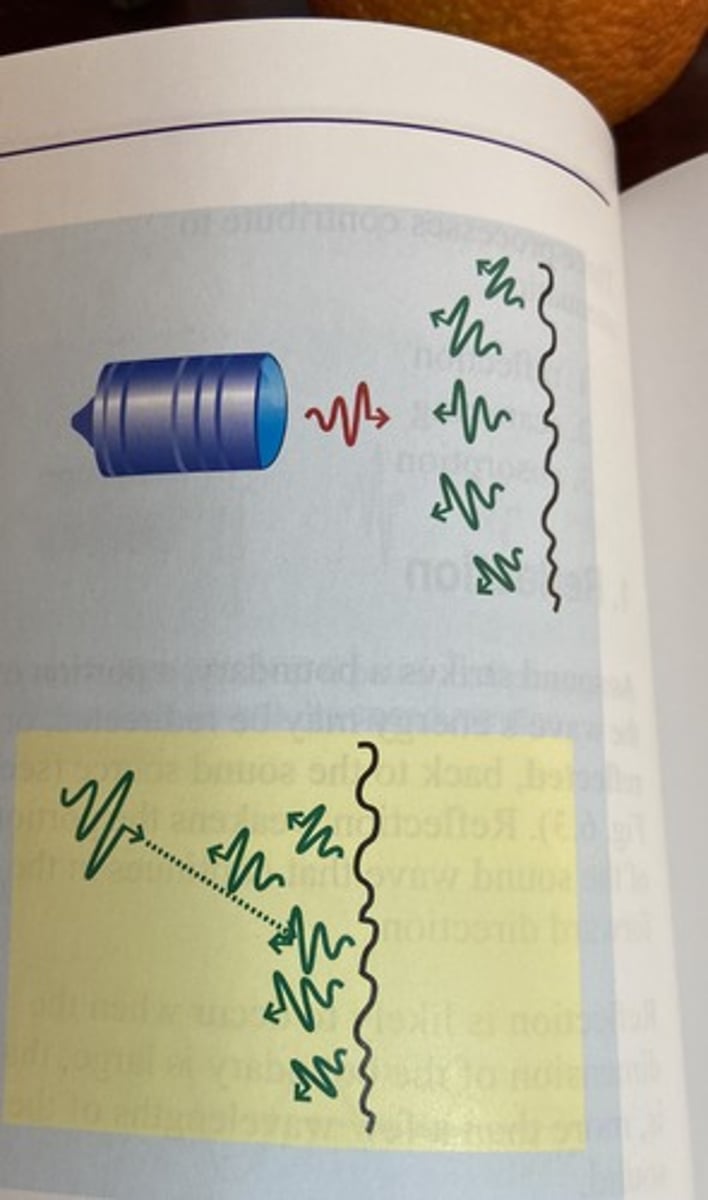
What is an advantage of diffuse reflection?
interfaces at suboptimal angles to the sound beam can still produce reflections that will return to the transducer
What is a disadvantage of diffuse reflections?
Backscattered signals have a lower strength than specular reflections
What is scattering of ultrasound?
the random redirection of sound in many directions
. disorganized
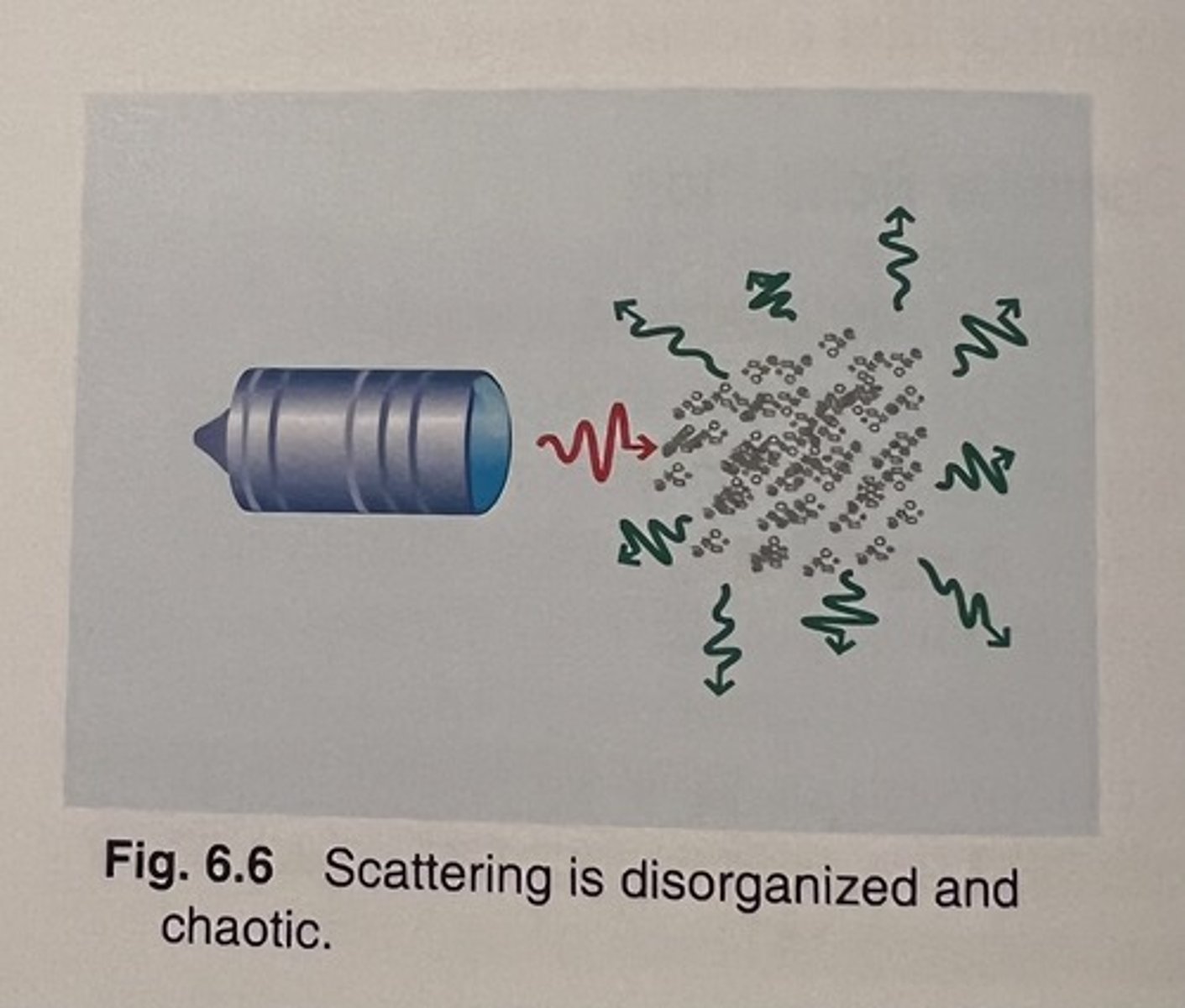
Sound scatters when tissue interface is
small; that is, equal to or less than the wavelength of the incident sound beam
Lungs are
a great scatterer, alveoli are filled with air
Which type of frequency sound beams scatter more?
higher frequency sound beams more than lower frq.
What is Rayleigh scattering?
Special form of scattering that occurs when the structure's dimensions are much smaller than the beam's wavelength
. organized
What does Rayleigh scattering do?
it redirects the sound wave equally in all directions
. omnidirectional (in all directions)
Sound scattered by red blood cells results in
rayleigh scattering
Scattering is related to
Frequency raised to the fourth power
Higher frequency sound waves produce shorter pulses resulting in
more accurate images
What is absorption?
.when ultrasonic energy is converted into another energy form, such as heat
.80% + of sound energy is absorbed and transformed into heat
As a result of absorption, higher frequency waves attenuate ______ lower frequency waves.
more
Bone is a great absorber, undergoes extensive absorption. the sound is absorbed resulting in......
little sound transmitted back to the transducer (Tx) to give an image, shadowing
What is the attenuation coefficient?
the number of decibels of attenuation that occurs when sound travels one centimeter
What are the units of attenuation coefficient?
dB/cm, decibels per centimeter
What does total attenuation (dB) equal?
atten. coefficient (dB/cm) x distance the sound wave traveled (cm)
For waves propagating in soft tissue attenuation coefficient is equal to ________.
frequency(MHz) divided by 2
what is an example of attenuation coef. equation?
ex. Frequency is 2MHz > atten. coef. is 2MHz/2> 1dB/cm
ex. Freq. is 6MHz > atten. coef. is 6MHz/2 > 3dB/cm
What is the order of attenuation in a medium from low to high?
. water = extremely low
. blood, urine, biologic fluids = low
. fat = low
. soft tissue = intermediate
. muscle = higher
. bone and lung = even higher
. air = extremely high
What is half value layer thickness?
.The distance that sound travels in a tissue that reduces the intensity of sound to one-half its original value
. may also be described as the depth of tissue that results in 3dB of attenuation to the intensity
What are the units of half-value layer thickness?
centimeters (cm) or any other unit of length
What is the typical half-value layer range ?
From 0.25 to 1.0 cm
What are other names for half-value layer thickness?
- penetration depth
- depth of penetration
- half-boundary layer
Half-value layer thickness depends on what 2 factors
. the medium
. the frequency of sound
The following 2 factors are characteristics of what?
. high frequency sound
. media with high attenuation rate
Thin half value
The following 2 factors are characteristics of what?
. low frequency sound
. media with low attenuation rate
Thick half value
What is acoustic impedance?
is the acoustic resistance to sound traveling in a medium.
Reflection of an ultrasound wave depends upon
The difference in acoustic impedances of the two media at a boundary
Acoustic impedance is reported in units of.....?
What symbol/letter is impedance represented by?
. reported in units of rayls
. represented by "Z"
What is the typical values impedances ranges from?
. from 1,250,00 to 1,750,000 rayls or
. 1.25 to 1.75 Mrayls
Impedance is associated with/ determined by ....
.the medium only,
. it is calculated not measured
Acoustic impedance is also known as ......
Characteristic impedance
How is acoustic impedance calculated?
density of medium x speed
. m/sec over rayl
what are incidences?
the description of the angle at which the wave strikes the boundary (determines the behavior of the pulse)
What are the 3 types of angles?
Acute- less than 90 degrees
Right - exactly 90 degrees
Obtuse - greater than 90 degrees
Angles with a measure other than 90 degrees are also called ______ angles.
oblique
What is normal incidence?
the incident sound beam strikes the boundary at exactly 90 degrees
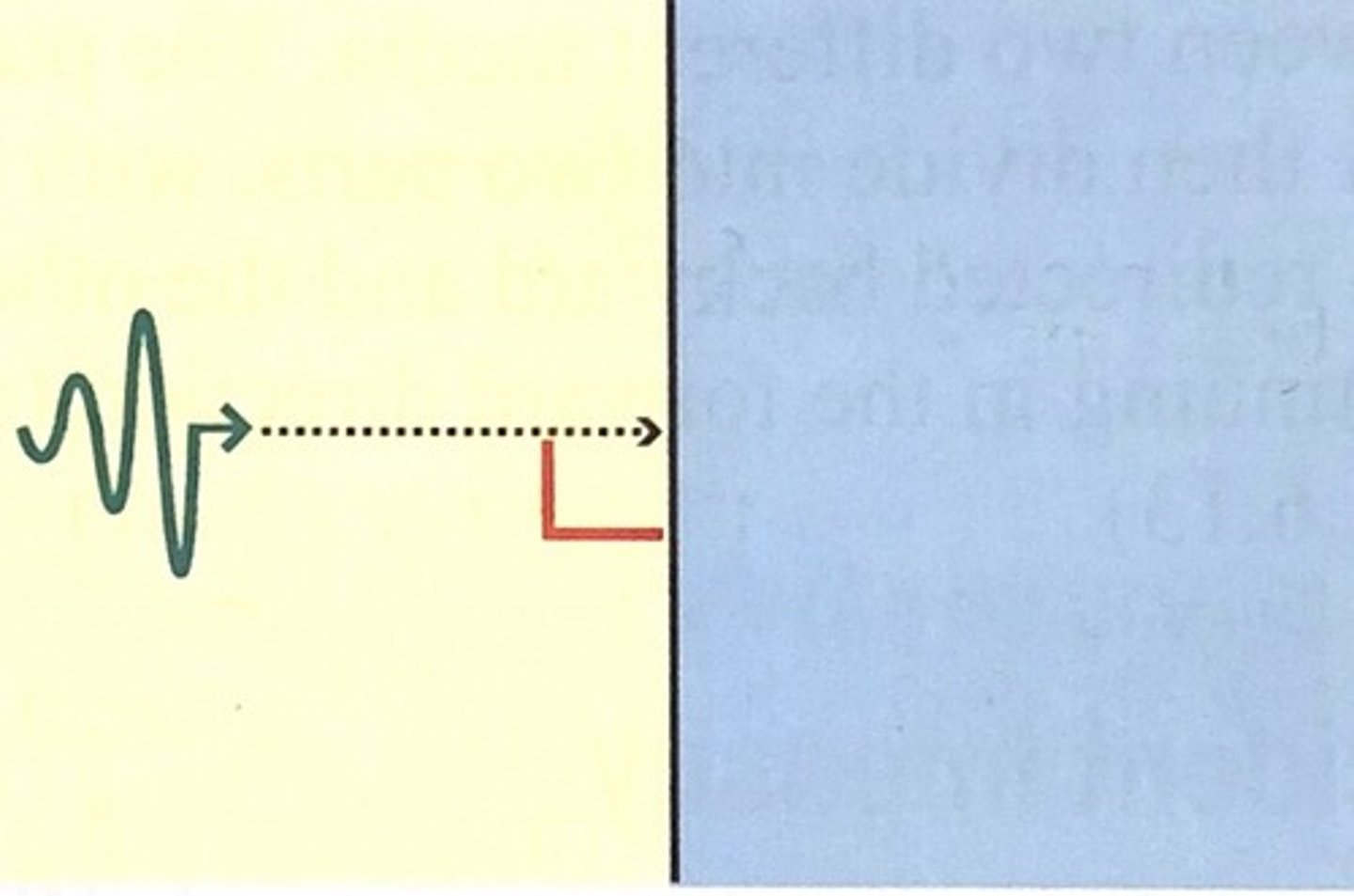
What is the typical value for incidence to be normal?
= to 90 degrees
What are the synonyms for normal incidence
P= perpendicular incidence
O= orthogonal incidence
R= right angle incidence
N= ninety degree incidence, 90 degrees
What is Oblique incidence?
When the incident sound beam strikes the boundary at any angle other than 90 degrees
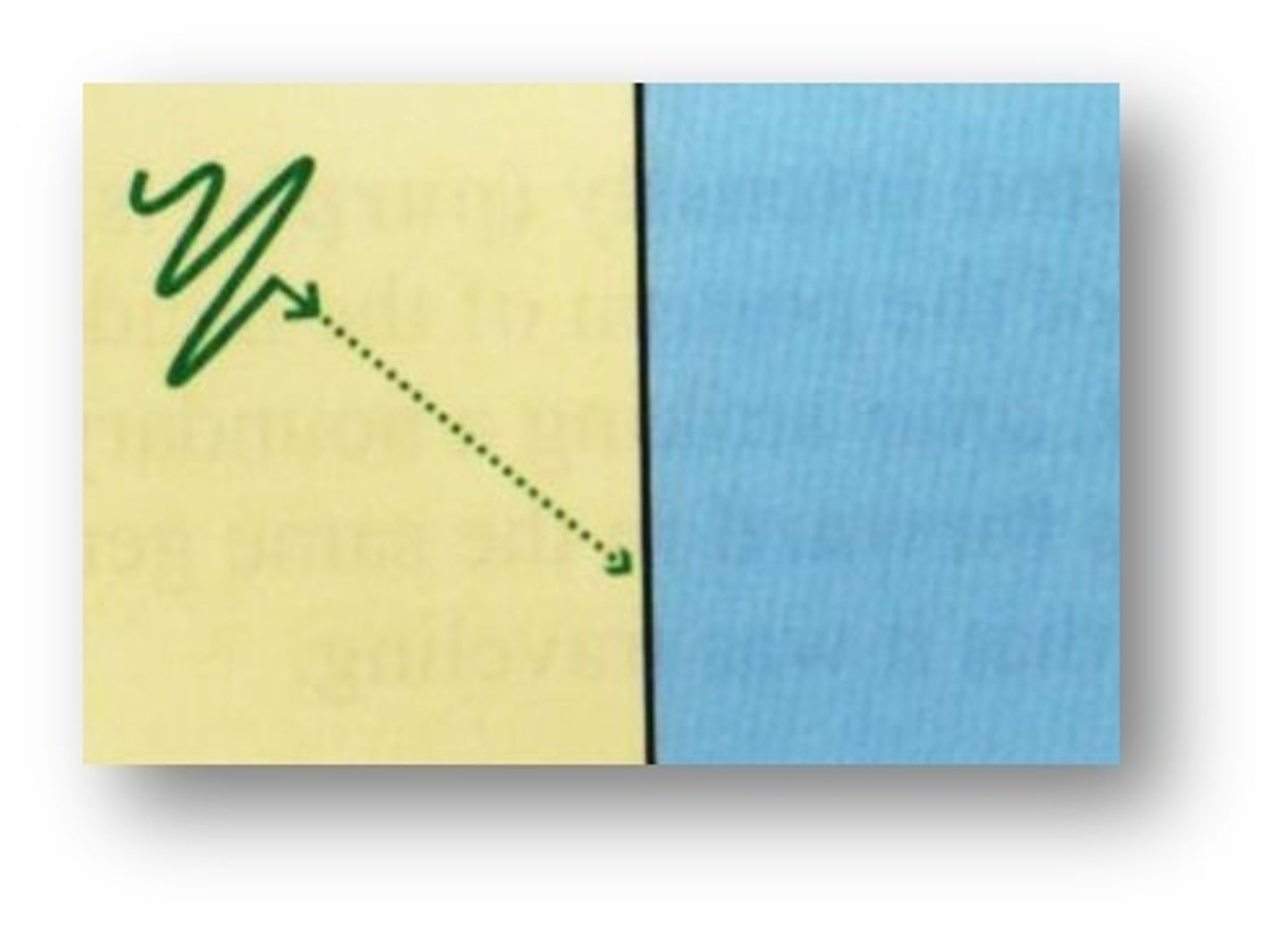
What is the typical value for incidence to be oblique?
the angle must not be equal to 90 degrees
What are synonyms for oblique incidence
- Non-perpendicular
- Non-orthogonal
- Not at right angles
What is incident intensity?
is the sound wave's intensity immediately BEFORE it strikes a boundary
What is reflected intensity?
is the intensity of the portion of the incident sound beam that, AFTER striking a boundary, RETURNS BACK from where it came.
What is transmitted intensity?
is the intensity of the portion of the incident beam that, AFTER striking a boundary, continues FORWARD in the same general direction it was traveling.
Incident intensity equation is
reflected intensity + transmitted intensity
What is the Intensity Reflection Coefficient (IRC)?
the percentage of the intensity that bounces back when a sound beam strikes the boundary between two media
How much of a sound waves intensity is reflected at a boundary between two soft tissues?
very little, (1% or less)
What is the Intensity Transmission Coefficient (ITC)?
is the percentage of intensity that passes in the forward direction when the beam strikes an interface between two media.
How much of a sound wave's intensity is transmitted at a boundary between two soft tissues?
most, (99% or more)
IRC and ITC are both reported as
percentages, therefore dimensionless.
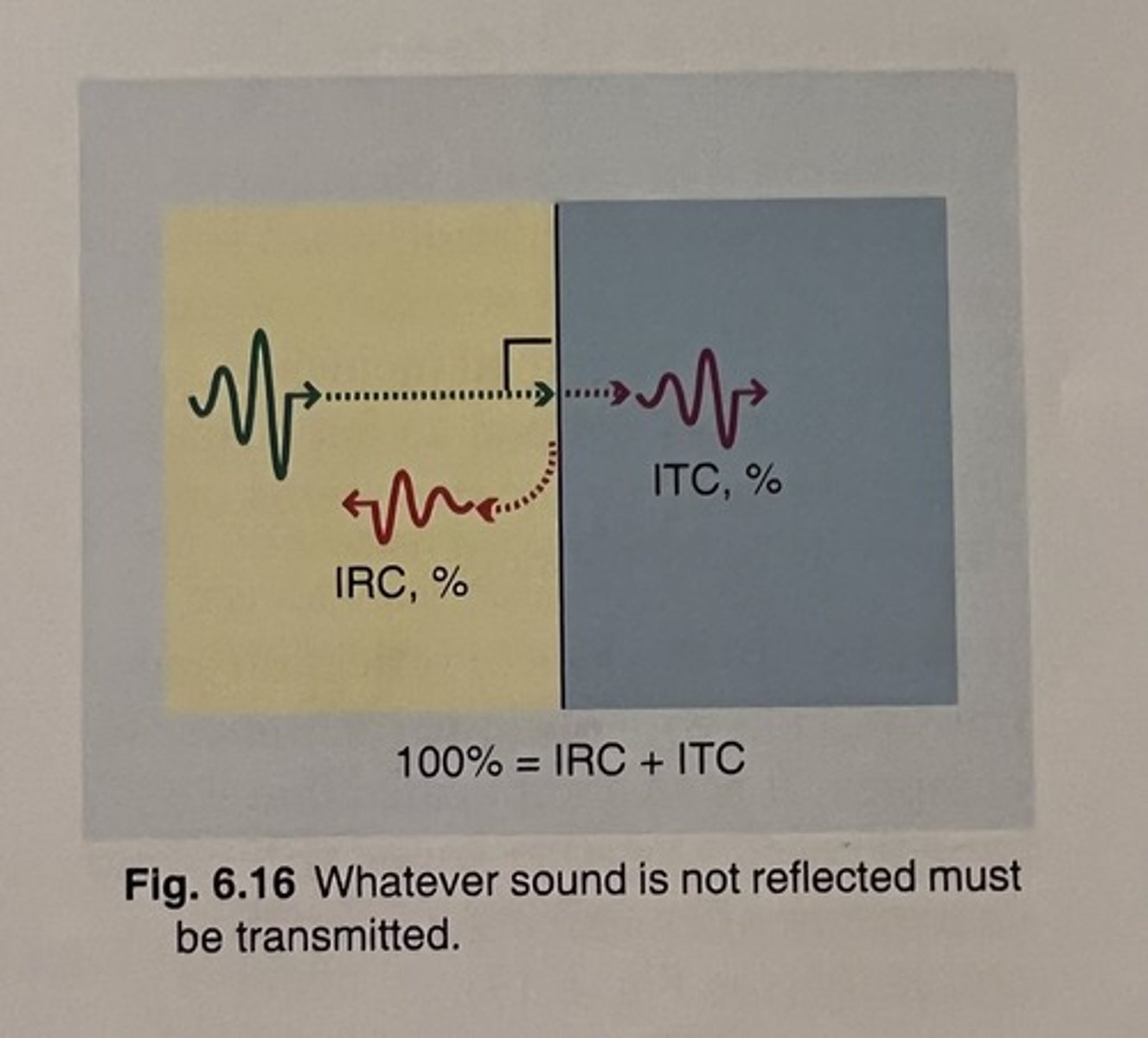
As a sound beam strikes a boundary, energy is conserved and 100% of the intensity must be accounted for?
What equation does 100% equal?
100% = IRC% + ITC%
With normal incidence, reflection only occurs if the media on the other side of the boundary have .....
different impedences
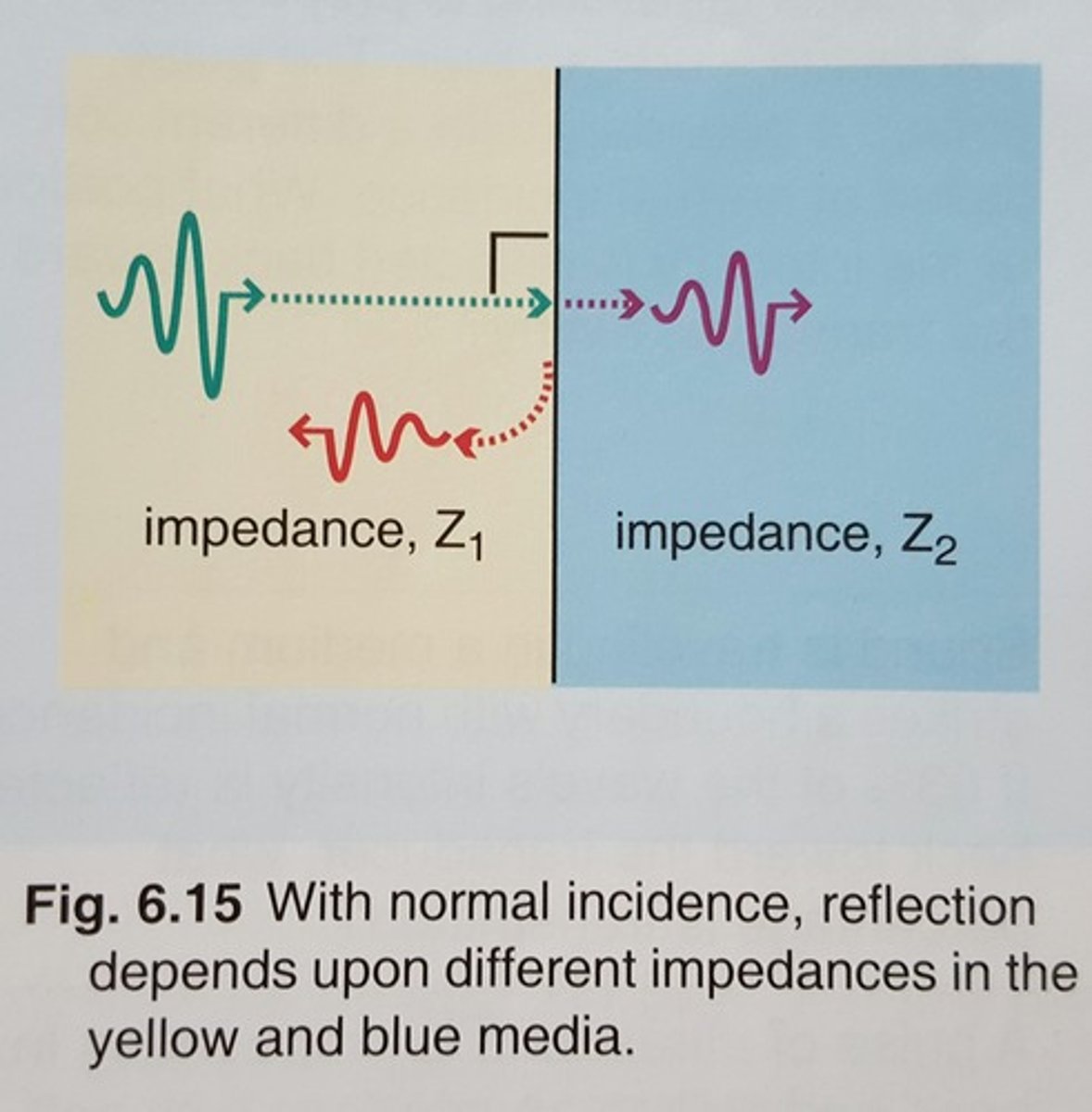
The greater the difference in impedances the .....
.greater the reflection will be
. the lesser the transmission will be
IRC% =
impedance 2 - impedance 1 / impedance 2 + impedance 1 > result x 100
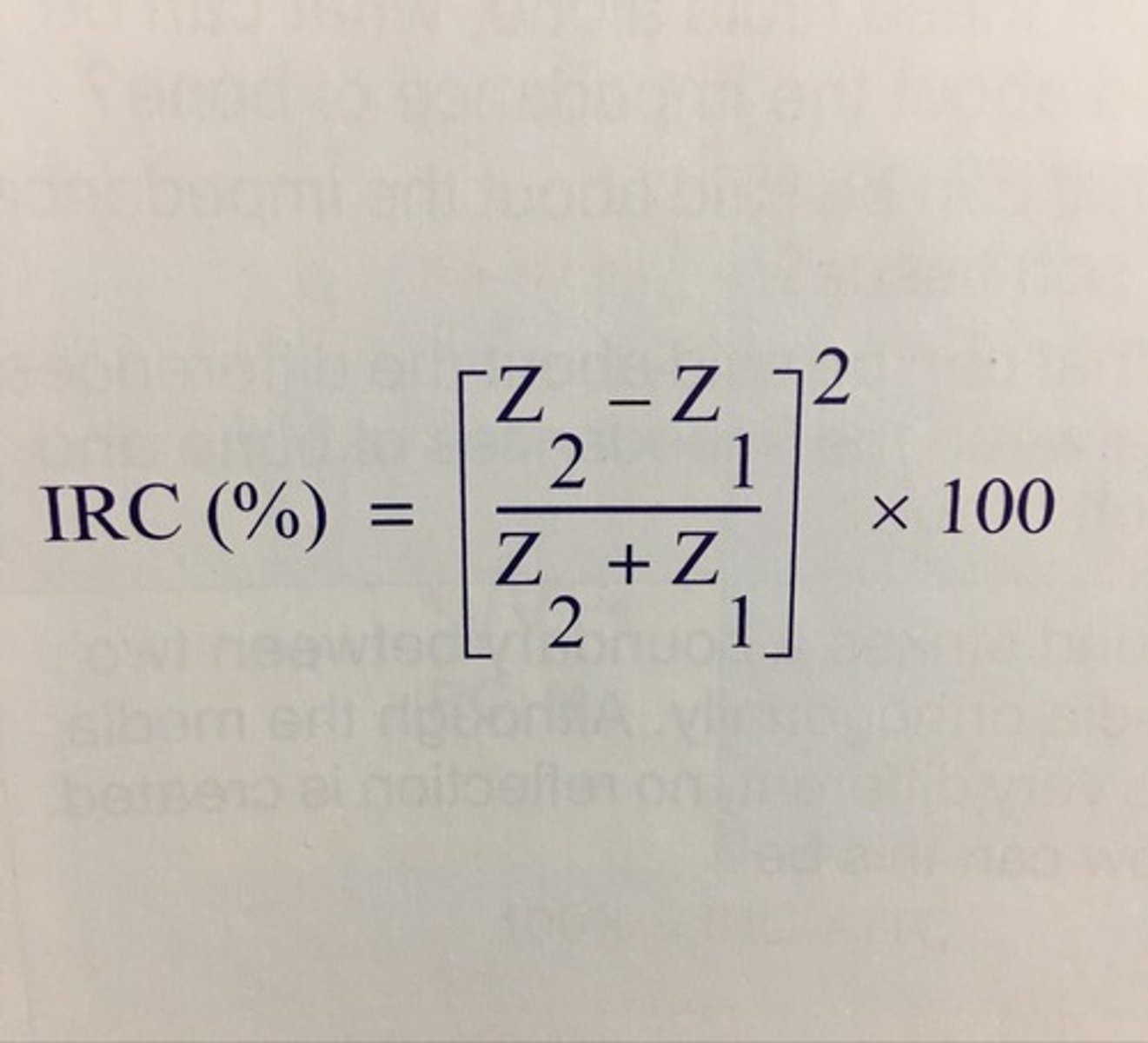
With normal incidence, if the two media have the same impedance, _____ incident intensity is transmitted.
all of sound
The value of ITC ranges from ____ to ____.
and is defined by the equations
0% to 100%
. ITC% = transmitted intensity/ incident intensity > x100
. 1 - intensity reflection coefficient
What 2 principles always apply to reflection with oblique incidence?
- conservation of energy
- reflection angle = incident angle
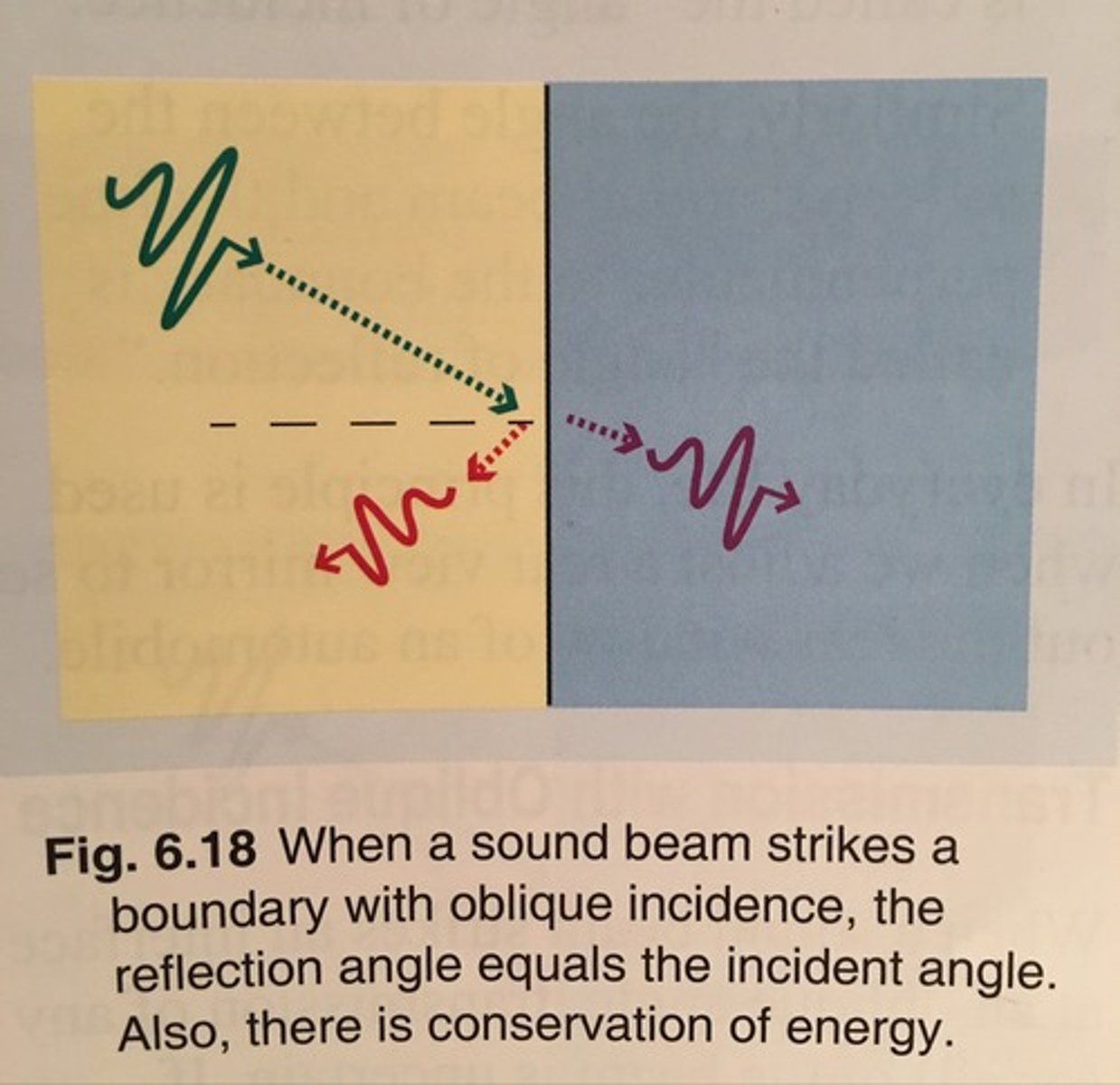
With oblique incidence, the law of conservation applies, so 100% =
100% = reflection coefficient + transmission coefficient
the direction of the reflected echo is ___ and ___ of the direction of the incident beam with oblique incidence
equal and opposite to
. angle of incidence = angle of reflection
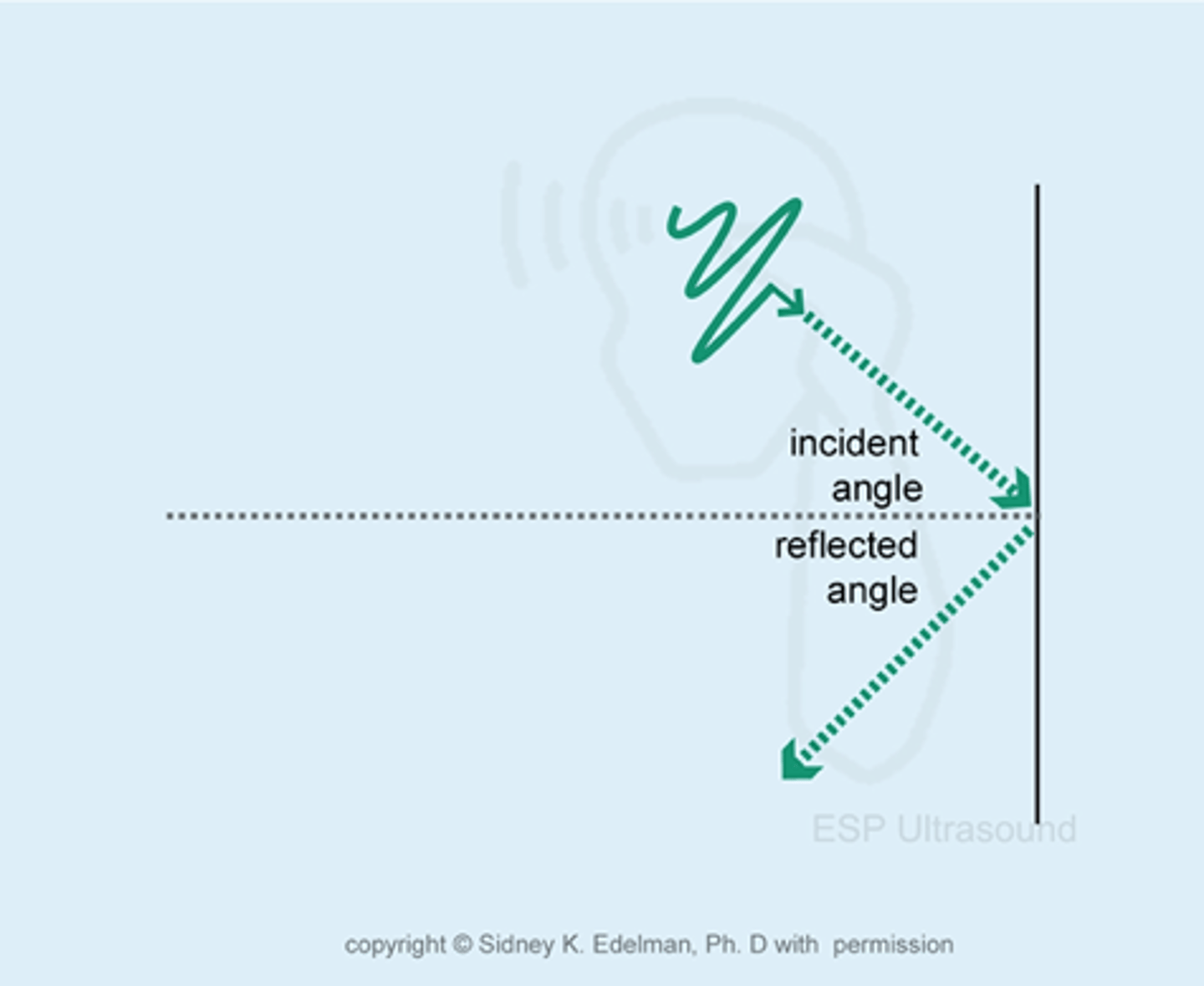
the angle between the incident sound beam and an imaginary line that is perpendicular to the boundary is called...
the angle of incidence
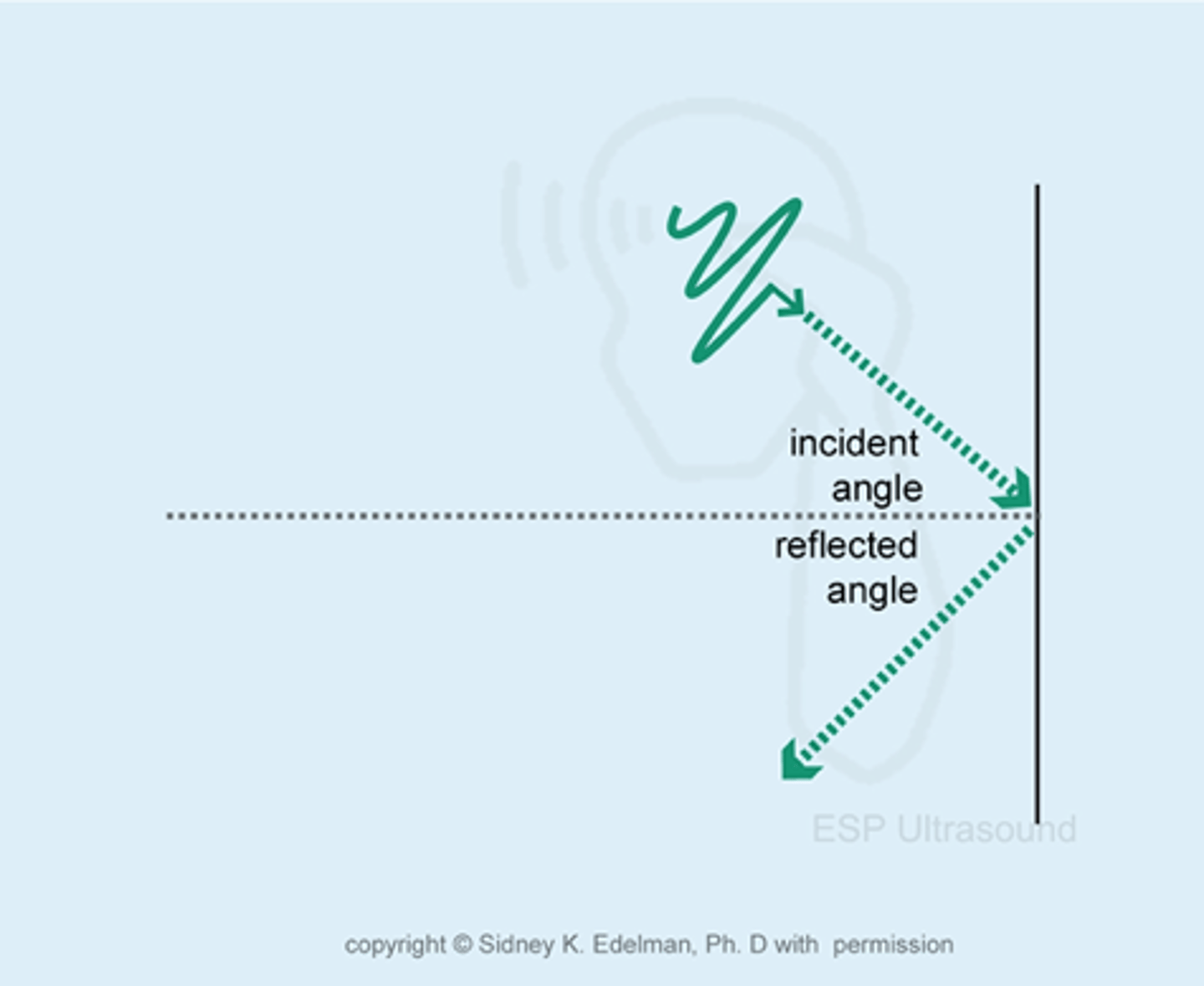
similarly the angle between the reflected sound beam and the line perpendicular to the boundary is called .....
angle of reflection
Regarding transmission with oblique incidence....
. Part of the wave is transmitted the wave might travel straight ahead or
. The sound beam might bend or change direction
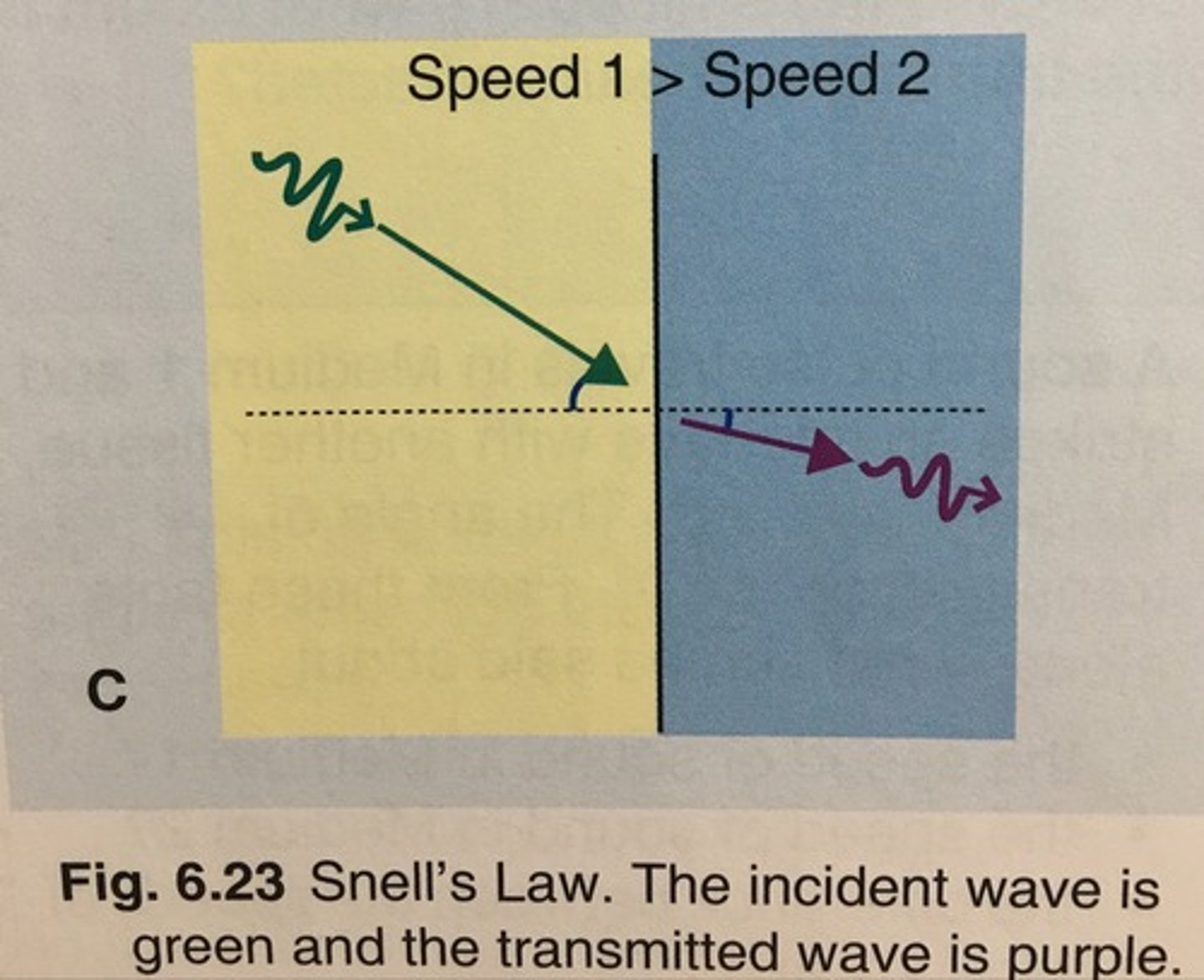
What is refraction?
a change in direction of wave propagation when traveling from one medium to another
. bending phenomenon of sound beam
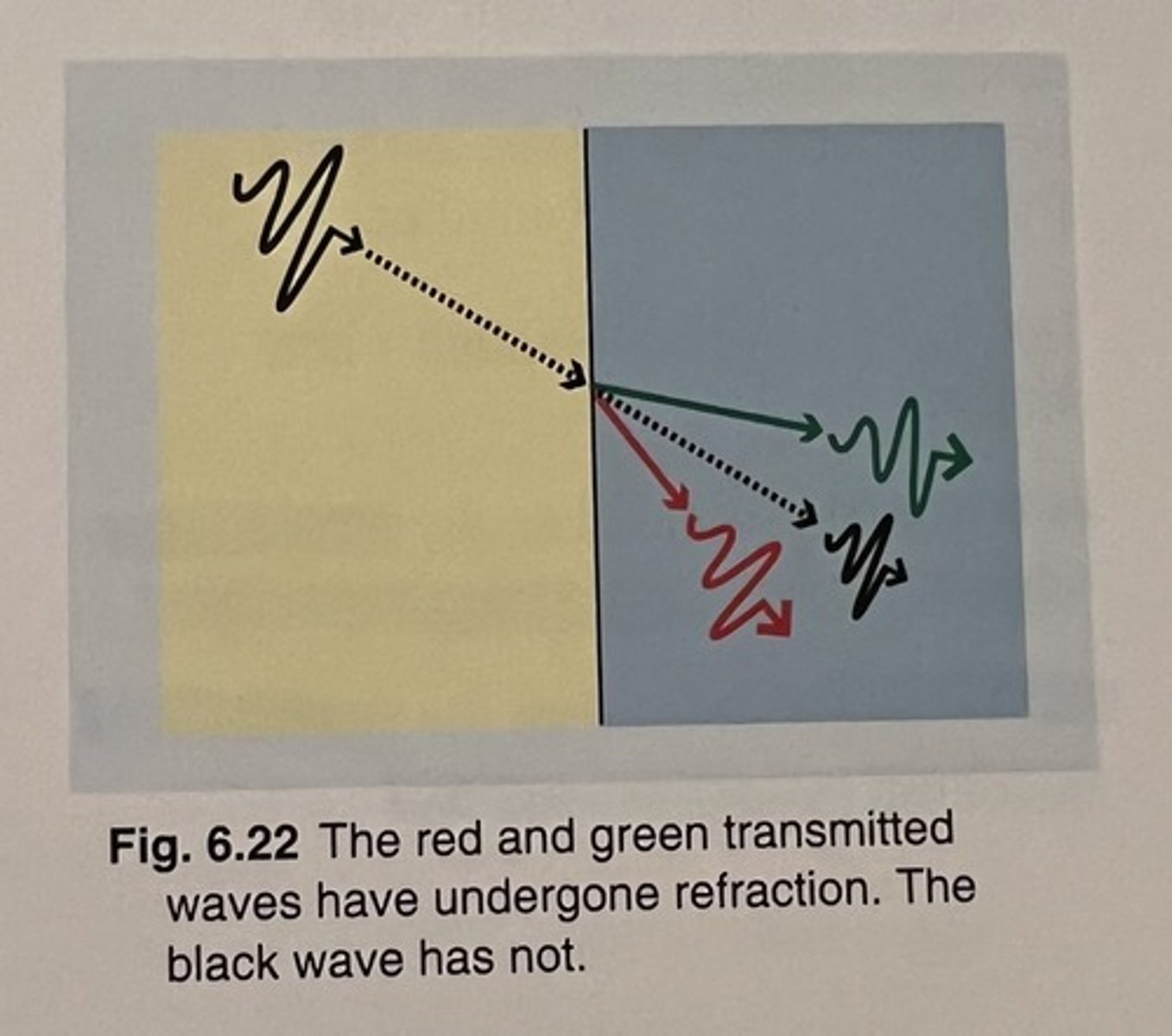
What are the 2 requirements for refraction to occur?
- oblique incidence
- different media with different propagation speeds
How will a sound beam bend in media with similar speeds of sound?
it will bend, at most, a few degrees
ex. soft tissue-fat interface
ex. muscle-blood interface
ex. soft tissue-fluid interface
How will a sound beam bend in media with a large difference in speeds of sound?
Bending is exaggerated
ex. bone-soft tissue interface
What will cause the transmission angle to be equal to the incident angle?
the speeds of two median are identical
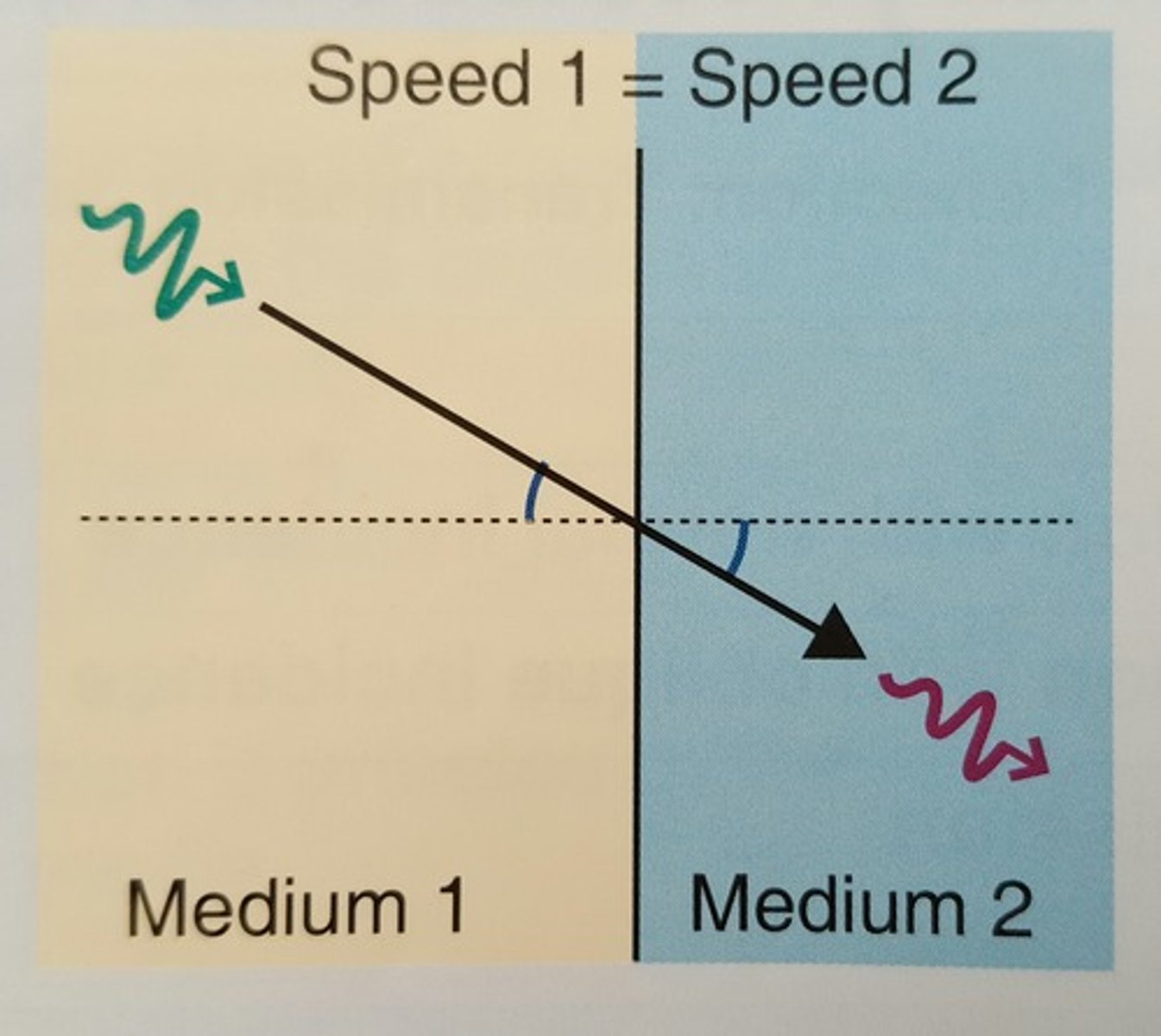
What will cause the transmission angle to be greater than the incident angle?
When the speed of media 2 is greater than the speed of media 1

What will cause the transmission angle to be less than the incident angle?
When the speed of media 2 is less than the speed of media 1