algebra exam
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Function Notation
A way to describe a function with symbols, typically written as f(x) to denote the function evaluated at x.
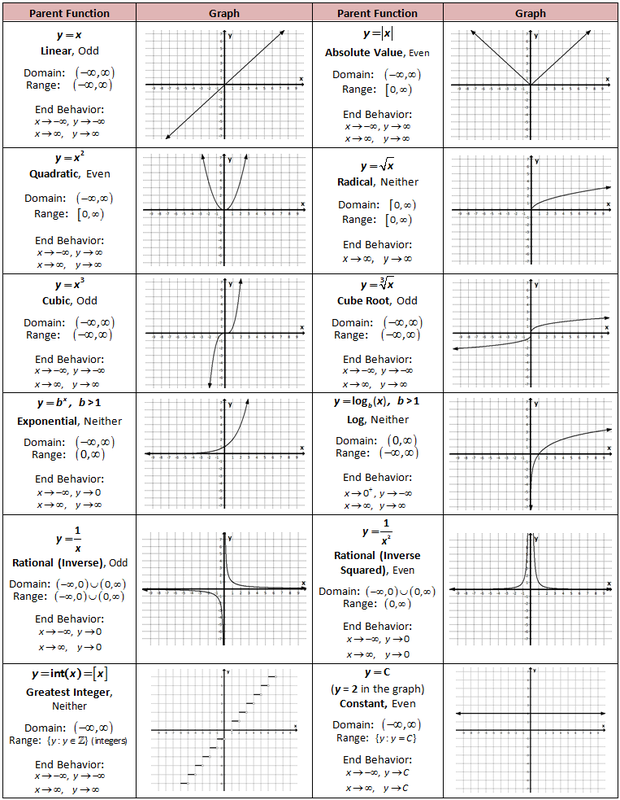
10 BFF Functions
Key functions commonly studied in algebra, including linear, quadratic, cubic, absolute value, exponential, logarithmic, rational, polynomial, and piecewise functions.
Domain
(x-values) (LEFT - RIGHT)
Range
(y-values) (BOTTOM - TOP)
Increasing Function
A function where as x increases, f(x) also increases.
Decreasing Function
A function where as x increases, f(x) decreases.
Piecewise Function
A function defined by different expressions for different parts of its domain.
Absolute Value Function
A function that describes the distance of a number from zero on the number line.
Linear Inequality
An inequality that involves a linear function, represented in the form ax + b < c or ax + b > c.
Compound Inequalities
Two inequalities that are connected by the words 'and' or 'or'.
Simplifying Expressions with Exponents
The process of reducing expressions that involve exponents to their simplest form.
Radical Operations
Mathematical actions involving radicals, such as simplifying, adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing.
Conjugates
A pair of binomials that are the same except for the sign between them, used to simplify expressions.
Factoring GCF
Finding the greatest common factor of expressions to simplify them.
Quadratic Formula
A formula used to solve quadratics represented as x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / (2a).
Extraneous Solutions
Solutions derived from solving an equation that do not satisfy the original equation.
Polynomial Long Division
A method used to divide polynomials similar to long division with numbers. BOX
Asymptotes
Lines that a graph approaches but never touches or crosses.
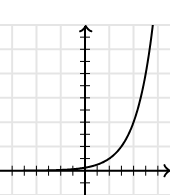
Exponential Function
A function in which an independent variable appears in the exponent.
Logarithmic Function
The inverse function of an exponential function, representing the power to which a base must be raised to produce a given number.
Function Composition
The combination of two functions where the output of one function becomes the input of another.
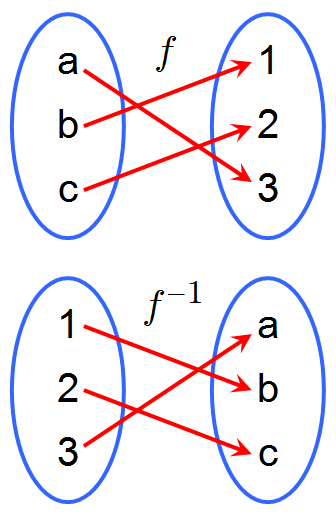
Inverse Functions
Functions that reverse the effect of the original function.