unit 8: exercise & physical activity for older adults ( 7 questions)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Aerobic physical activity
At least 150 minutes at moderate intensity per week
Or 75 minutes at vigorous intensity per week
Or an equivalent combination at moderate and vigorous intensity
At least 2 days of activities that strengthen the major muscle groups
Activities to improve balance
Current recommendations for physical activity to achieve health benefits are
Benefits of Physical Activity for Older Adults
Slowing physiological changes of aging that impair exercise capacity Optimizing age-related changes in body composition
Promoting psychological and cognitive well-being
Managing chronic diseases
Reducing the risks of physical disability
Increase longevity
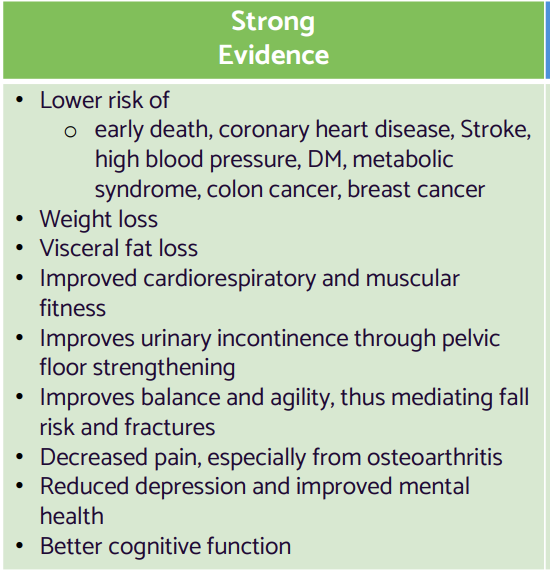
Benefits of Physical Activity for Older Adult chart
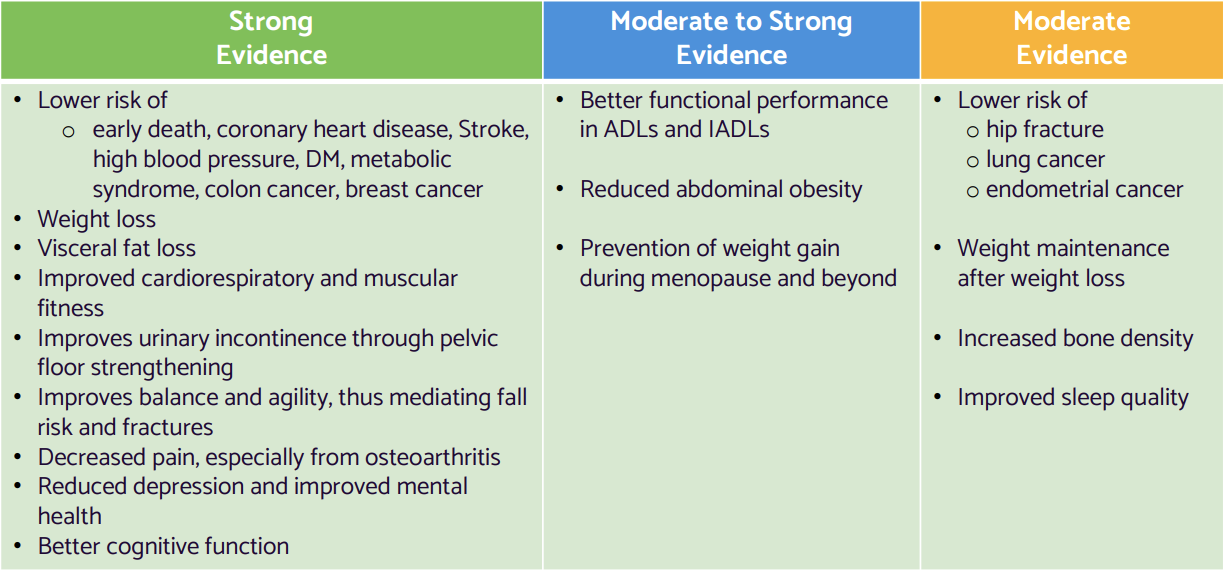
strong evidence
moderate to strong evidence

moderate evidence

Older adults are the least physically active of all age groups
Only 12% of individuals aged ≥65 years engage in regular aerobic and muscle strengthening activities.
Less than 5% of individuals aged ≥85 years are engaging in regular aerobic and muscle strengthening activities.
physical therapists as movement specialists
Improve mobility and function
Prevent and mitigate physical inactivity related disability
Adapt physical activity and exercise programs to accommodate pain or other disability that challenges movement ability
Exercise Testing
Most older adults do not require an exercise test prior to initiating a moderate intensity physical activity (PA) program.
If exercise testing is recommended, the associated ECG has higher sensitivity and lower specificity than in younger age groups, producing a higher rate of false positives.
Although there are no specific exercise termination criteria for older adults beyond those presented for all adults, the increased prevalence of cardiovascular, metabolic, and orthopedic problems among older adults increases the overall likelihood of an early test termination.
do not
Most older adults __require an exercise test prior to initiating a moderate intensity physical activity (PA) program
no specific exercise termination criteria
Although there are__ for older adults beyond those presented for all adults, the increased prevalence of cardiovascular, metabolic, and orthopedic problems among older adults increases the overall likelihood of an early test termination
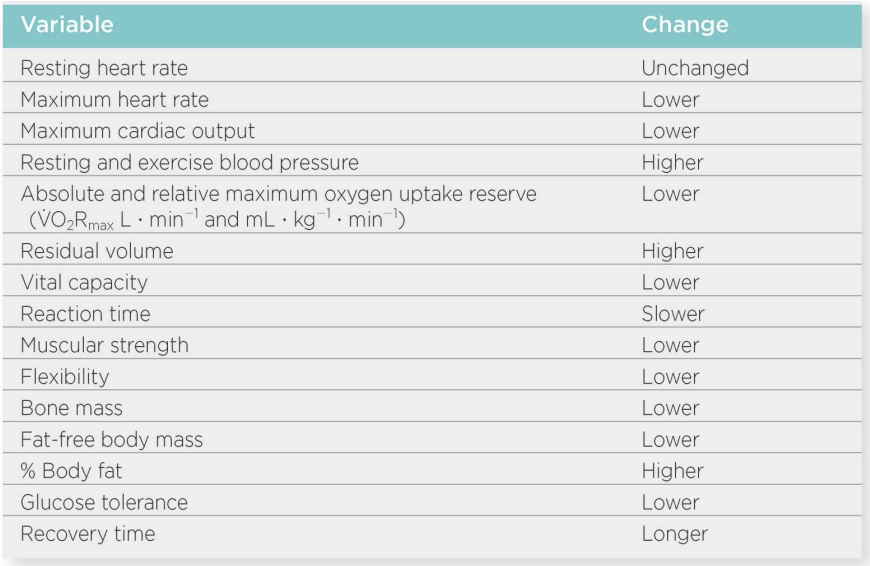
Effects of Aging on Selected Physiologic and Health-Related Variables
contraindications to symptom limited maximal exercise testing

indications for terminating a symptom limited maximal exercise test

Special Considerations When Testing Older Adults
The initial workload should be light (<3 metabolic equivalents [METs]) and workload increments should be small (i.e., 0.5–1.0 MET) for those with low work capacities.
A cycle ergometer may be preferable to a treadmill for those with poor balance, poor neuromotor coordination, impaired vision, impaired gait patterns, weightbearing limitations, and/or foot problems. However, local muscle fatigue may be a factor for premature test termination when using a cycle ergometer.
low work capacities.
The initial workload should be light (<3 metabolic equivalents [METs]) and workload increments should be small (i.e., 0.5–1.0 MET) for those with __
cycle ergometer
A __ may be preferable to a treadmill for those with poor balance, poor neuromotor coordination, impaired vision, impaired gait patterns, weightbearing limitations, and/or foot problems. However, local muscle fatigue may be a factor for premature test termination when using a cycle ergometer.
reduced balance, decreased muscular strength, poor neuromotor coordination, and fear.
Special Considerations When Testing Older Adults pt.2:
Adding a treadmill handrail support may be required because of ________
However, handrail support for gait abnormalities will reduce the accuracy of estimating peak MET capacity based on the exercise duration or peak workload achieved.
Treadmill workload may need to be adapted according to walking ability by increasing grade rather than speed.
age-predicted HRmax
Special Considerations When Testing Older Adults pt.3:
Many older adults exceed the __ during a maximal exercise test, which should be taken into account when considering test termination.
The influence of prescribed medications on the electrocardiographic (ECG) and hemodynamic responses to exercise may differ from usual expectations.
Physical Performance Testing
___ testing has largely replaced exercise stress testing for the assessment of functional status of older adults.
Most physical performance tests
require little space, equipment, and cost;
can be administered by lay or health/fitness personnel with minimal training;
are considered extremely safe in healthy and clinical populations
require little space, equipment, and cost;
can be administered by lay or health/fitness personnel with minimal training;
are considered extremely safe in healthy and clinical populations
Most physical performance tests
Senior Fitness Test
Short Physical Performance Battery
Usual Gait Speed
6-Min Walk Test
Commonly used physical performance tests:
Exercise Prescription
The general principles of exercise prescription apply to adults of all ages.
Low aerobic capacity, muscle weakness, and deconditioning are more common in older adults than in any other age group and contribute to loss of independence.
Therefore, an appropriate exercise prescription should include aerobic, resistance training, balance, and flexibility exercises.
adults of all ages.
The general principles of exercise prescription apply to __
older adults than in any other age group and contribute to loss of independence.
Low aerobic capacity, muscle weakness, and deconditioning are more common in
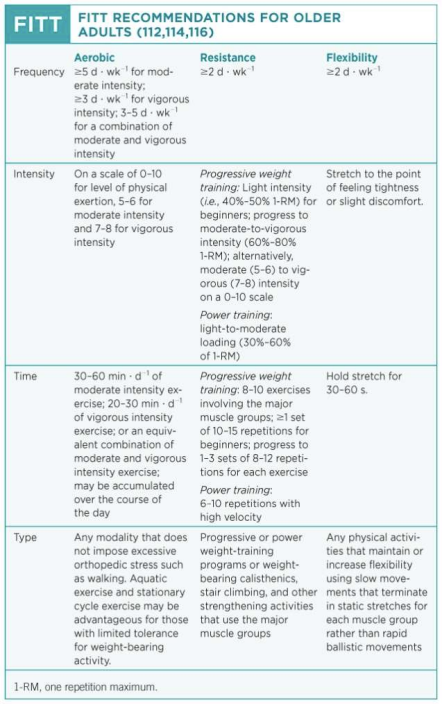
FITT recommendations for Older adults
Measuring an RM for a Functional Movement:
If an older adult is not able to rise from a standard chair, the therapist must create a situation where the person can be successful, such as raising the surface to allow the individual to complete the task independently.
The number of times the person can rise from the raised surface becomes that person’s repetition maximum.
For example, if the surface height is 21 inches and the person can stand 10 times without using his or her arms, the person has achieved a 10RM from a 21- inch height surface (10RM = 75% to 80% of 1RM)
create a situation where the person can be successful, such as raising the surface to allow the individual to complete the task independently.
If an older adult is not able to rise from a standard chair, the therapist must
light at the beginning
Special Considerations for Exercise Programming pt.4
Intensity and duration of PA should be __ in particular for older adults who are highly deconditioned, functionally limited, or have chronic conditions that affect their ability to perform physical tasks.
Progression of PA should be individualized and tailored to tolerance and preference.
Muscular strength decreases rapidly with age, especially for those >50 years; therefore, resistance training becomes more important with increasing age.
individualized
Progression of PA should be __ and tailored to tolerance and preference.
Muscular strength
__ decreases rapidly with age, especially for those >50 years; therefore, resistance training becomes more important with increasing age.
supervised and monitored
Special Considerations for Exercise Programming pt.5
For strength training involving use of selectorized machines or free weights, initial training sessions should be __ by personnel who are sensitive to the special needs of older adults.
Individuals with sarcopenia need to increase muscular strength before engaging in aerobic training.
If chronic conditions preclude activity at the recommended minimum amount, older adults should perform PA as tolerated to avoid being sedentary.
sarcopenia
Individuals with __ need to increase muscular strength before engaging in aerobic training.
dual tasking
Special Considerations for Exercise Programming pt.6
Older adults should consider exceeding the recommended minimum amounts of PA to improve management of chronic diseases and health conditions for which a higher level of PA is known to confer a therapeutic benefit.
Moderate intensity PA (especially __) should be encouraged for individuals with cognitive decline given the known benefits of PA activity on cognition.
Individuals with significant cognitive impairment can engage in physical activity but may require individualized assistance.
management of chronic diseases and health conditions for which a higher level of PA is known to confer a therapeutic benefit.
Older adults should consider exceeding the recommended minimum amounts of PA to improve
cognitive impairment
Individuals with significant __ can engage in physical activity but may require individualized assistance
CVD
Special Considerations for Exercise Programming pt.7
Structured physical activity sessions should end with an appropriate cool-down, particularly among individuals with __
The cool-down should include a gradual reduction of effort and intensity and, optimally, flexibility exercises.
pain
Although pain is a common complaint of an older adult, there is no evidence supporting the decision to curtail exercise in the presence of pain.
Most pain complaints in older adults may be considering long-standing, or chronic.
Studies show the improvement in pain levels with progressive exercise for a variety of conditions including osteoarthritis, low back pain, and chronic pain.
Certainly, the therapist should be aware of pain caused by acute inflammation or injury.
osteoarthritis, low back pain, and chronic pain.
Studies show the improvement in pain levels with progressive exercise for a variety of conditions including __
acute inflammation or injury.
Certainly, the therapist should be aware of pain caused by
aquatic exercise
The use of aquatic exercise allow a patient, who may be otherwise be unable to exercise because of pain or instability, the ability to be more physically active and to gain initial levels of strength to permit land-based exercise.
Older adults may have lower body density and a higher level of buoyancy
Employing aquatic equipment such as floats and paddles to increase or decrease resistance
pain or instability
The use of aquatic exercise allow a patient, who may be otherwise be unable to exercise because of __, the ability to be more physically active and to gain initial levels of strength to permit land-based exercise.
Aquatic Exercise pt.2
Patients who have osteoarthritis, are overweight, or have recently undergone surgery may initially benefit from aquatic exercise.
Most pools are heated, which may have a therapeutic effect on painful joints.
Those patients who have significant balance disorders or a fear of falling may derive some initial benefits from the water before progressing to land-based exercises.
The effects of water turbulence offer periods of instability
osteoarthritis, overweight, undergone surgery
Patients who have __, are __, or have recently undergone surgery may initially benefit from aquatic exercise.
balance disorders or a fear of falling
Those patients who have significant balance disorders or a fear of falling may derive some initial benefits from the water before progressing to land-based exercises.
functional training
Activities of Daily Living
Basic Activities of Daily Living (Basic ADLs)
Include all of the fundamental tasks and activities necessary for survival, hygiene, and self-care within the home.
Eating, bathing, grooming, dressing, bed mobility, and transfer
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs)
are tasks that allow an individual to live independently in a community.
Ability to use the telephone, laundry, shopping, transportation, meal preparation, medication management, house cleaning, managing finances
Basic Activities of Daily Living (Basic ADLs)
Include all of the fundamental tasks and activities necessary for survival, hygiene, and self-care within the home.
Eating, bathing, grooming, dressing, bed mobility, and transfer
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs)
are tasks that allow an individual to live independently in a community.
Ability to use the telephone, laundry, shopping, transportation, meal preparation, medication management, house cleaning, managing finances
functional task is also practiced
Functional training is particularly effective in improving performance in ADLs of older adults.
Improvements in functional abilities are likely a result of strength and power training but are more likely to occur if the__
The optimal intensity of functional training has not been determined.
However, improvement in functional performance from frequencies of ≥ 2 to 3 days/week with exercise sessions of ≥ 20 to 30 minutes in duration for a total of ≥ 60 minutes per week were found.
the functional task is also practiced.
Improvements in functional abilities are likely a result of strength and power training but are more likely to occur if __
functional exercises
Functional Training pt.3
Integrating __ into daily life is an alternative to structured exercise programs, especially for the very old and frail.
Tandem walking on the way to the kitchen
Stair climbing
Obstacle crossing
Rising from a chair
Purposeful walking to store, church
specificity
The closer the training routine is to the conditions of the desired outcome (i.e. specific exercise task), the better will be the outcome.
Specific exercise
For example, if improved tolerance to exercise is desired, the exercise prescription would call for lower intensity and more time on task (endurance training).
type of muscle contraction
Specificity pt.2:
For example, trunk muscles are often used as stabilizers during movement and therefore should be trained isometrically in multiple planes and actions.
Enjoyment and Value
A significant challenge of geriatric rehabilitation is engaging older patients to fully participate and adhere to their rehabilitation or physical activity program.
Adherence occurs when the activities match their
interest
comfort level
Providing choice and incorporating factors that add personal benefit to older adults are important contributors to adherence.
A significant challenge of geriatric rehabilitation is __ older patients to fully participate and adhere to their rehabilitation or physical activity program.
engaging
Adherence occurs when the activities match their
interest
comfort level
Enjoyment and Value pt.2
To increase engagement, exercise programs should focus on fun, sociable, and achievable activities.
Challenging activities can empower older adults as they succeed at new challenges.
They must also feel confident that the level of challenge is safe.
Music of the appropriate tempo also adds interest and positive experiences to exercise programs and improve participations.
Variety is also important, to decrease boredom and continue engagement
fun, sociable, and achievable activities.
To increase engagement, exercise programs should focus on __
Challenging
__ activities can empower older adults as they succeed at new challenges.
safe
They must also feel confident that the level of challenge is __.
interest
Music of the appropriate tempo also adds __ and positive experiences to exercise programs and improve participations
Variety
__ is also important, to decrease boredom and continue engagement
group exercise
is an effective method of achieving recommended doses of physical activity
preferred by most older adult (women more than men)
Group exercise programs have the added benefit of
socialization
peer support
supervision
Better long-term adherence
Group exercise programs have the added benefit of
socialization
peer support
supervision
Better long-term adherence
Barriers to Older Adult Participation in Group Programs
Lack of transportation
Unwillingness to join a group
Aversion to exercise e.g. “I’m not sporty”
Environmental factors
Barriers to Older Adult Participation in Group Programs pt.2
Lack of sidewalks
Proximity to a park
Adverse weather
Lack of convenient exercise facility
Perceived lack of safety
Factors that increase the likelihood of an older adult engaging in physical activity and exercise
Perceived health and proximity to a health facility
Self-efficacy
Outcome expectations and perceived benefits
Proximity to home
Exercising outdoors even in warmer and colder months
Programs that were challenging and those that had functional intent
Ultimately, exercise preferences should be considered on an individual basis as a means to promoting physical activity
individual basis
Ultimately, exercise preferences should be considered on an __ as a means to promoting physical activity
Safety
Exercise is generally safe for older people to perform.
However, there are relative and absolute contraindications for aerobic exercise of which the physical therapist should be aware.
For patients with unstable cardiac conditions, the monitoring of blood pressure and heart rates should be routinely performed.
Patients should be advised to report any adverse such as lightheadedness, dizziness, excessive sweating, or nausea.
β-Blockers
Safety pt.2
Physical therapists should be knowledgeable about an individual’s medication.
__ decrease both the force of contraction of heart muscle and heart rate, keeping the heart rate artificially low during exercise.
An RPE (rates of perceived exertion) is an acceptable alternate to taking a pulse in the presence of β-Blockers
Exercise changes the need for insulin in patients with diabetes
Close monitoring of the patient with insulin-dependent diabetes is required.
β-Blockers
decrease both the force of contraction of heart muscle and heart rate, keeping the heart rate artificially low during exercise.
Older adults
safety pt.3:
Education regarding precautionary measures such as adequate hydration, cushioned shoes (especially if reduced sensation is identified), and close monitoring of blood sugar is part of the exercise prescription.
__ seen in the rehabilitation setting require one-on-one supervision during the entirely of the exercise training to ensure appropriate form, intensity, and response.
An older adult may need encouragement to maintain proper form, to breathe properly, and to attend to his or her level of joint or muscle discomfort.
Education
__ regarding precautionary measures such as adequate hydration, cushioned shoes (especially if reduced sensation is identified), and close monitoring of blood sugar is part of the exercise prescription.
maintain proper form, to breathe properly, and to attend to his or her level of joint or muscle discomfort.
An older adult may need encouragement to