FINA 363/FINA Scholars Prep
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
W lawson
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is a DCF in one sentence?
Discount forecasted free cash flows at WACC to get Enterprise Value, then bridge to Equity value
Method of evaluating a company by taking future cash inflows and bringing them to their present value
List the 5 core steps of a DCF:
Assess future FCFFs, Find Terminal Value, Add Tv to final cash flow, Discount all cash flows by dividing by (1 + i)^n, Sum = enterprise value(measure of a company’s value)
What is FCFF (free cash flow to the firm)?
Cash available to debt & equity holders
What cash flows does EV represent and how is it bridged to equity value?
Cash flows available to all capital providers(debt + equity), equity value is found by subtracting net debt, which equals total debt minus cash, from enterprise value
Why is cash subtracted when calculating equity value from enterprise value?
It is a non-operating asset and ultimately belongs to equity holders after debt is paid
What are the two terminal value methods and when are they used?
Perpetuity growth is used for mature stable companies with predictable long-term growth, Exit multiple is used when there are reliable market comparable and growth is difficult to estimate
Why are cash flows discounted at the weighted average cost of capital?
It reflects the required return of both debt and equity investors given the company’s risk
What are common pitfalls when building a discounted cash flow model?
Mis-timing cash flows, mixing free cash flow to the firm with free cash flow to equity, and forgetting to include the tac shield on debt
What is the weighted average cost of capital and why is it important?
The blended required return of a company’s debt and equity investors, its important because it serves as the discount rate for valuing the company’s free cash flows in a DCF analysis
What is the formula for weighted average cost of capital(WACC)?
Equity weight times the cost of equity plus the debt weight times the after tax cost of debt: (E/V) x Re + (D/V) x Rd x (1-T)
Why is the cost of debt adjusted for taxes in WACC?
Interest expense is tax-deductible, which creates a tax shield that lowers the effective cost of debt to the company
What is the capital asset pricing model and what does it estimate?
Estimates the cost of equity as the risk-free rate plus beta times the market risk premium, reflecting the return investors require for bearing systematic market risk
What does beta measure in the CAPM?
The sensitivity of a securities returns to movements in the overall market, so a beta above one indicates higher volatility that the market and a beta below one indicates a lower volatility
Which risks are priced in the CAPM and which are not?
The CAPM prices only systematic risk that cannot be diversified away, while unsystematic, company-specific risk is not priced because diversified investors can eliminate it
How do changes in inputs affect the cost of equity under the CAPM?
The cost of equity increase when the risk-free rate, the market risk premium, or beta increases, and it decreases when any of those inputs decline
Why are market value weights preferred over book value weights when calculating the WACC?
They reflect current investor expectations and the true opportunity costs of debt and equity capital, whereas book values may be outdated and ecconmically irrelevant
What is yield to maturity (YTM) and why us it important?
The annualized internal rate of return earned on a bond if it is held until maturity, assuming all coupons are paid and reinvested at the same yield, and it is important because it reflects the true required return on the bond
How do bond prices and yields move in relation to each other?
Bond prices and yields move inversely, meaning that the yields rise, prices fall, and when yields fall, prices rise
How can you tell if a bond is trading at par, a premium, or a discount?
A bond trades at par when its YTM equals its coupon rate, at a premium when its YTM is lower than its coupon rate, and at a discount when its YTD is higher than its coupon rate
What is duration and what does it measure?
The weighted average time to receive a bond’s cash flows and it measure the sensitivity if the bond’s price to changes in yield
How do coupon payments affect duration?
Higher coupon payments shorten duration because more cash is received earlier, while lower coupon payments lenghten duration
How does maturity length affect duration?
Longer maturities increase duration because cash flows are received further in the future, making the non more sensitive to interest rate changes
What is modified duration and how is it used?
Estimates the percentage change in a bond’s price for a one percent change in yield, using the formula ΔP/P - Duration x Δy
What is convexity and why does it matter?
Measure the curvature of the price-yield relationship, and it matters because it improves estimates of bond price changes for larger yield movements by showing that prices fall less and rise more than duration alone would predict
What is yield curve and what does it show?
The yield curve is a graph that shows the relationship between bond yields and their maturities for bonds of similar credit quality, usually U.S. Treasuries
What are the three main shapes of the yield curve?
Normal, which slopes upward; flat, which is relatively level; and inverted, which slopes downward
What does a normal yield curve usually indicate about the economy?
Usually indicates expectations of future economic growth and potentially higher inflation
What does an inverted yield curve usually indicate about the economy?
Usually signals a higher risk of recession because investors expect interest rates to decline in the future
What is a credit spread?
The difference in yield between a corporate bind and a risk-free treasury bond of the same maturity, reflecting default risk and investor risk appetite
How do credit spreads behave during times of economic stress?
Credit spreads widen during times of stress because investors demand higher compensation for taking on credit risk
What does a steepening yield curve typically imply?
Typically implies expectations of stronger economic growth, higher inflation, or higher term premiums
What does a flattening yield curve typically imply?
Typically implies slowing economic growth or expectations that interest rates are near their peak
What is the difference between systematic and unsystematic risk?
Systematic risk is market-wide risk that cannot be diversified away, while unsystematic risk is company-specific risk that can be reduced through diversification
Why does diversification reduce risk in a portfolio?
Diversification reduces risk because combining assets with imperfect correlations lower overall portfolio volatility
What is an example of systematic risk?
A recession or a market-wide interest rate change
What is an example of unsystematic risk?
A product recall or a major company scandal
What is alpha in the context of CAPM?
Alpha is the excess return a security earns above the return predicted by the CAPM
Why does financial leverage increase equity risk?
Debt amplifies the volatility of equity returns and raises the company’s beta
What is the difference between hedging and diversification?
Hedging reduces risk by directly offsetting exposures, while diversification spreads risk across multiple assets to lower portfolio variance
What are the there forms of market efficiency?
Weak form, semi-strong form, and strong form
What does weak form efficiency state?
All past trading information, such as prices and volumes, is already reflected in current prices
What does semi-strong form efficiency state?
All publicly available information is already reflected in current prices, so neither technical nir fundamental analysis can consistently beat the market
What does strong form efficiency state?
All information, both public and private, is already reflected in current prices, though this really holds true in reality
What is the implication of semi-strong form efficiency for investors?
Implies that public news is quickly absorbed into prices, so it is nearly impossible to consistently earn abnormal profits using public information
Why is investing considered a zero-sum game before costs in efficient markets?
One investor’s outperformance relative to the market must come from another investor’s underperformance
What are the limits to arbitrage in market efficiency?
Limits to arbitrage include constraints such as limited capital, risk of losses, and timing mismatches that prevent traders from quickly correcting mispricings
Why does market efficiency not mean prices are always correct
Mispricings are difficult to exploit consistently after accounting for costs
What is the formula for free cash flow to the firm (FCFF)?
EBIT multiplied by one mines the tax rate, plus depreciation and amortization, minus capital expenditures, minus the change in networking capital
FCFF = EBIT(1−T) + D&A − CapEx − ΔNWC
What is the formula for enterprise value (EV)?
Equity value plus debt minus cash
EV = Equity Value + Debt − Cash
What is the formula for equity value per share(EQV)?
Equity value divided by diluted shares outstanding
Price per Share = Diluted Shares/Equity Value
What is the formula for terminal value using the perpetuity growth method(TV)?
Terminal value equals the next year’s free cash flow divided by the difference between the WACC and the perpetual growth rate

What is the formula for the cost of equity using the CAPM?
The cost of equity equals the risk-free rate plus beta times the market premium
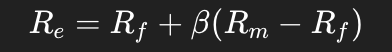
What is the formula for the after-tax cost of debt?
The after-tax cost of debt equals the yield to maturity of debt multiplied by one minute the tax rate
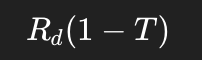
What is the formula for beta in terms of covariance and variance?
Beta equals the covariance of the asset’s return with the market return divided by the variance of the market return
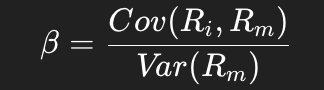
What is the formula for the expected return of a portfolio?
The expected return of a portfolio equals the weighted sum of the expected returns of the individual assets

Why is the formula for the variance of a two-asset portfolio?
Portfolio variance he weighted sum of variances plus twice the product of weights, standard deviations, and correlation
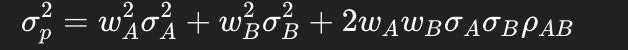
What is the approximate formula for the percentage price change of a bond using modified duration?
The percentage price change equals negative modified duration times the change in yield
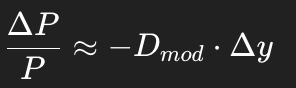
What is the formula for current yield of a bond?
Current yield equals the annual coupon payment divided by the current bond price
Current Yield = Coupon/Price