NET4009-Module 5a- Tshooting Conditional fwding redistribution
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Conditional Matching
matching a route using access control lists and prefix lists
Two step process for defining a standard ACL
Define the ACL by using the command IP access-list standard {acl-number | acl-name}
Configure the specific ACE entry with the command [sequence] permit | deny source srouce-wildard
What makes extended ACLs for BGP different then regular
The source fields match against the network portion of the route, and the destination fieldsmatch against the network mask
Route maps
can filter networks much the same way as ACLs but they also provie additional capability through the addition or modification of network attributes
Four components of Route maps
Sequence number
Conditional matching criteria
processing action
optional action
Route map command
route-map route-map-name [permit | deny] [sequence-number]
Policy-Based Routing (PBR)
conditional forwarding of packets based on packetcharacteristics besides the destination IP address
PBR Characteristics
• Routing by protocol type (ICMP, TCP, UDP, and so on)
• Routing by source IP address, destination IP address, or both
• Manual assignment of different network paths to the same destination, based on tolerance, link speed or utilization
Drawbacks of PBR
• Administrative burden in scalability
• Lack of network intelligence
• Troubleshooting complexity
4 steps to configure PBR
Configure the route map
Identify the conditional match criteria
Use the command “set IP [default] next-hop ip-address [IP]
apply the route map to the inbound interface by using the interface parameter command IP policy route-map <route-map-name>
Sequential Protocol Redistribution
redistribution between multiple protocols over a series of routers
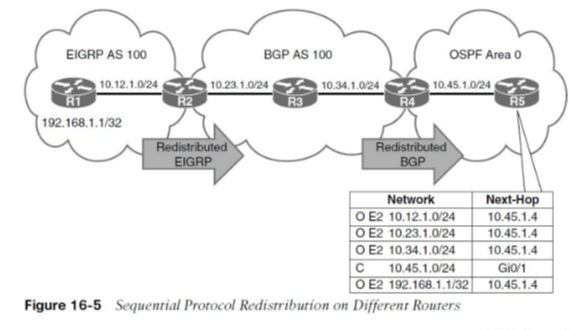
A route must exist in the RIB (routing table) of router doing redistribution in order for it to be redistributed into the destination protocol
True
EIGRP-to-EIGRP Redistribution Characteristic
EIGRP autonomous systems preserves the path metrics during redistribution.
Destination Specific Behaviors: OSPF
• The seed metric is 1 for BGP-sourced routes and 20 for all other protocols.
• The exception is that if OSPF redistributes from another OSPF process, the path metric is transferred
The main differences between Type 1 and Type 2 External OSPF routes
Type 1 routes are preferred over Type 2
Type 1 metric equals the redistribution metric plus the total path metric
Type 2 metric equals only the redistribution metric
Why is the OSPF process number locally significant for redistribution?
Allows linking the OSPF-enabled interfaces to a process
OSPF-to-OSPF Redistribution path metrics
Redistributing routes between OSPF processes preserves the path metric during redistribution, independent of the metric type