Chapter 29: Chordates
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
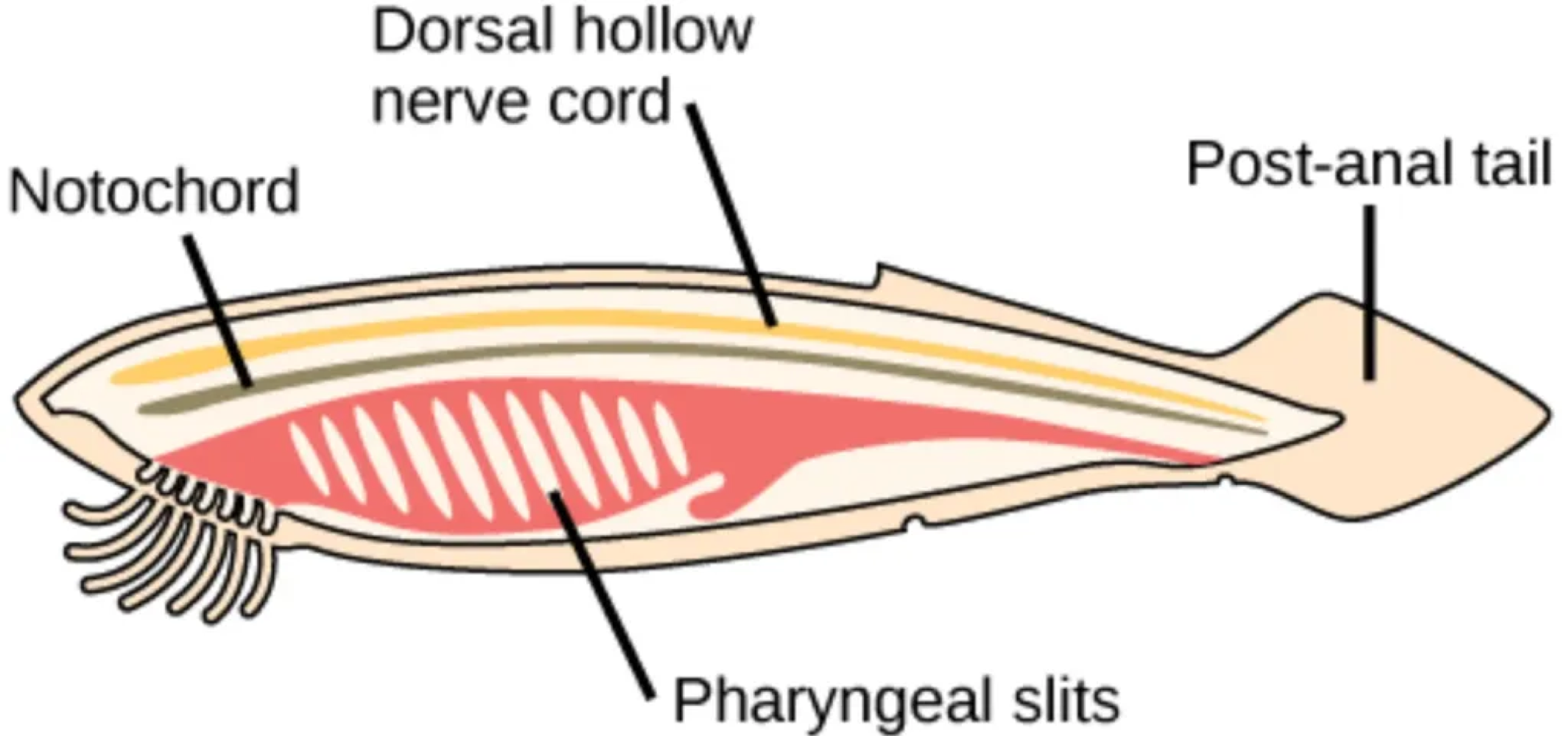
Chordates share five characteristics that are always present in the embryonic/juvenile stage, including a dorsal hollow nerve cord, which is defined as a ___
hollow tube located on the back end, direct from ectoderm that often gets filled by the spinal cord in some chordates
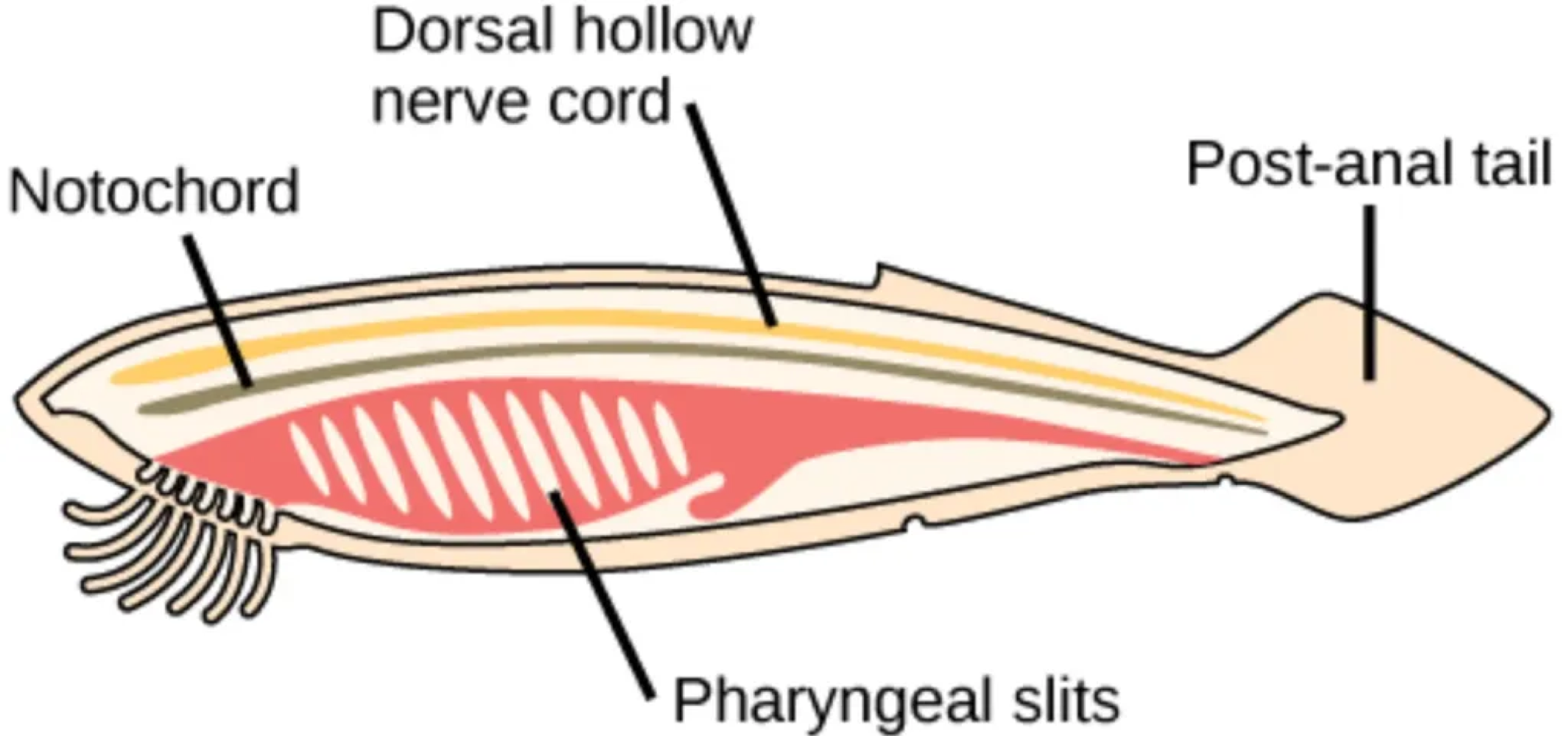
Chordates share five characteristics that are always present in the embryonic/juvenile stage, including a post anal tail, which is defined as a ___
structure located posterior to the anus
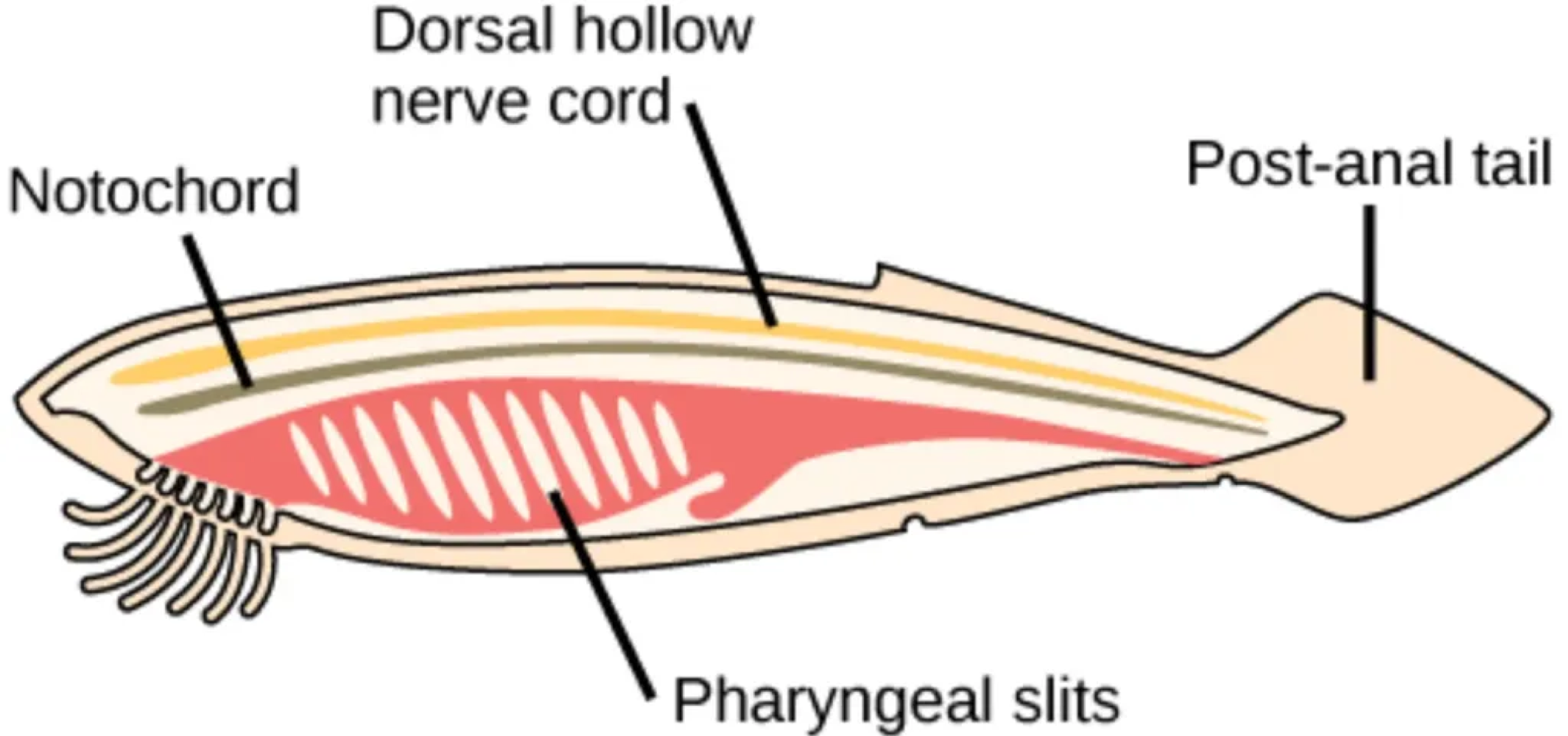
Chordates share five characteristics that are always present in the embryonic/juvenile stage, including pharyngeal slits, which are defined as a ___
opening of the pharynx extending to the outside environment that often turns into gills for fish
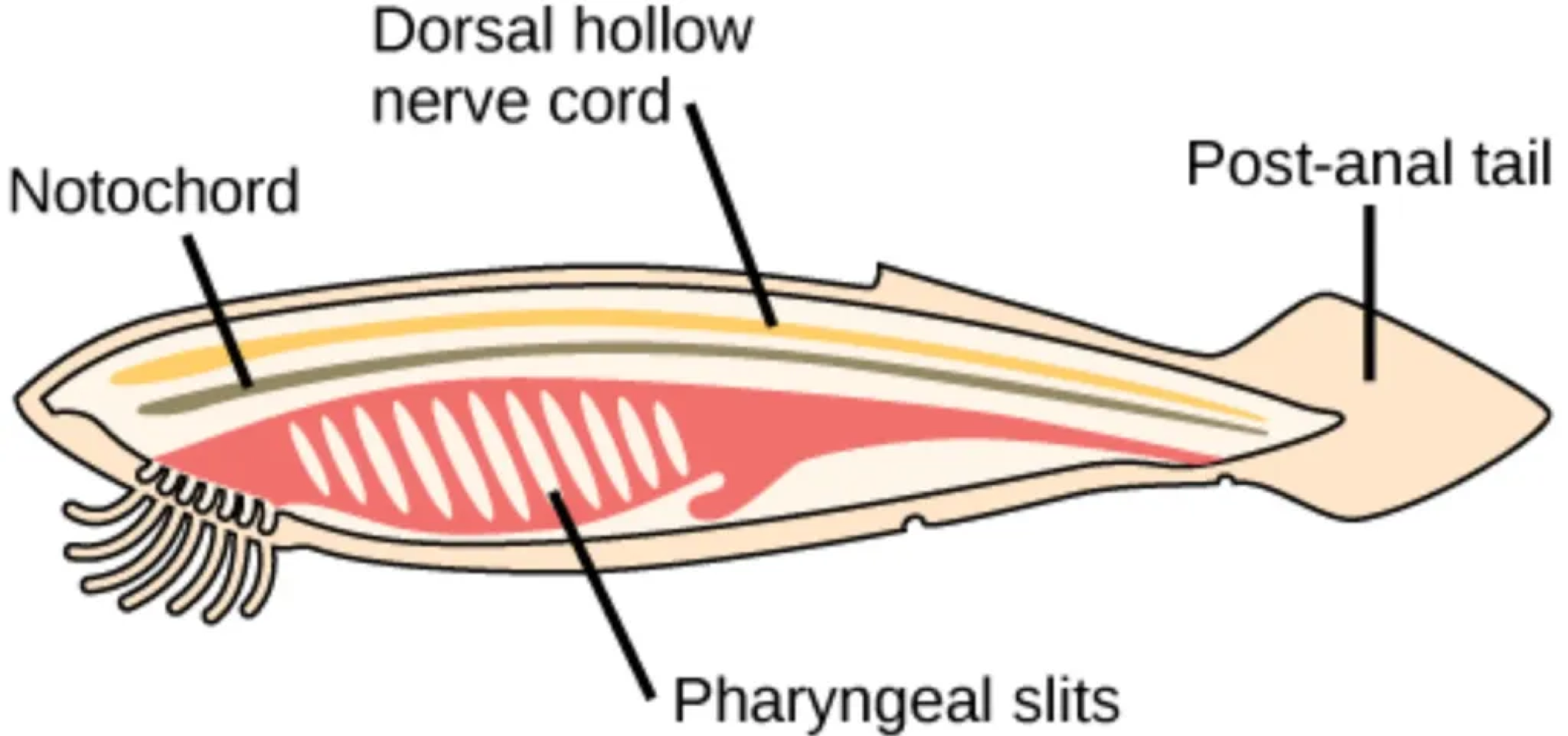
Chordates share five characteristics that are always present in the embryonic/juvenile stage, including a notochord, which is defined as a ___
flexible rod-shaped structure located between the digestive tube and nerve cord that often develops into the vertebral column
Chordates share five characteristics that are always present in the embryonic/juvenile stage, including an endostyle/thyroid gland, which is defined as a ___
structure located in the neck that secrete hormones, and regulates calcium metabolism in humans
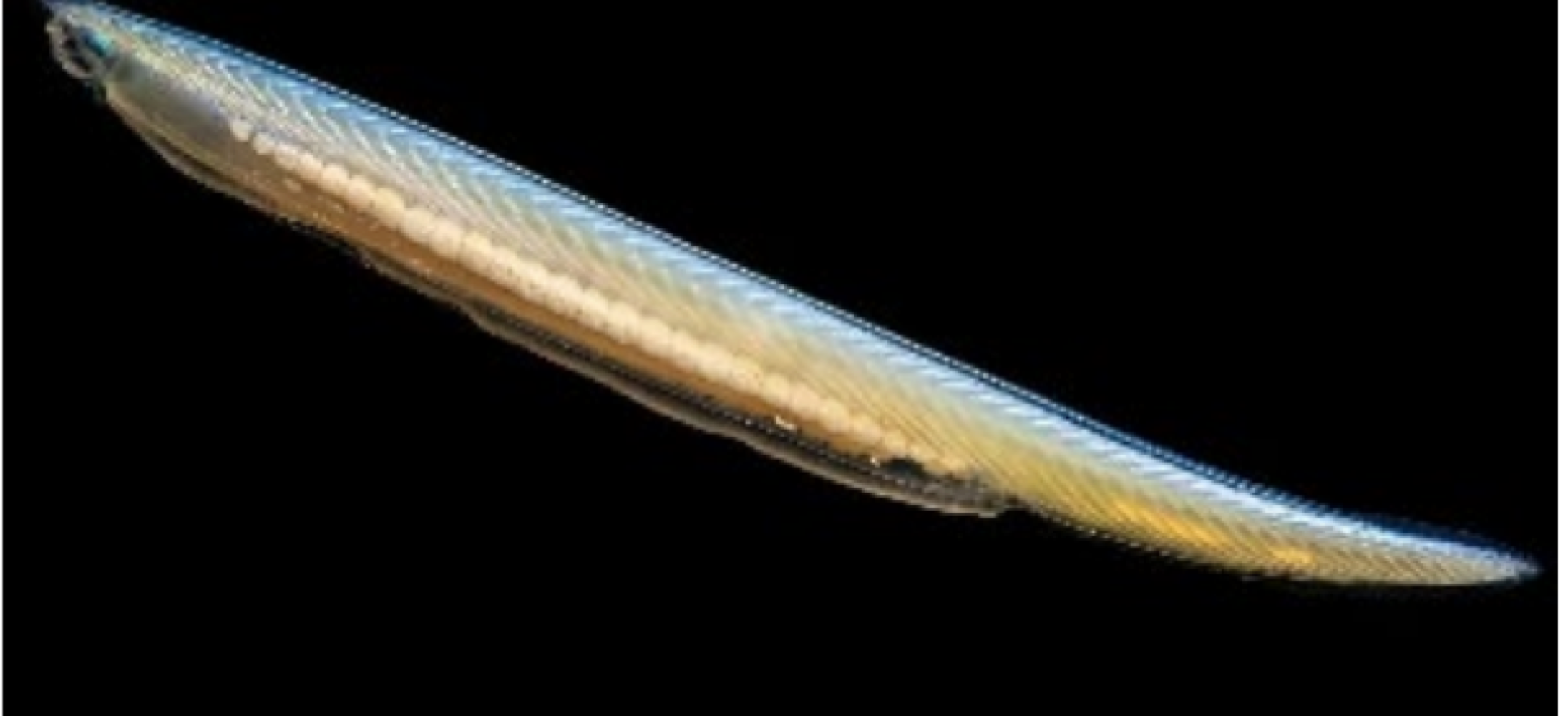

Cephalochordates (Lancelets) are defined as ___
aquatic invertebrate chordates whose notochord extends into the head, lacks a well-defined brain, has a simple nervous system, and resides in sand at the sea floor
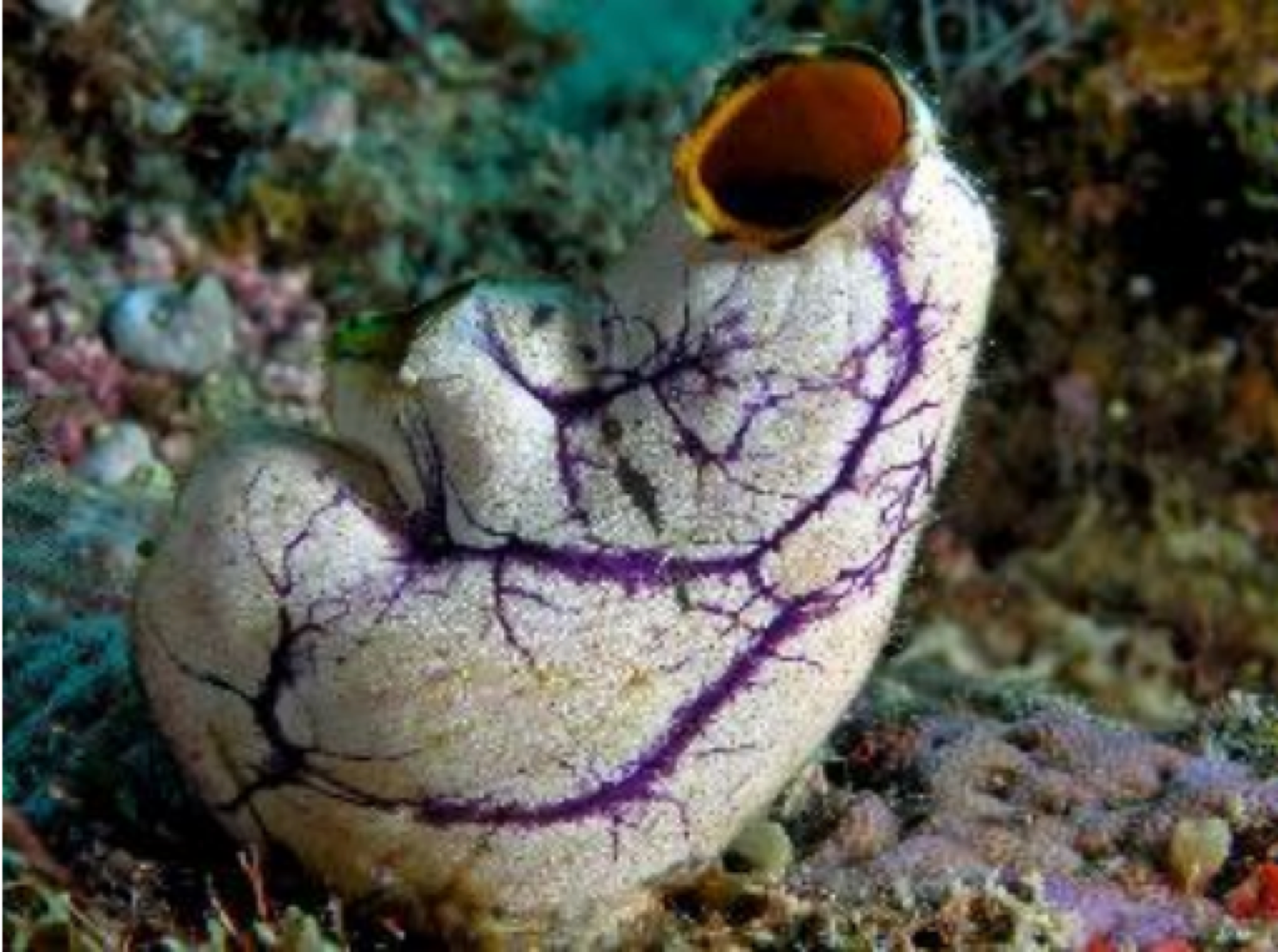

Urochordates (Tunicates) are defined as ___
aquatic invertebrate chordates whose body is covered in tunic (cellulose-like material), and lacks a notochord, nerve cord, and post-anal tail
all vertebrates have a cranium (head), which is defined as a ___
bony, cartilaginous, or fibrous structure surrounding the brain, jaw, (not always necessary), and facial bones
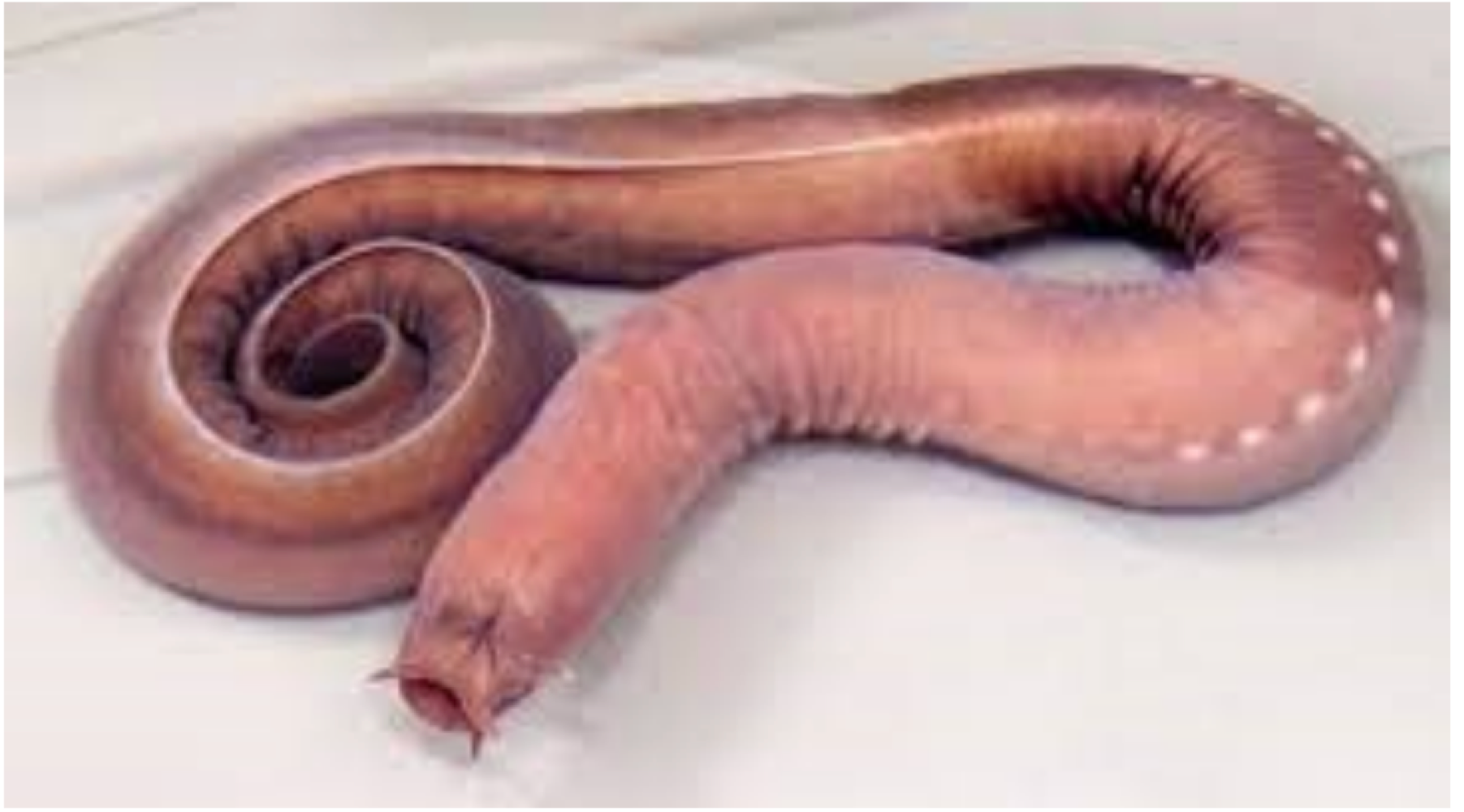

myxini (hagfish) are defined as
a group of marine craniates with a partial cranium made of cartilage, but no vertebrae
all vertebrates have a vertebral column, which is defined as a ___
dorsal supporting structure that replaces the notochord during early development and allows organisms to grow more
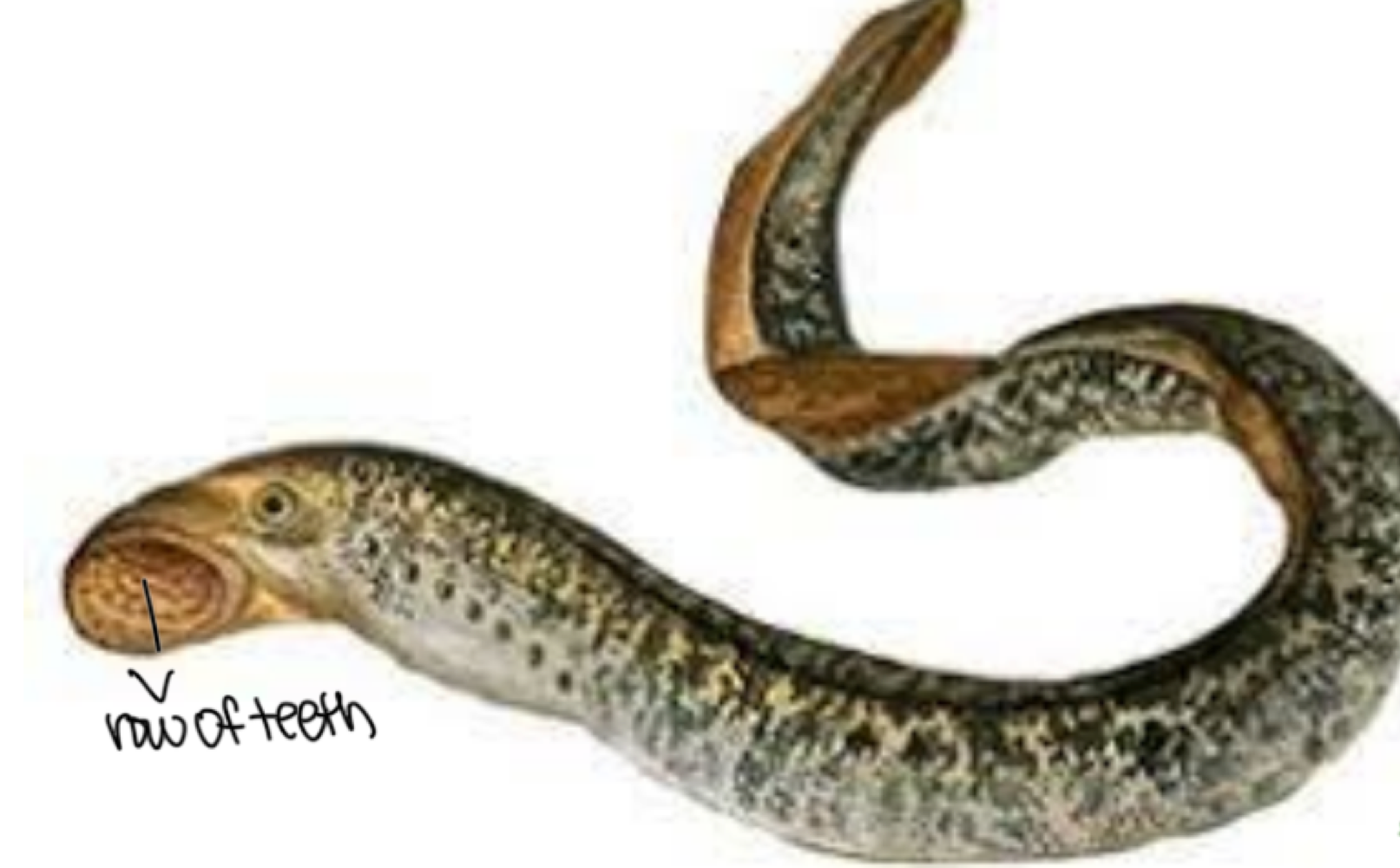

Petromyzontida (lampreys) are defined as ___
the most primitive vertebrates who lack a jaw, have a rasping tongue with a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth, a notochord, and are often parasites to fish
all vertebrates have a well developed ___ system on the heart side of the body, and a rigid ___ system, not always bone
circulatory, skeletal
a true jaw is defined as ___
a hinge structure attached to the cranium that moves, allowing for attacking and tearing
Gnathostomes are defined as
vertebrates that have a jaw, mouth, and at least 2 sets of fins—all of which help organisms hunt and move with more control (e.g., jawed fishes)
Gnathostomes have pectoral fins, which are located ___
on the anterior body
Gnathostomes have pelvic fins, which are located ___
on the posterior
Cartilaginous Fishes (Chondrichthyes) are defined as ___
fish with a skeleton (jaw, vertebral column, cranium) composed of firm, pliable cartilage (e.g., sharks, rays, sawfishes)
sharks reproduce sexually via ovoviviparous, during which fertilization is ___
internal, eggs hatch in the uterus, and young are born alive and fully functional
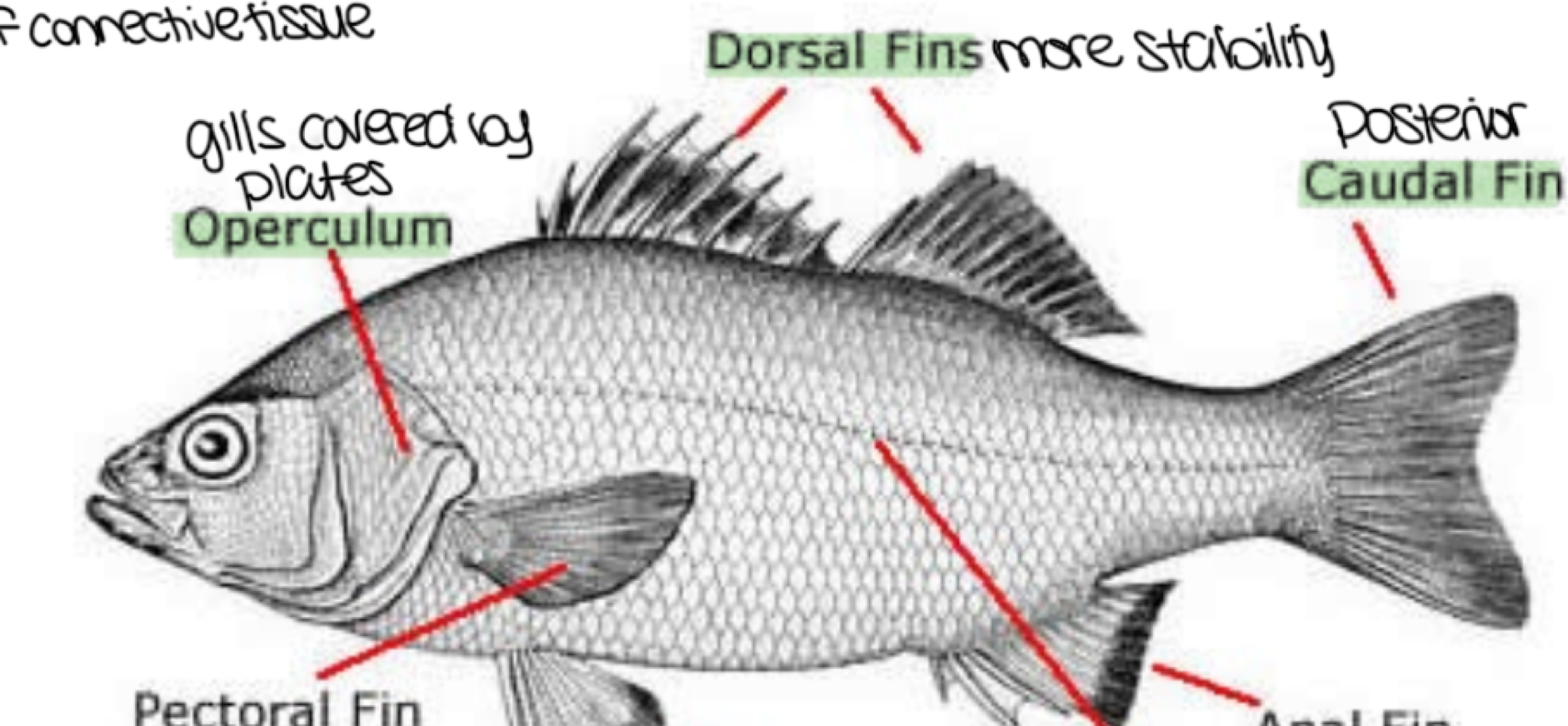
Bony Fishes (osteichthye) are defined as ___
fish with an internal skeleton (jaw, vertebral, column, cranium) of calcified rigid bone, overlapping scales with an inner layer (connective tissue) and outer layer (calcium), and membrane covered gills
Bony Fishes (osteichthye) have an operculum, which is defined as ___
gills protected by plates
Bony Fishes (osteichthye) have dorsal fins (at least one), which are located on the ___
dorsal side for more stability
Bony Fishes (osteichthye) have caudal fins, which are located on the ___
caudal/posterior side for additional support
Bony Fishes (osteichthye) have a swim bladder, which is defined as a ___
gas-filled organ that helps with buoyancy control
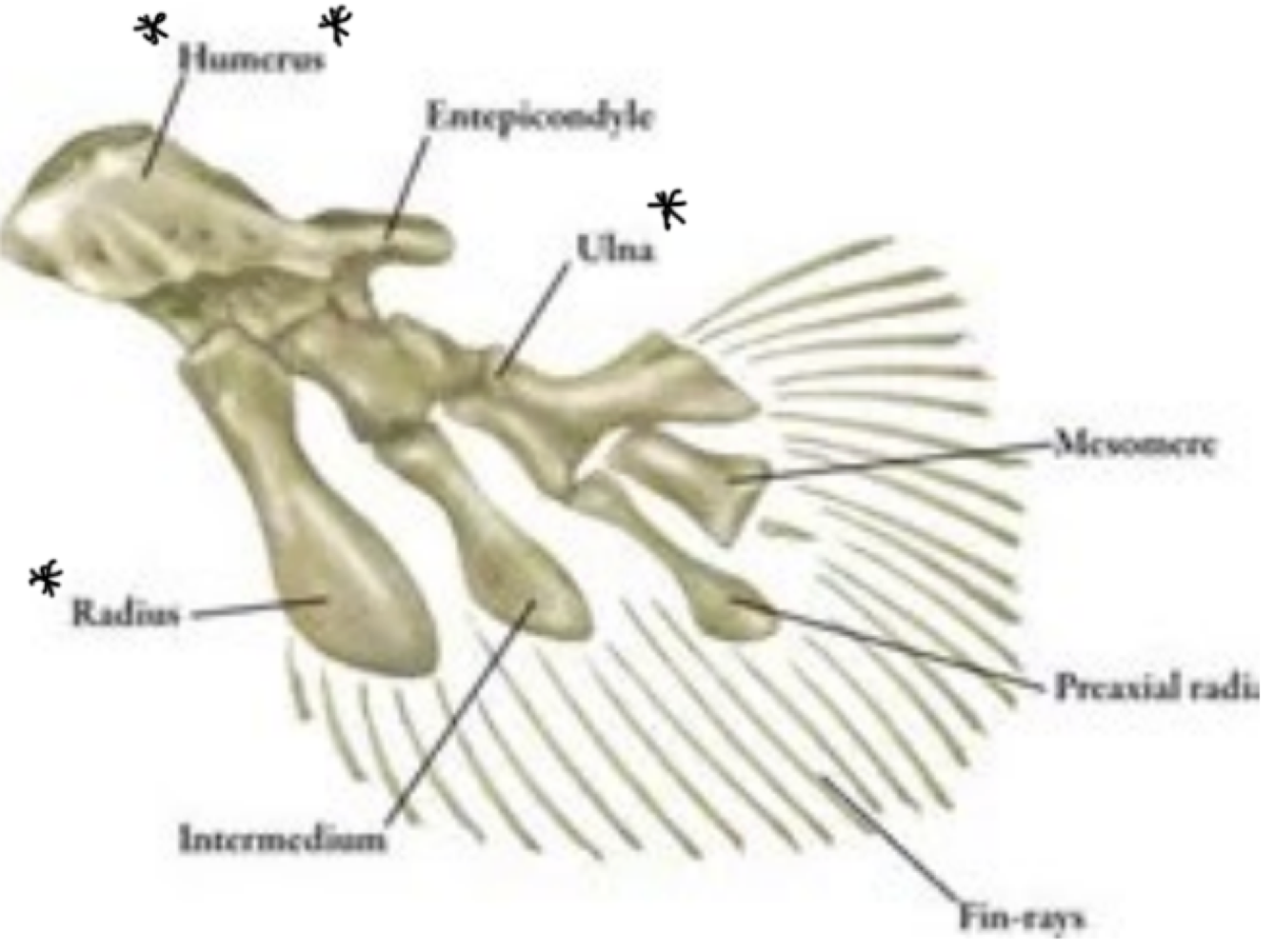
Lobe finned fish are a type of Bony Fishes (osteichthye) that have the presence of ___
thick, supportive bones in the fins that allow them to walk around the surface
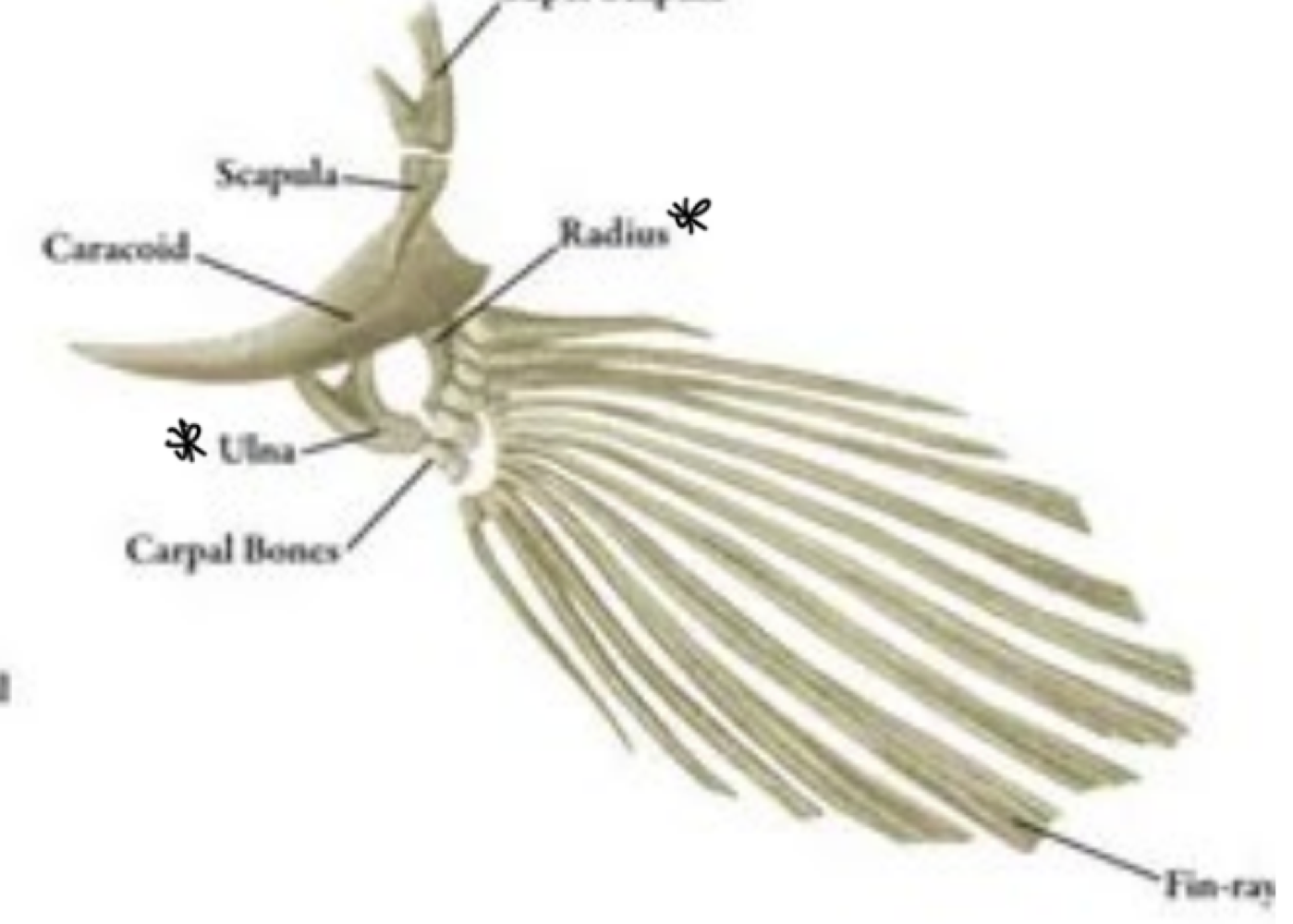
Ray finned fish are a type of Bony Fishes (osteichthye) that have the presence of ___
thin, smaller fins
Tetrapods are defined as
vertebrates suspected to have evolved from aquatic lobe-limbed bony fish who became adapted to life on land for terrestrial food sources, eventually gaining 4 limbs
Amphibians are defined as___
tetrapods with a “dual life” because of the metamorphosis many undergo, and the mixture of aquatic and terrestrial environments throughout life
Frogs (Anura) are defined as ___
amphibians whose reproduction, fertilization, development, and metamorphosis/limb development occurs in the water
Salamanders (Urodela) are defined as ___
amphibians who require regular water access, lack lungs but respirate through the skin (exceptions) and move side to side
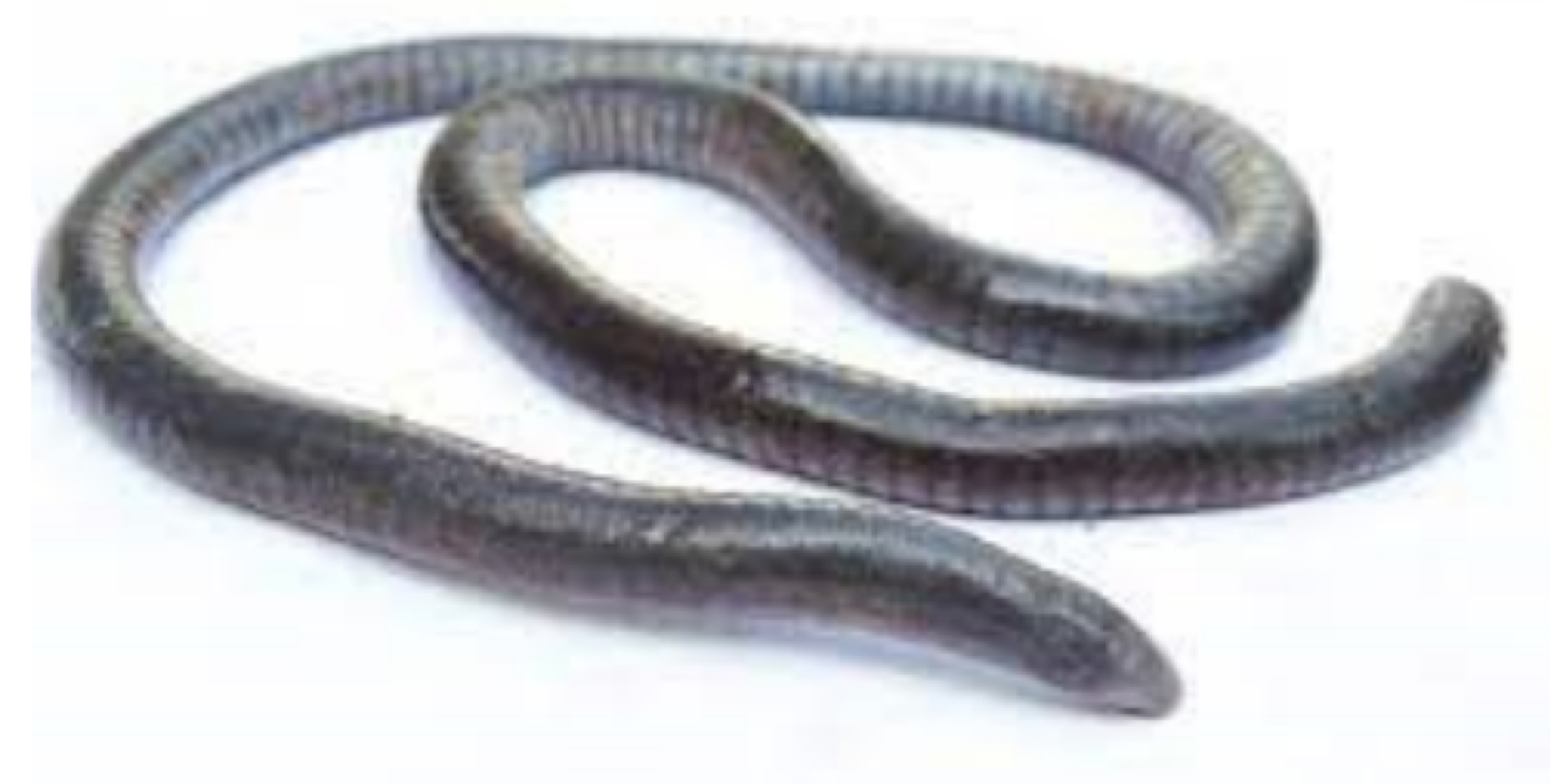

Caecilians (Apoda) are defined as ___
amphibians whose limbs are present in juvenile stages but lost in adulthood, are nearly blind, and bury beneath the soil
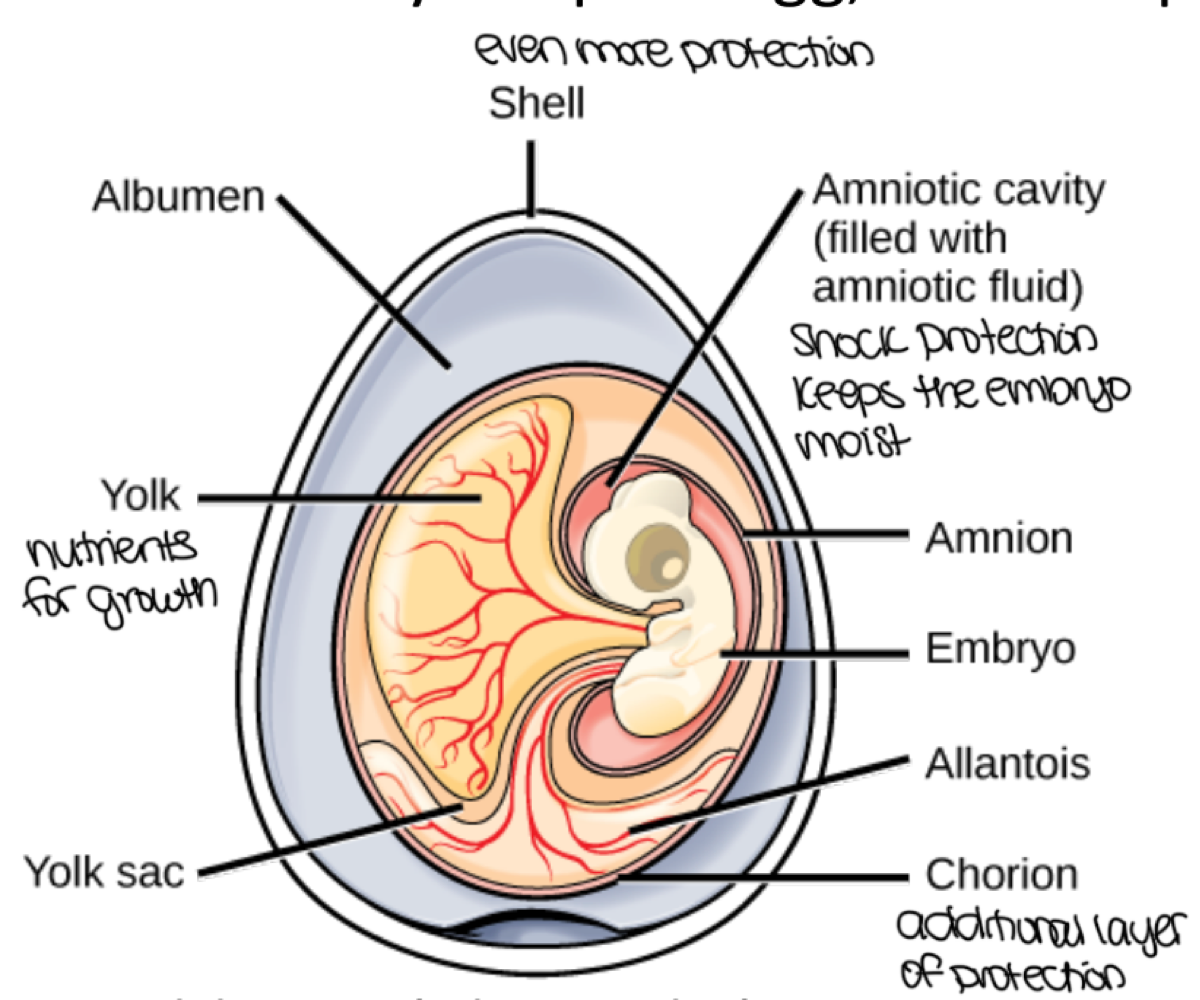
Amniotes are defined as ___
tetrapods who lay terrestrially adapted eggs protected by amniotic membranes providing the embryo with an aquatic environment, allowing the amniotes to reside in drier environments
Reptiles are defined as ___
amniotes who lay eggs enclosed in shells on land, reproduce sexually via internal fertilization, have scaly skin made of keratin and waxy lipids for reduced water loss, have lungs, and are ectothermic (body temperature depends on external environment)
Squamates are reptiles that are defined as ___
lizards, who vary in size, are carnivores, but some (e.g., iguanas) are herbivores; and snakes, who are carnivores, and many have a flexible skull with 8 rotational joints
Testudines (turtles) are defined as ___
reptiles who have a bony or cartilaginous shell with a ventral surface (plastron) and a dorsal surface (carapace) developing from the ribs
Pterosaurs are reptiles defined as ___
pseudodinosaurs who developed the ability to fly, and whose wings are membrane-surrounded arms
Ornithischians and Sauropods are reptiles defined as ___
true dinosaurs who were herbivores
Theropods are reptiles defined as ___
bird ancestors who evolved from bipedal dinosaur predators that have similar hip and wrist bone structures
birds are the only endodermic reptiles, which mean that they have the ability to ___
regulate their internal temperature
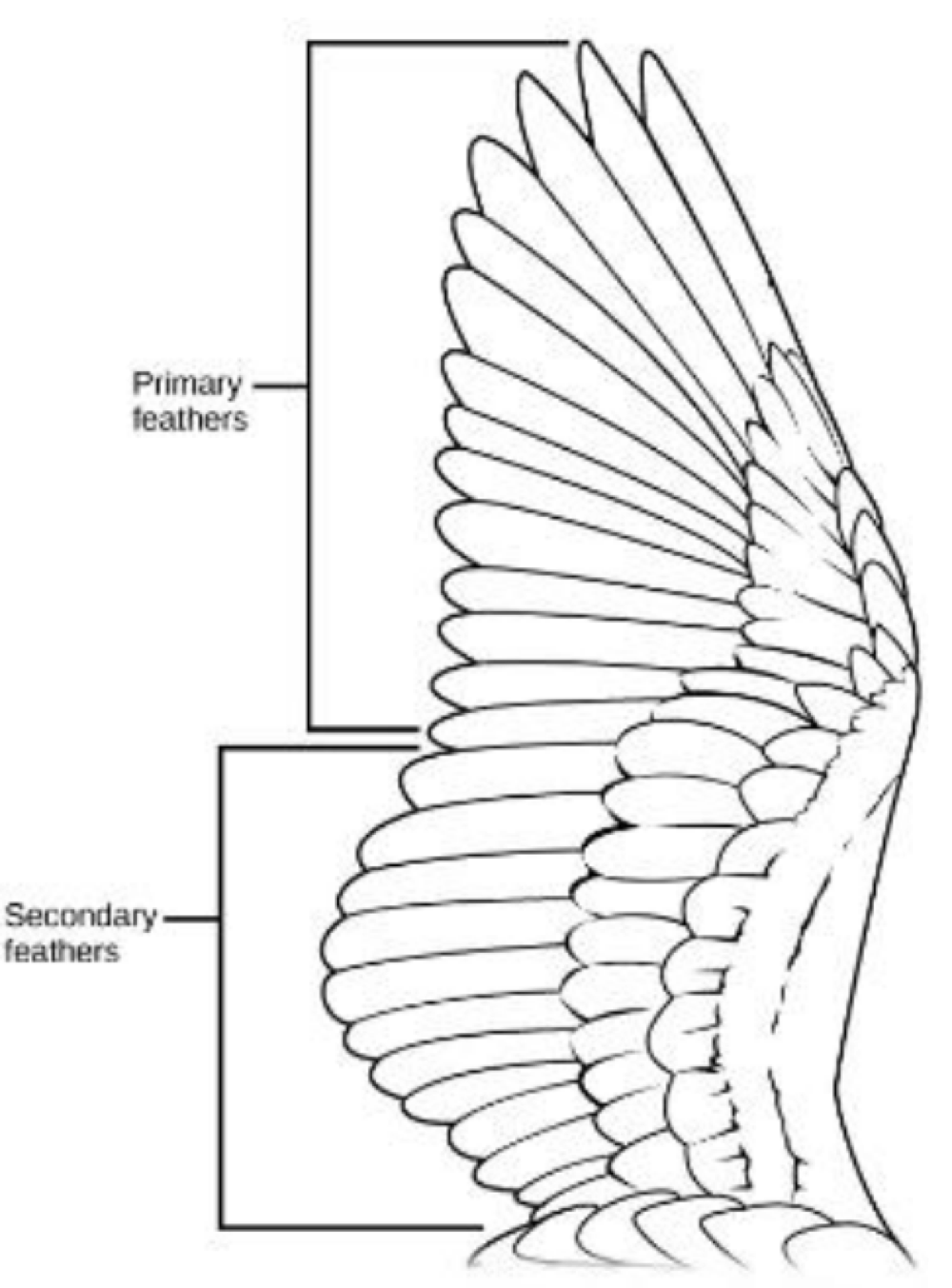
bird’s feathers provide insulation and allow for flight. secondary feathers are ___ and provide ___, whereas primary feathers are ___ and provide ___
medial, lift, lateral, thrust
Mammals share four characteristics, including sweat glands, which ___
secrete evaporated sweat
Mammals share four characteristics, including mammary glands, which ___
secrete milk for newborns (in females)
Mammals share four characteristics, including hair, which ___
provides protection and insulation
Mammals share four characteristics, including a four ___
chambered heart
Monotremes are defined as ___
the smallest, most primitive mammals who lay eggs rather than give birth
Marsupials are defined as ___
mammals who possess a pouch (mammary glands located) where premature young reside after birth, receive milk, and continue growing
Eutherians (placental mammals) are defined as ___
the most widespread mammals who possess a complex placenta connecting the fetus and mother and allowing for gas, fluid, and nutrient exchange
Primates evolved from relatively small ___
arborea, insectivorous eutherians
Prosimians are a type of primates consisting of ___
lemurs, and lorises and galagos
Antrhopoids are primates that include ___
monkeys, apes, and humans
Lesser Apes are Antrhopoids that include ___
gibbons

Great Apes (Family Hominidae) are Antrhopoids that include genera ___
Pan (chimpanzees and bonobos), Gorilla (gorillas), Pongo (Orangutanes), and Homo (humans)