Mycology
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Recognize and discern how fungi differ structurally from bacteria
Fungi: Cell wall - Chitin + beta-glucan and long polymer of D-glucose / Cell Membrane - Ergosterol
Bacteria: Peptidoglycan / Cholesterol
Recognize and discern two fungal cell structures that are medically important
Chitin and Ergosterol - med important b/c antibiotics targeting peptidoglycan and cholesterol will not affect fungi
beta-glucan is the site of action of the antifungal drug caspofungin
ID the two types of fungi and recognize how they differ
Yeasts: Unicellular reproduction by budding, producing daughter cells with different sizes
Mold: Multicellular consisting of hyphae (long filaments) and reproduction via cell division producing daughter cells of equal sizes
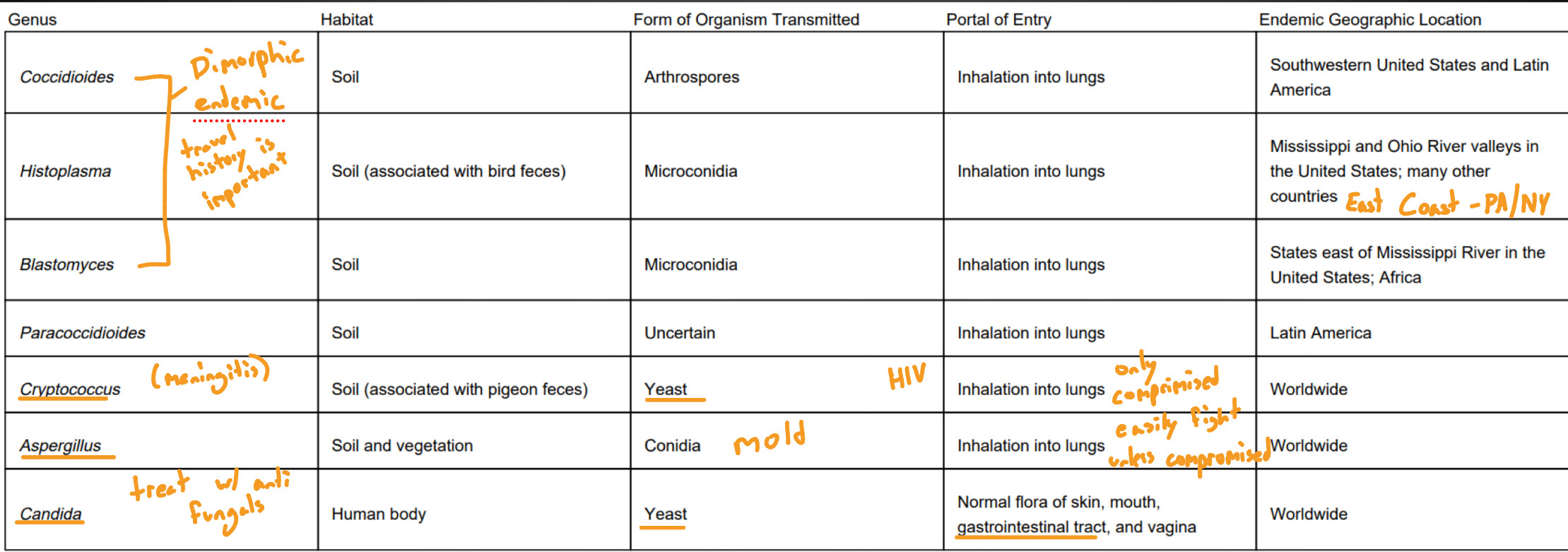
ID the route of transmission and habitat of medically important fungi
ID four commonly used approaches to the laboratory diagnosis of fungal diseases
Direct Microscopic Examination
Medium Culture
PCR - DNA probe collection sample, fast ID of colonies
Seroligc Testing - blood sample to test serum for presence of antibodies and complement activation indicating infetion
ID what structures in fungi allow antifungal drugs to be effective
Drugs will either target the inhibition or altercation synthesis of chitin (cell wall) & ergosterol (cell membrane)
Recognize four categories of medical mycoses and list 1-2 examples of disease in each category
Cutaneous - Ringworm
Subcutaneous - sporotrichosis + mycetoma
Systemic - Histoplasmosis + Blastomycosis
Opportunistic - Candidiasis + Aspergillosis
Recognize the important clinical findings associated with Coccidioides, Histoplasma, Blastomyces, Paracoccidioides
Clinical findings
Cocc - asymptomatic or symptomatic lung infection (fever, cough)
Hist - usually asymptomatic, Severe exposure - lung infections/lesions, bone involvement, coughing up blood/SOB/chest pain
Blast - usually self limiting and mild, spread to CNS, bones, joints, skin
Para - asymptomatic infection, oral mucous membrane lesion, lymph node enlargment
Recognize the definition of opportunistic fungi and ID the five genera of medically important fungi
Oppor - thrive in immunocompromised patients
Candida
Cryptococcus
Aspergillus
Mucus and Rhizopus