biol 241 - reproduction/population growth
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
what is the ideal Eproduction?
unlimited resources to support maximal growth, long life, and unlimited continuous production of offspring
what is the life history theory?
every species has a pattern of growth and development, reproduction, and death shaped by natural selection
the environment affects life history traits by influencing energy budgets: amount of light, food choice, shelter, wind, precipitation
maximizing reproductive success involves trade-offs due to fixed energy budgets + selective pressures
can you maximize 2 life history traits silmultanesouly is they compete for a share of limited resources?
No, any gains by one trait will result in a loss by the other
What are life history traits?
growth rate
parental investment
number of offspring (fecundity)
frequency of reproduction (parity)
size/age at sexual maturity
size of offspring
longevity/life expectancy (mortality rate)
parental investment - what is passive care
pre-birth energy expense
parental investment - what is active care
post-birth energy exposure
what does semelparity mean?
individuals of the same species can breed only once in its lifetime
what does iteroparity mean?
individual of the same species can breed more than once in its lifetime
life history strategies - what is r-selected?
low energy, high numbers
life history strategies - what is k-selected?
high energy, low numbers
what are r-selected species
small adult/offspring size
early sexual maturity
semelparous
high fecundity (number of offspring)
low parental investment
low juvenile survival
short lifespan
what are k-selected species
large adult/offspring size
later sexual maturity
iteroparous
low fecundity
high parental investment
high juvenile survival
long lifespan
what do life history tables tell us?
summarize info on age structure, size, history (reproductive) stage, and survivorship of a population
used to predict how a population will change over time
useful in managing: crops/livestock, conservation, pest/weed control
life history tables legend - what does x indicate
age
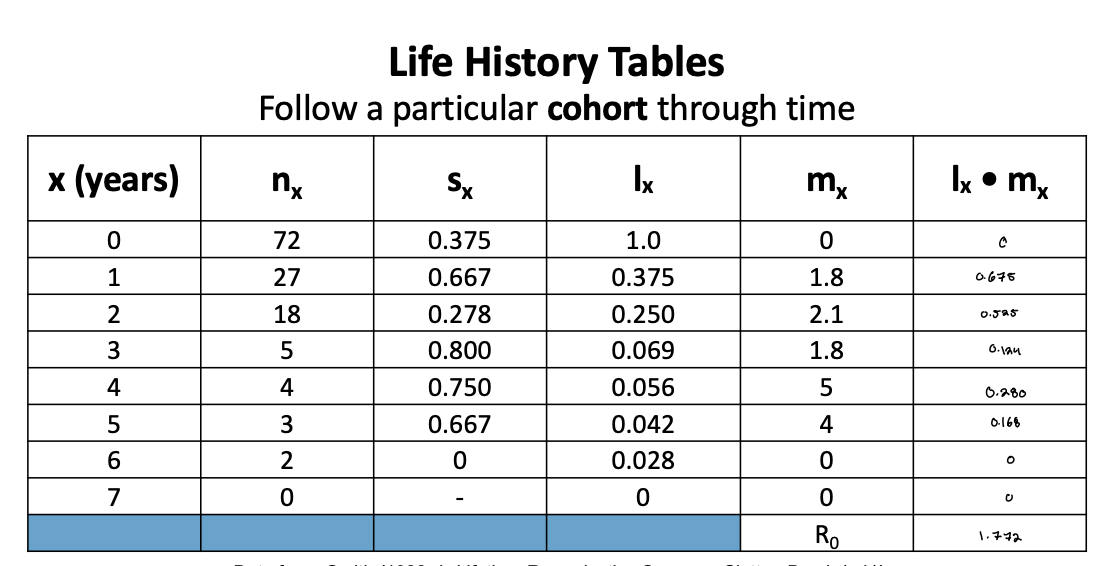
life history tables legend - what does nx indicate
number of females at each age (x)
life history tables legend - what does sx indicate
survival rate from one age to the next (sx= nt + 1/ nt)
life history tables legend - what does lx indicate
survivorship (fraction of original cohort still alive) lx = nt/no
life history tables legend - what does mx indicate
fecundity (avg number of female offspring each living female produces)
life history tables legend - what does Ro indicate
net reproductive rate (avg number of female offspring per female in cohort over the cohorts lifespan) Ro=∑(lx x mx)
What does Ro bigger, less or close to 1 signify
Ro> 1: population growing
Ro < 1: population decreasing
Ro = 1 = 0.95-1: population is steady
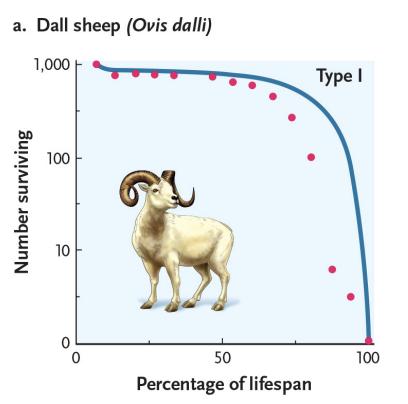
survivorship curves - type 1
high juvenile survival throughout lifespan
mortality at old age
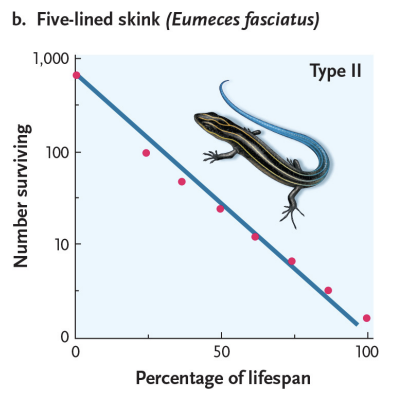
survivorship curves - type 2
constant mortality throughout lifespan
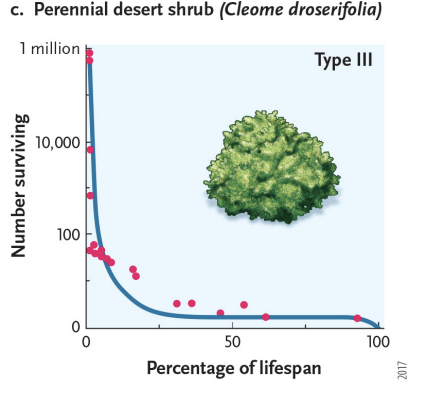
survivorship curves - type 3
low juvenile survival throughout lifespan and then high survival
for this course, what is population size influenced by?
births and deaths
What formula can we use to study the change in total numbers of individuals in a population?
dN/dt = B-D
N = population size
t= time
B = # of births
D = # of deaths
what formulas can be used to track the per capita birth rate (b) and per capita death rate (d) in a population?
b = B/N, d = D/N
how can we use the per capita growth rate (r ) in a formula to predict population size changes?
r = b - d
what is the formula for calculating the change in population growth?
dN/dt = rN0
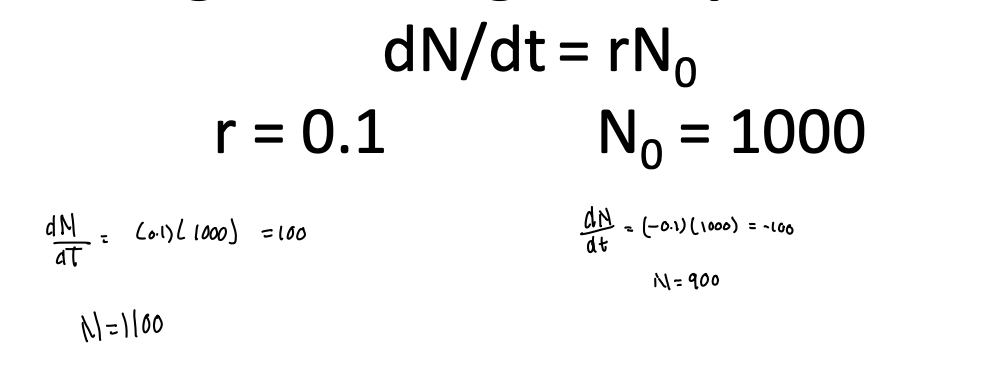
exponential model of population growth - under ideal conditions what would the per capita growth rate be for a population?
the per capita growth rate (r ) will be at a max, r = rmax = intrinsic rate of incresae
exponential model of population growth - in this model rmax is always….
positive and constant over time
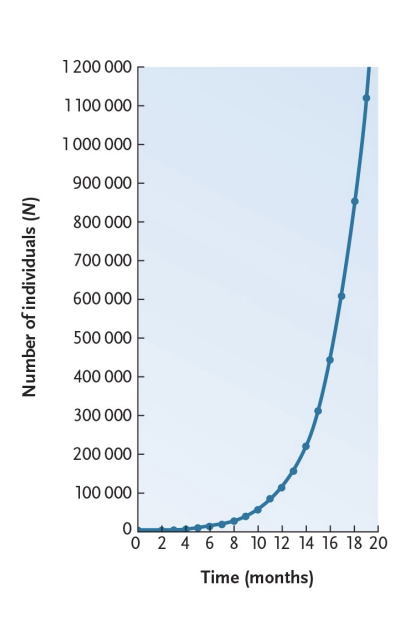
exponential model of population growth - rmax varies by species, large vs small?
small organisms = large rmax
large organisms = small rmax
what formula should you use to calculate exponential growth?
Nt = N0(1+ rmax)^t
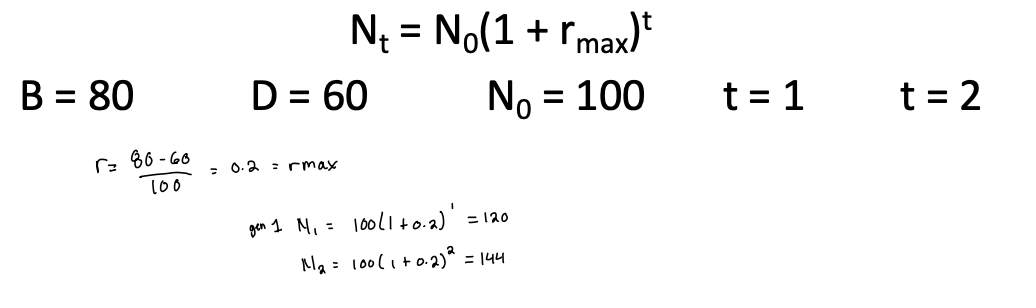
what limits population growht?
Ein, temperature, water, predators
most environments can only support a certain population size, this is referred to as…
carrying capacity (K)
what does the population size (N) being close to the carrying capacity (K) change?
the per capita growth rate
r is never going to be rmax
as the value N increases, the value of r does what?
decreases
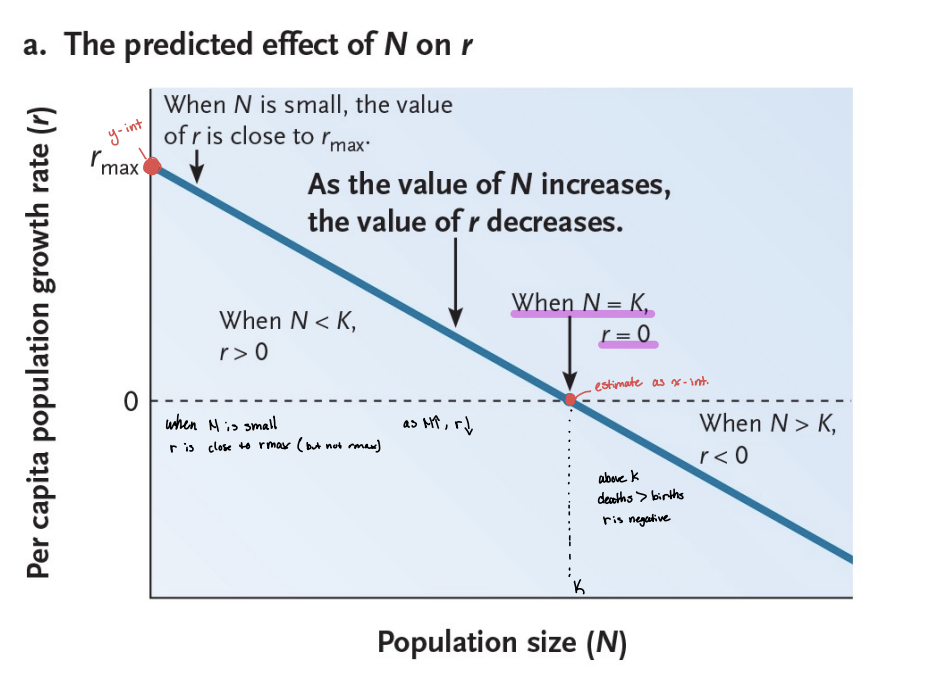
when N=K what does r equal?
r=0
when N>K, what does r equal? when N<K?
when N>K, r<0
when N<K, r>0
as populations grow, death and birth rates do what?
death rates increase, birth rates decrease
r decreases as the population grows and reaches k
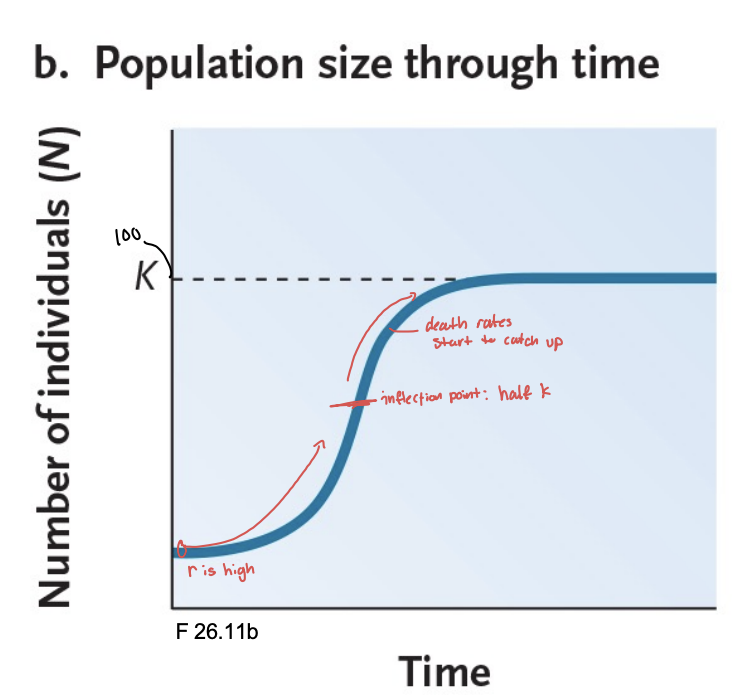
what is the formula for being influenced by the fraction of k available, rt=?
rt=rmax((K-Nt)/K)
to determine the size of a population growing logistically what formula do we use?
Nt+1 = nt(1+rt)^1