biology topic 5a
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
energy and ecosystems, nutrient cycles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
what is biomass?
the total mass of carbon or dry mass of tissue per given area at a given time. measured in gm-2(area) or gm-3(volume)
in an ecosystem, what do plants synthesise organic compounds from?
atmospheric or aquatic carbon dioxide
what are most sugars synthesised by plants used as? what are the rest used for?
respiratory substrates. rest are used to make other biological molecules (DNA, RNA, phospholipids…) which form biomass
why is dry mass or carbon measured and not fresh mass?
fresh mass includes water, which varies so its unreliable
whats a problem with using carbon or dry mass to measure biomass?
organism must be killed, so only small sample which may not be representative
how can you measure the chemical energy store in dry mass? describe method
calorimetry
dry to constant mass in oven to reove water
measure mass of dry mass before
burn dry biomass in pure oxygen in bomb calorimeter
measure volume of water
measure temperature change
use q=mct
where is all energy for ecosystem derived from?
the sun
how do producers asborb light energy?
during process of photosynthesis they fix it into chemical energy in the form of organic molecules which is passed up the trophic levels.
whats a problem with energy transfer in ecosystems?
energy transfer into ecosystems and up trophic levels is nowhere near 100%
what is gross primary production?
the chemical energy store in plant biomass, in a given area or volume ie result of photosynthesis
what may be a problem with the suns energy which causes lots of energy to be lost up trophic levels?
not all the suns energy is converted into organic molecules → over 90% of suns light never reaches the plant, not all wavelengths absorbed (green light reflected back), light not falling on chlorophyll molecule etc. energy that is converted to organic molecules is the GPP
what are trophic levels?
each stage in food chain
what is net primary production? (NPP)
the chemical energy store in plant biomass after respiratory losses to the environment have been taken into account (amount of energy that can be passed onto the next trophic level)
how can energy be lost from energy that is fixed into organic molecules (GPP)?
some of it (20-50%) is used in respiration. glucose made in photosynthesis is used in respiration and the energy contained is lost as heat therefore not available to be made into other organic molecules
what are examples of organic molecules?
DNA, RNA, proteins, phospholipids
how do you calculate NPP?
NPP=GPP-R
R is respiratory losses
what is NPP available for?
plant growth and reproduction (growth via cell divison, where DNA needs to be replicated, new organelles etc)
how do you calculate the net production of consumers?
N= I - (F+R)
I is chemical energy store in indigested food
F is energy lost to environment in faeces and urine
R is respiratory losses to environment
as a summary, why is so much energy lost at each trophic level?
in plants, some light energy is reflected/transmitted through leaves/not right wavelength → efficiency of photosynthesis is low
some energy is lost to surroundings as heat from respiration
some energy is lost in faeces and urine
some parts of organisms are not eaten, not transferred to next trophic level
how is energy lost when a consumer eats a producer?
less than 10% of NPP is incorporated into primary consumers biomass hence only 10% passed up to next trophic level
due to:
some organism not being consumed
some parts lost as faeces or urine
some energy lost as heat via respiration like plants
why are food chains often limited to 4-5 trophic levels?
if energy is lost at each trophic level then efficiency of energy transfer is low
total biomass is less at higher tropic levels
therefore insufficient energy available to support a large breeding population if more than 4-5
how do you calculate percentage efficiency?
=(energy available after transfer/energy available before transfer) x 100
whats the difference between production and productivity?
productivity includes over a certain period of time, production doesnt
how are farming practises designed to increase the efficiency of energy transfer?
simplify food webs ie reduce energy losses to nonhuman food chains, increasing NPP by eg using pesticides so energy isnt lost when pests feed on crops
reducing respiratory losses within a human food chain ie control conditions livestock are kept in eg restrict movement so less energy lost as heat from respiration or keep them warm so less energy used to generate body heat from respiration
what are primary and secondary productivity?
the rate of primary and secondary production respecitvely. its measured as biomass in a given area in a given time eg kJha-1year-1
what are saprobionts?
microorganisms that live in detritus (pieces of dead organic matter)
what do nutrient cycles rely on?
saprobionts to break down organic molecules into simple inorganic molecules and ions which plants can make use of.
what so saprobionts feed by and how?
extracellular digestion
secrete digestive enzymes
absorb the soluble nutrients released
convert organic into inorganic compounds eg phosphates, nitrates
what are detritivores?
break larger leaves etc into smaller pieces (increases Sa for saprobionts to act upon)
why is nitrogen deficiency most common cause of poor plant growth if it makes up 78% of the atmopshere?
N2 gas has a triple bond therefore very unreactive, not easily converted to other compounds
blurt the nitrogen cycle
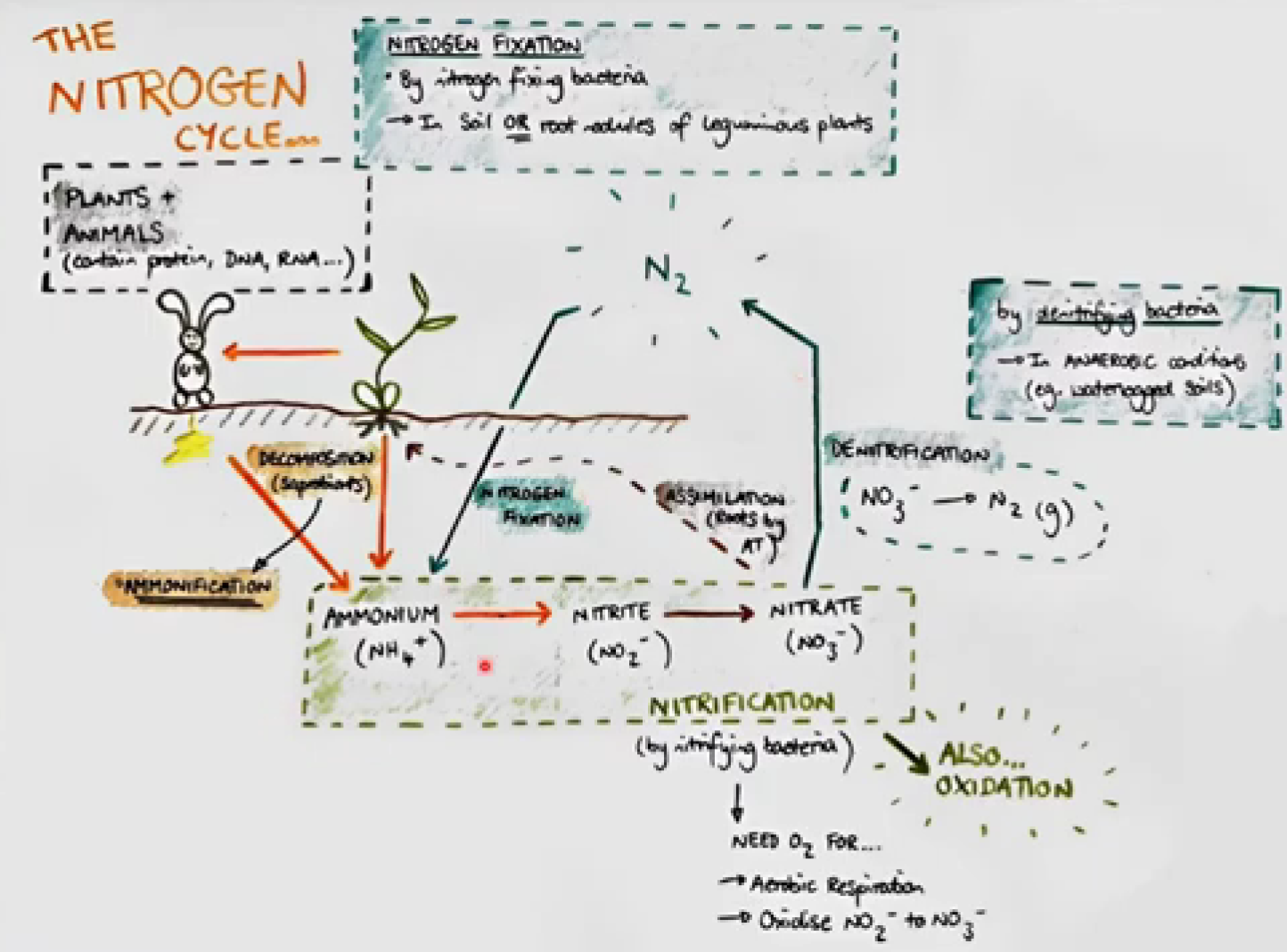
describe the 4 stages of the nitrogen cycle
AMMONIFICATION
nitrogen containing organic compounds eg phospholipids, DNA from dead organisms and waste from animals hydrolysed and converted into NH3/NH4+ by saprobionts
NITRFICATION
NH3/NH4+ in soil oxidised into nitrite ions (lil bite) (NO2-) which are oxidised into nitrate ions (NO3-) both carried out by nitrifying bacteria.
DENITRIFICATION
nitrates in soil converted to N2 gas by denitrifying bacteria. occurs when theres low oxygen conc (fewer aerobic nitrifying bacteria and nitrogen fixing bacteria)
NITROGEN FIXATION
nitrogen gas is converted to NH3/NH4+ in 3 ways; lightning; free living nitrogen fixing bacteria in soil; mutualistic nitrogen fixing bacteria
whats the main source of phosphorous?
its mineral ion form (PO43-) in sedimentary rock deposits in the sea
what is mycorrhizae?
fungal associations between plant roots and beneficial fungi
how is mycorrhizae beneficial for plant growth?
increase surface area for water and mineral absorption so increases rare of absorption
acts as a sponge to hold water and minerals around roots to better withstand dry conditions/drought
makes it more drought resistant and able to take up more inorganic ions
whats the relationship in mycorrhizae?
a mutualistic relationship between plant and fungi (plant gains water and nutrients, fungi recieves organic compounds eg amino acids)
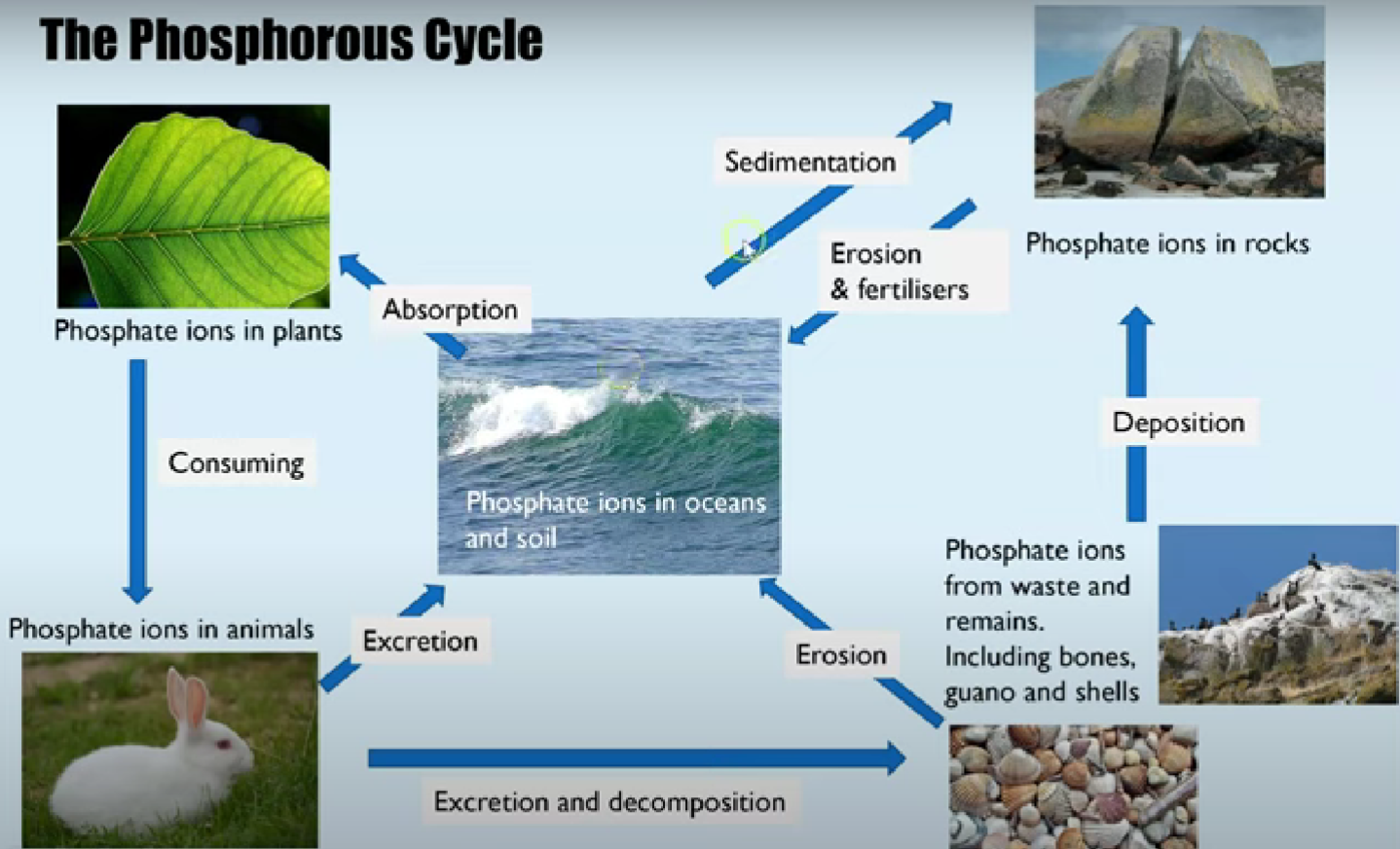
blurt and describe the phosphate cycle
phosphate ions dissolved in water or in soil are absorbed by organic molecule in producers by active transport.
consumers feed and digested these producers into their biological molecules
some excretion and death go through saprobionts which are decomposed and back into oceans, lakes, soil
some excretion and death lead to waste and remains which contain phosphate ions such as bones, guano, and shells.
overtime some erode and go back into the ocean, lakes, soils. some go through deposition which then erode and run as fertilisers back into oceans and soil
sedimentation can occur which create rocks containing phosphate which will erode.
why are fertilisers used?
to replenish nitrate and phosphate ion concentrations in the soil (otherwise would be limiting factor) that are lost when harvested and removed rom nutrient cycles
what are the 2 fertilisers?
artificial fertilisers (inorganic chemicals (pure))
natural fertilisers (organic, manure)
pros and cons of natural fertilisers
pros: cheaper and often free if farmer owns animals, leaching less likely as ions contained in organic molecules and need to be decomposed by microorganisms before released
cons: cannot control proportions of exact minerals
pros and cons of artificial fertilisers
pros: created to contain exact proportions of minerals
cons: inorganic substances are more water soluble, more ions dissolve in water causing leaching (when more fertiliser is added to field than used) so when it rains, theyre washed out of the soil into waterways leading to eutrophication
what is leaching?
when water soluble compounds are washed away often into rivers or ponds, can lead to eutrophication
what are the steps of eutrophication?
ions leached from fertilised fields which results in rapid growth of algae in ponds/rivers
algae blocks light preventing it from reaching plants below so they cant photosynthesise
results in death of plants
saprobiontic bacteria decompose the dead plant matter, reducing oxygen concentration of the water as bacteria respire aerobically
leads to death of aquatic organisms due to lack of dissolved oxygen in water