Physics - ch 1: kinematics and dynamics miledown
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
[...] are physical quantities that have both magnitude and direction
vectors
examples: displacement, velocity, acceleration and force
[...] are quantities that have only a magnitude
scalars
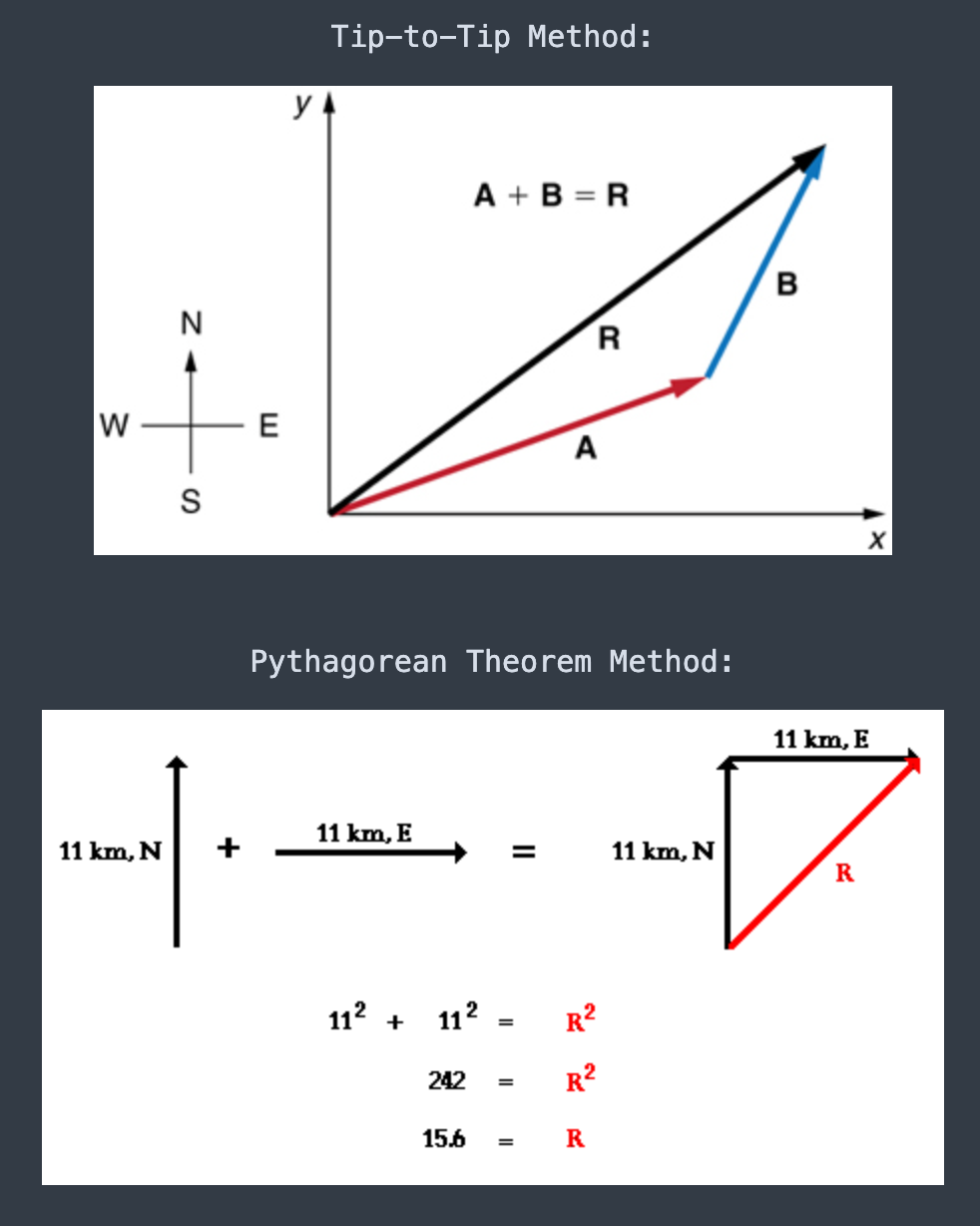
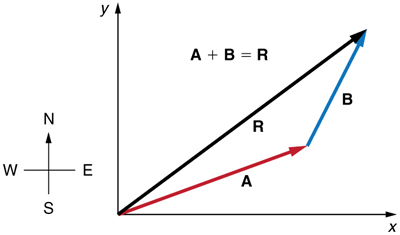
For vector addition, use the [...] method, or you can break the vector into its component parts and use the [...]
tip-to-tip method or pythagorean theorem
For vector subtraction, you must change the [...] of the subtracted vector and then do a tip-to-tail addition
direction
Free body diagrams are representations of the [...] acting on an object
forces
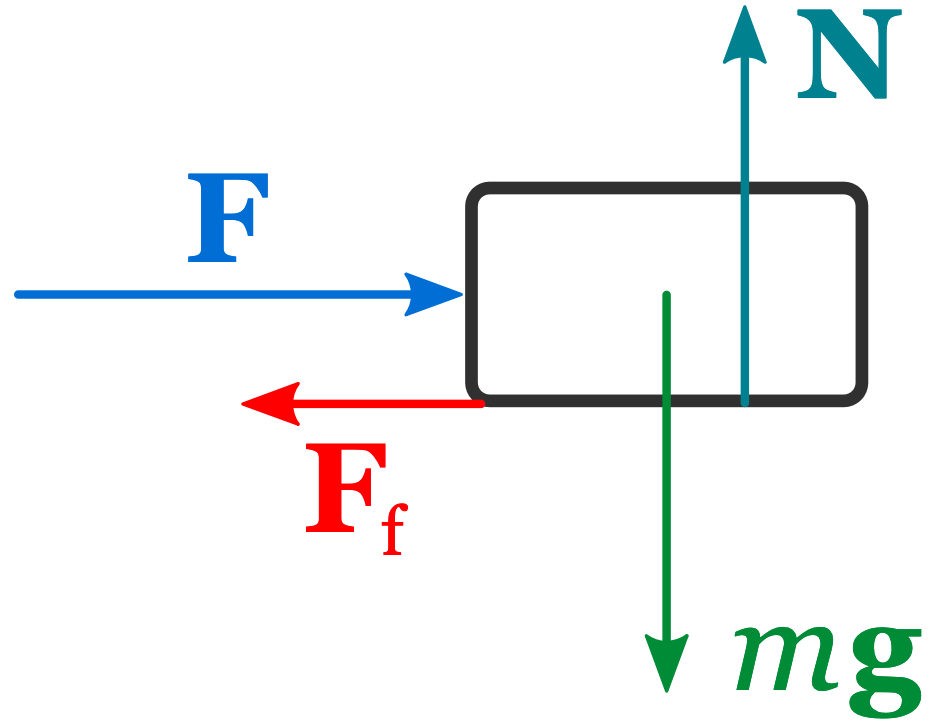
[... equilibrium] occurs in the absence of any net forces acting on an object
Translational equilibrium
(constant velocity means translational equilibrium equals 0)
[... equilibrium] occurs in the absence of any net torques acting on an object
Rotational equilibrium is when the total torque acting on an object is zero, resulting in no angular acceleration.
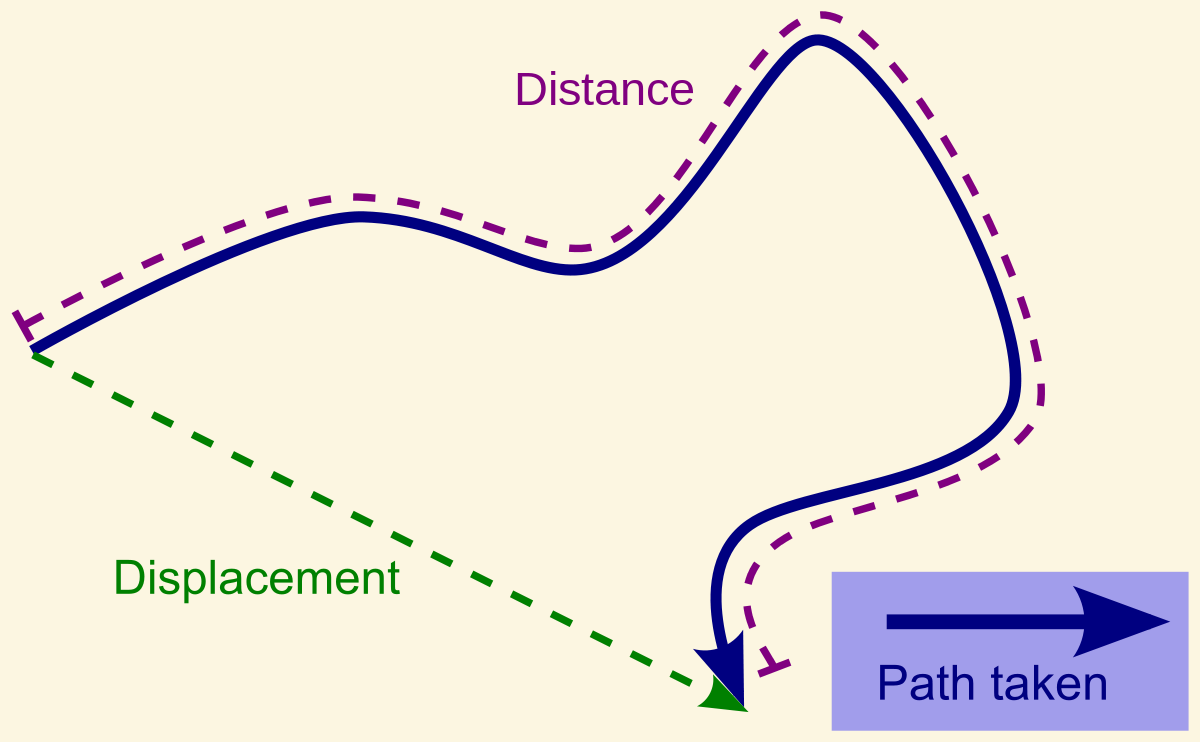
Displacement is path [dependent or independent]
independent
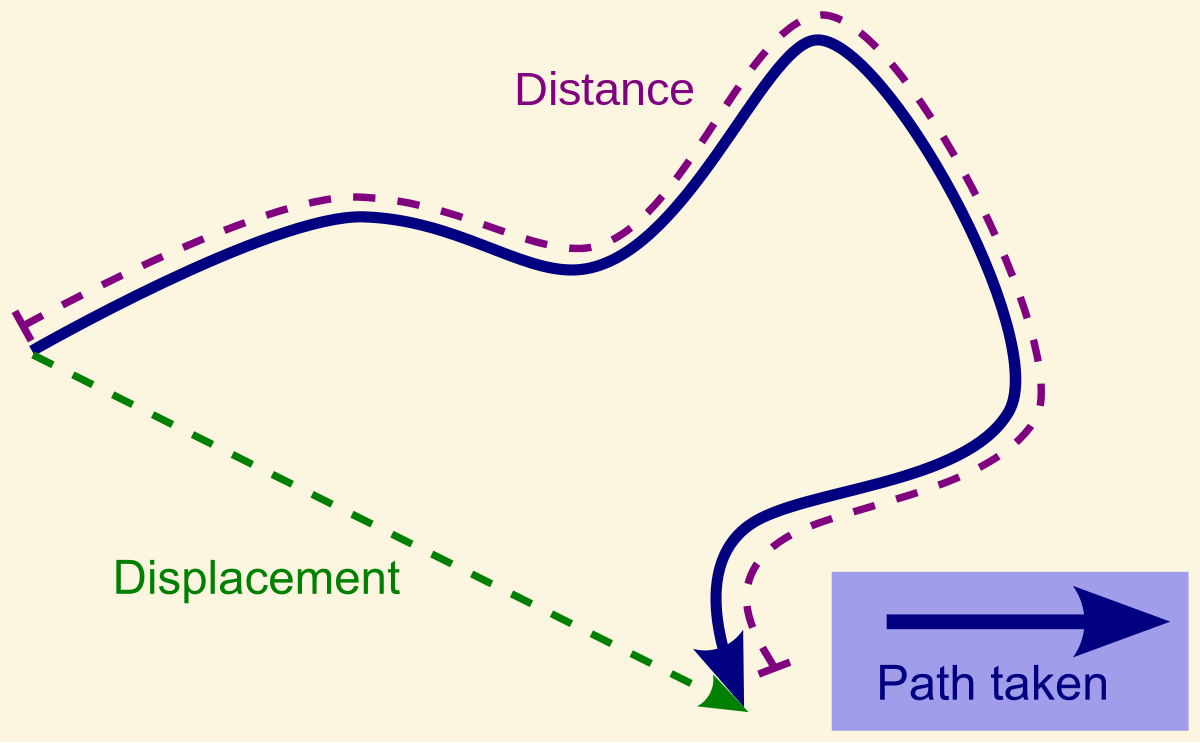
Distance is path [dependent or independent]
dependent
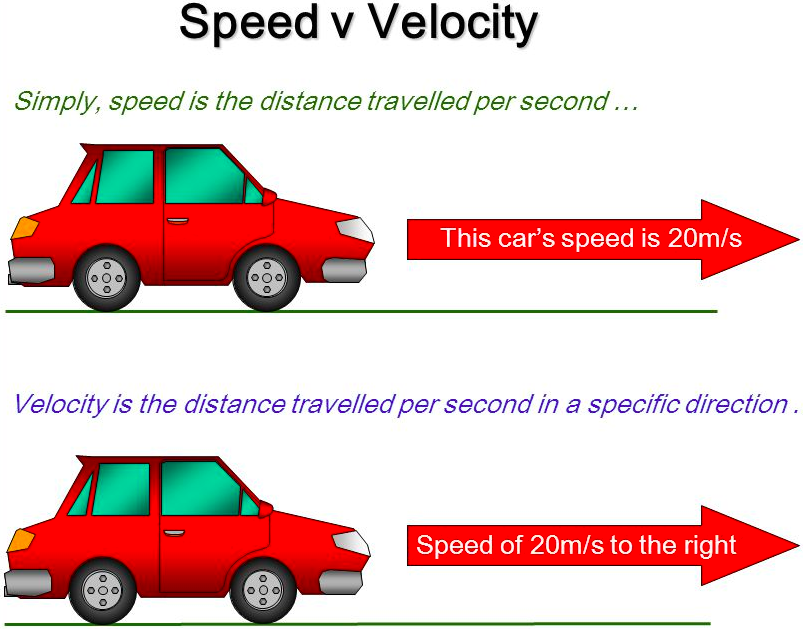
Velocity is a [vector or scalar] and includes both [...] and [...]
vector and includes magnitude and direction
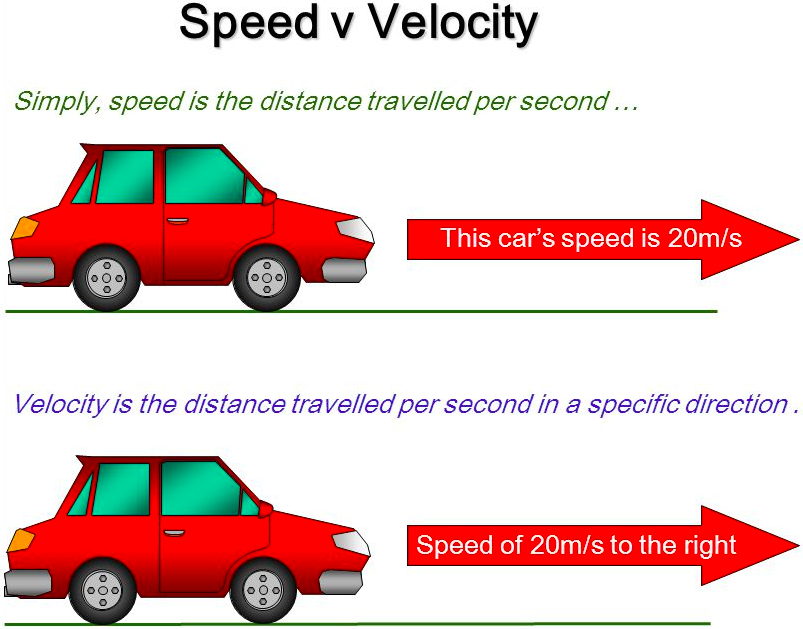
Speed is a [vector or scalar] and includes only the [...]
vector and includes onlt the magnitude of the rate of change
A/an [...] is any push or pull that has the potential to result in an acceleration
force
[...] is the attractive force between two objects as a result of their masses
gravity
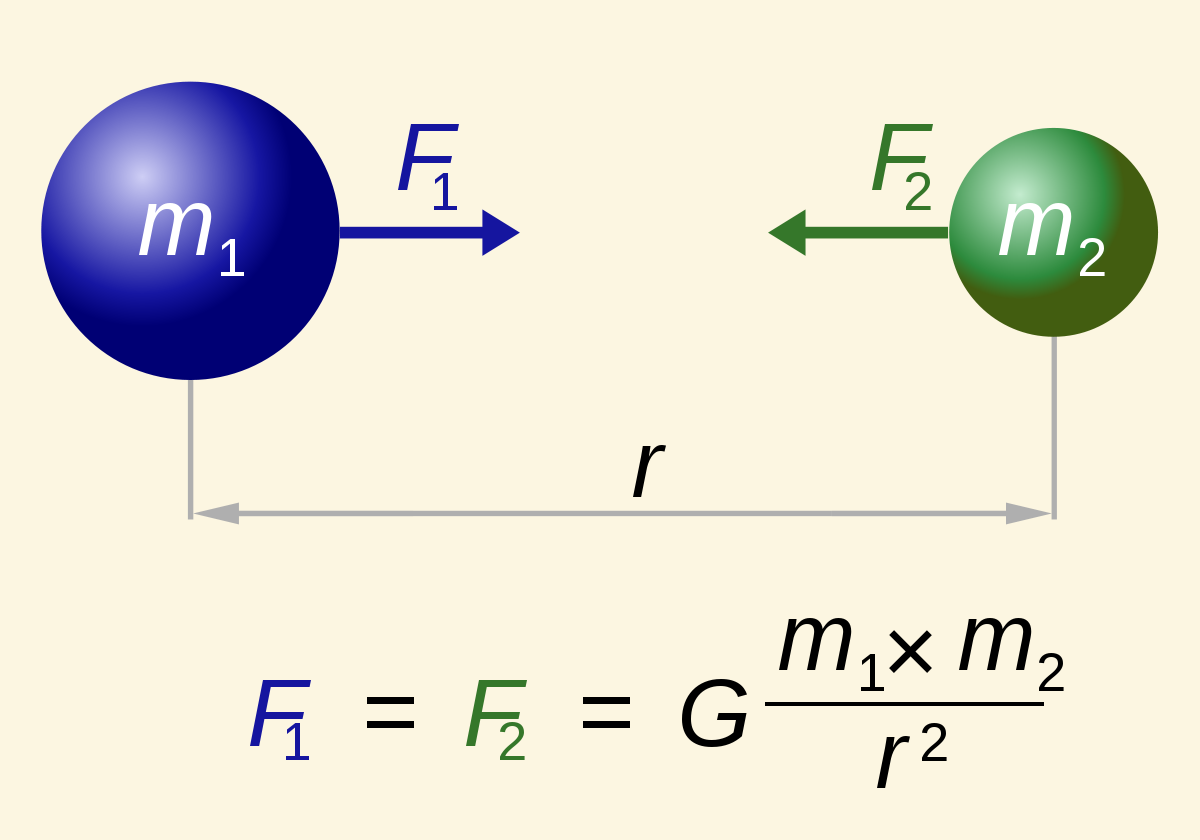
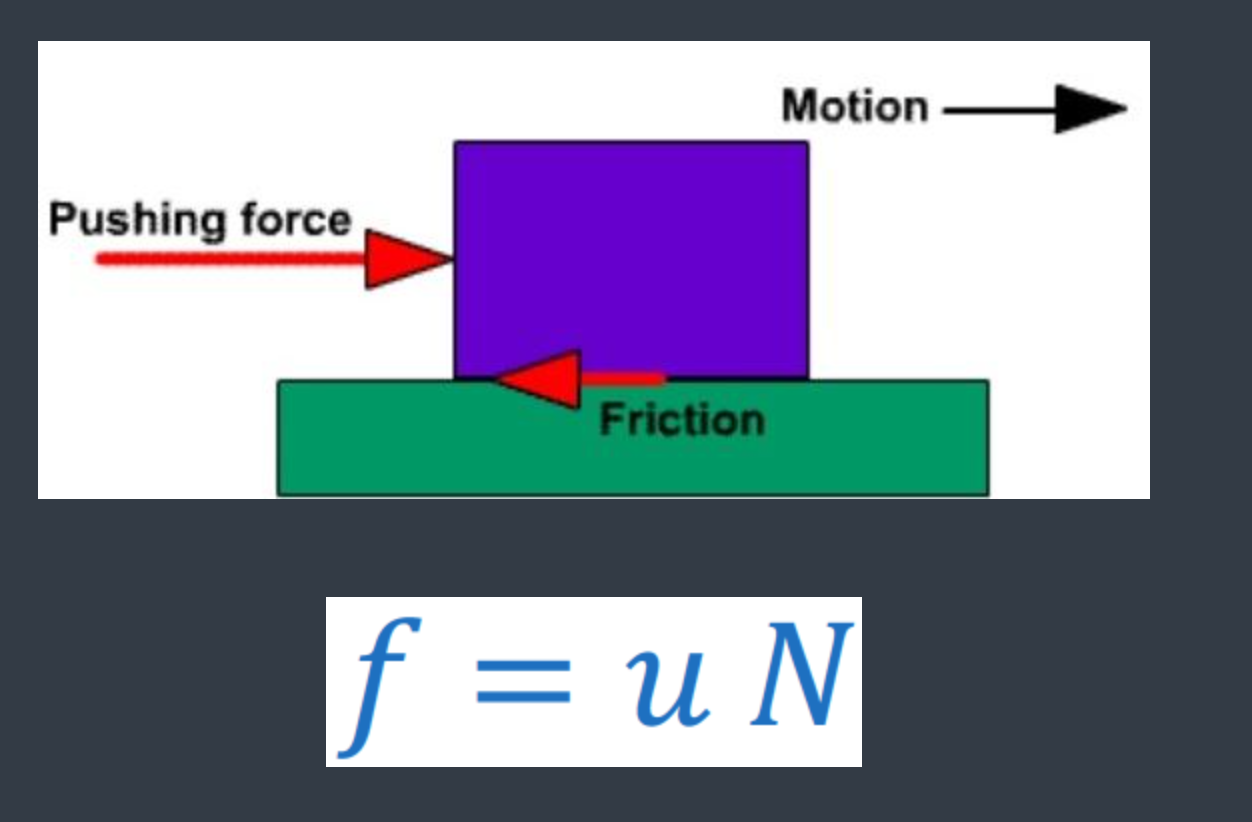
[...] is a force that opposes motion as a function of electrostatic interactions at the surfaces between two objects
Friction
static friction = stationary object
kinetic friction = sliding objects
[...] is a measure of the inertia of an object; its amount of material
mass
[...] is the force experienced by a given mass due to the gravitational attraction to the Earth
weight
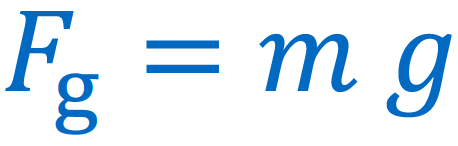
[...] is the vector representation of the change in velocity over time
acceleration
change in velocity over time
unit ex: mph/seconds east
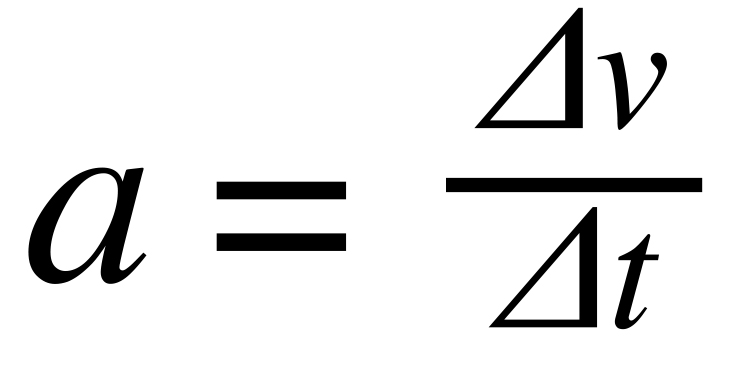
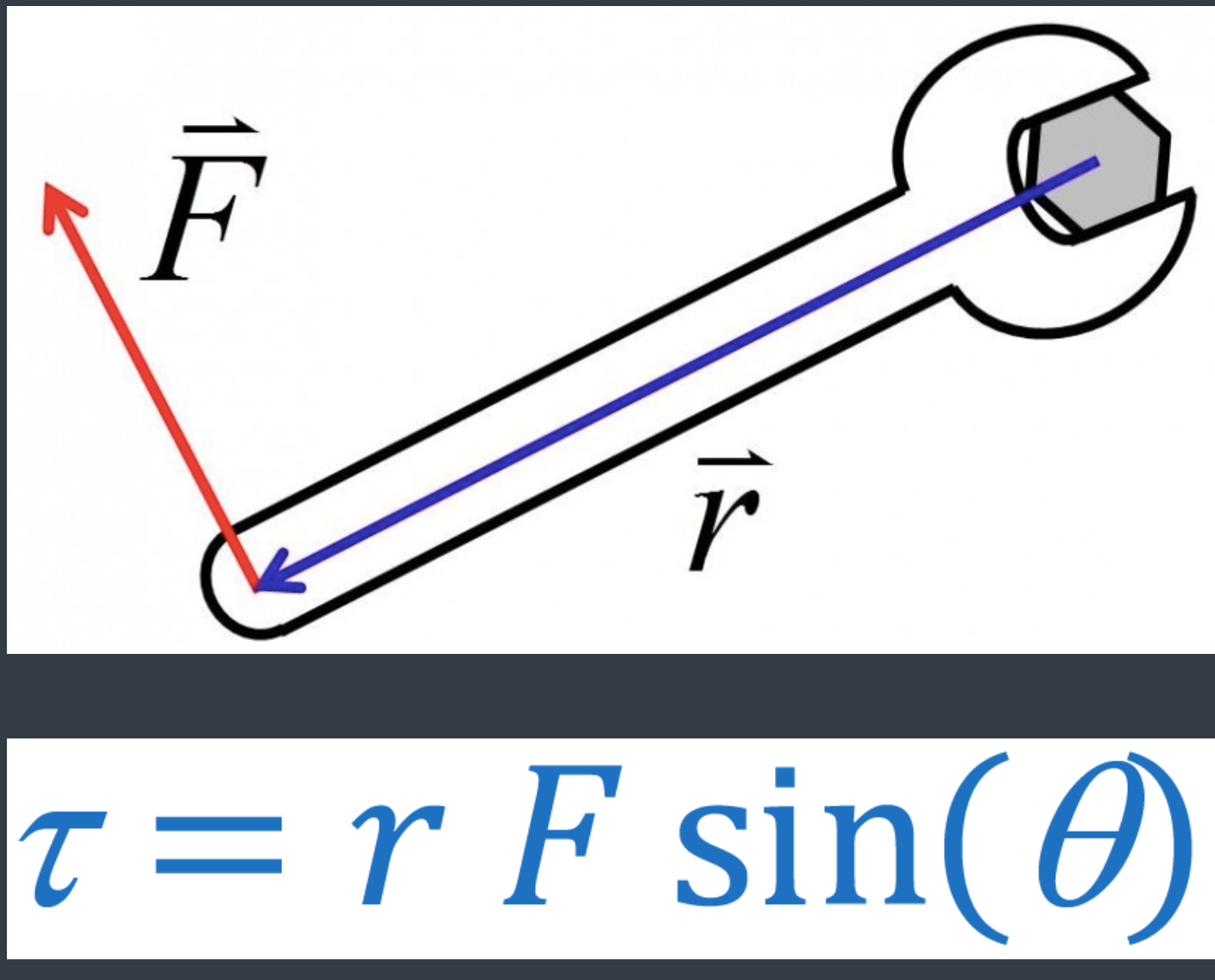
[...] is a twisting force that causes rotation
torque
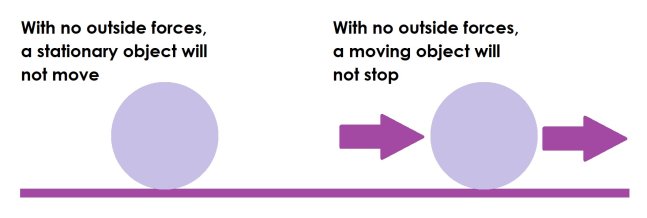
Newton’s first law of motion
an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by a net force > 0.
Newton’s second law of motion
any acceleration is the result a net force > 0

Newton’s third law of motion
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction

units for joule

[... energy]is the energy of motion, observable as the movement of an object
Kinetic energy
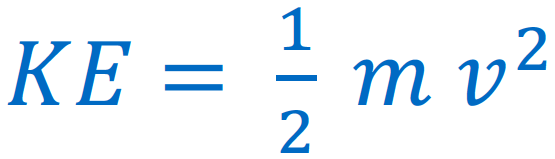
[... energy] is a type of energy an object has because of its position
Potential energy
the energy stored within a system
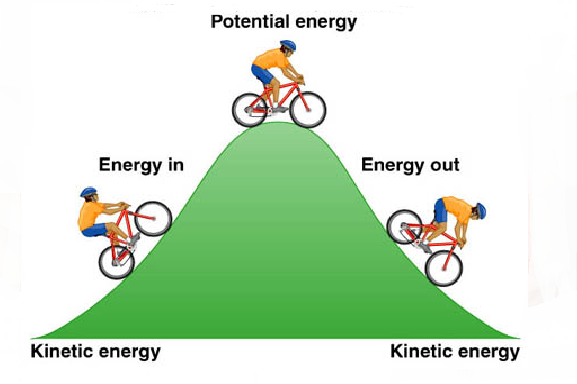
[... energy] is the potential an object has to do work as a result of being located at a particular position in a gravitational field
gravitational potential energy

[... energy] is created when stretching or compressing an elastic object
Elastic potential energy
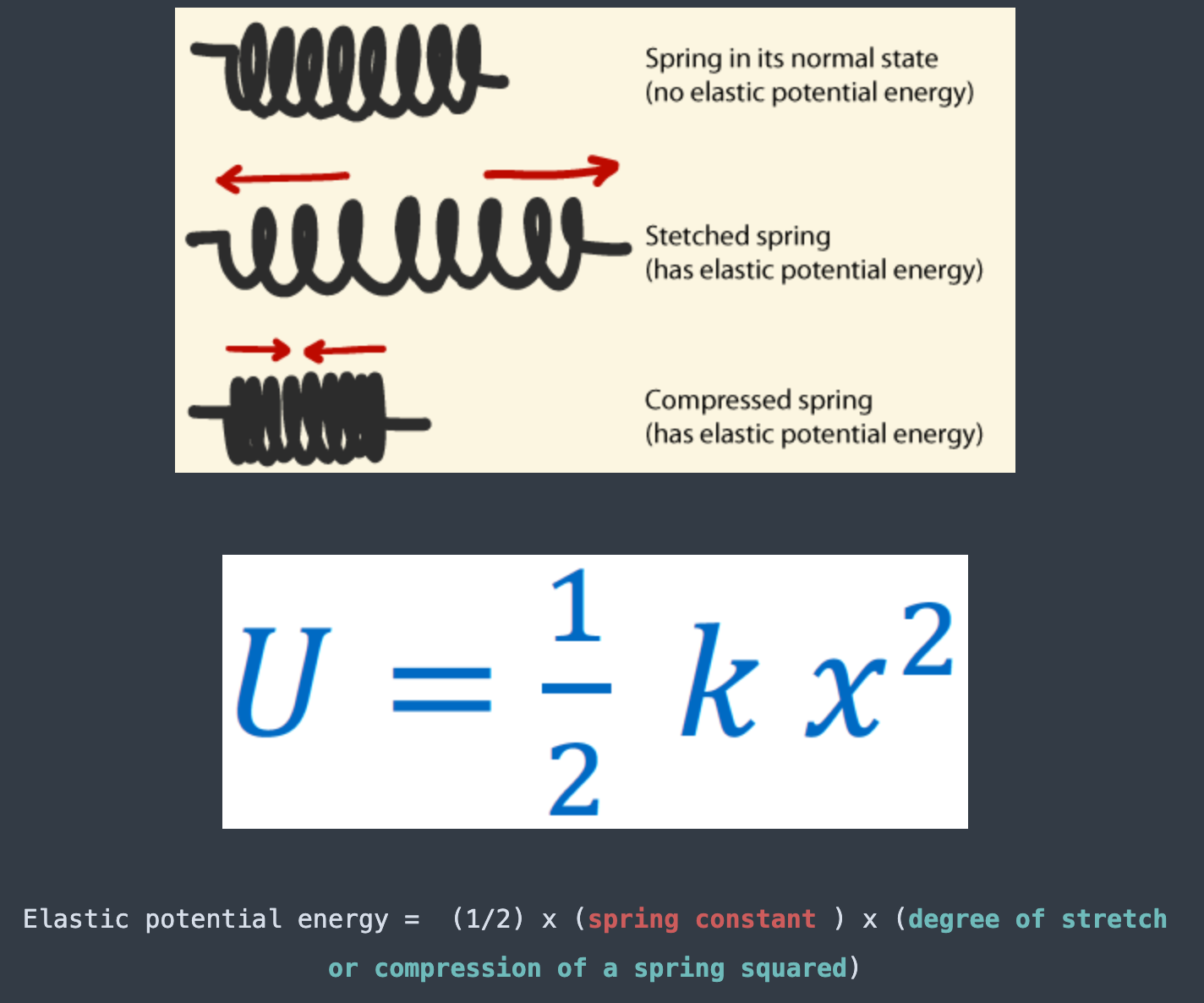
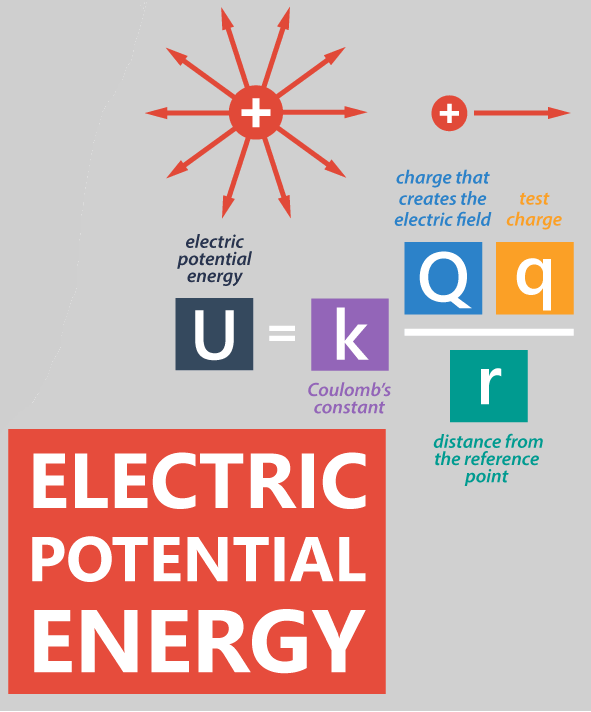
[... energy] is the energy between two charged particles
electrical potential energy
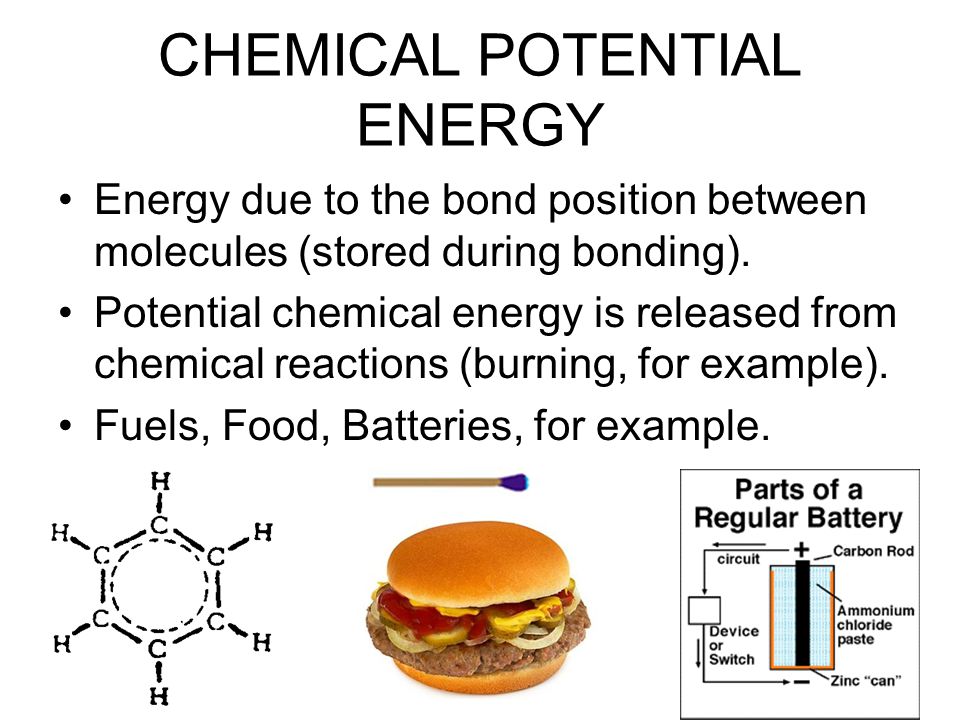
[...energy] is the energy stored in the bonds of compounds
chemical potential energy
Conservative forces are path [dependent or independent]
independent
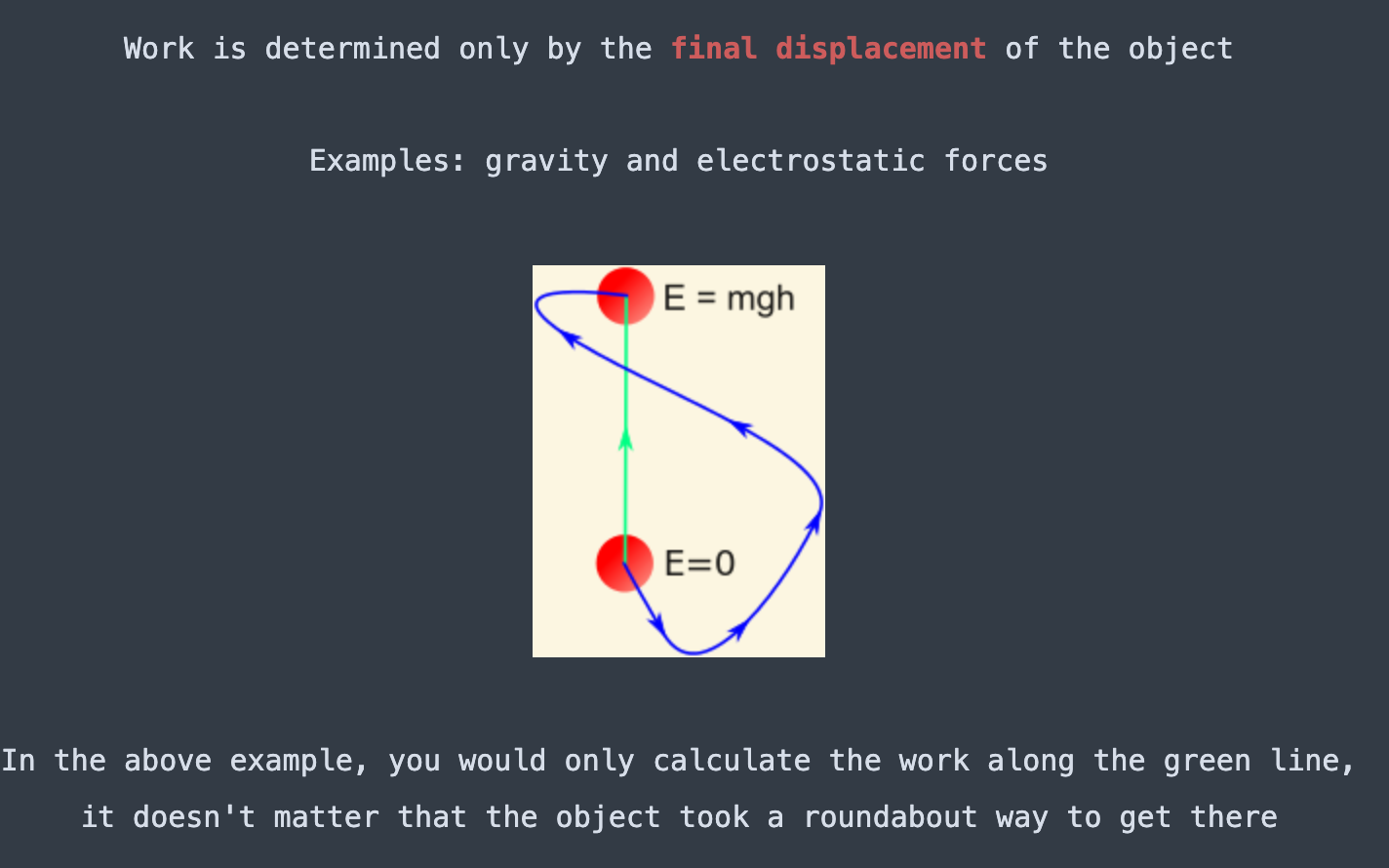
Non-conservative forces are path [dependent or independent]
dependent
