Forces
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What are scalar quantities
These are quantities that only have magnitude
What are vector quantities
These are quantities that have magnitude and direction
Explain why reaction time affects thinking distance of a car
distance = speed x time
So longer reaction time= longer distance
Examples of scalar quantities
distance
Speed
Mass
Energy
Volume
Density
Power
Examples of vector quantities
Displacement
Velocity
Weight
Force
Acceleration
Momentum
What is a force
This is a push or pull that acts on a object due to an interaction with another object
How does force affect an object
changes speed
Changes shape
Changes direction
What is weight
This is the amount of gravity acting on an object
What is electrostatic force
This is the force between two charged objects
What is thrust
The force causing an object to move
What is air resistance (drag)
The friction of the air on a moving object
What is upthrusr
The force of a fluid pushing a liquid upwards making it to float
What is compression
A force that acts inward on an object squeezing it
What is tension
This is a force transmitted by a string when pulled upon by forces acting on its opposite ends
What is reaction force
This is a force due a contact between two objects
What are the types of forces
contact
Non contact
What is a contact force
A force that acts between two objects physically touching
Examples of contact forces
friction
Tension
Reaction force
What is a non contact force
This a force that acts at a distance without any contact between bodies due to the action of a field
Examples of non contact forces
gravitational attraction
Electrostatic
Magnetic
What is weight
This a force acting on an object due to gravitational attraction
What are the importances of weight
objects stay firmly on the ground
Objects always fall to the ground
Keeps satellites in orbit
What is mass
This is the amount of matter in an object
What is Centre of mass
The point through the weight of an object acts
What is a resultant force
This is the addition of all the forces acting on an object
What does resultant force determine
the direction thr object will move in
The magnitude of the final force experienced by the object
What are balanced firces
This means that the forces acting on a object have combined in a way that they cancel each other and there’s no resultant
What are unbalanced forces
This means the forces acting on an object combine is such a way they don’t cancel each other out completely and there is a resultant force
What is normal contact force
The forces arising when an object rests against another object acting at a 90 angle to the plane of contact
What is work done
This is when an object is moved over a distance by a force applied in the direction of its displacement
What happens when a force acts in the opposite direction of an objects movement
The object will lose energy
What happens when a force acts in the direction of an objects movement
The object gains energy
What is friction
This is a force that opposes the motion of an object
What happens when friction is present
Energy is transferred by heating this raises the temperature and energy is transferred to the thermal store of the object and its surroundings
What is stretching
These are forces in opposite directions away from the object
What is bending
These are forces that distort the object
What is compressing
Forces in the opposite direction towards the object
When an object is compressed what forces are acting
weight of the mass
Reaction force from the surface to the spring
they act towards each other
What forces are acting on a stretched object
The weight of the mass
The tension in the spring
they act away from each other
What forces are acting on a bent object
weight of the mass
Reaction force
What is deformation
This is a change of shape
What are the types of deformation
elastic
Inelastic
What is elastic deformation
When an object returns go the original shape when the stretching force is removed e.g rubber bands, fabrics, steel springs
What is inelasic deformation
This is when objects remain stretched and do not return to their original shape when the stretching force is removed e.g plastic clay glass
What is hookes law
The extension of an object is directly proportional to the force applied up to the limit of proportionality
What does spring constant show
The higher the spring constant the stiffer the object
What is elastic potential energy
The energy stored in an elastic object when work is done on it
Required practical

What are the possible systematic errors when measuring extension
make sure measurements are taken at eye level to avoid parallax error
What are random errors in measuring extension
The accuracy of an experiment is reduced if there is no pointer
What are the safetY considerations when measuring extension
wear goggles in case spring snaps
Stand up during experiment to make sure no feet are directly under the mass
Place a mat below the masses to prevent any damage in case they fall
Use a G clamp to secure the clamp stand to the desk so that the clamp and masses do not fall over
What is a couple
These are two forces that are equal and opposite which act on an object without passing through the same point
What is a moment
This is the turning effect of a force about a pivot
M=F x D
Why is the door handle place on the opposite side of the hinge
This means for a given force the perpendicular distance from the pivot is larger this creates a larger moment making it easier to open the door
What is the principle of moments
If an object is balanced the total clockwise moment about a pivot equals the total anticlockwise moment about that pivot
What is pressure
This is the force per unit area
What is the formula for pressure in a liquid
P= h x p x g
P= pressure
H= height
p= density of the liquid in kg/m cubed
g= gravitational field strength
What is upthrust
This is a force that pushes upwards on an object submerged in a fluid
How does upthrust affect sinking
If the upthrust of an object is greater than its weight it will float and if it is lower it will sink
How does density affect sinking
If the density of the object is less than the density of the fluid it is immersed in it will float and if it is higher it will sink
Why will an object sink if it’s density is greater than the fluid it is in
This is because if the density of the object is greater than the fluid the object can never displace enough fluid to create an upthrust that will hold its weight up
What is distance
This is a measure of how far an object travels
What is displacement
This is a measure of how far something is from its starting point along with its direction
What is speed
This is the distance an object travels every second
What is acceleration
This is the rate of change of velocity
What information do velocity time graphs show
if an object is moving at constant acceleration or deceleration
The magnitude of acceleration or deceleration
What is Newton’s first law of motion
Objects will remain at rest or move at constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force
What is Newton’s second law
The acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on it and inversely proportional to the objects mass
What is Newton’s third law
When two bodies interact the forces they exert on each other are equal and opposite
What is inertia
This is the tendency of an object to continue in its state of rest or uniform action unless acted upon by an external force
What is the formula for inertial mass
Inertial mass = mass/acceleration
What is the relationship between inertial masses and acceleration
The larger the inertial masses the smaller the accelerations and vice versa
What is the stopping distance of a car
This is the total distance travelled during the time it takes for a car to stop in response to an emergency
Formula for stopping distance
Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
What is thinking distance
The distance travelled by a car from when a driver realizes they need to break to when they apply the brakes
What is braking distance
The distance travelled under the breaking force
What is the formula for reaction distance
Reaction distance= speed of the car x drivers reaction time
What factors affect thinking distance
speed
Tiredness
Distractions
Intoxication
What factors affect breaking distance
vehicle condition
Road condition
Vehicle mass
What is the work done by brakes when a vehicle slows down to a halt
Breaking force x breaking distance = kinetic energy
What is the formula for momentum
p=mv
When does momentum change
the object accelerates or decelerates
The object changes direction
The mass of the object changes
What is momentum in a closed system
The total momentum before an event is equal to the total momentum after the event
What are the types of collisions
elastic
In elastic
What is an elastic collision
This is where objects collide and move in opposite directions
What is inelastic collision
This is when objects collide and move in the same direction together
What is the formula for force in termd of momentum
Change in momentum / change in time
What are the safety precautions in cars
seat belts
Air bags
Crumple zones
Required practical: how does force affect acceleration

Required practical: how does mass affect acceleration

What are the systematic errors when considering effect of force
Ensure any weights removed from the weight hanger are transferred to the toy car or troller to ensure the total mass of the system remains constant
What are the random errors when considering effect of force and mass on acceleration
Inaccurate measurement of time ensure to take repeat readings when timing intervals and calculate an average to keep error yo a minimum
Start the toy car by releasing it allowing it to accelerate under the force of the weights attached to the string ensure not to give a push
What is friction
The resistance an object encounters when moving over a solid or through a fluid
Why do cars have maximum speed
there is a maximum forward force as the speed of the car increases air resistance increases until the air resistance is equal in size to forward force so the car can no longer accelerate
Why do hailstones reach terminal velocity
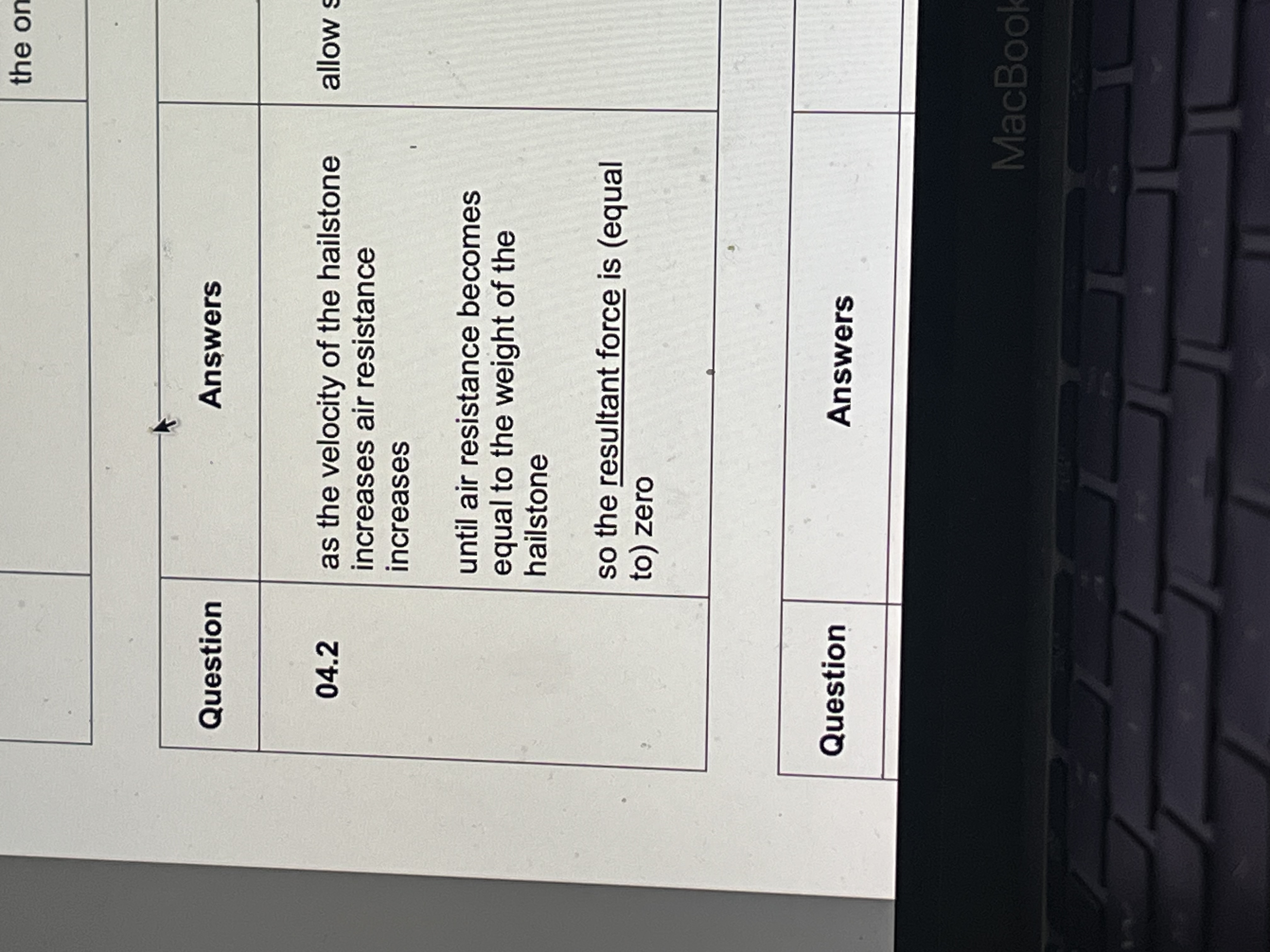
Why does temp of brakes increase as they are used
work is done due to friction
This causes an increase in the internal energy of brakes
How does a bumper reduce damage during collision
Increases the time taken to stop during the collisions
So the rate of change of momentum decreases
Reducing the force on the people