Biology - Unit 2 Section 1 (Cell Structure) - Structure and Function of Eukaryotic Cells
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
List all the organelles found in all eukaryotic cells.
centrioles
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
nucleus
ribosomes
cell-surface membrane
lysosome
golgi apparatus + vesicules
mitochondria
which organelles do only plant cells contain?
chloroplasts
cell wall
permanent vacuole
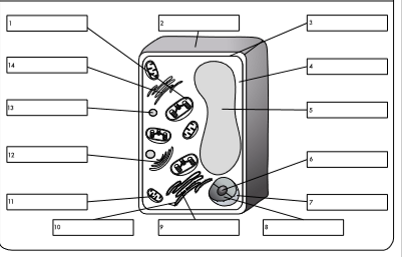
what is organelle 1?
chloroplast
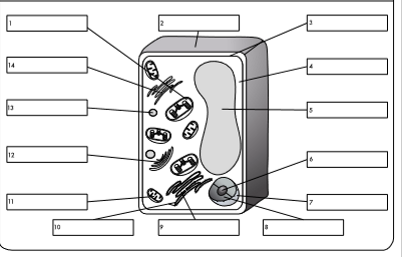
what is organelle 2?
cell wall
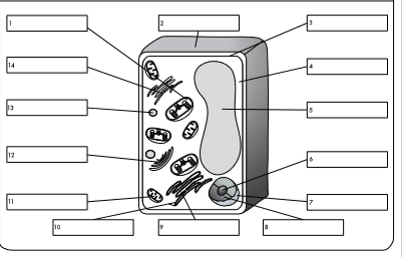
what is organelle 3?
cell membrane
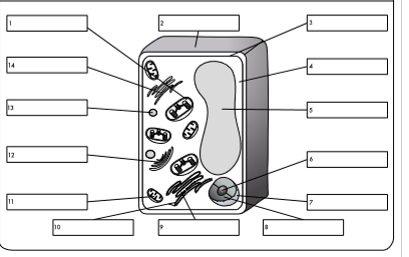
what is organelle 4?
cytoplasm
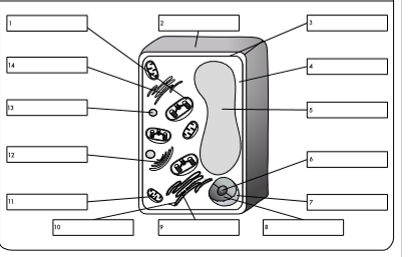
what is organelle 5?
permanent vacuole
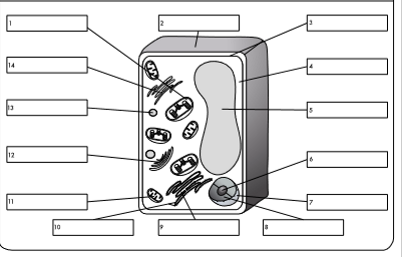
what is organelle 6?
nucleolus
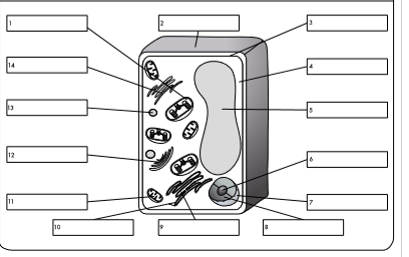
what is organelle 7?
nuclear envelope
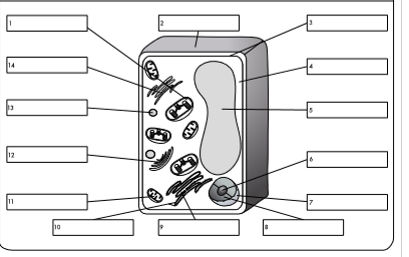
what is organelle 8?
nucleoplasm
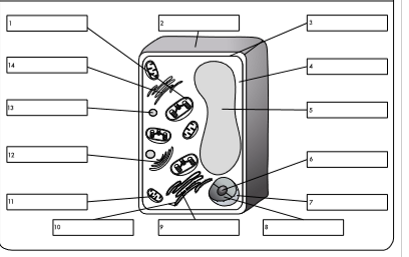
what is organelle 9?
rough endoplasmic reticulum
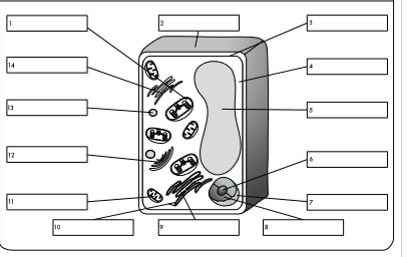
what is organelle 10?
ribosome
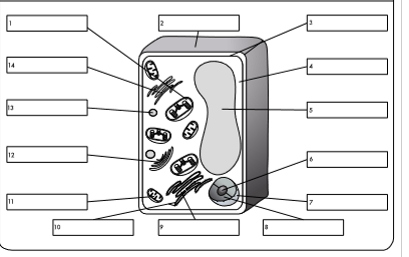
what is organelle 11?
mitochondrion
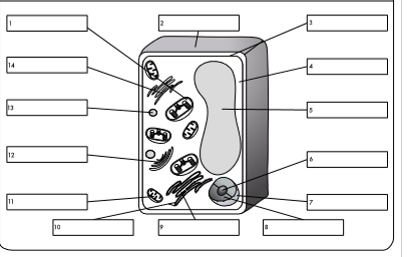
what is organelle 12?
golgi body
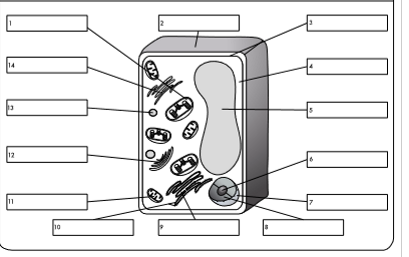
what is organelle 13?
lysosome
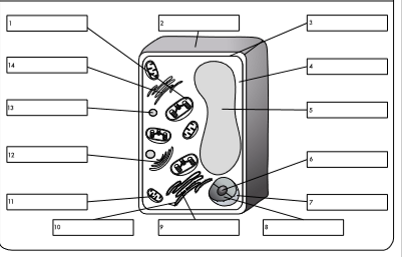
what is organelle 14?
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
describe the structure of the Nucleus
it is a membrane bound organelle, containing a nucleolus and chromatin (DNA stored in the nucleus in an uncoiled form), which are contained in the nucleoplasm
it has a double membrane called the nuclear envelope which has small holes in called the nuclear pores
the outer nuclear membrane is continuous with RER membranes
largest organelle
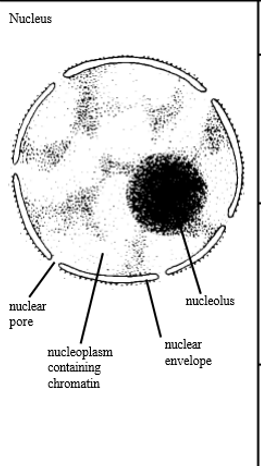
describe the function of the nucleus
envelope encloses and protects DNA
nuclear pores allow entry and exit of substances such as nucleotides and mRNA
chromatin condenses to form chromosomes for cell division, produces semi-complete ribosomes, coenzymes, nucleotides, proteins
describe the structure of the mitochondria
double membrane
inner membrane folded to form cristae
the space in between the cristae is called the matrix and is filled with fluid
the mitochondrion contains ribosomes (70S, smaller) , DNA and enzymes
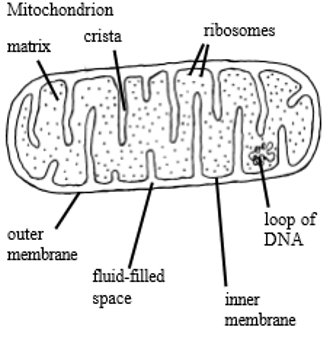
describe the function of the mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration, release energy and synthesise ATP
enzymes in matrix catalyse reactions
cristae hold these enzymes in place
produce some of the proteins they require (ribosomes)
cristae also increase surface area for aerobic respiration + metabolic reactions
describe the structure of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
system of hollow tubes and sacs, that are interconnected and flattened
covered with ribosomes
channels are called cisternae
describe the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
folds and processes proteins that have been made at the ribosomes
cavities of RER allow for transport of proteins
describe the structure of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
system of hollow tubes and sacs, that are interconnected and flattened
describe the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
synthesises and processes lipids
modifies substances such as steroid hormones
describe the structure of the golgi body
flattened cisternae - fluid filled membrane bound cavities/sacs - which are stacked on top of each other
connected to RER
has vesicles at edge
describe the function of the golgi body
processes and packages new lipids and proteins - modifies them before secretion (proteins)
makes lysosomes
cells that secrete a lot of enzymes contain a lot of RER and golgi apparatus
describe the structure of the golgi vesicles
small fluid filled sacs in the cytoplasm surrounded by a membrane
stores lipids and proteins made by the golgi apparatus and transports them out of the cell
describe the structure of the ribosomes
made up of a small subunit and a large subunit
made of rRNA and protein
float free in the cytoplasm or are attached to the RER
describe the function of ribosomes
site of protein synthesis and thus function relates to the steps of this
describe the structure of the lysosomes
vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes/digestive enzymes
type of golgi vesicle
membrane-bound
describe the function of the lysosomes
contains digestive enzymes called lysozymes - kept separate from cytoplasm by the membrane
can be used to digest cellular waste or invading cells
describe the structure of the chloroplasts
bound by a double membrane
contains membranes called thylakoid membranes
membranes are stacked up in some parts of the chloroplast to form grana
grana are linked by lamellae - thin, flat pieces of thylakoid membrane
contains thick fluid called stroma
contain some DNA
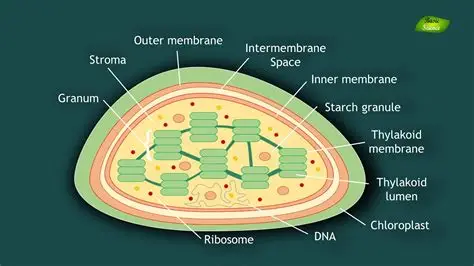
describe the function of the chloroplast
site of photosynthesis - some parts take place in grana, others in stroma
grana allow a large surface area for the assembly of chlorophyll and so photosynthesis
describe the structure of the cell membrane
found either on the surface of the cell or just inside the cell wall
made of a phospholipid bilayer and protein
describe the function of the cell membrane
regulates movement of substances into and out of the cell
has receptor molecules on out allowing it to respond to hormones
describe the structure of the cell wall
plants and algae - made of cellulose
microfibrils are embedded in a background material of pectin
describe the function of the cell wall
maintains the shape of the cell and allows it to remain turgid when water moves into it by osmosis, preventing it from bursting
describe the structure of the cell vacuole
membrane bound organelle
contains cell sap
membrane is called tonoplast
describe the function of the cell vacuole
maintains pressure inside the cell and keeps it rigid