Wade Moore's Radiation Physics EXAM 3
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
The Atom
fundamental unit of matter made up of Protons(+) Neutrons(+,-) Electrons (-)
Binding energy
what holds electrons in shell or the amount of energy needed to boot an electron from it's shell.
*Specific to ind. atoms and the shell where electron is located.
J to eV
1eV=1.6x10^-19J
SI Unit
J
Common Unit
erg
Influence chemical properties
Number and distribution of electrons
Determines stability and configuration of electrons
Number and distribution of protons and neutrons (nucleons)
Atomic Mass Unit (amu)
1/12 the mass of a C-12 atom.
1 AMU
1.66 x 10^-27 kg
AMU to MeV
1 amu = 931 MeV
Proton amu
1.0073 amu
Neutron amu
1.0087
Electron amu
0.00055
Atomic Mass of Atom
Addition of Protons and Neutrons
Strong Nuclear Force
the powerful attractive force that binds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus.
Nuclear Binding Energy
the energy required to decompose an atomic nucleus into its component protons and neutrons
Mass of Atom vs. Mass of its parts
Protons (amu) + Neutrons (amu) + Electrons (amu) = a mass higher than the atomic mass, therefore the mass of its parts is more than the mass of the atom.
Mass Defect
the difference between the mass of an atom and the sum of the masses of its protons, neutrons, and electrons. "missing" mass has been converted into the binding energy that holds the nucleus together.
If Carbon's mass defect is 0.09894amu, how much energy is created when this mass is converted into binding energy?
0.09894 amu x 931 MeV = 92 MeV
Expression of the relationship between energy and mass
E=mc^2
Speed of light
c=2.998x10^8 m/s
X superscript
A=Atomic Mass (# of protons + neutrons)
X subscript
Z=Atomic Number (# of protons)
As Mass Number increases (more protons)
it gets harder for atom to stay together.
How does atom compensate for increase mass number.
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear Fission
A nuclear reaction in which a massive nucleus splits into smaller nuclei with the simultaneous release of energy.
(Nuclear reactors and weapons)
*Waste and Heat byproduct
Fission Reaction
add neutron to U-235 to make U-236 = very unstable and begins fission, creating a "chain reaction."
U-236 breaks apart into different elements and release energy, the extra neutrons from this continually feed U-235 and create chain reaction.
Nuclear Fusion
a nuclear reaction in which atomic nuclei of low atomic number fuse to form a heavier nucleus with the release of energy. (Powers the stars)
*No waste, but engineering not capable yet. For now takes more energy than it creates.
Hydrogen Bombs
Combo of nuclear fission and fusion
Isotope
Atomic # (Z): Same
Neutrons: Different
Mass # (A): Different
Isotones
Atomic # (Z): Different
Neutrons: Same
Mass # (A): Different
Isobars
Atomic # (Z): Different
Neutrons: Different
Mass # (A): Same
Isomers
Atomic # (Z): Same
Neutrons: Same
Mass # (A): Same
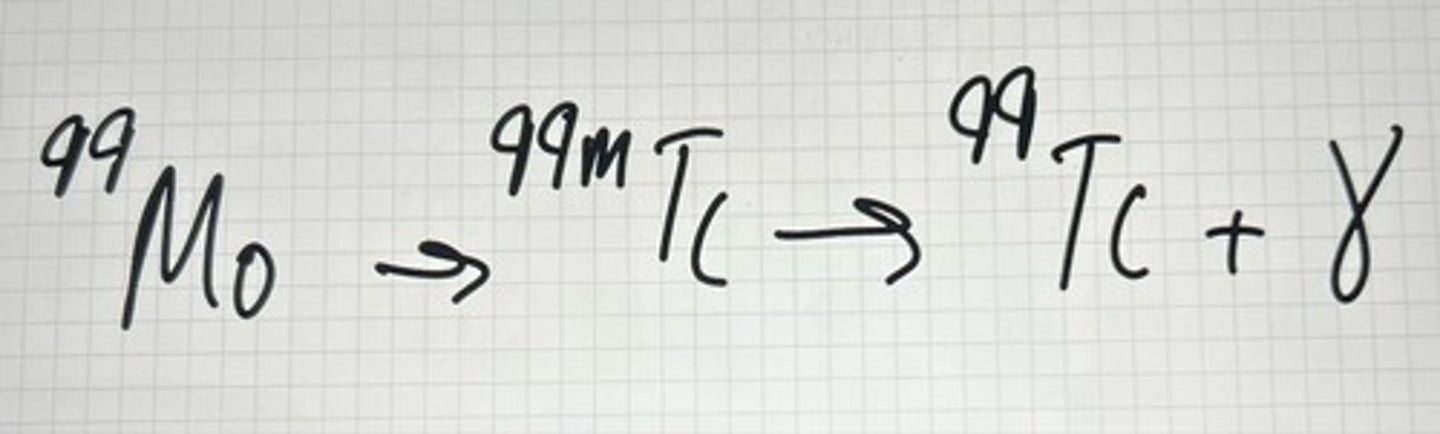
99mTc and 99Tc
Isomers
m in 99mTc
Metastable
Basic unit for measuring radioactivity
disintegration per unit of time (dps)
Common Unit for radioactivity
Curie (Ci)
MI Unit for radioactivity
Becquerel (Bq)
Conversions for radioactivity
1Bq = 1dps
1Ci = 3.7x10^10 dps or Bq
Activity formula
A=λN
λ=decay constant or 0.693/T^1/2
N=number of atoms
Decay formula
At=AoE^-λt
Secondary Decay formula
At=Ao/2^n
n=# of half lives
Half Life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay.
Physical Half Life
the time required for 50% of its atoms to decay to a more stable state
Biological Half Life
the time it takes for excretion processes to lower the amount of unchanged medication by half
Effective Half Life
the difference between the physical half-life and the biological half-life
Effective Half Life formula
Te=(Tp)(Tb)/Tp+Tb
Tp= Physical half life
Tb= Biological half life
Secular Equilibrium
Half life of parent is much longer than the daughter.
Over time daughter activity builds up to activity of parent and appear to have equivalent half lives. The daughter activity builds up quickly because the parent's decay is so long that it is constantly feeding new daughters.
Transient Equilibrium
If the parent half-life is longer than the child half-life but is not that long.
Daughter activity appears the same as the parent because the parent's decay is feeding the production of the daughter but since their half-lives are similar enough, the eventually come to a point of equilibrium with a decay curve following the same line.
Transient Equilibrium in Nuclear Medicine
In 99Mo (T1/2=66hr) --> 99mTc (T1/2=6hr)--> 99Tc, the peak time is about 24 hours. That is, we should extract 99mTc activity from the generator once a day at the same time.
Particulate radiation
tiny particles of matter that possess mass and travel in straight lines and at high speeds
Alpha Particles ⍺
⍺ (2p & 2n) charge is +2 and its massive from atomic perspective; 4amu.
neutron/proton (n/p) ratio too low
always release 2 electrons
*Atomic # of parent greater 82, get ⍺ release.
Very low penetration.
Energy released formula for Alpha particle
Q=Mp-Md-M⍺-2Me
*don't forget to convert amu to MeV
Energy of the ⍺ particle formula
E⍺=Q/1+M⍺/Md
⍺ particle decay scheme
down and to the left.
⍺ are mono-energetic in that an atom releases the same amount of energy every time it decays.
Pure β emitters
does not result in gamma only β
Beta Particles β-
very small with a - charge, same as electron except they originate in the nucleus, specifically a neutron.
(no neutrons or protons; same mass of electron)
Occurs when neutron/proton (n/p) ratio is too high.
Intermediate penetration power.
Neutrino v
uncharged infinitely small particle that go through essentially everything.
*Share energy release with β
Energy released for a β- particle formula
Q=Mp-Md-Mβ-+e
Mβ and e cancel out and formula becomes
*Q=Mp-Md (don't forget to convert amu to MeV)
β- spectrum, Mean energy
1/3 Emax or Q
*rare that they occur at max energy because β and v share the energy.
β- decay scheme
down and to the right because the atomic # went up.
Positron β+
positive charge beta particle. Neutron/proton (n/p) ratio too low but atomic # is less than 82.
Intermediate penetration power.
Energy released for a β+ particle formula
Q=Mp-Md-Mβ+-Me
Decay scheme for β+
down and to the left, *but they don't occur in nature because β+ and e are attracted to each other and instantly destroy themselves.
Annihilation Radiation
When β+ and e collide they always release energy at 180 degree angles and allow us to do PET imaging. (Helps determine where an event occurred in the body)
*Result in 2, 511 keV photons.
Example of ⍺
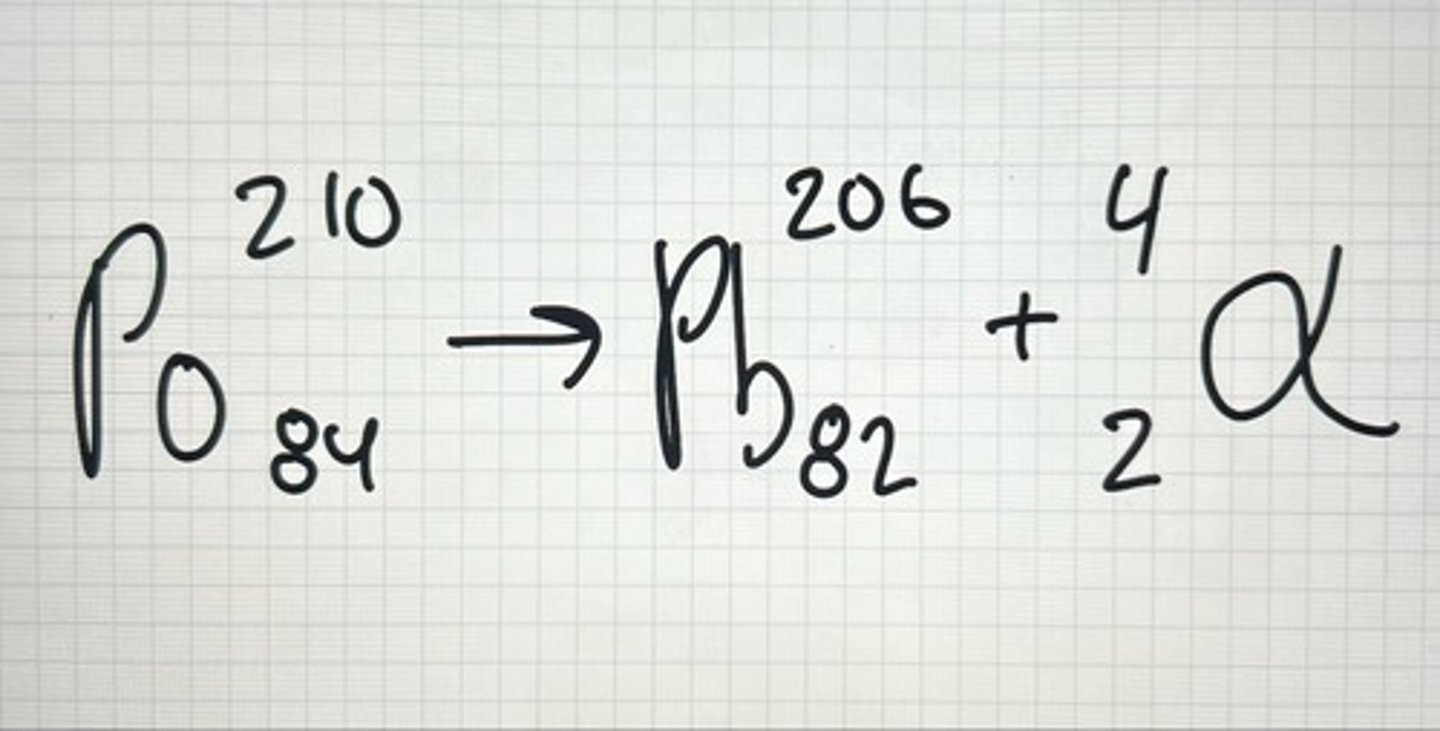
Example of β-
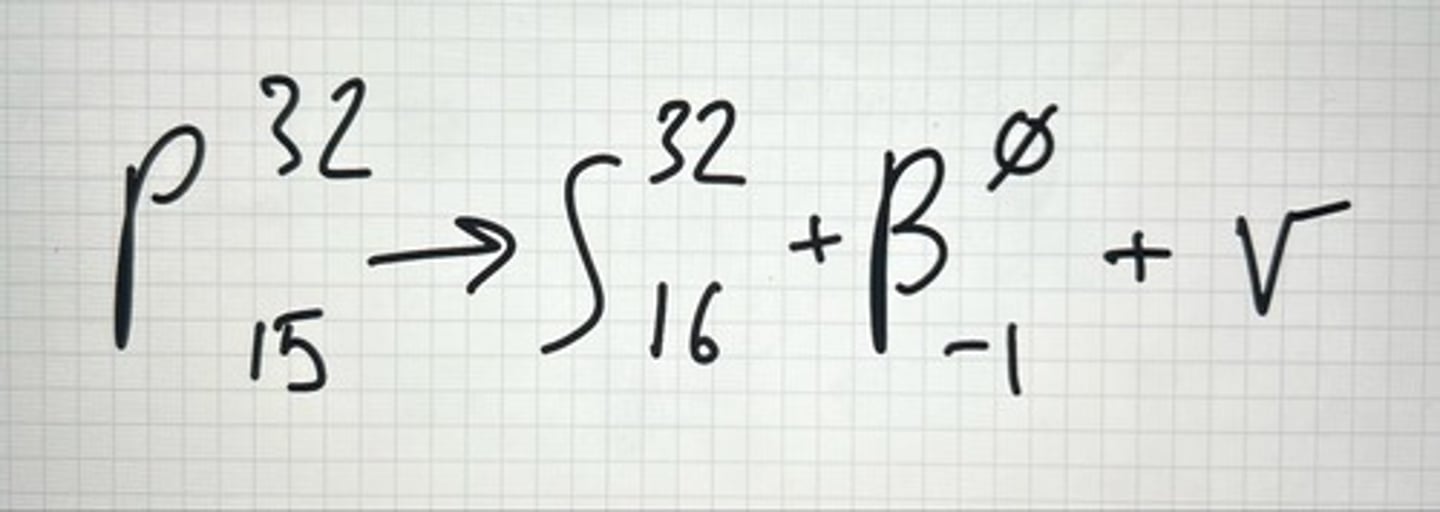
Example of β+
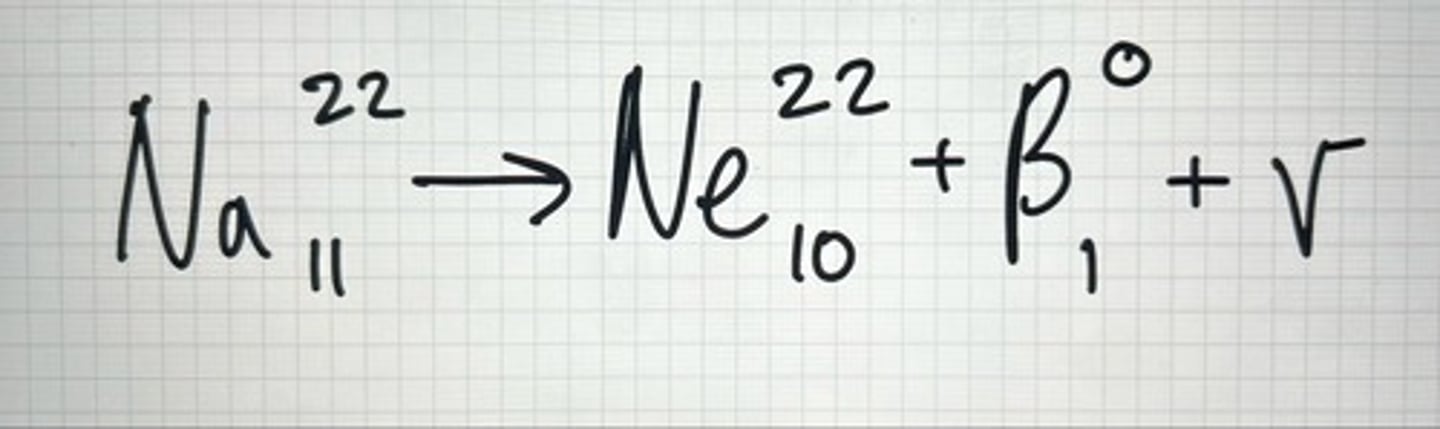
Electromagnetic radiation
a kind of radiation including radio waves, infrared, visible light, UV, X- ray, and gamma rays that have wave (photon) and particle behavior but have no mass.
Electron capture
When n/p ratio is too low but instead of releasing β+, an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus of its own atom.
When k-shell e pulled to nucleus, L-shell e moves down to replace it, releasing energy in an X-ray.
Characteristic X-rays
x-rays produced by transitions of orbital electrons from outer to inner shells.
Have distinct energies from atom to atom.
Bremsstrahlung x-rays
Produced when a projectile electron or β- is slowed by the nuclear field of a target atom nucleus. A spectrum of energies that also generate heat.
*e or β- interact with matter
Bremsstrahlung x-rays and Atomic # of the medium its passing.
directly proportional, Atomic # ⬆️ = Bremsstrahlung ⬆️
X-ray and high atomic number materials
generate more x-rays. (Lead, Tungsten)
X-rays and low atomic number materials
generate lower energy x-rays (Carbon)
How we use x-ray
electrons are accelerated from the cathode to a rotating tungsten anode, where their kinetic energy is converted into x-rays. The rotating anode helps dissipate heat. X-rays are emitted in all directions but are directed through a window and collimator towards the patient. Filters remove low-energy radiation to reduce patient exposure.
Gamma Rays (ɣ)
high energy photons emitted from excited nuclei (high energy state), following the beginning of a radioactive decay. (no such thing as a pure gamma-emitter, nucleus must undergo another type of decay first, such as alpha or beta). No change in atomic number or mass.
Gamma Ray example
Auger Electron (Competing Event)
Inner shell electron gets ionized, another drops down, emits energy but this energy ejects another (outer shell) electron from atom. No characteristic x-rays produced.
Conversion Electron (Competing Event)
Starts from within the nucleus. Instead of a gamma ray the nucleus transfers excess energy directly to an inner shell electron and is ejected from the atom.
Gamma Rays can result in......
conversion electrons, auger electrons, and characteristic x-rays.
Ionizing Radiation
incident radiation with enough energy to knock electrons off atoms or molecules, producing ions
Ion pair
Original atom & emitted orbital electron
Ionizing potential & binding energy relationship
all ionization potentials are binding energies but not all binding energies are ionization potentials.
Ionizing potential
The amount of energy required to ionize (remove) the least tightly bound electron in an atom of that element (outermost shell). If the free electron has enough energy it can also cause ionizations.
Excitation
instead of electron emitting out of atom, it can just move up a shell, losing energy. It will eventually drop back down to its ground state giving off photons of visible light.
Specific Ionization
number of ion pairs formed per unit distance, traveled by the incident radiation.
Linear Energy Transfer (LET)
average energy deposited per unit length/distance traveled by the incident radiation.
High LET
Alpha particles, a lot of energy in a short distance.
*pose internal risk, but are not penetrating so are not an external risk. (easy to shield).
Low LET
Beta particles, x-rays and gamma rays