Biochemistry - Urea Cycle
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the 5 basic steps for breakdown of amino acids?
1. remove amino group
2. take amino group to liver for nitrogen excretion
3. entry into mitochondria
4. prepare nitrogen to enter urea cycle
5. urea cycle
What are the 2 end products of the urea / ornithine cycle?
urea and arginine
What 2 waste products are excreted as urea?
nitrogen and CO2
What are the symptoms of hyperammonemia?
an intoxicated person: slurred speech, confusion, stumbling gate, etc.
What causes hyperammonemia, generally?
pathologies of the liver
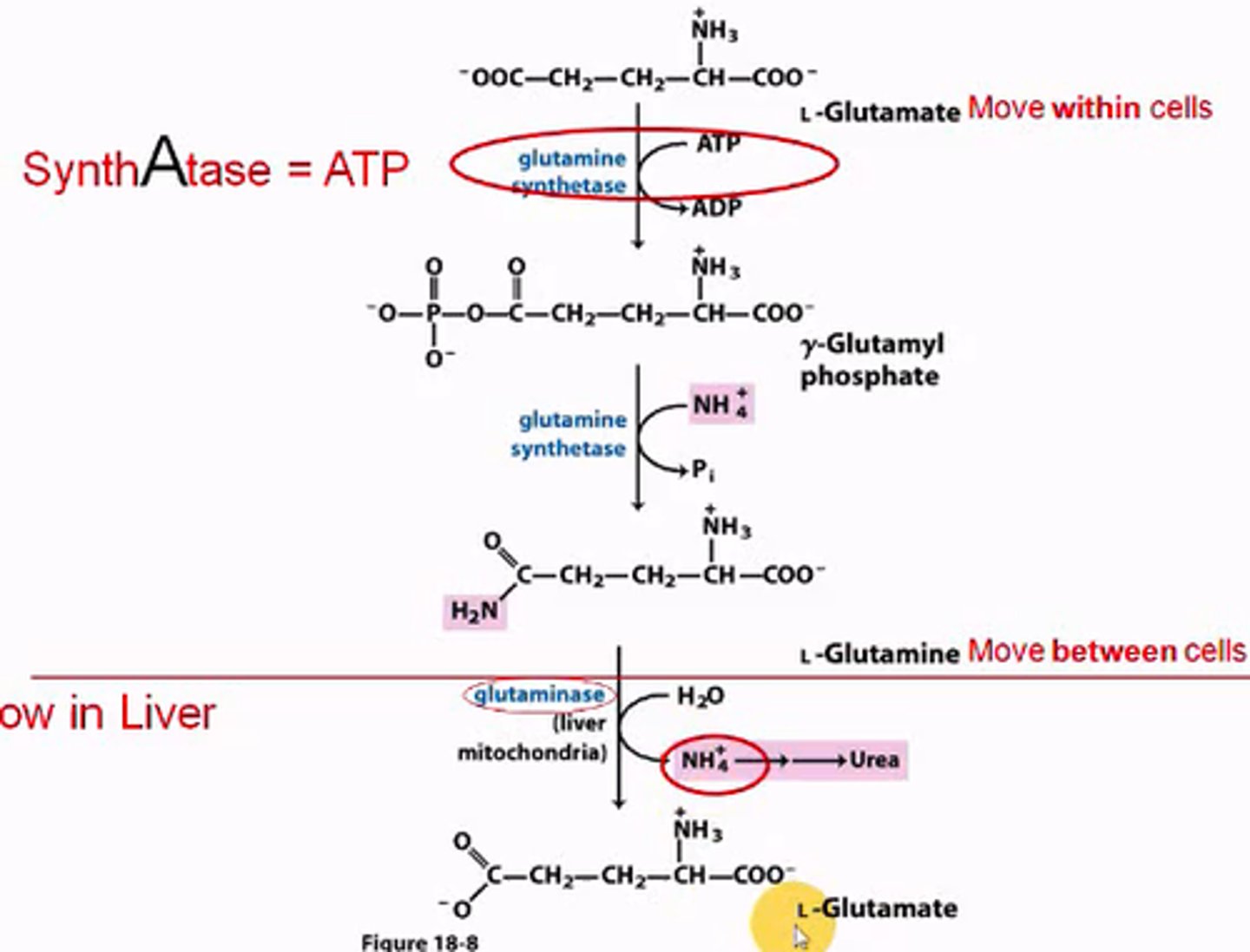
Which enzyme adds free nitrogen to glutamate to form glutamine (the principle nitrogen carrier)?
glutamine synthetase
What are the 3 carriers of nitrogen, and what distinguishes each?
1. Glutamate:
1 amine group transferred
moves WITHIN cells
aminotransferase-makes glutamate
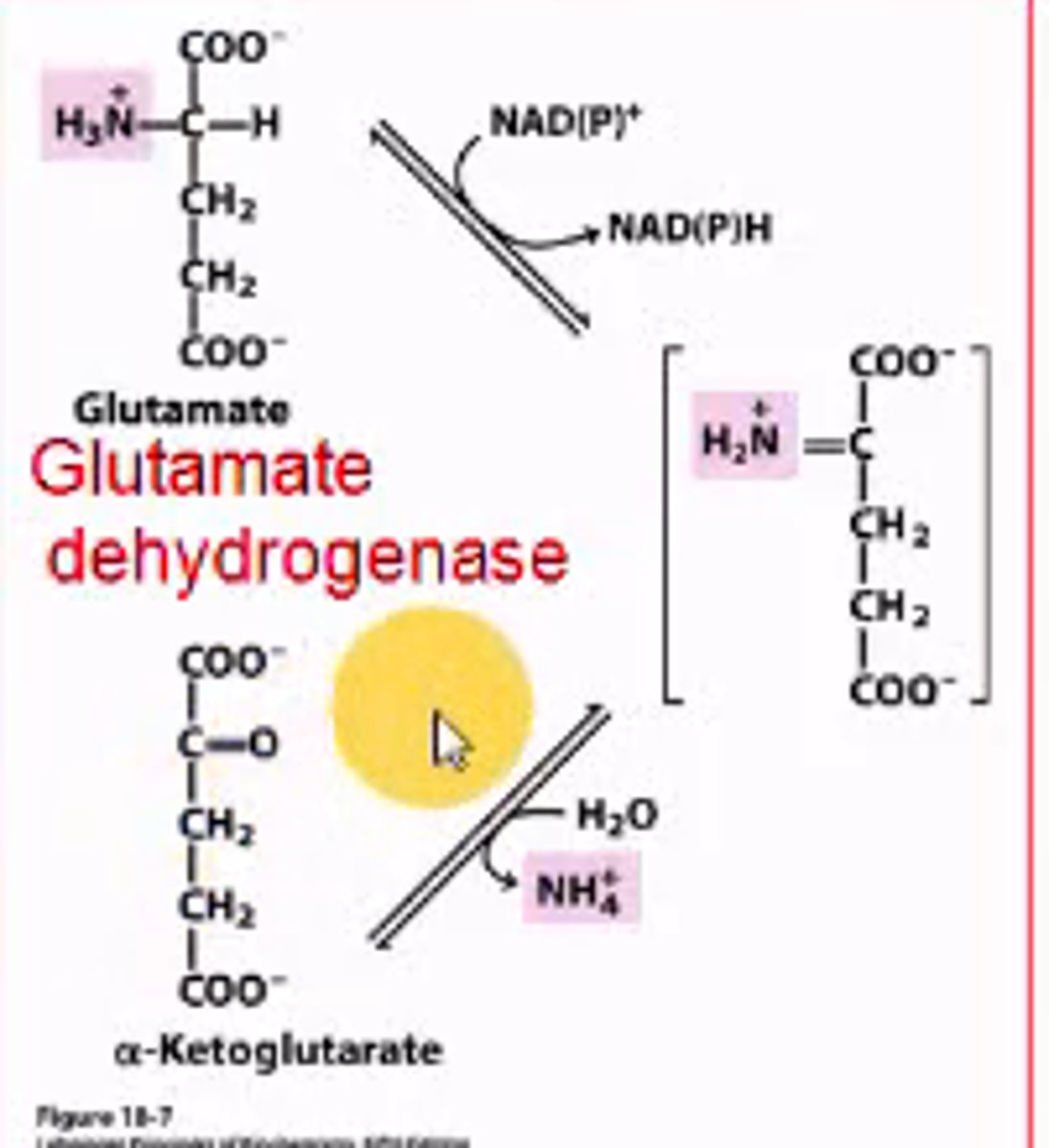
glutamate dehydrogenase-opposite
2. Glutamine
2 amine groups transferred
moves BETWEEN cells
3. Alanine
from muscles
In the liver arginine stimulates which enzyme to process glutamate, and to what is glutamate processed by this enzyme?
N-acetyl-glutamate synthetase;
N-acetyl-glutamate
Which enzyme removes nitrogen from glutamine in the liver? What is formed? Where in the liver cell does this process occur?
glutaminase;
glutamate;
the mitochondria
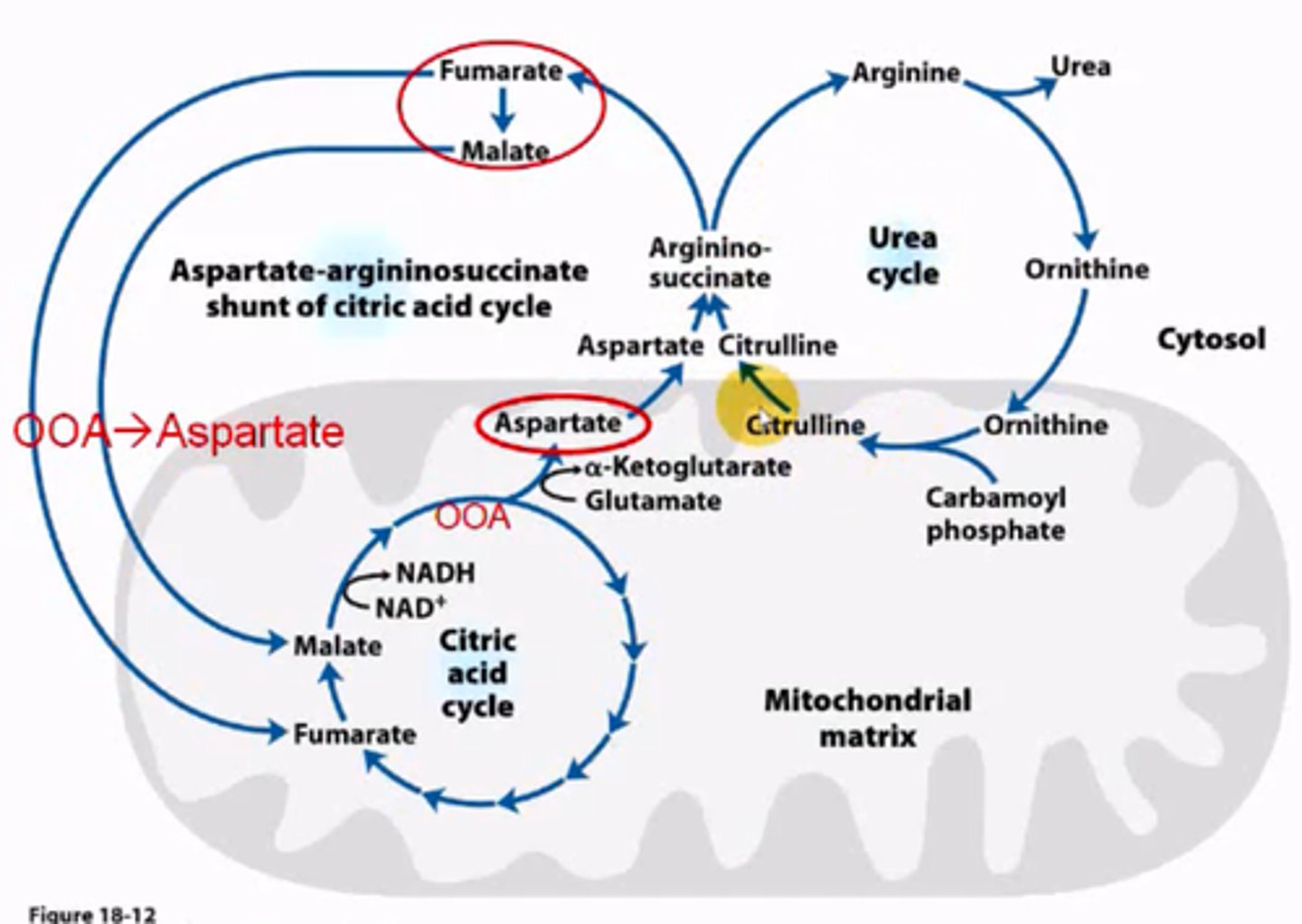
What is the Aspartate-arginino-succinate shunt of the citric acid cycle?
connects urea cycle and TCA by fumarate and oxaloacetate
Which enzyme removes the amine group from an amino acid? What is it's coenzyme?
aminotransferase;
coenzyme = PLP
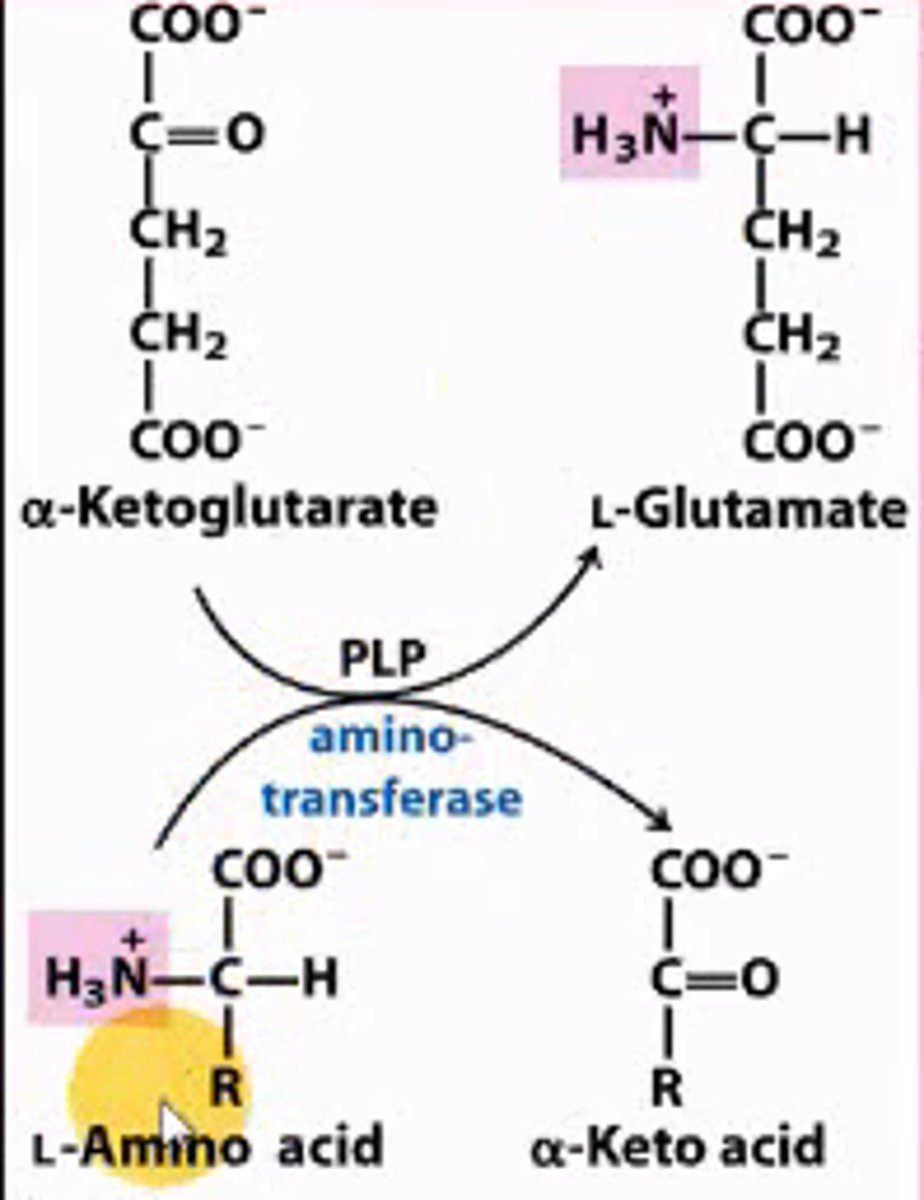
What is formed when an amino acid has it's amine group removed?
an alpha-keto acid
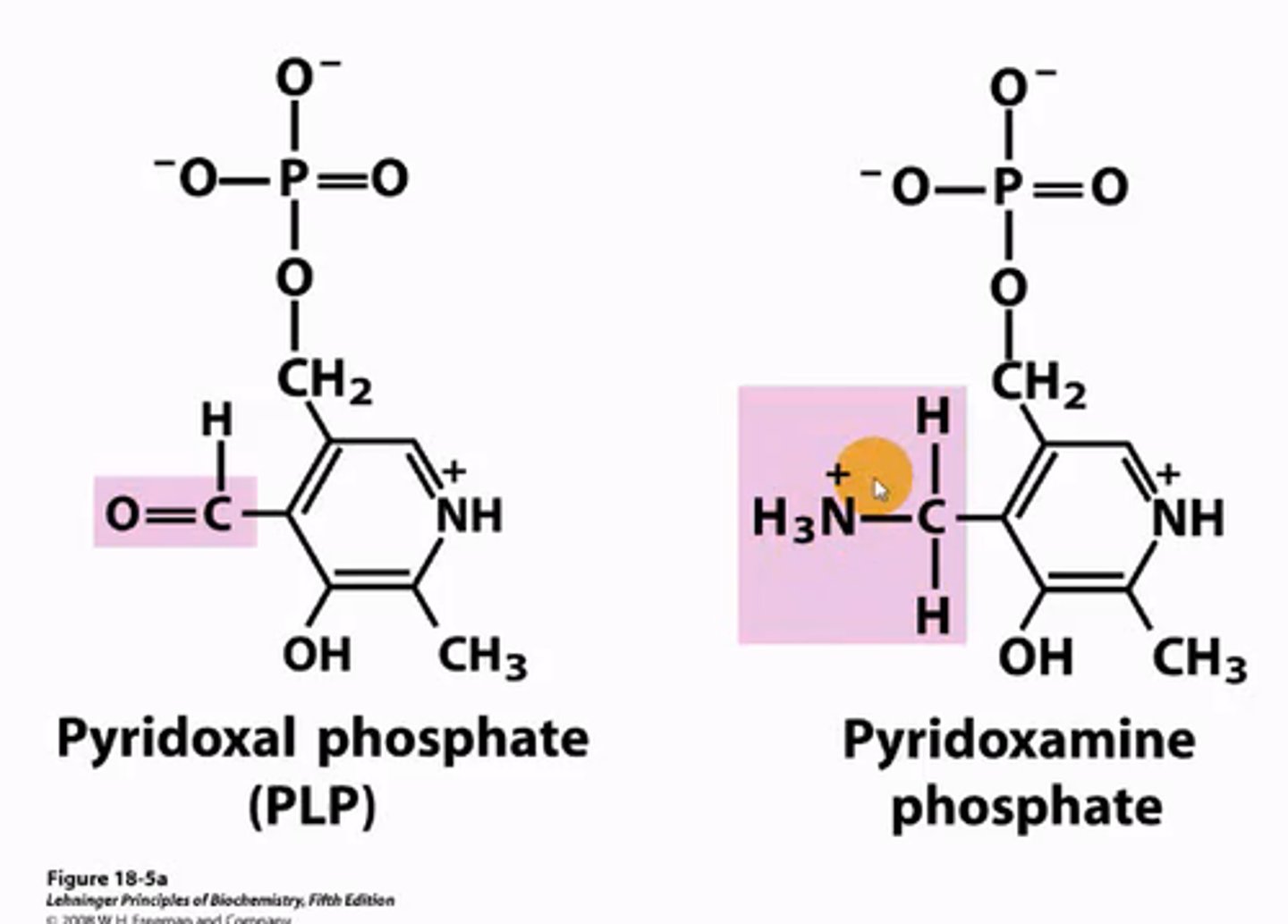
What is PLP?
PLP = Pyridoxyl Phosphate
attaches to the amine group being removed from an amino acid by aminotransferase to become pyridoxine phosphate.
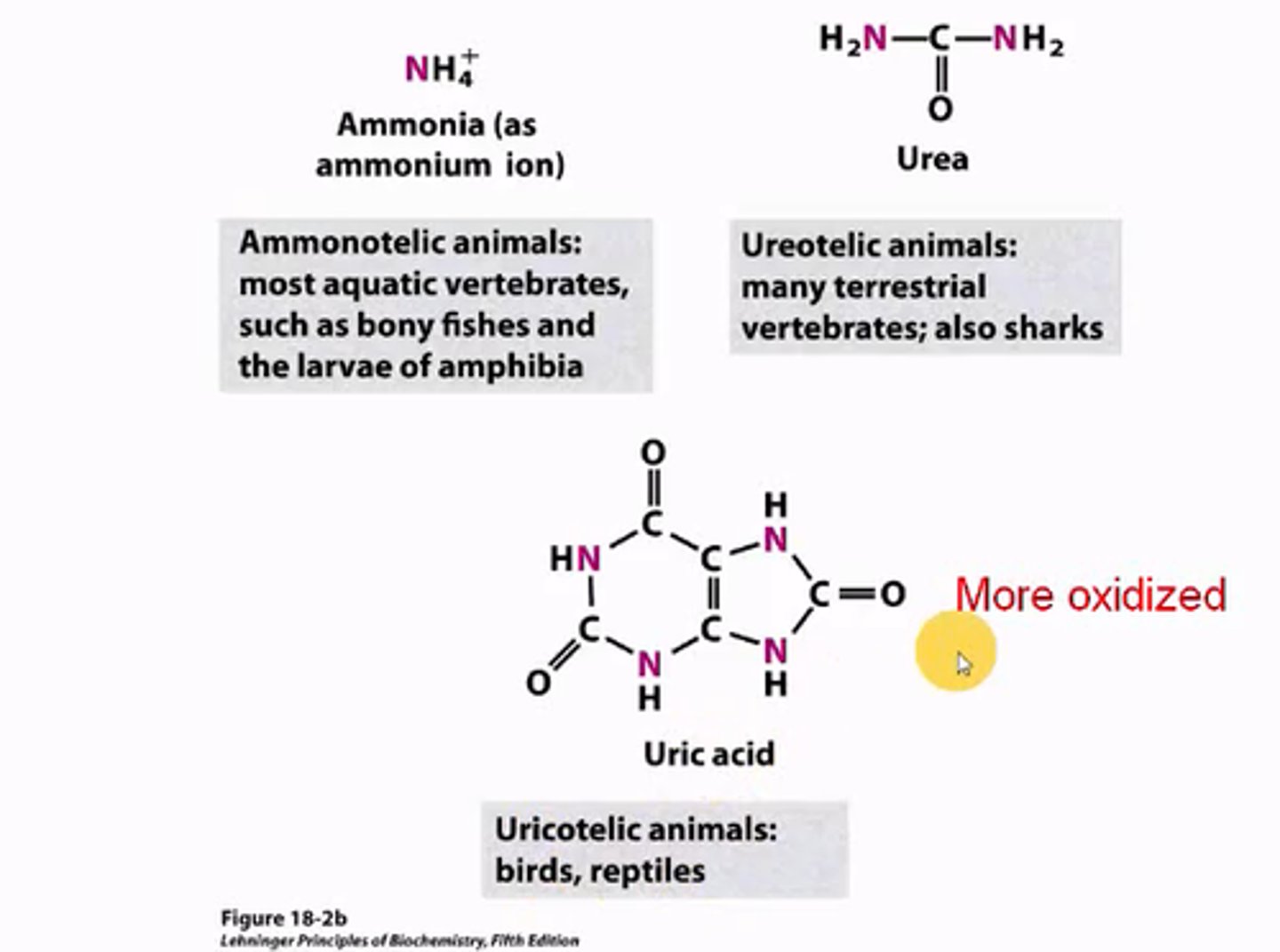
What are the 3 forms of nitrogenous waste excreted, and which organisms excrete each?
What inactivates pepsinogen once it enters the duodenum?
the ~neutral pH
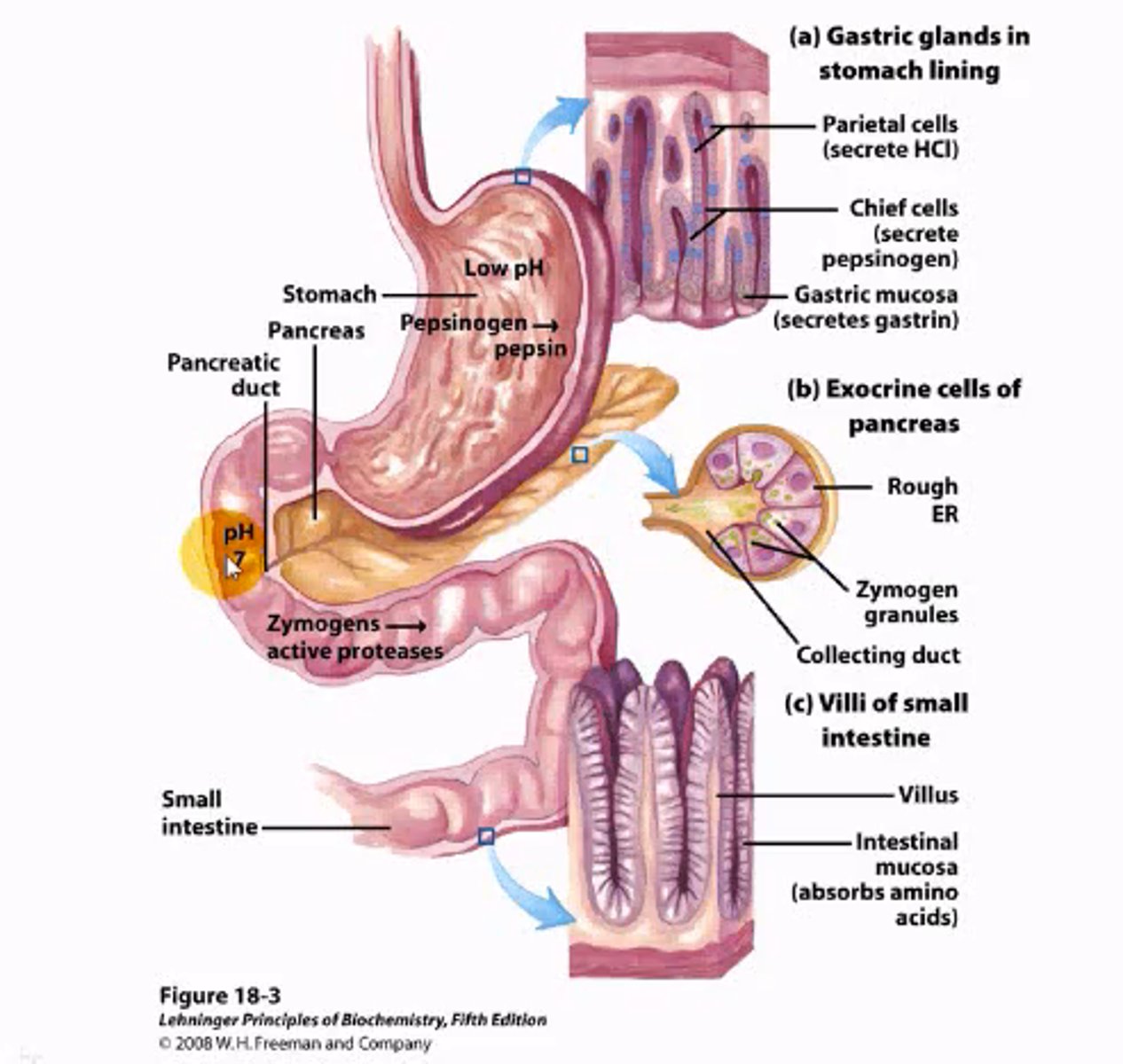
What 3 reactions does PLP catalyze?
1. Transamination of Amino Acids
2. Racemization
3. Decarboxylation (when a nitrogen transfer is involved, otherwise TPP)
What is TPP?
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP or ThPP), or thiamine diphosphate (ThDP), is a thiamine (vitamin B1) derivative which is produced by the enzyme thiamine pyrophosphatase. Thiamine pyrophosphate is a coenzyme that is present in all living systems, in which it catalyzes several biochemical reactions. It was first discovered as an essential nutrient (vitamin) in humans through its link with the peripheral nervous system disease Beriberi, which results from a deficiency of thiamine in the diet.[1]
Which enzyme removes the nitrogen from glutamate in the liver, and what is the product?
glutamate dehydrogenase;
alpha-ketoglutarate
What is the mechanism for glutamine synthetase's conversion of glutamate into glutamine, and what happens to glutamine after this conversion?
G.S. uses ATP to phosphorylate the gamma carboxyl, then replaces the phosphate with an ammonium group (nitrogen) forming glutamine. Glutamine can now move between cells to the liver where glutaminase hydrolyzes the ammonia off as ammonium, and converts glutamine back into glutamate.
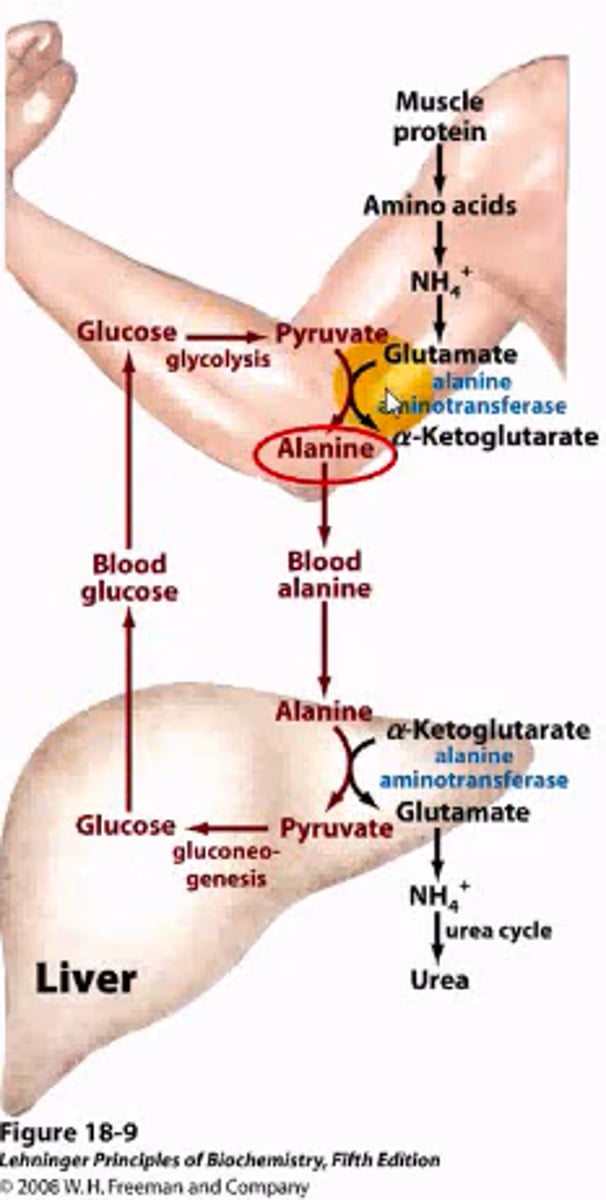
What is the pathway for alanine mediated transfer of nitrogen, and which tissue is this method associated with?
Muscle tissue is broken down into amino acids, and the nitrogen from these aminos is transferred to glutamate. Alanine aminotransferase transfers the nitrogen to alanine (derived from pyruvate through muscle glycolysis), leaving alpha-ketogluterate, and sending alanine to the liver. Alanine from here is converted back to pyruvate for gluconeogenesis, having it's nitrogen attached onto another alpha-ketogluterate by alanine aminotransferase which forms glutamate. Glutamate is then sent to the urea cycle.
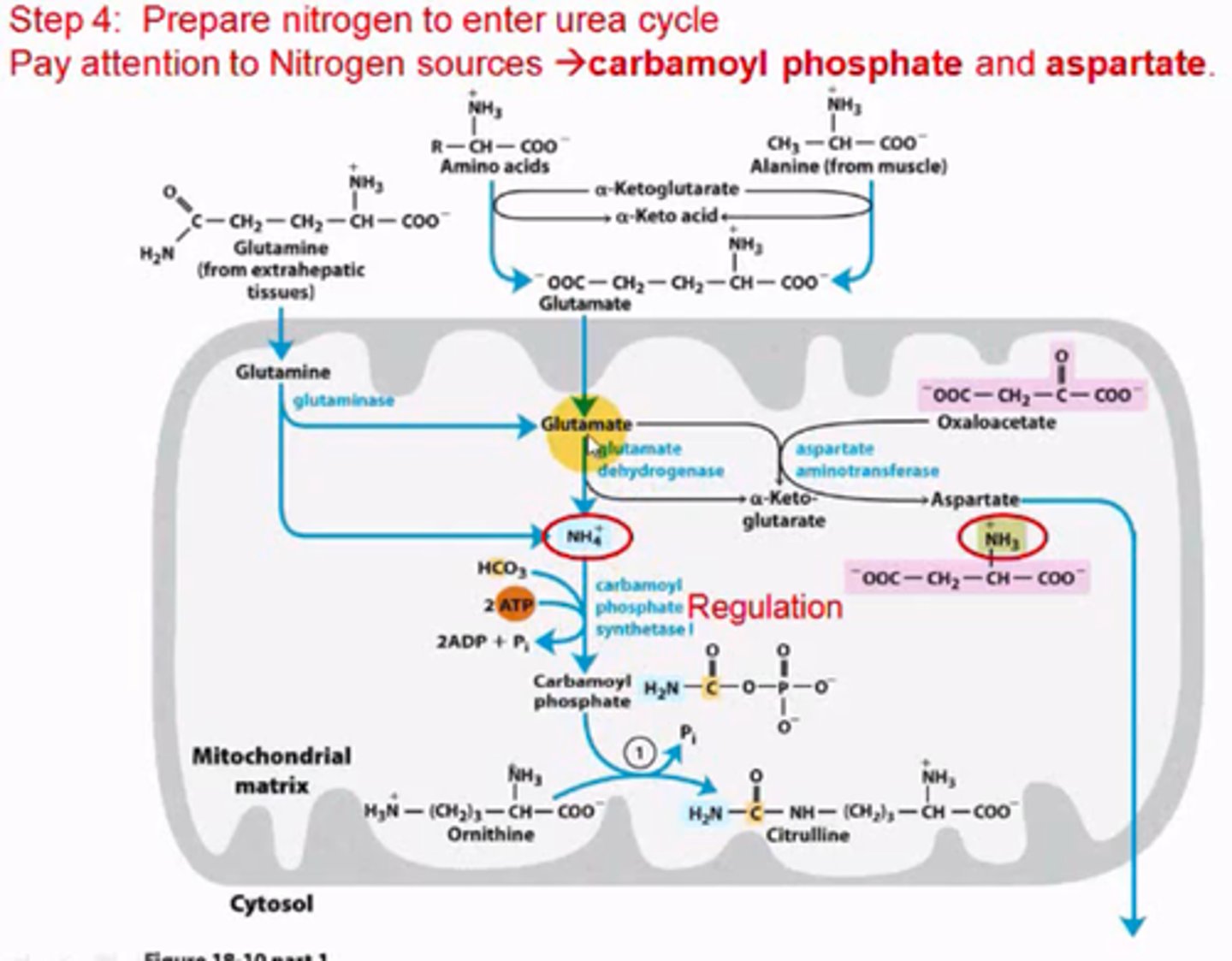
Where is regulation centered for the urea cycle, and why?
Up or down-regulation of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase; requires 2 ATP to form carbamoyl phosphate from ammonium and bicarbonate.
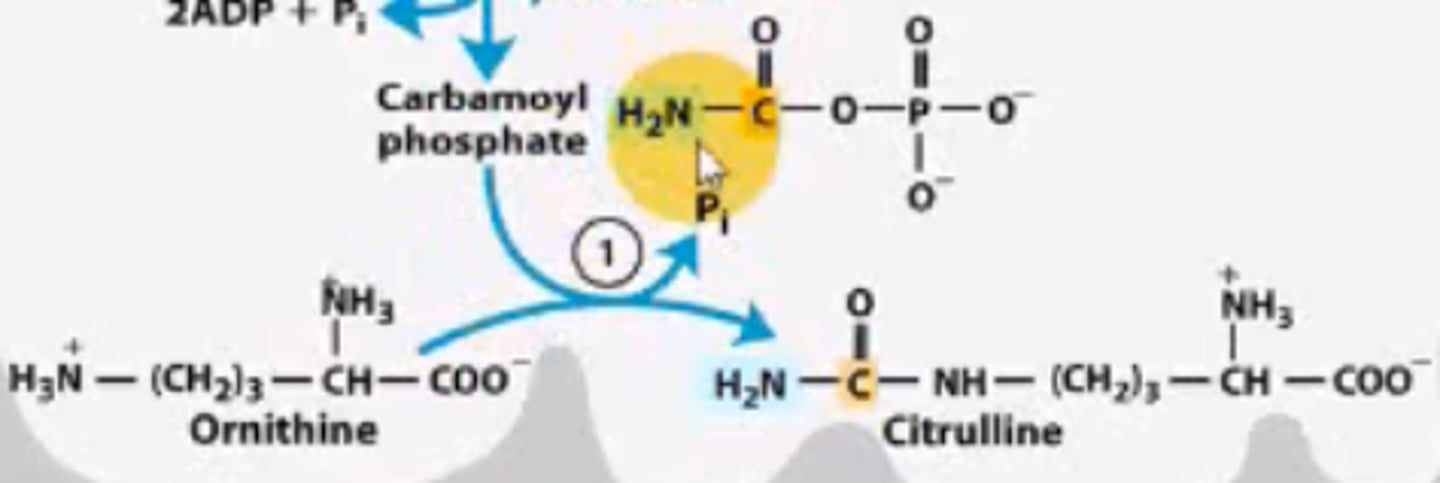
What is step 1 of the urea cycle?
Condensation of Ornithine with carbamoyl phosphate to form citrulline.
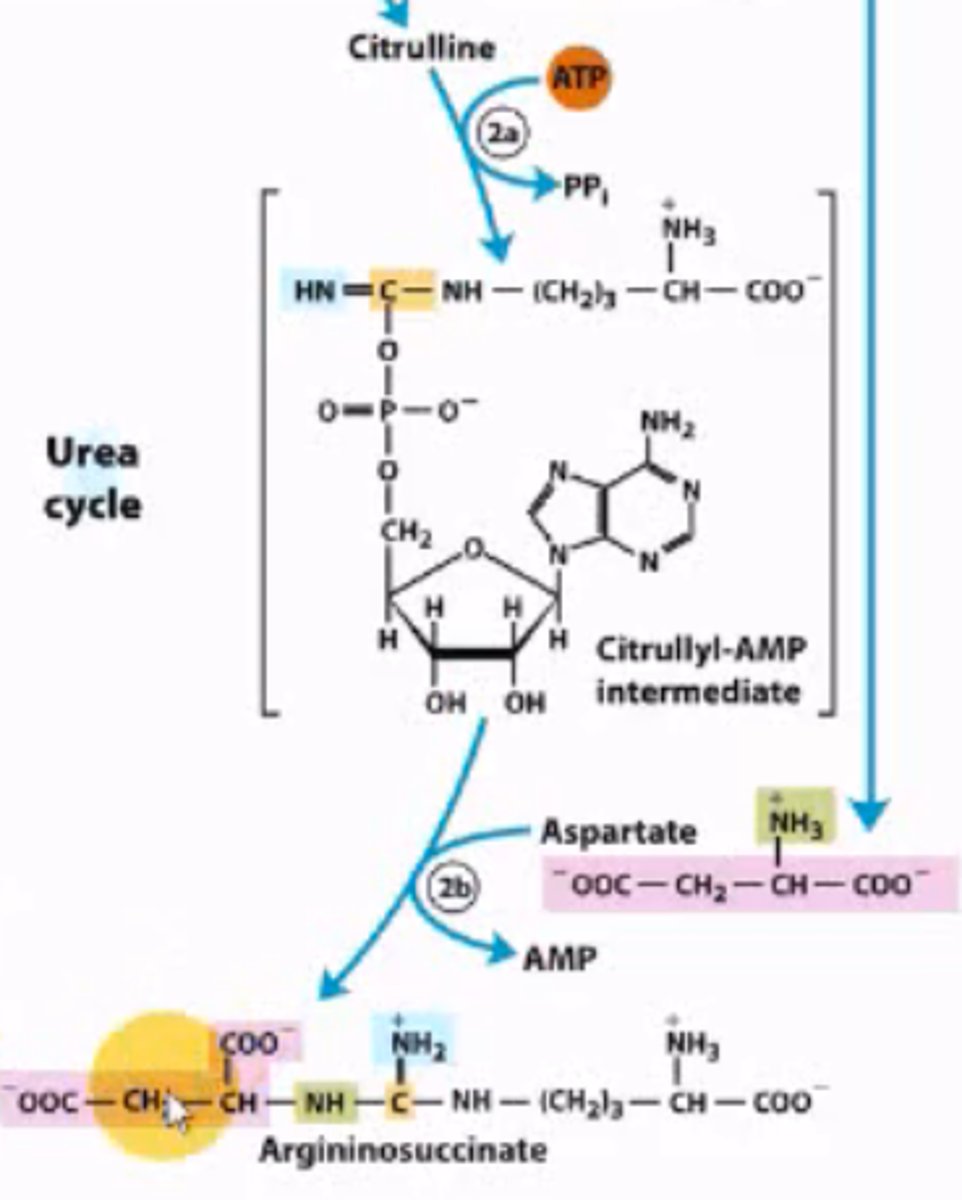
What is the 2nd step in the urea cycle?
2 parts:
1. An ATP is used to convert Citrulline into citrullyl-AMP intermediate.
2. Which condenses with aspartate, i.e. the 2nd source of nitrogen) to form argininosuccinate.
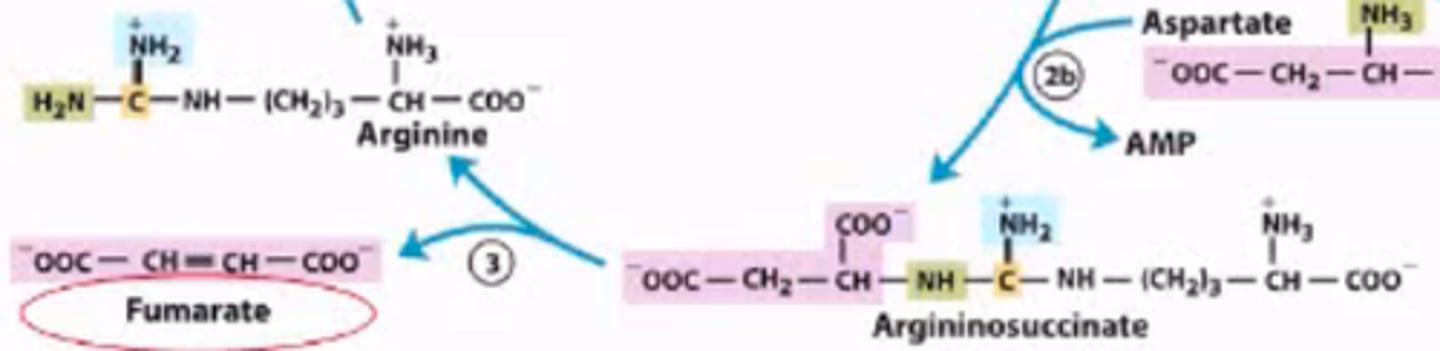
What is the third step of the urea cycle?
Argininosuccinate breaks into fumarate and arginine. Fumarate becomes an intermediate in the Aspartate-arginino-succinate shunt of the citric acid cycle.
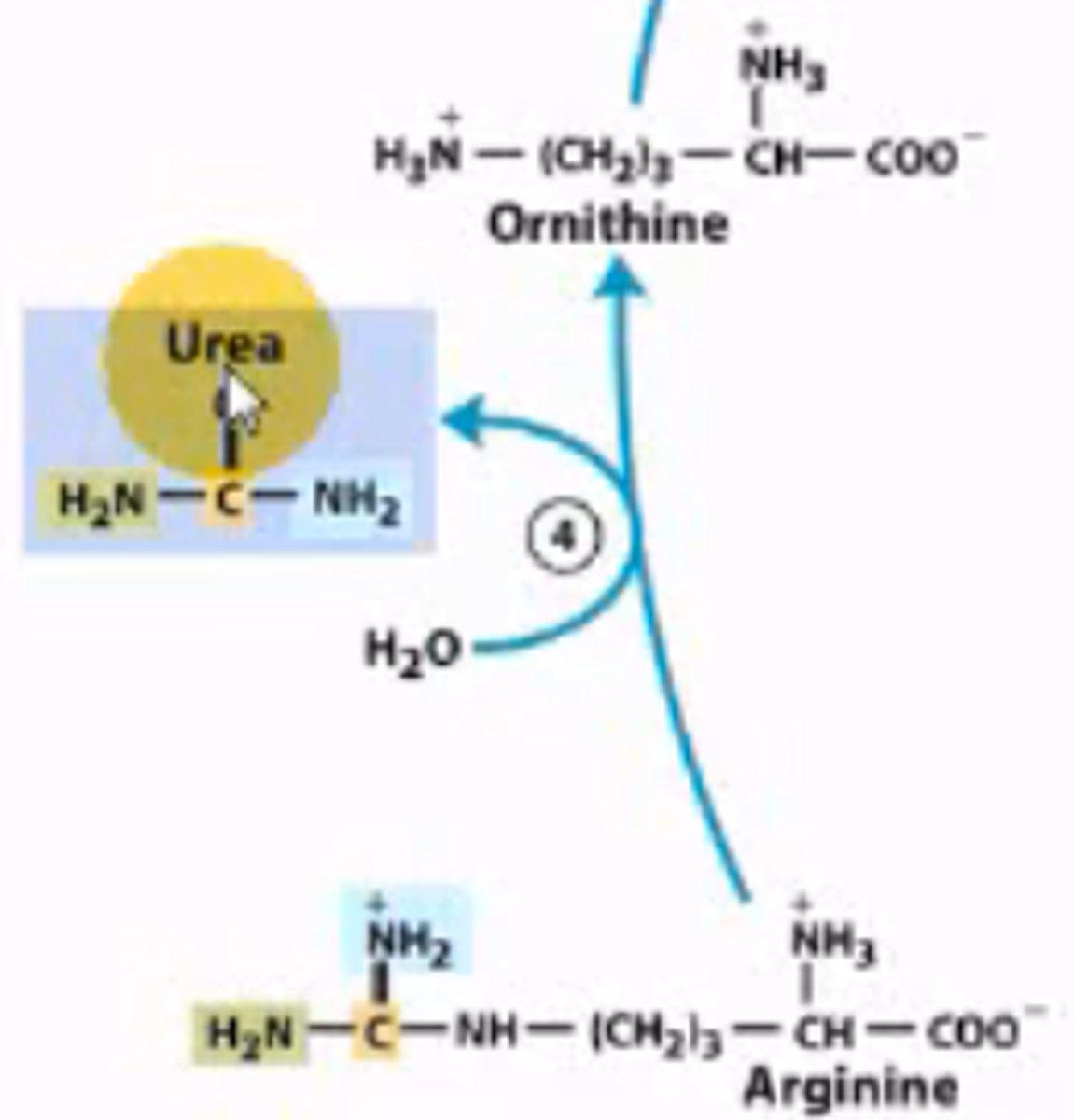
What is the fourth step of the urea cycle?
Arginine breaks into urea and ornithine. Urea is transported to the kidneys for excretion, and ornithine is recycled throughout the urea cycle.
What are the 2 sources of nitrogen for the urea cycle?
1. carbamoyl phosphate
2. aspartate
Part of the urea cycle takes place in the mitochondria, the other part takes place in the cytosol. Which takes place where?
The condensation of ornithine with carbamoyl phosphate to form citrulline occurs in the mitochondria. Everything else occurs in the cytosol.