2. developing fuels
4.0(2)
4.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/82
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
1
New cards
gas volume
same for any one mole at room temperature and pressure
2
New cards
number of moles
= volume in dm3 ÷ 24dm3
3
New cards
room temperature and pressure
298k or 25 ˚c
100 kPa
100 kPa
4
New cards
ideal gas equation
pV = nRT
p = pressure (Pa), V = volume (m3), n = moles, R = gas constant , t = temperature (K)
p = pressure (Pa), V = volume (m3), n = moles, R = gas constant , t = temperature (K)
5
New cards
pV÷RT =
moles, rearranged equation of pV = nRT
6
New cards
gas syringe
used to measure gas volume produced
7
New cards
enthalpy change
∆h is the heat energy transferred in reaction at constant pressure, kJ mol -1
8
New cards
exothermic
gives out energy ∆H is negative, typically oxidation like combustion
9
New cards
endothermic
absorbs energy ∆H is positive eg thermal decomposition or photosynthesis
10
New cards
breaking bonds
energy is required so endothermic ∆H positive
11
New cards
forming bonds
energy released so is exothermic ∆H negative
12
New cards
average bond enthalpies
used to calculate enthalpy changes, for each individual bond , energy needed to break one mole of bonds in gas phase, averaged over many compounds
13
New cards
enthalpy change of reaction
energy absorbed to break bonds - energy released in making bonds
14
New cards
short bond length
means theres a higher bond enthalpy due to there been high attraction between atoms
15
New cards
balanced forces
relation between repulsion between nuclei / electrons and attraction between nuclei and electrons are…
16
New cards
standard enthalpy change of reaction
∆rHø, when as reaction occurs in molar quantities shown in equation
17
New cards
standard enthalpy change of formation
∆fHø, when 1 mole of compound is from formed from its elements in standard states under standard condition
18
New cards
standard enthalpy change of combustion
∆cHø, when 1 mole of substance is completely burnt in oxygen under standard conditions
19
New cards
hess law
total enthalpy change of a reaction is always the same regardless of the route taken
20
New cards
enthalpy of reaction
= enthalpy of formation (products) - enthalpy of formation (reactants)
drawn with elements going to reactants and products
drawn with elements going to reactants and products
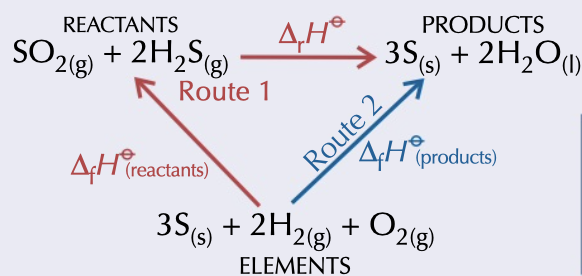
21
New cards
enthalpy of formation
= enthalpy of combustion (products) - enthalpy of combustion (reactants)
drawn with products and reactants going to products of combustion
drawn with products and reactants going to products of combustion
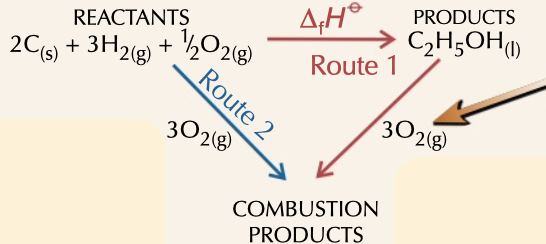
22
New cards
reactant enthalpy
bond enthalpy (reactants) - bond enthalpy (products)
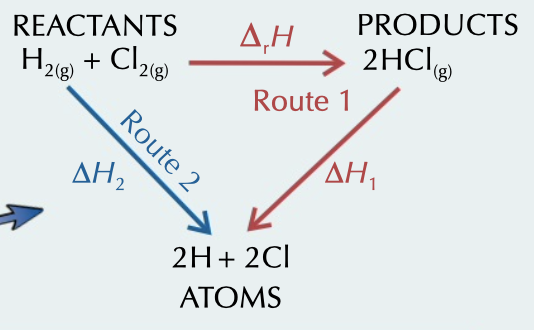
23
New cards
endothermic reaction
enthalpy of reaction increases, with products ending with more energy than reactants started with
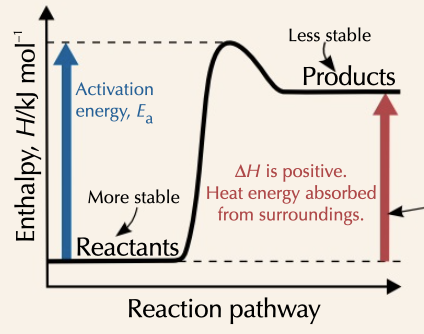
24
New cards
exothermic reaction
enthalpy of reaction decreases, with products ending with less energy than reactants started with
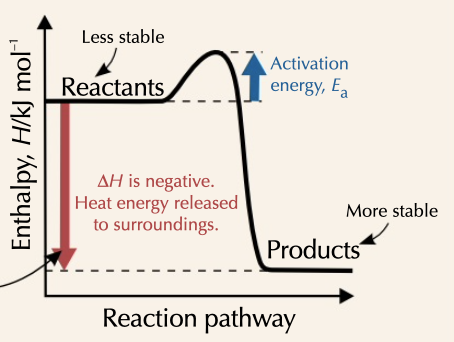
25
New cards
enthalpy level digram
a diagram showing reactants, intermediates and products allowing you to see different routes and activation energy
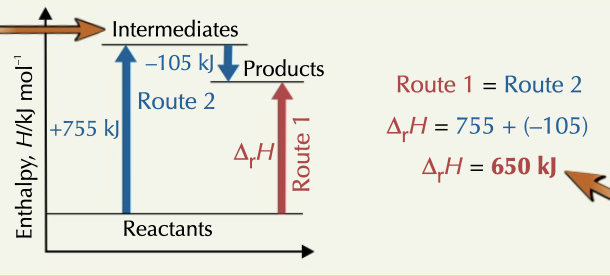
26
New cards
calorimetry
used to determine energy given out or absorbed by a reaction by measuring temperature change of water
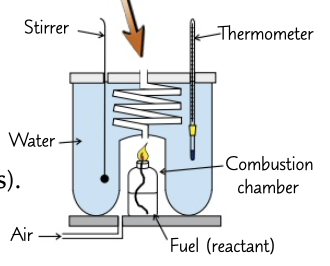
27
New cards
standard enthalpy change of neutralisation
enthalpy change when an acid and and alkali react to form 1 mole of water
28
New cards
calorimetry of a flammable liquid
burn a amount of liquid and heat water, record the temperature change and the mass of water
29
New cards
calorimetry of a solution
add a known volume of acid alkali to a insulated container record the start and end temperature and mass
30
New cards
calculate enthalpy change kJ mol-1
q = mc∆T
q - enthalpy change
m - mass of water or solution
c - specific heat capacity of water
∆T - change in temp of water or solution
q - enthalpy change
m - mass of water or solution
c - specific heat capacity of water
∆T - change in temp of water or solution
31
New cards
cause of error in calorimetry
heat loss- shield
incomplete combustion
evaporation
flame distance
incomplete combustion
evaporation
flame distance
32
New cards
catalysts
increases rate of reaction by providing an alternative pathway with an lower activation energy, without been used by
33
New cards
haber process
uses an iron catalyst
34
New cards
cracking
splitting of a long chain hydrocarbon in to smaller hydrocarbons using using a catalyst to reduce the temp needed to 450˚c
35
New cards
heterogeneous catalyst
catalysts that are in a different physical state as reactants
36
New cards
heterogeneous catalysts process
reactants adsorb to catalyst surface
bond are weakened so break (forms radicals)
new bonds made and desorb
bond are weakened so break (forms radicals)
new bonds made and desorb
37
New cards
adsorption
process of a reactant bonding just enough to catalyst surface that bonds can be easily broken and released
38
New cards
catalysts poisons
causes them not to work due to surface been covered eg iron by CO or lead on platinum catalytic converters
39
New cards
alkane
saturated hydrocarbon with general formula CnH2n+2
40
New cards
alkenes
unsaturated hydrocarbon with double bonds, general formula of CnH2n
41
New cards
cycloalkanes
saturated hydrocarbon that forms ring, general formula CnH2n
42
New cards
cyclic alkene
a unsaturated hydrocarbon ring with 2 less H than alkenes, stable due to delocalised structure eg benzene and cyclopentene
43
New cards
aromatic compounds or arenes
names for compounds with benzene rings
44
New cards
alcohols
compounds containing -OH hydroxyl group
45
New cards
electron repulsion
shape is created by electrons trying to be as far aspart as possible
46
New cards
tetrahedral
shape of alkenes with a bond angle of 109.5
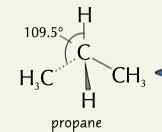
47
New cards
trigonal planar
shape around a double bond with a bond angle of 120˚
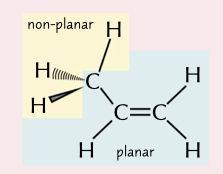
48
New cards
sigma
type of bond between a single covalent bond between atoms, due to the 2 orbitals overlapping in a straight line
49
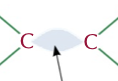
New cards
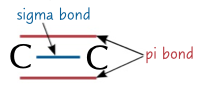
sigma and pi bond
type of bond between a double covalent bond, 1 central bond and 1 caused by the overlap of 2 p orbitals sideways, this second one is weaker than the first
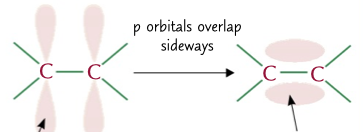
50
New cards
general formula
formula that can describe any member of a family of compounds eg CnH2n+1OH
51
New cards
molecular formula
formula with the actual number of atoms in a molecule eg C2H10O
52
New cards
shortened structural formula
shows the atoms carbon by carbon with attached atoms and functional groups eg CH3CH2OH
53
New cards
structural formula
formula showing how the atoms are arranged with their bonds
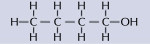
54
New cards
skeletal formula
shows the bonds of the carbon chain only with any functional groups
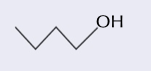
55
New cards
different carbon skeleton
isomers with the carbon chain arranged differently, similar chemical properties but different physical properties
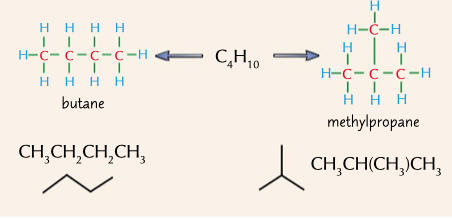
56
New cards
functional group location
the carbon chain is the same but the functional group is attached to a different carbon, different physical properties and may have different chemical properties
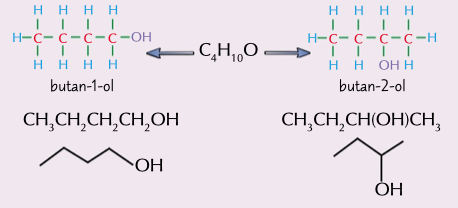
57
New cards
different functional groups
same atoms arranged into different functional groups very different physical and chemical properties
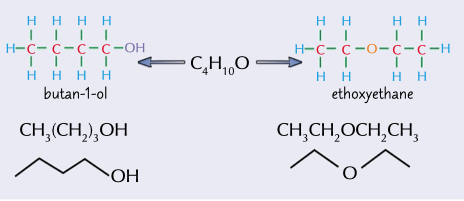
58
New cards
double bonds
bonds which atoms cannot freely rotate around causing E/Z isomerism
59
New cards
stereoisomers
molecules with the same shortened structural formula but different arrangement
60
New cards
E/Z isomerism
occurs due to lack of rotation around double bonds and different atoms/groups bonded the the carbons, involves H
61
New cards
opposite sides
E or trans isomer
62
New cards
same side
Z or cis is
63
New cards
cis/trans isomerism
isomerism if no H on both sides
64
New cards
addition polymer
formed when the double bonds in alkens break and bond to each other
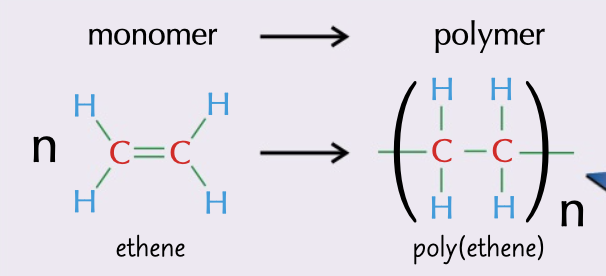
65
New cards
hydrogen added
added to change an alkene to an alkane in the presence of a nickel catalyst at 150
˚c and high pressure or platinum and room temp and pressure
66
New cards
bromine water
used to test for alkanes as it bonds to the double bond causing a colour change orange to colourless
67
New cards
electrophilic addition
double bonds open up and atoms are added
68
New cards
electrophiles
electron pair acceptors eg positively charged ions or polar molecules (double bond)
69
New cards
electrophilic addition mechanism
1. double bond repels electrons in Br2 polarising it ∂+Br-Br∂-
2. electrons are transferred to one Br from the bond, electrons from the double bond are transferred to the other Br and it bonds
1. a positively charged carbocation intermediate is formed which Br- bonds to
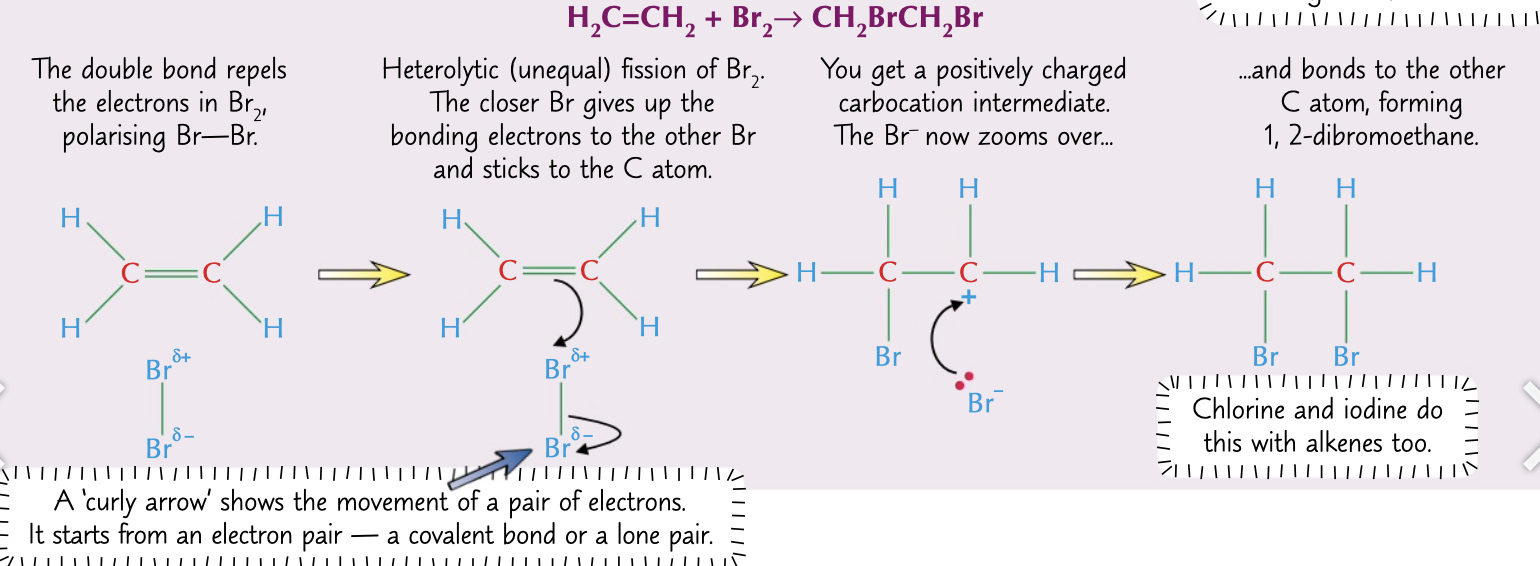
70
New cards
hydrating alkanes in presence of acid catalyst
produces an alcohol by electrophilic addition
71
New cards
alcohol making process
1. cold conc sulphuric acid reacts with an alkene in electrophilic addition reaction to make an intermediate
1. add cold water and warm to hydrolyse in to product by removing the SO2 regenerating H2SO4
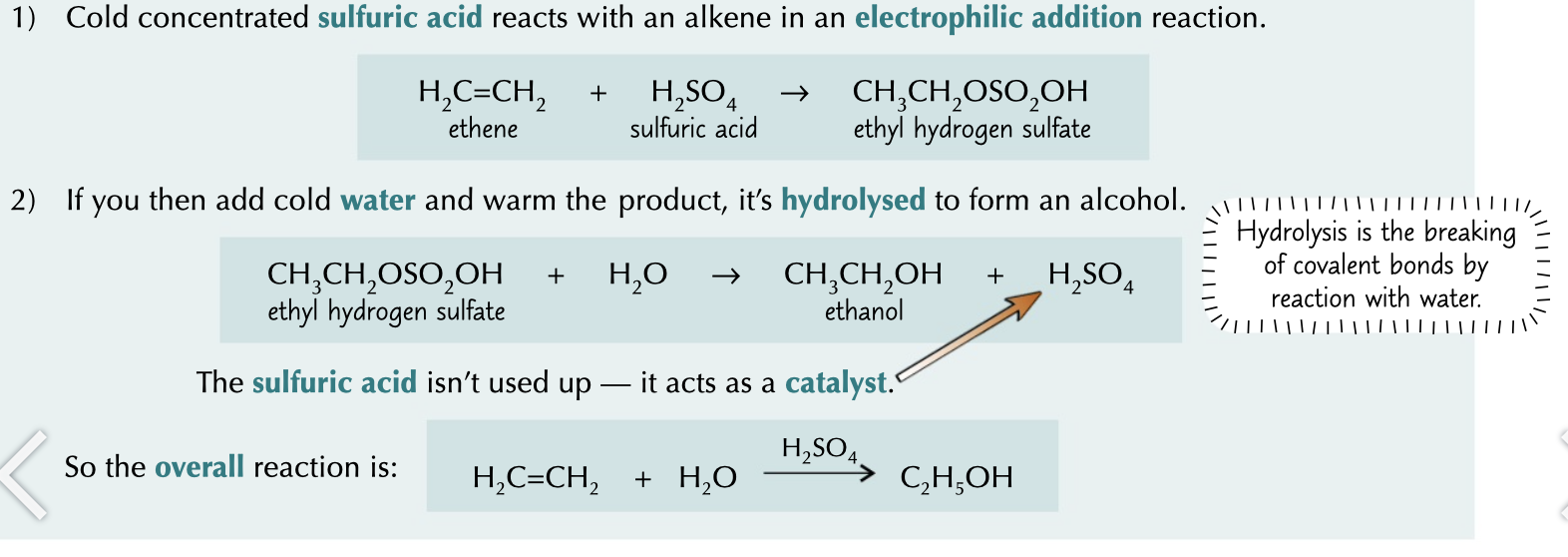
72
New cards
steam hydration
used to make ethanol by hydrating in steam at 300˚c and 60 atm using solid phosphoric acid catalyst, reversible and low yield 5% but recycles to yield 95%
73
New cards
complete combustion
exothermic reaction of alkane in oxygen produces CO2 and water
74
New cards
green house effect
earth radiates infrared radiation and greenhouse gases absorb some of this in the atmosphere keeping earth warm
75
New cards
incomplete combustion
results in formation of carbon monoxide
76
New cards
carbon monoxide
mainly produced in car engines and poisonous
77
New cards
nitrogen oxides
contribute to smog, formed in high pressure and temp of car engines, reacts with sunlight to form ground level ozone which is an irritant
78
New cards
sulfur dioxide
leads to acid rain, produce when fuel contains it, once in atmosphere it dissolves in moisture forming an acid, which destroys vegetation , corrodes buildings and kills fish in lakes, removed from fuels using calcium oxide
79
New cards
particulates
tiny particles of liquid or solids suspended in air, which can settle in lungs and cause issues, removed with wet scrubbers and filters
80
New cards
fossil fuels
non renewable resources like coal, oil and natural ga
81
New cards
decrease pollution
* change laws
* emissions test, compulsory catalytic converter
* tax fuel
* car share, public transport, bikes
* emissions test, compulsory catalytic converter
* tax fuel
* car share, public transport, bikes
82
New cards
renewable fuels
wind, solar and wave power, expensive and need to be extensive
biofuels- produce CO2 and take up farm land
hydrogen- burnt or fuel cell, energy transporter, difficult to transport(liquified)
biofuels- produce CO2 and take up farm land
hydrogen- burnt or fuel cell, energy transporter, difficult to transport(liquified)
83
New cards
energy security
make sure there is enough clean and affordable energy