microscopic anatomy of the reproductive system
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
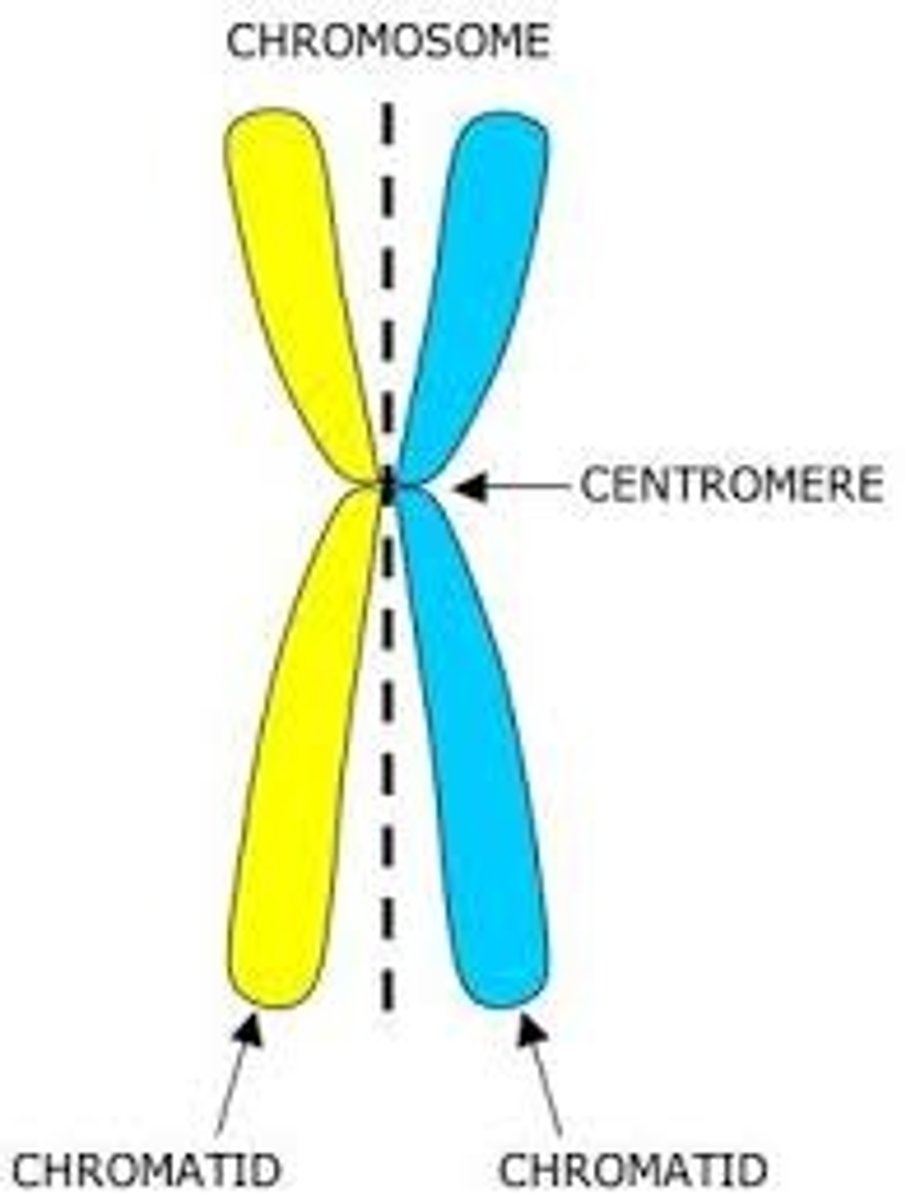
chromosome
the strands of DNA that hold the genetic blueprint for all of our cells, tissues, and organs).
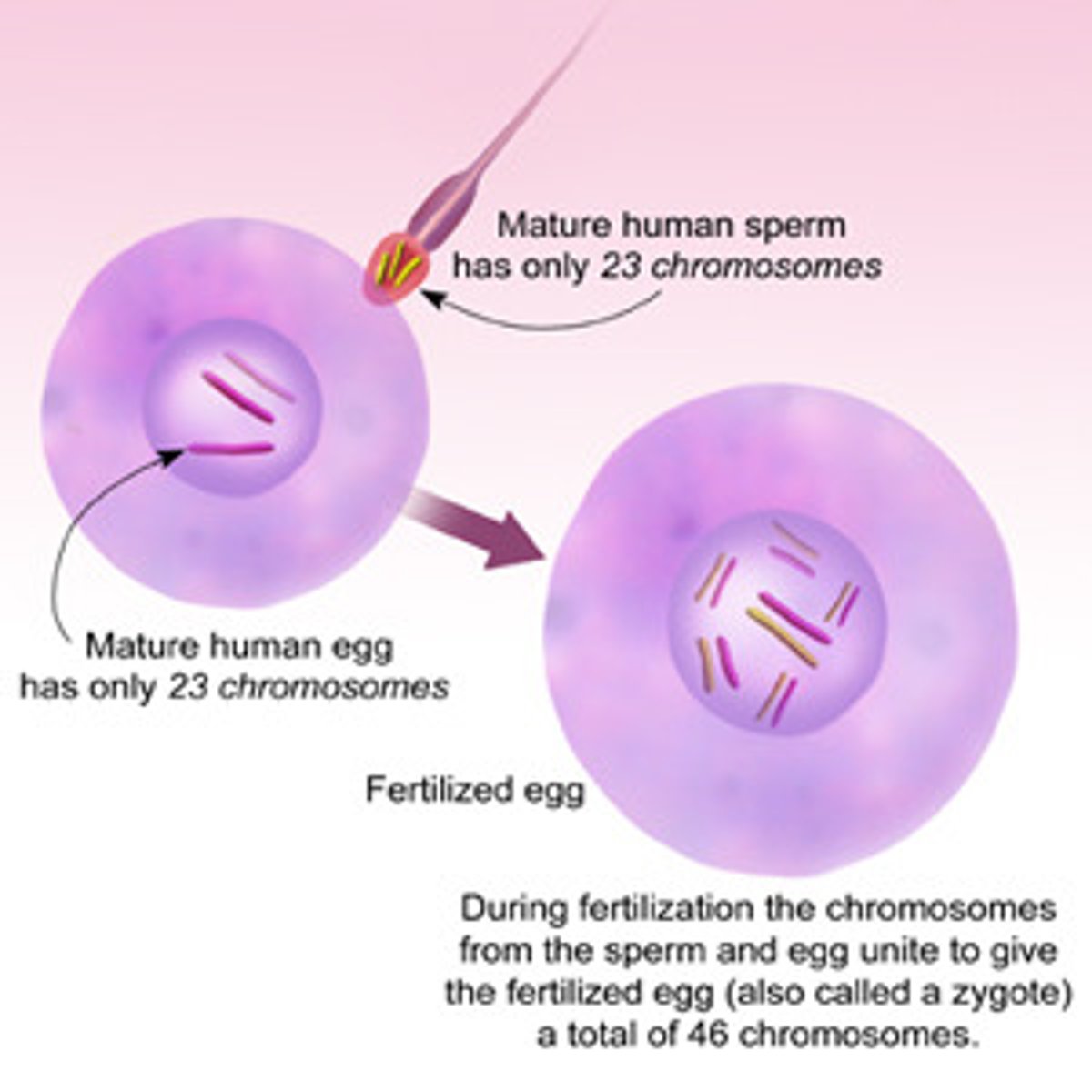
What are the total number of chromosomes in each cell?
46 chromosomes in each cell 23: from mom and 23 from dad
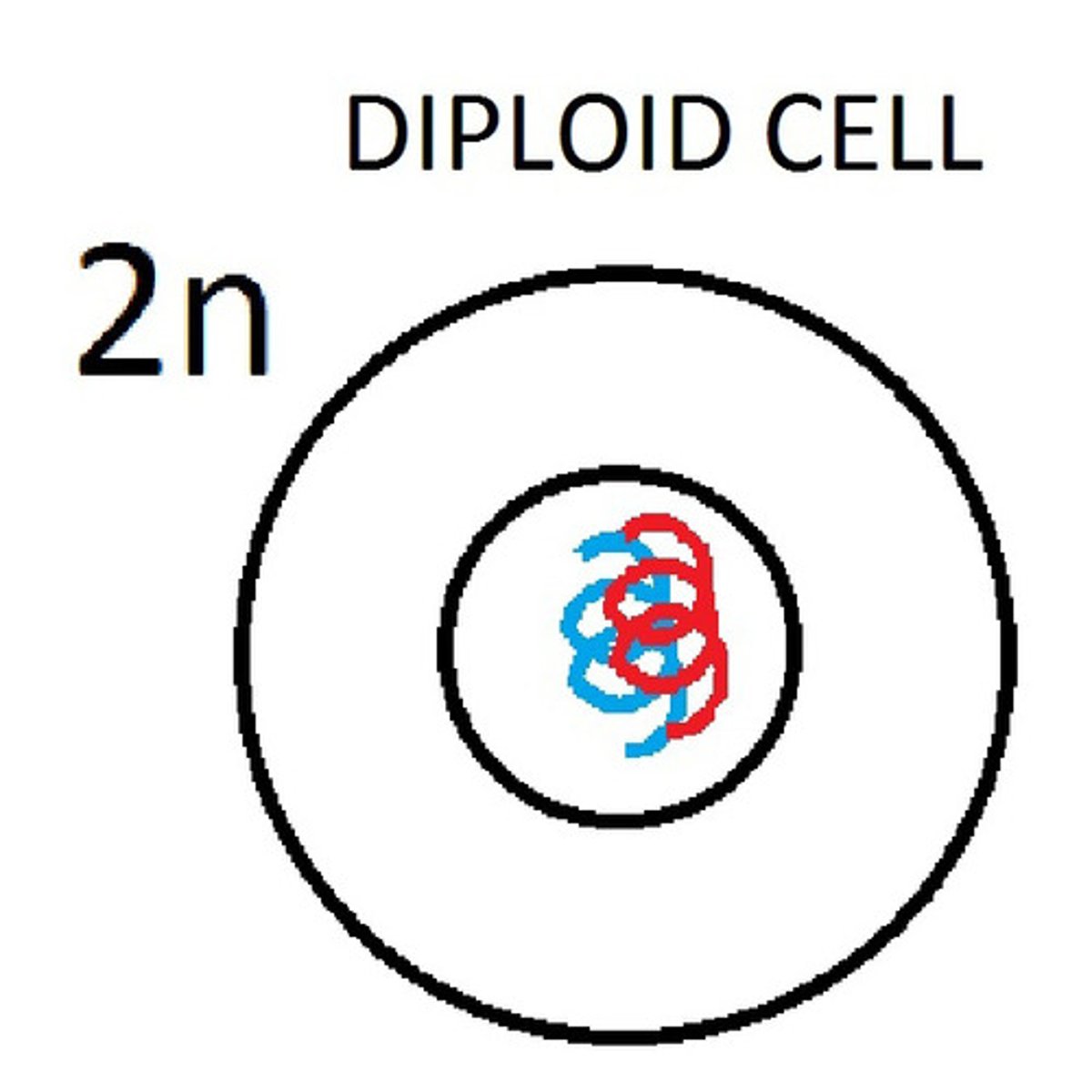
Diploid (2n)
contain 2 copies of each chromosome
sex cells (gametes)
(sperm and eggs) have half the number of chromosomes of a normal body cell
Haploid cells (1n)
Cells with one set of chromosomes (n).
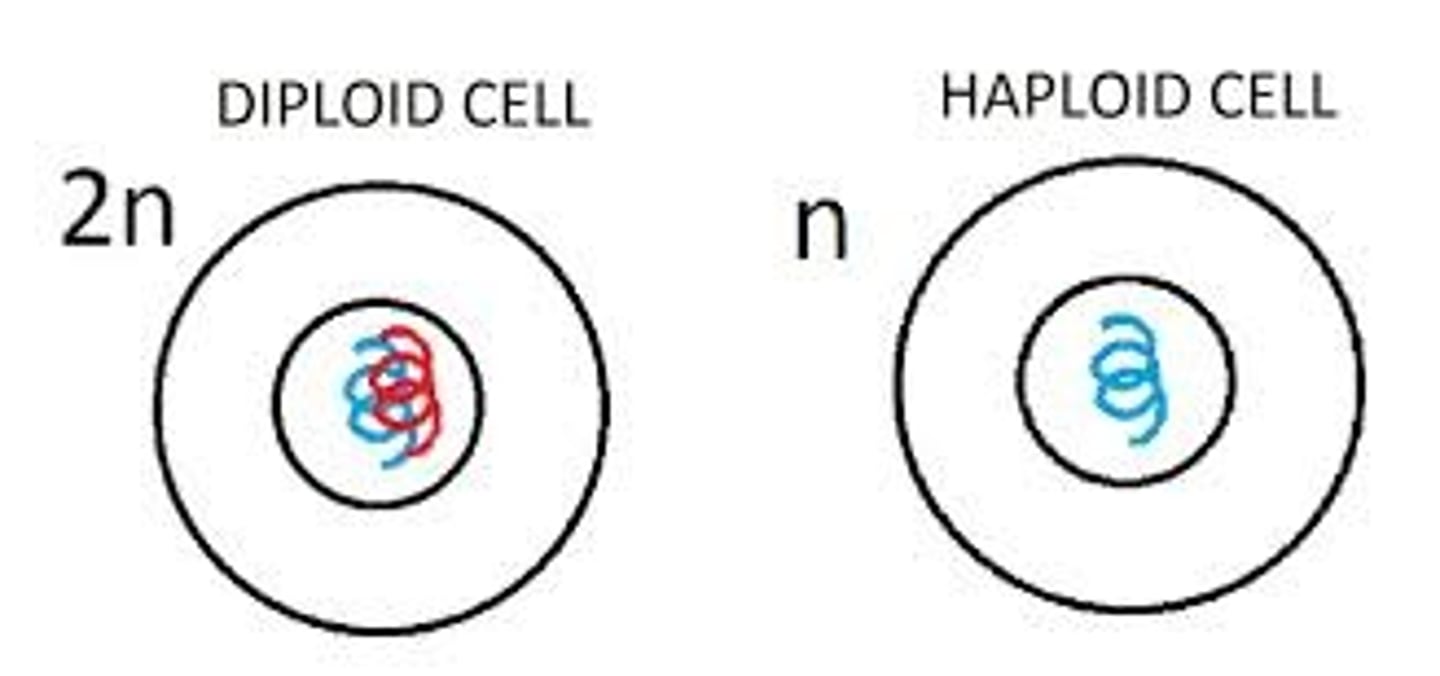
Why are sperm and egg cells said to be haploid?
they contain only 23 individual (unpaired) chromosomes
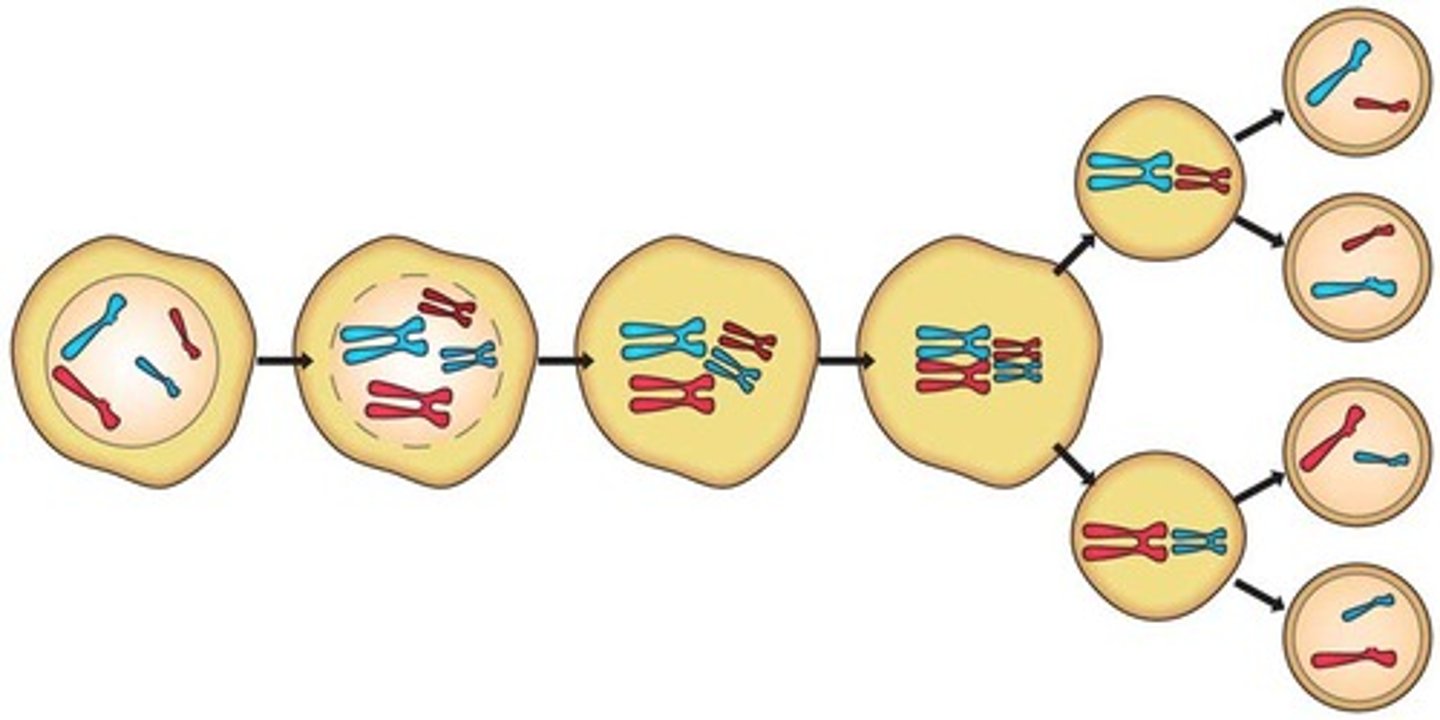
meiosis
the process of becoming a haploid cell.
tunica albuginea (testes)
a dense, fibrous connective tissue capsule that surrounds each testis.
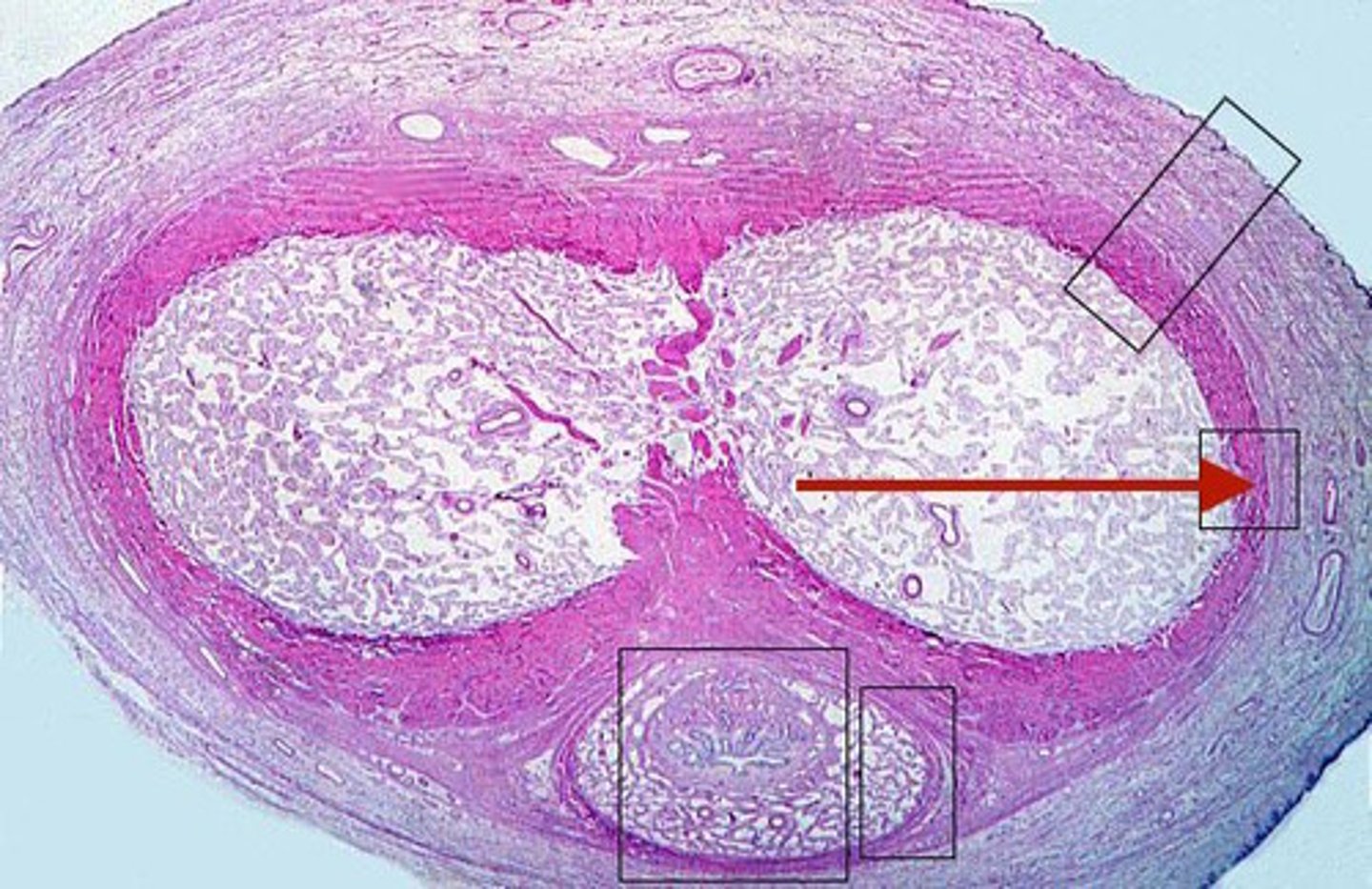
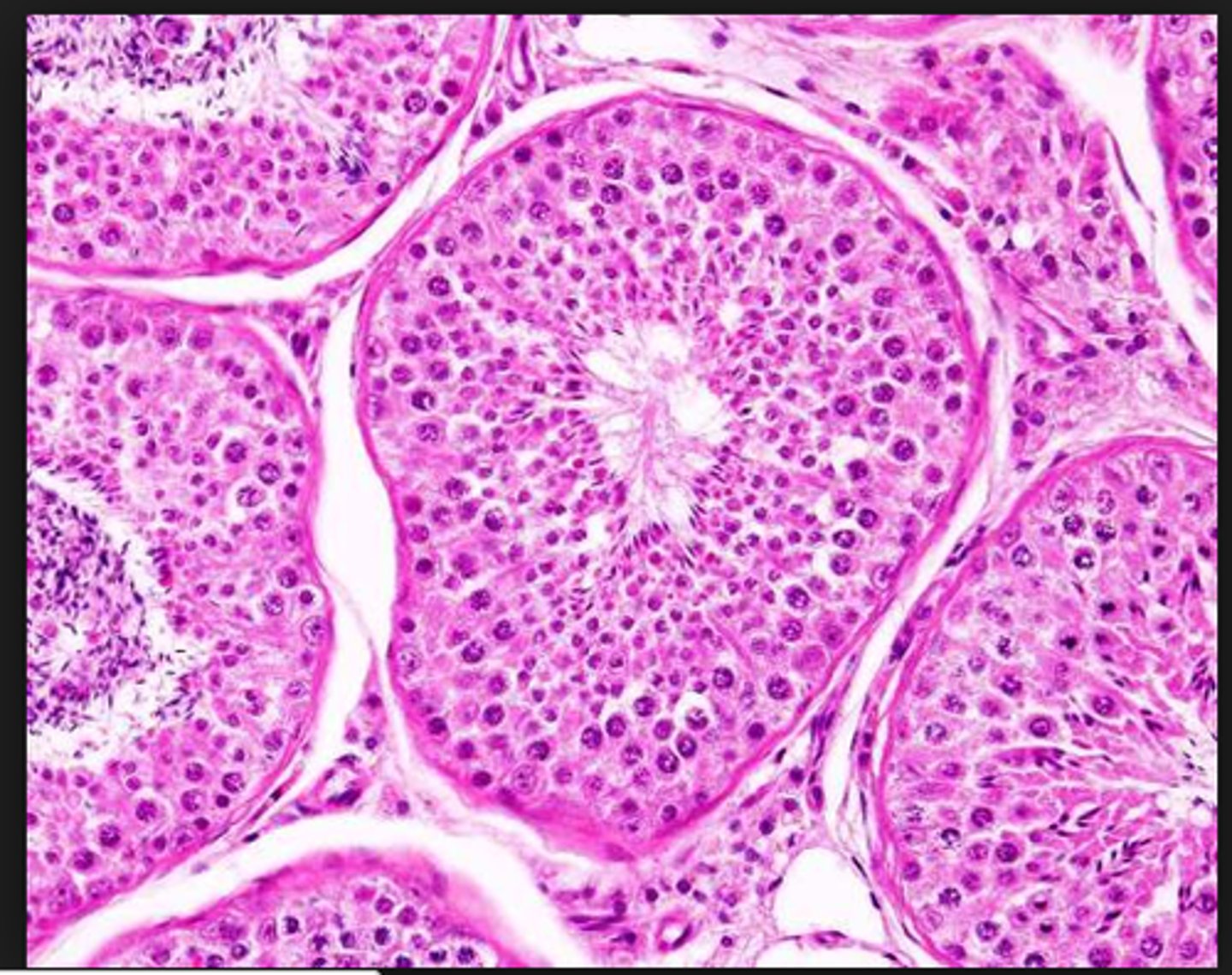
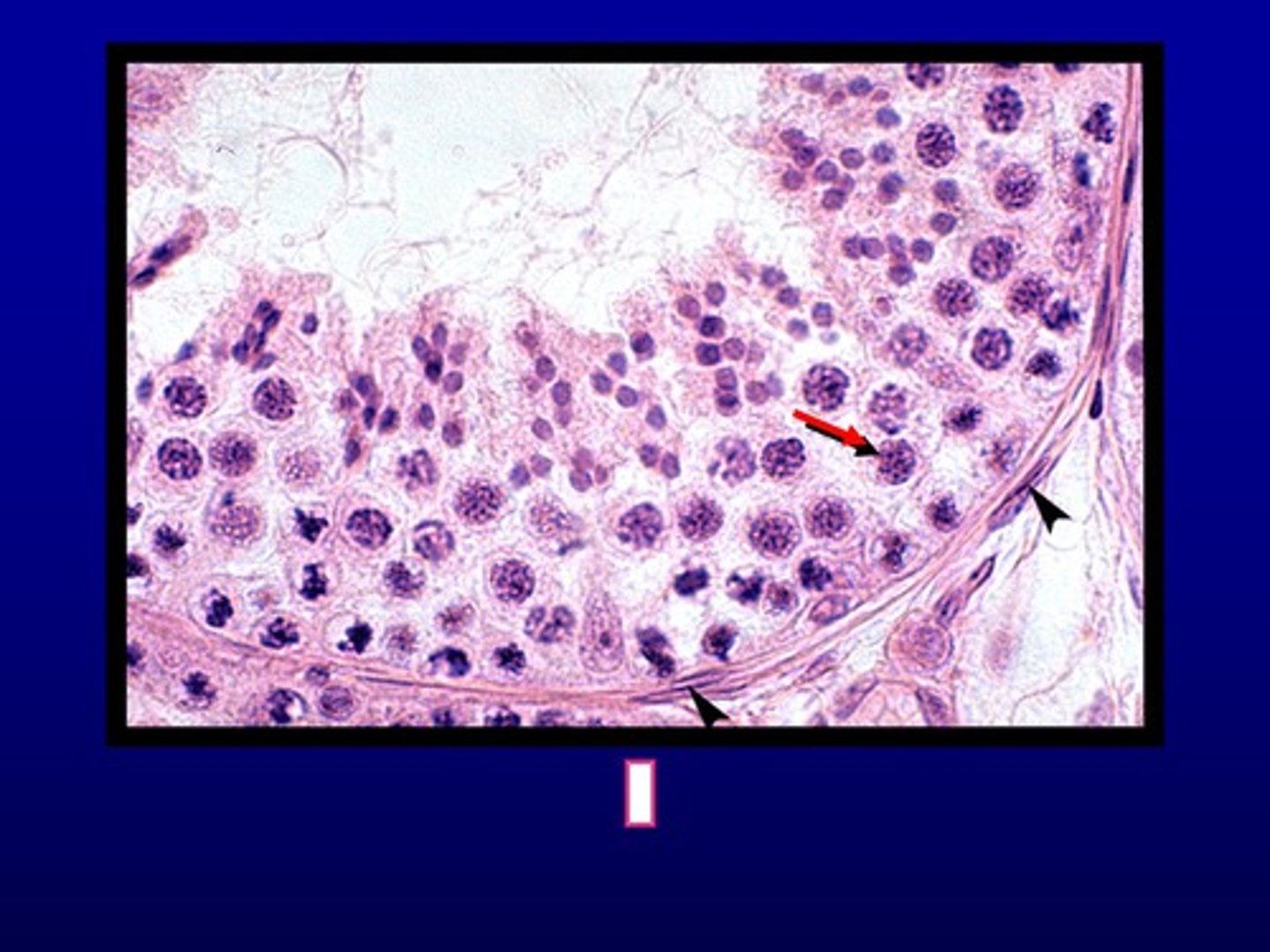
seminiferous tubules
densely cellular tubules confined in the tunica albuginea. They are the site for sperm production
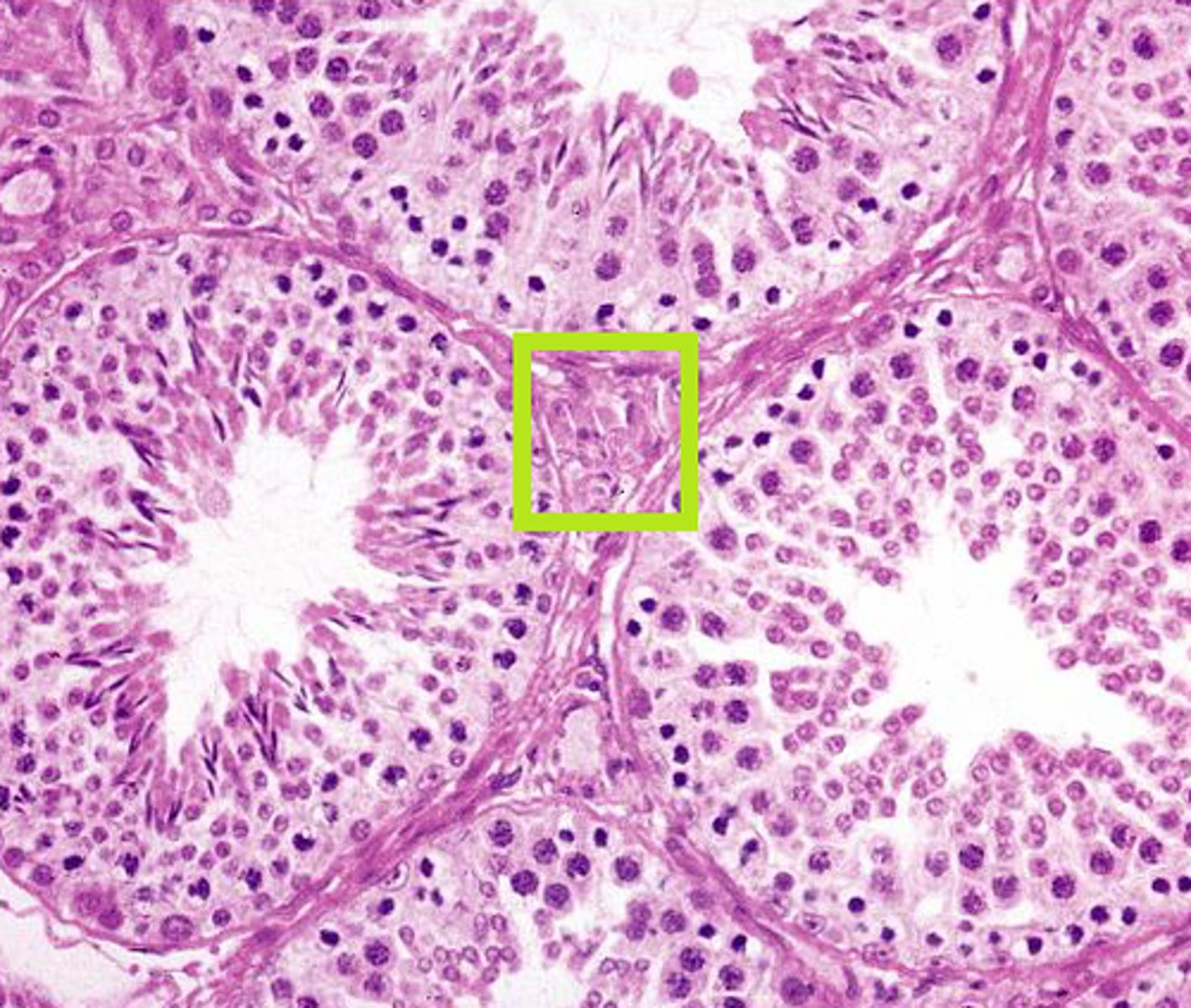
interstitial cells (Leydig cells)
small clusters of cells scattered in between the seminiferous tubules often in triangular shape. They produce testosterone
Testosterone
Male sex hormone
Why does it make sense that interstitial cells are typically intimately associated with blood vessels?
they produce hormones (like testosterone) that need to be quickly distributed throughout the body. Their proximity to blood vessels allows these hormones to efficiently enter the bloodstream and reach target tissues
spermatogenic cells
cells that make up the wall of layers around the seminiferous tubule.
They are involved in the development of a sperm cell.
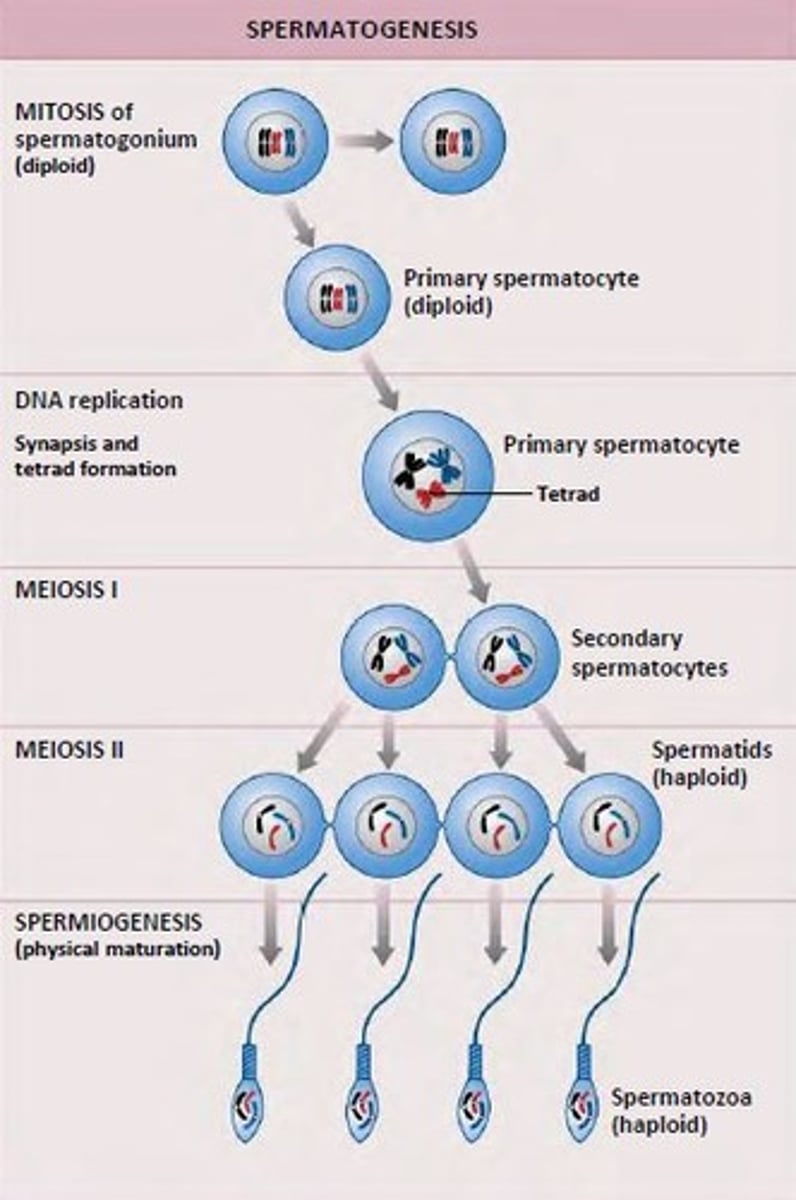
spermatogenesis
the process of sperm formation
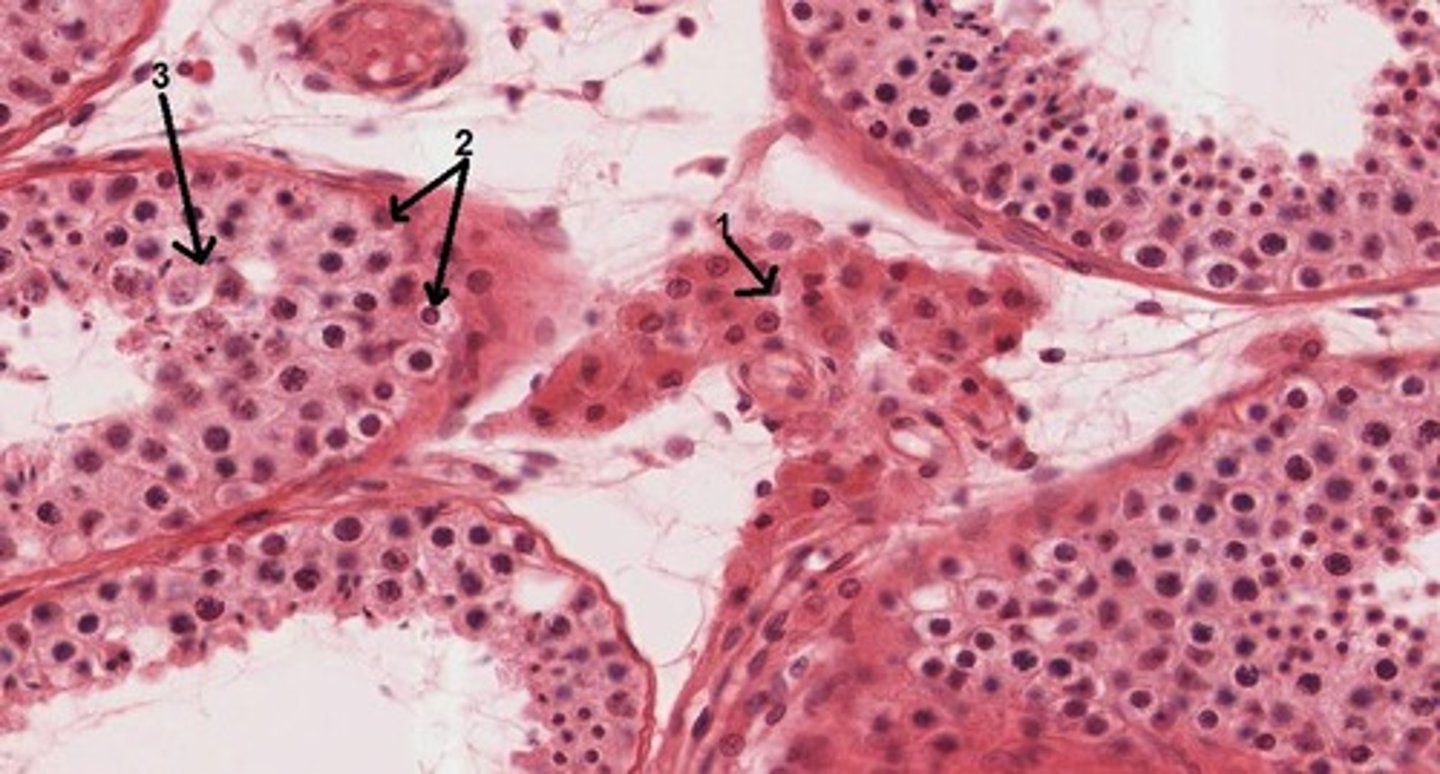
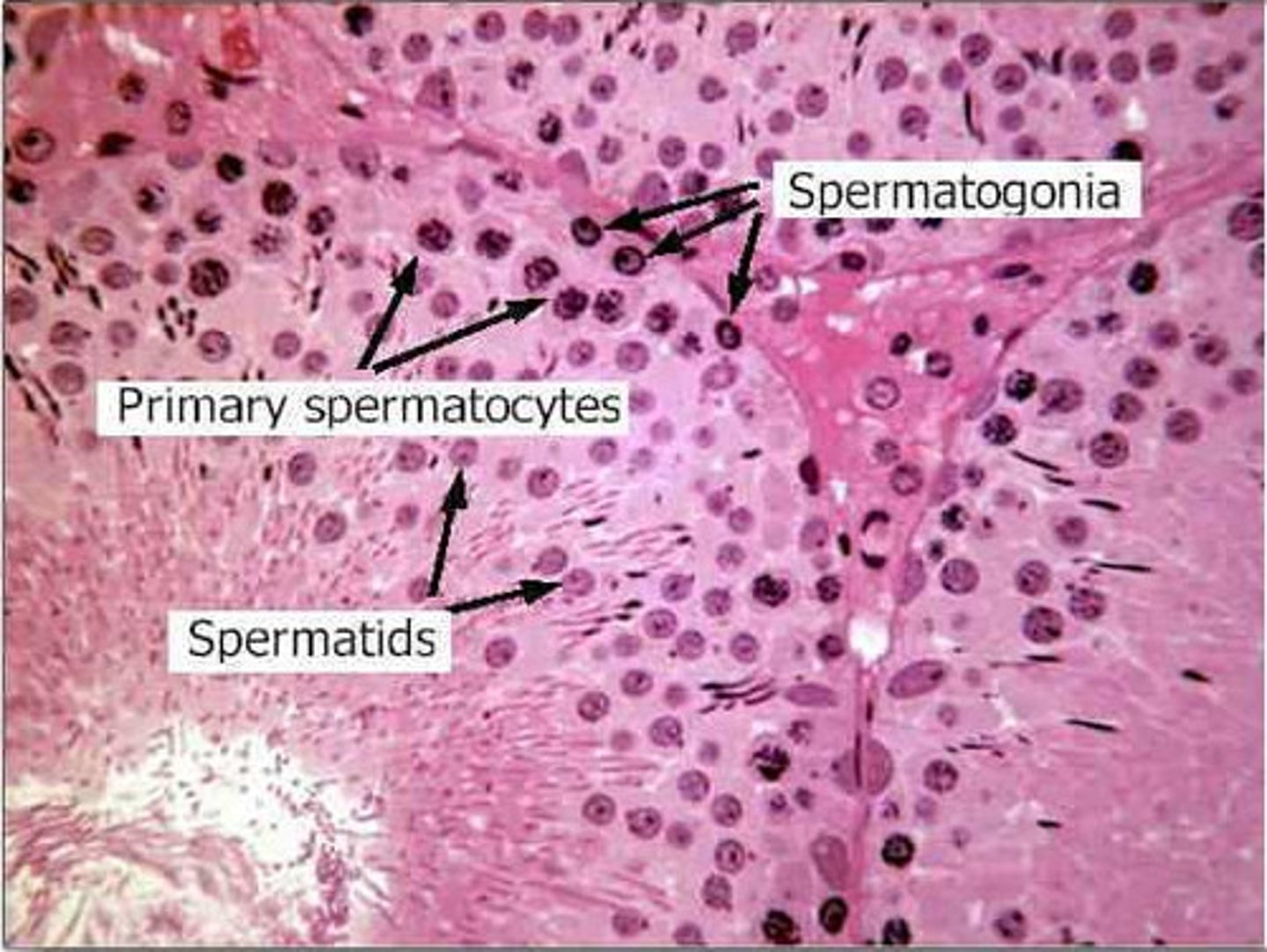
spermatogonia
the cells comprising the outer rim of the seminiferous tubule. They are the diploid stem cells from which all sperm will arise.
how many chromosomes do the spermatogonia contain?
Spermatogonia contain 46 chromosomes (23 pairs), as they are diploid cells.
primary spermatocyte
when the spermatogonium replicates its DNA content. Found just inside the spermatogonia, making up the next-to-last layer of the tubule.
second spermatocyte
result of each diploid primary spermatocyte going through cell division to create two haploid cells.
These cells are extremely short-lived
spermatids
formed from two secondary spermatocytes that undergo another round of cell division to make two haploids.
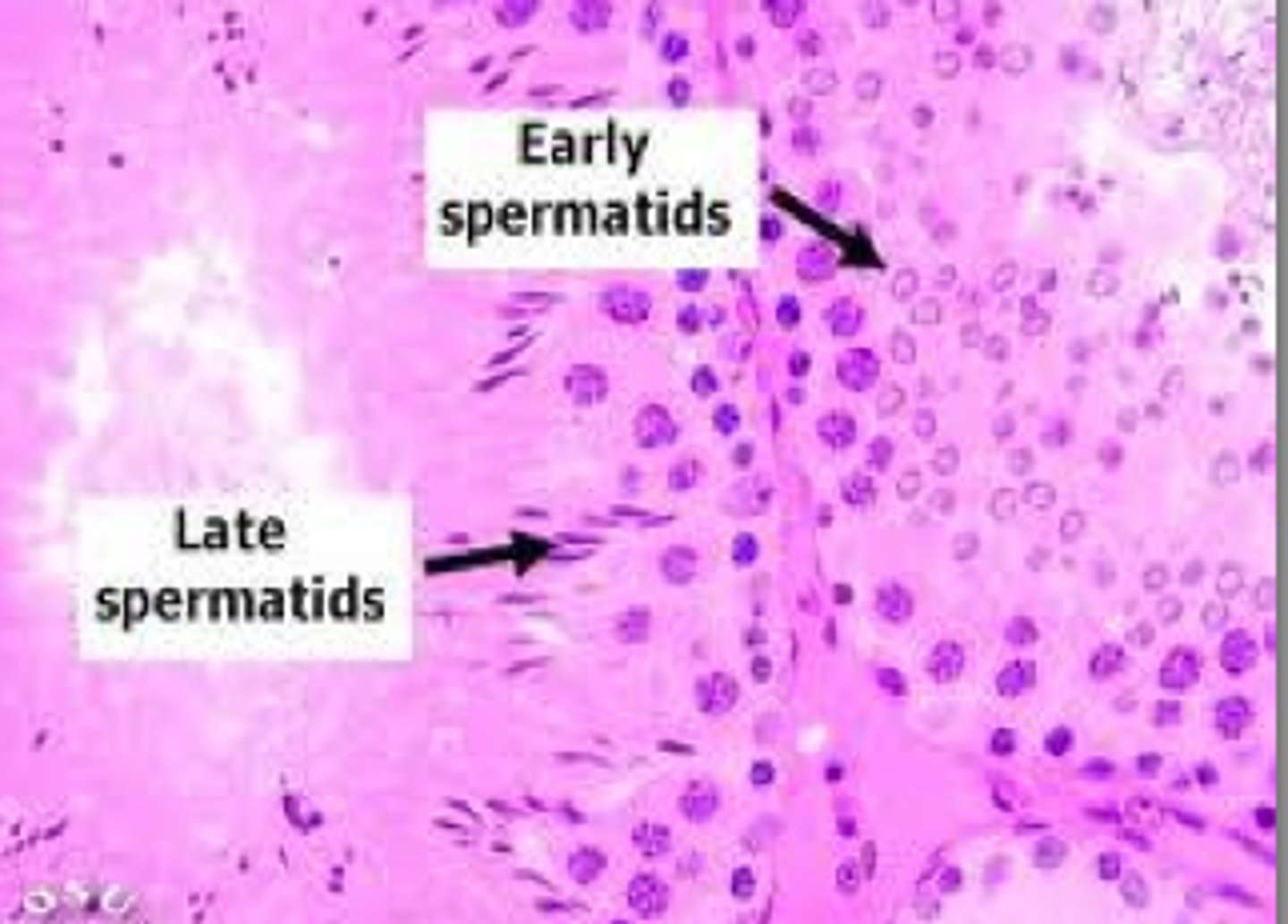
meiosis (sperm)
the process by which a diploid spermatogonium undergoes successive rounds of division to yield haploid spermatids.
how many haploid spermatids are produced during the meiosis of a single spermatogonium?
four haploid spermatids
What is the function of a spermatid?
To differentiate into a sperm cell by acquiring a streamlined shape, mitochondria-packed midsection, and a long supple propulsive tail.
flagellum
a long supple propulsive tail on a sperm cell that allows it to move
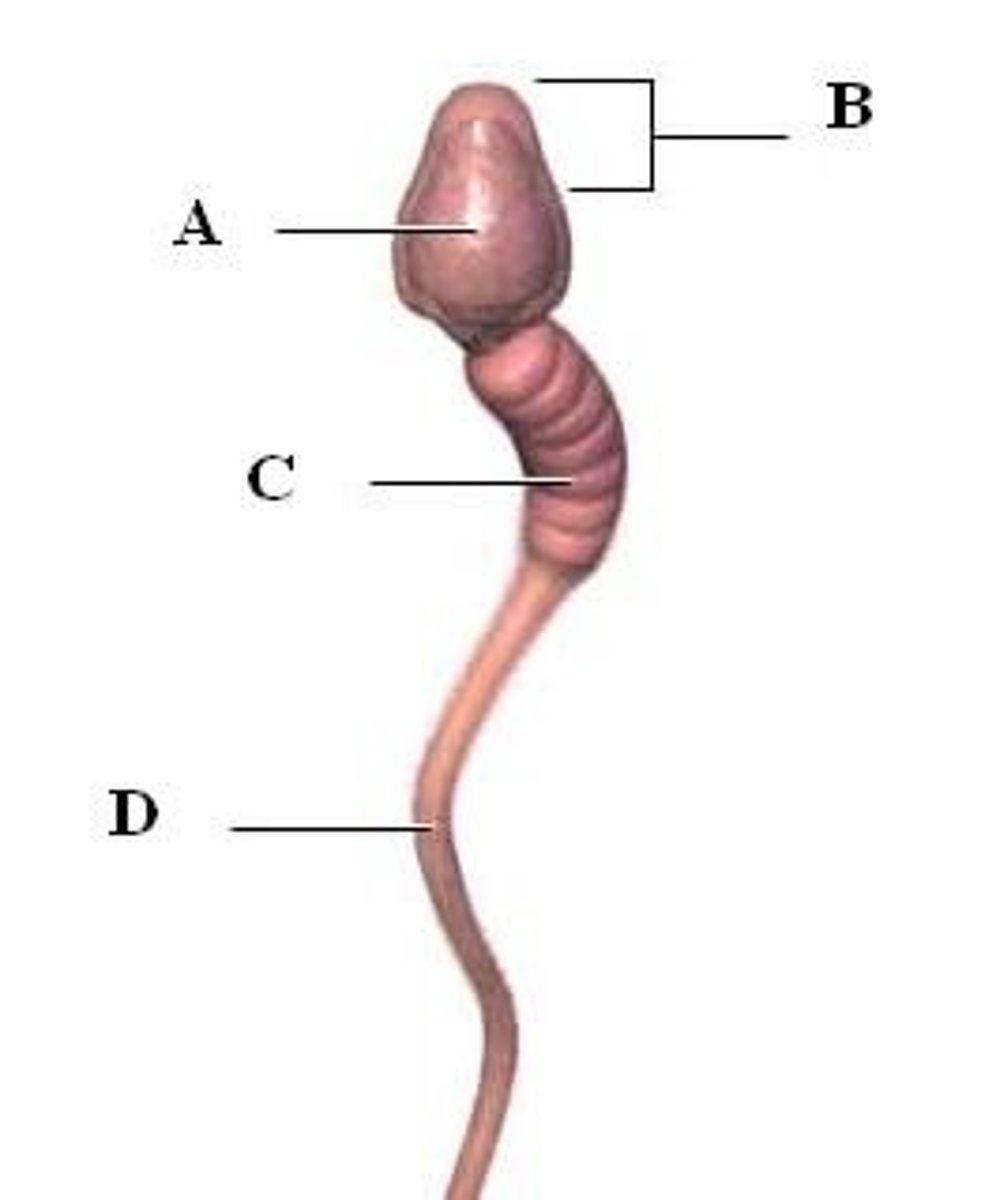
Spermiogenesis
the process of going from a round spermatid to a sleek sperm.
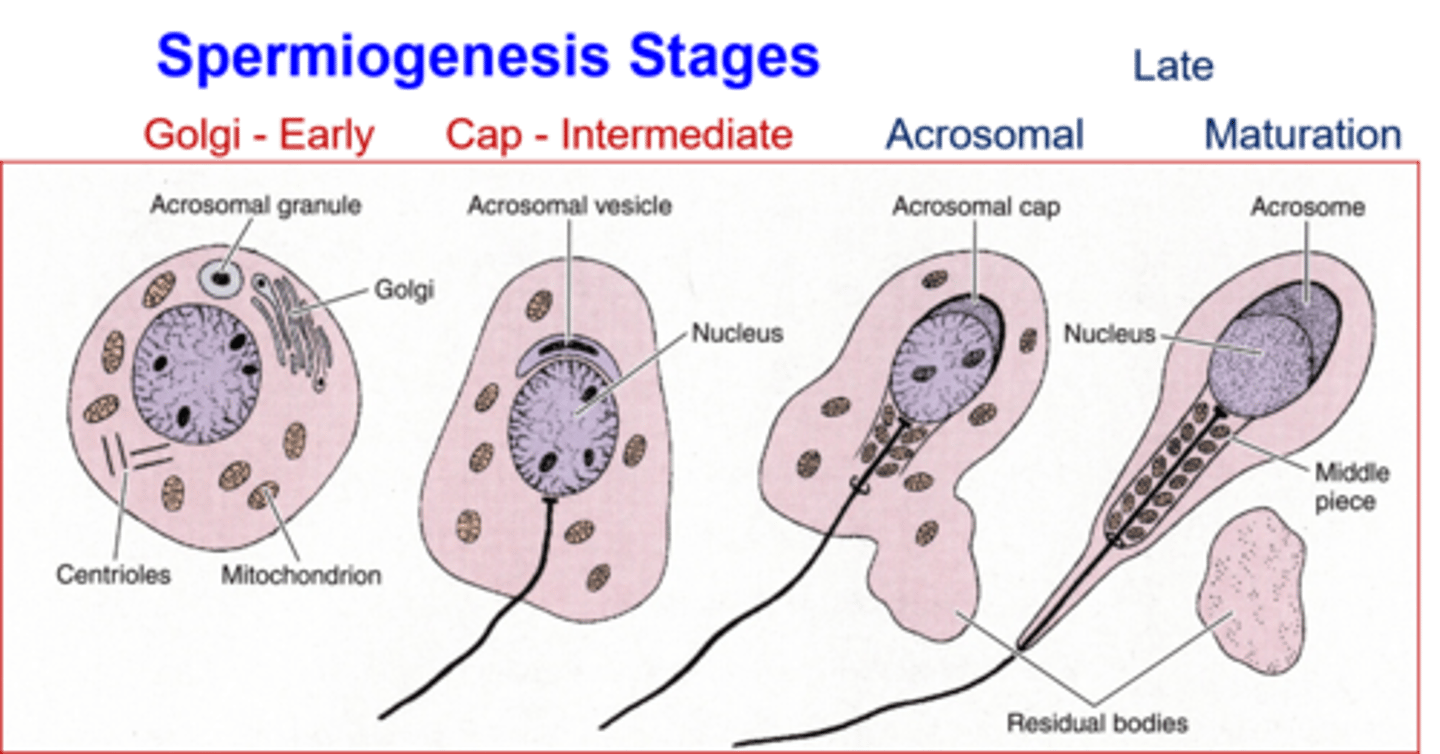
What two things encompasses the entire process of spermatogenesis?
meiosis and spermiogenesis
epididymis
A long, coiled duct on the outside of the testis in which the immature sperm cells continue to mature after spermatogenesis.
germinal epithelium
outermost surface of the ovary made of simple cuboidal epithelium.
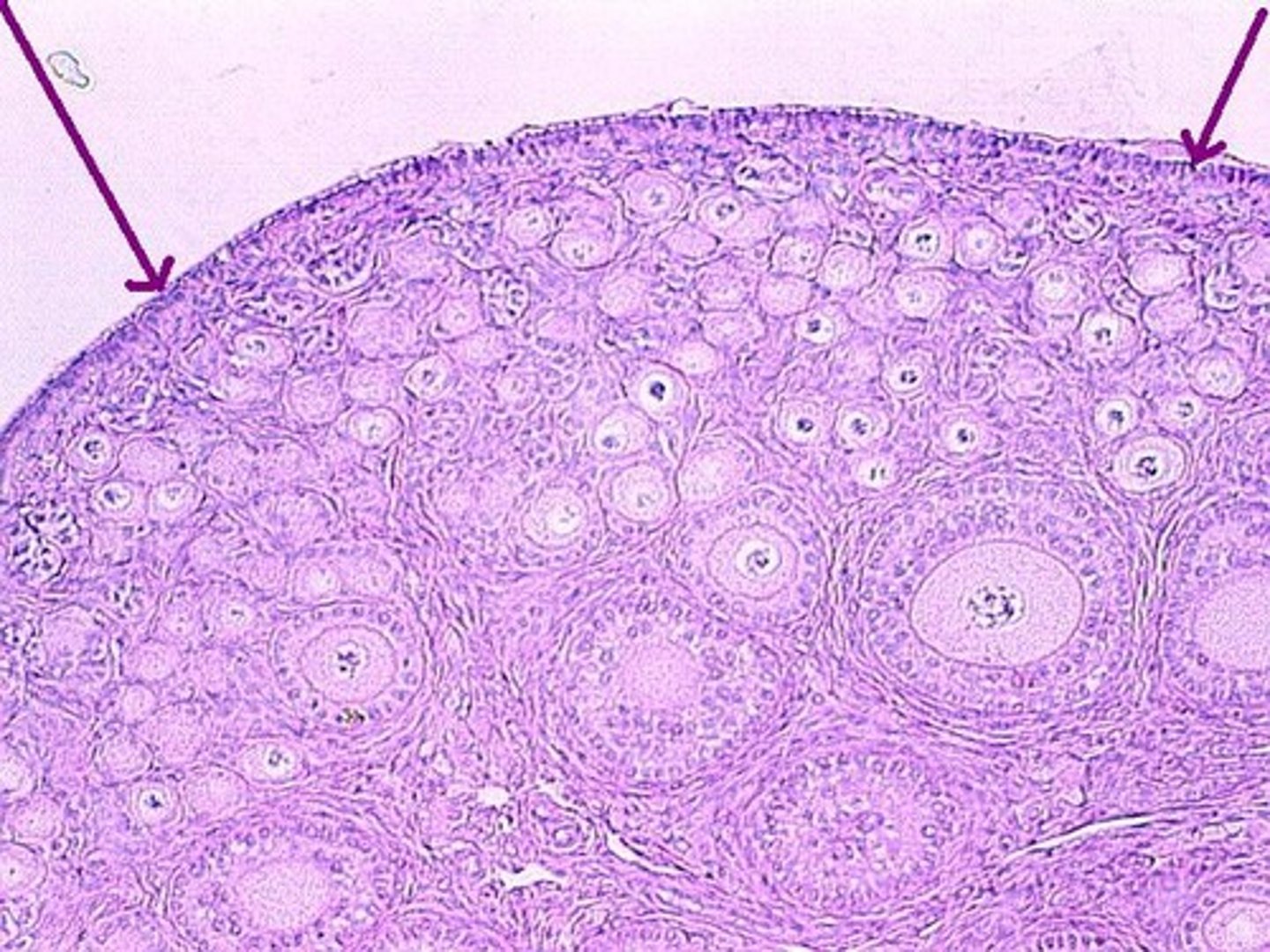
what gave germinal epithelium its name?
It was originally thought to be a site of the progenitor cells of the female gametes.
tunica albuginea
a layer of wavy connective tissue beneath the germinal epithelium
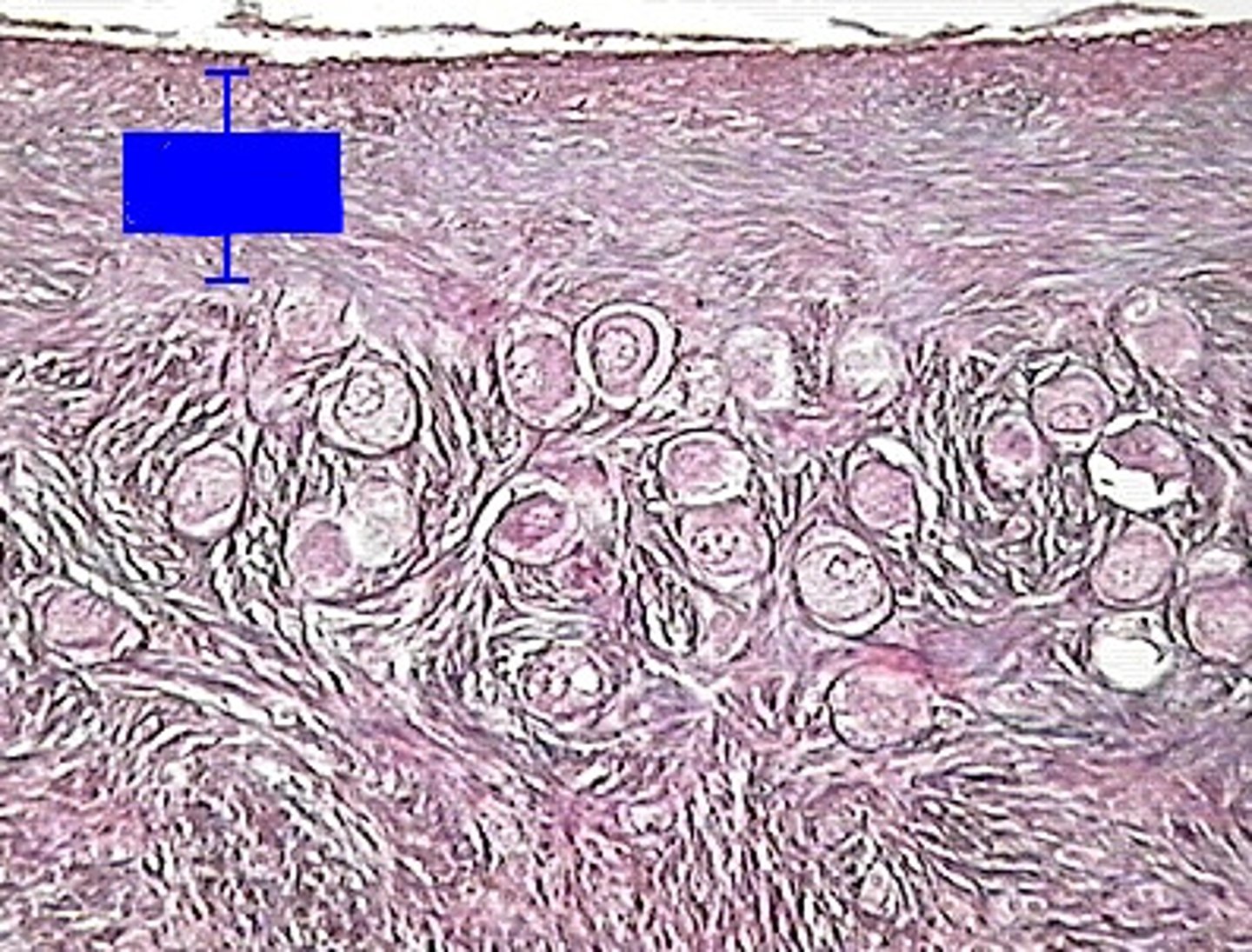
primoradial follicles
clear spherical cells clustered together in the ovarian cortex.
Is a developing oocyte (egg cell) and its surrounding support cells.
primary oocyte
contained in the primordial follicle surrounded by simple squamous layer of follicle cells.
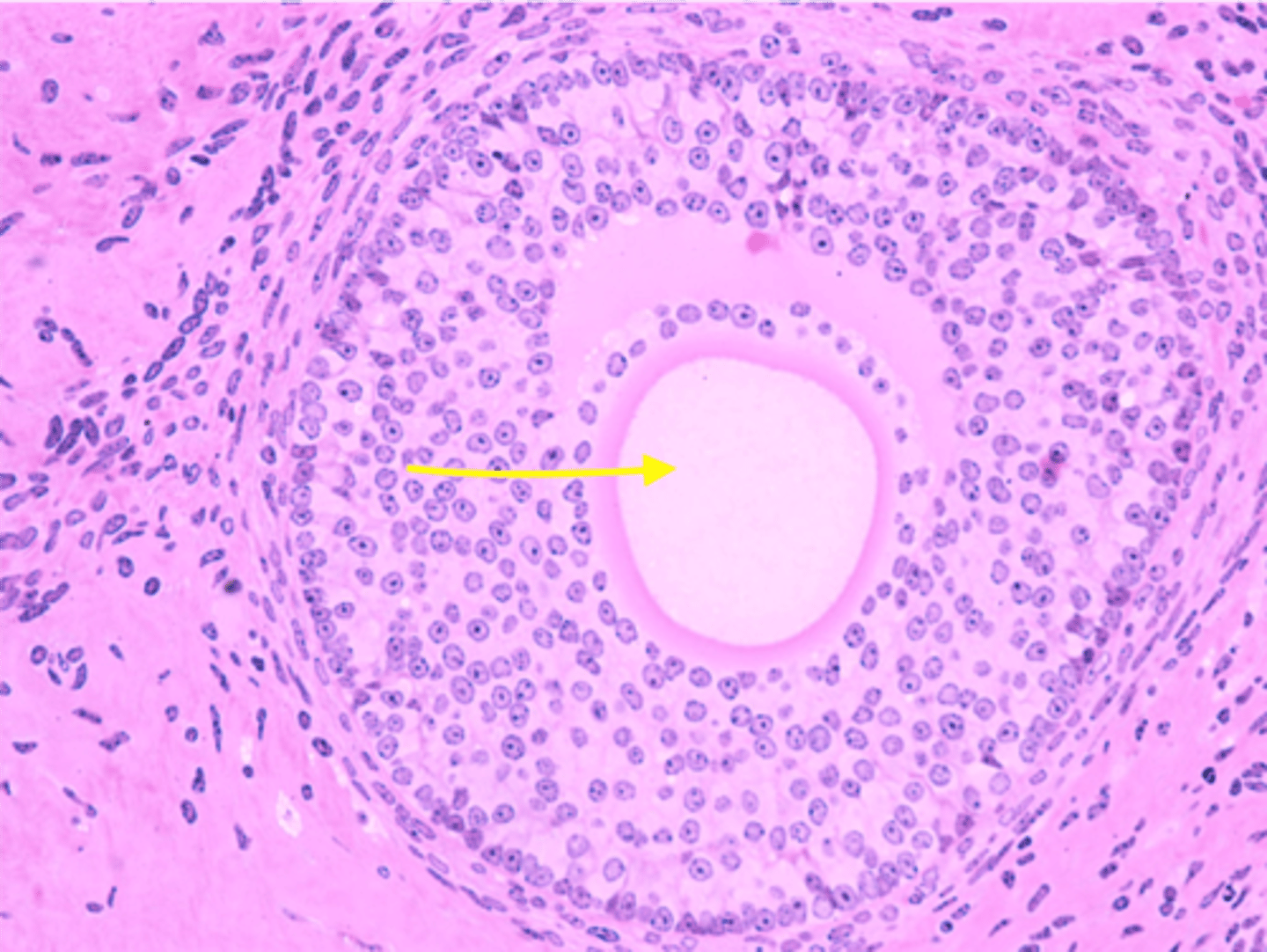
follicle cells
somatic cells that surround the oocyte and support cells during egg development
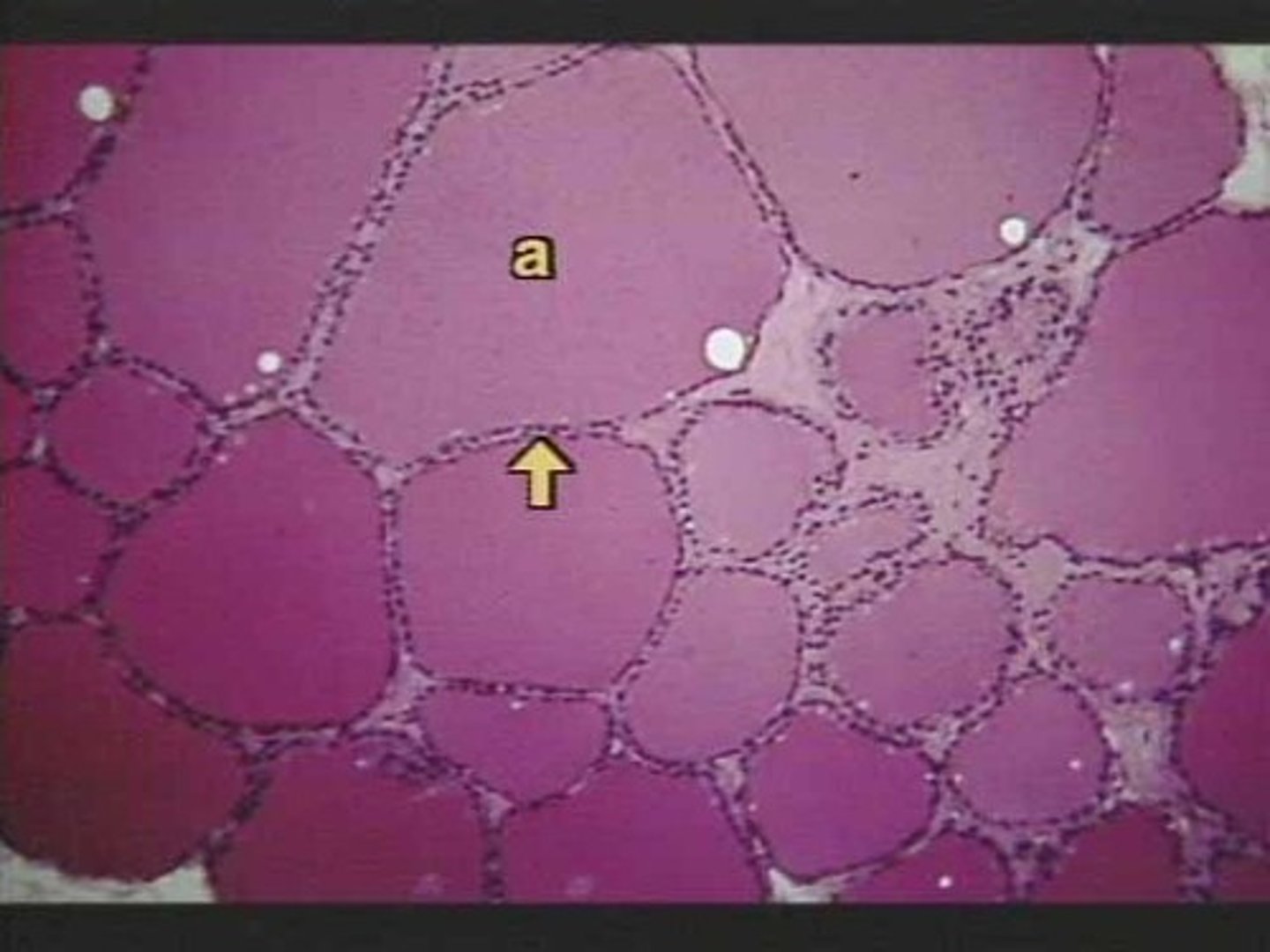
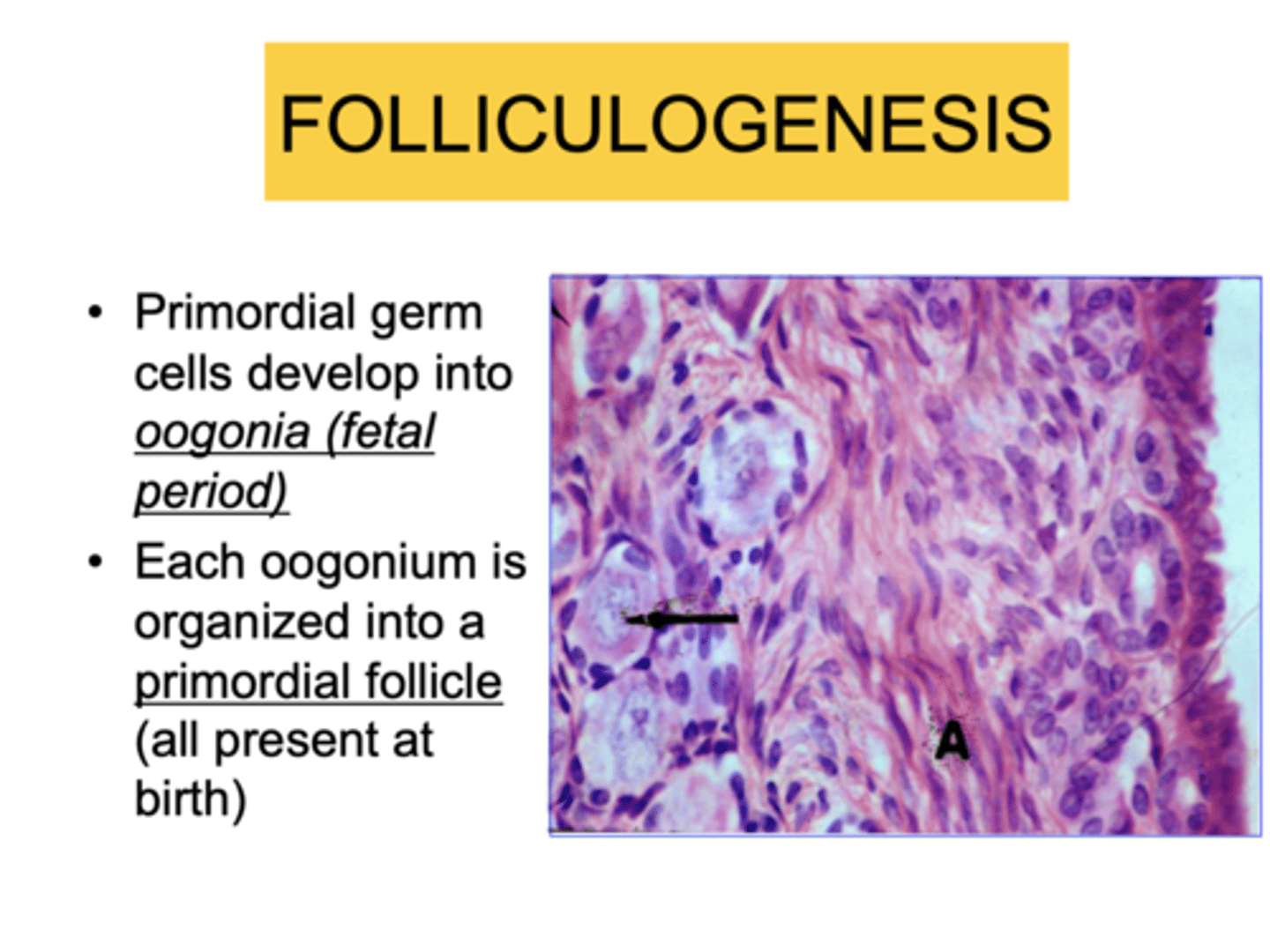
oogonium
the female equivalent of a spermatogonium. a diploid found in the primordial follicles
What do oogonia do prior to giving birth?
Duplicate their DNA and become primary oocytes.
primary follicles
Is slightly larger than a primordial follicle and has simple cuboidal layer of follicle cells surrounding a primary oocyte.
multilaminar primary follicle
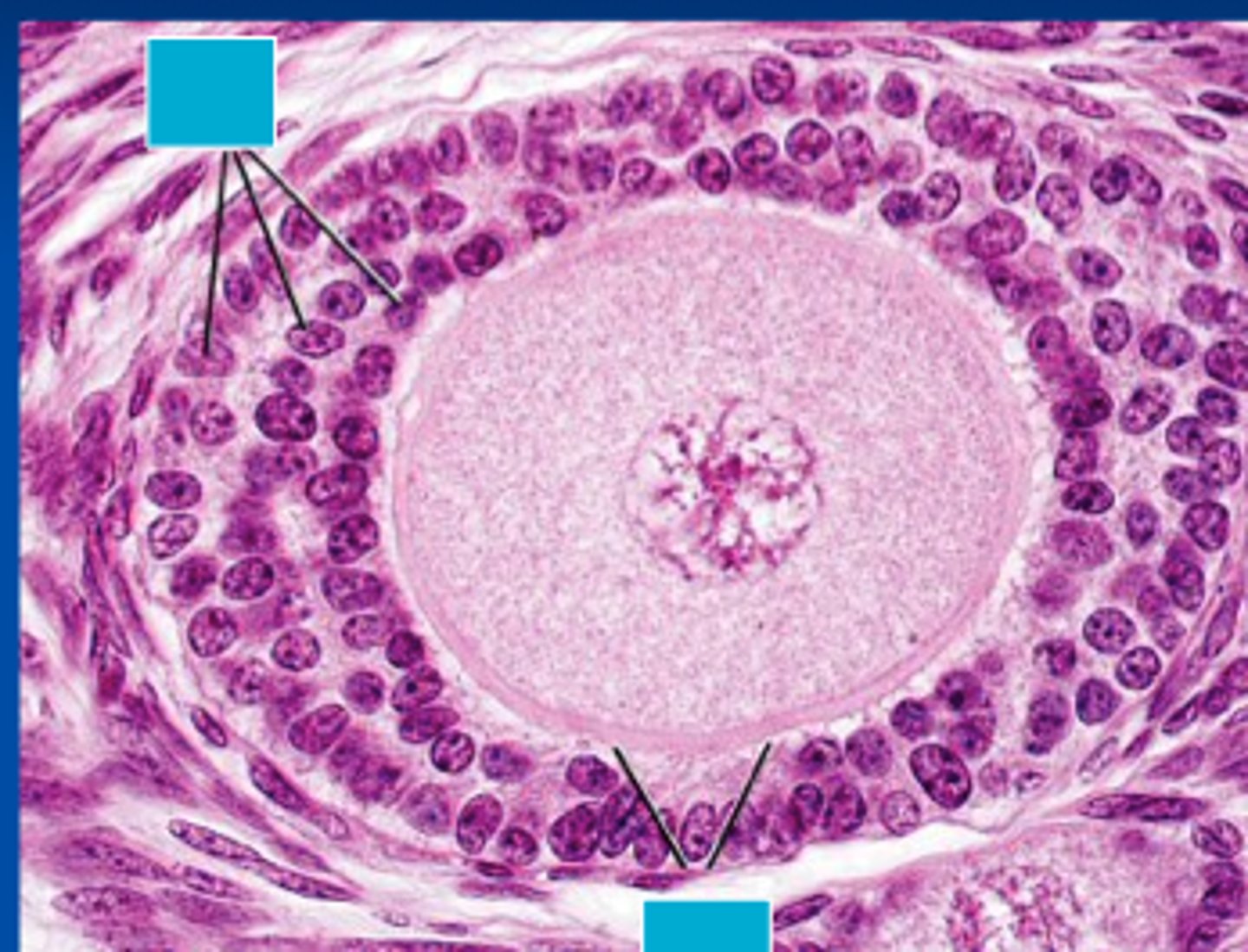
What happens as a primary follicle is developing?
As a primary follicle develops, its surrounding cells multiply from a simple cuboidal epithelium to stratified cuboidal epithelium.
estrogen
female sex hormone
Which would you expect to find more of primordial follicles or primary follicles? Why?
primordial follicles are the earliest stage of follicle development and make up the majority of the ovarian follicle reserve. As follicles develop into primary follicles, many undergo degeneration, reducing their numbers.
secondary follicle
fluid-filled spaces between follicle cells. It contains a primary oocyte
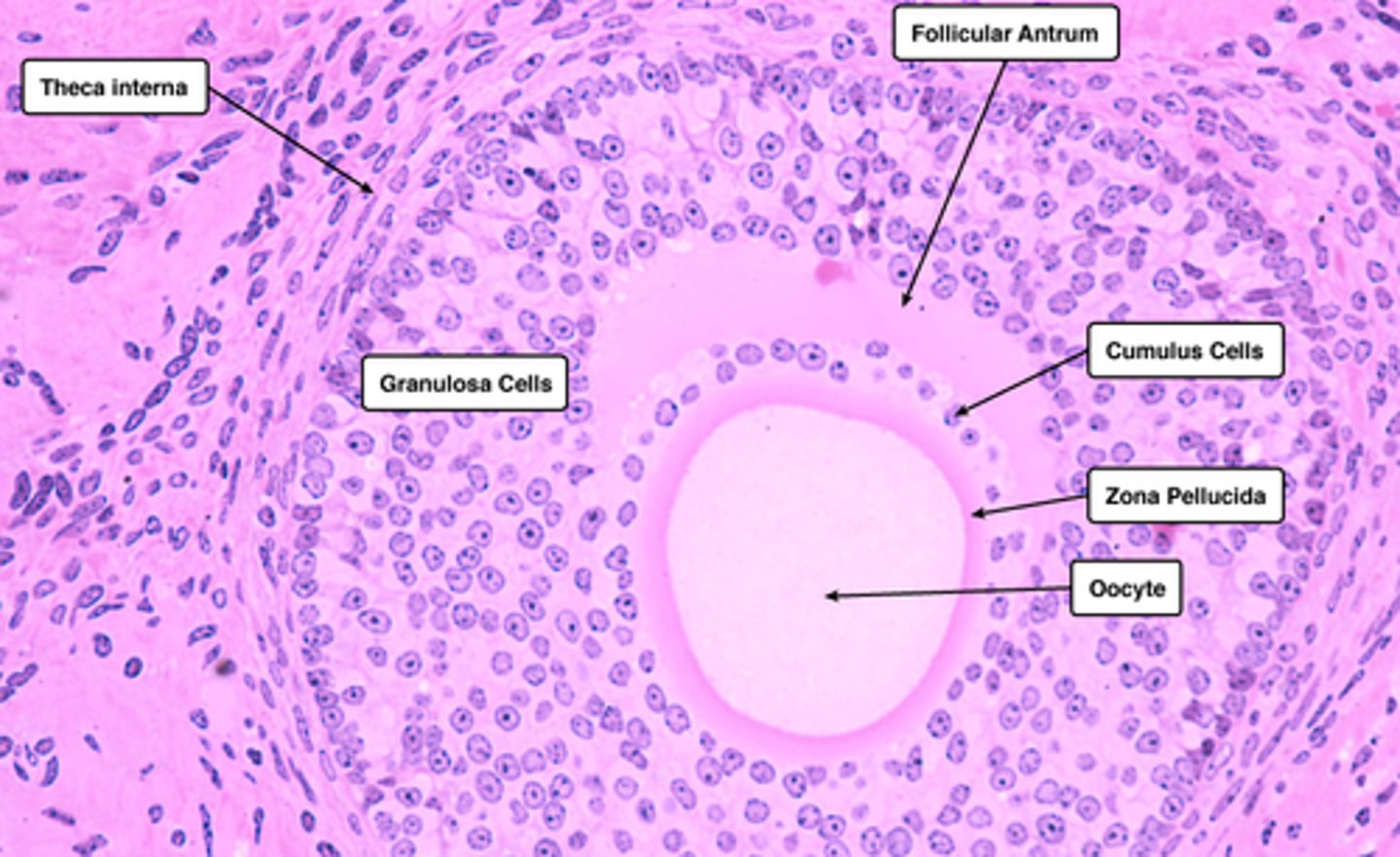
antrum
a single substantial cavity formed from the enlargement and coalesce of the secondary follicle
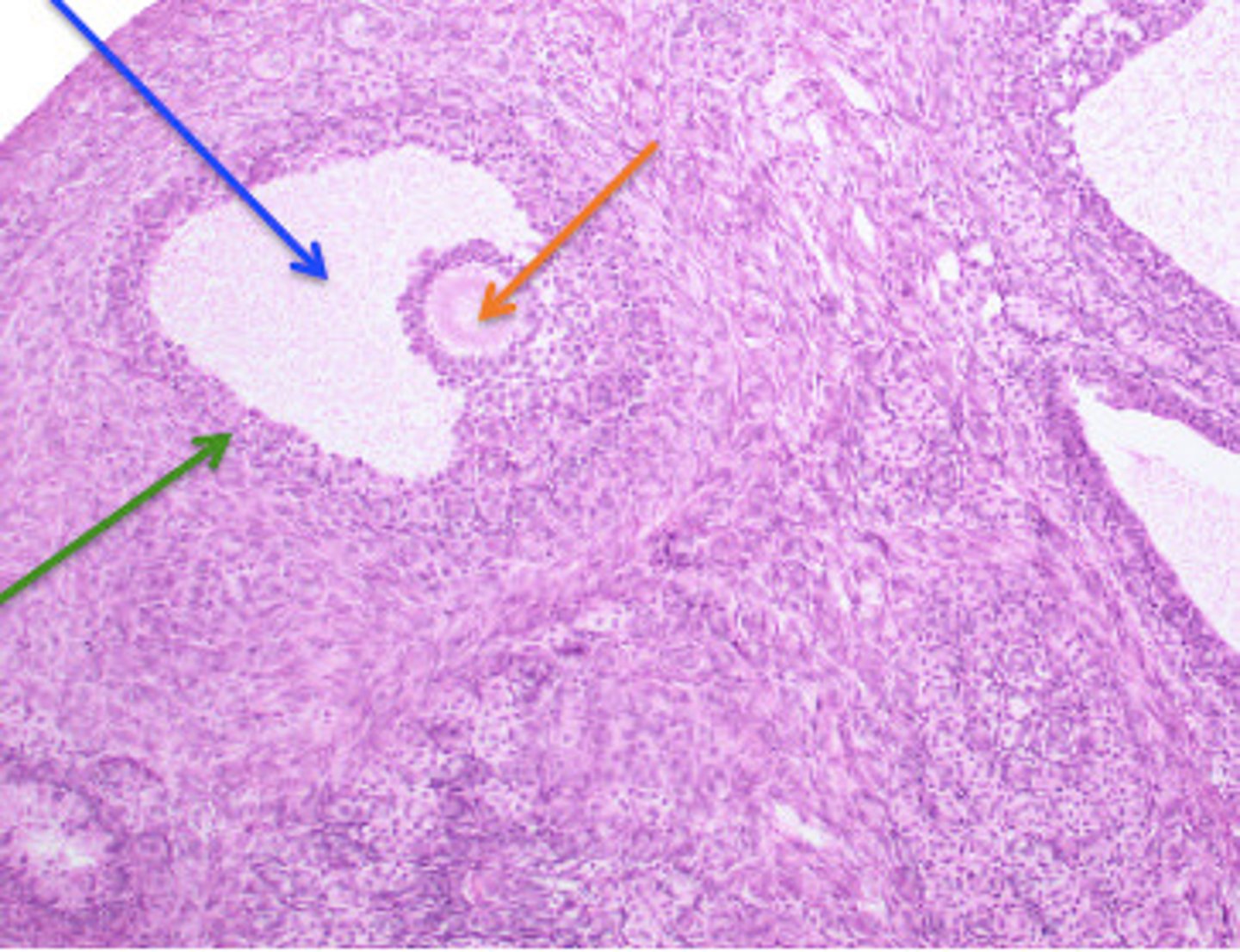
Vesicular follicle (Graafian follicle)
final stage of follicle development before ovulation.
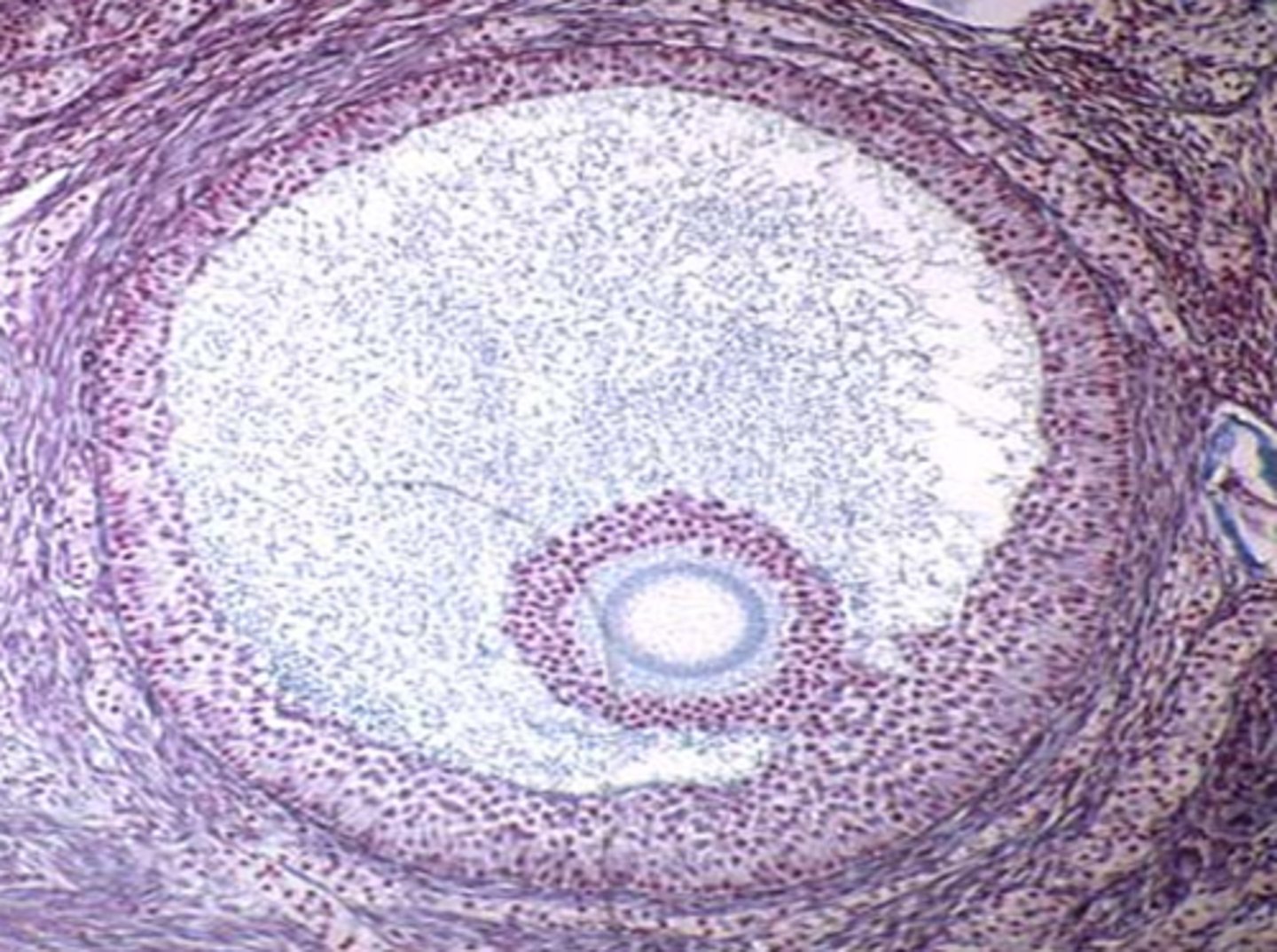
ovulation
The process of releasing a mature ovum into the fallopian tube each month
luteinizing hormone (LH)
secreted by the pituitary gland to promote ovulation.
secondary oocyte and polar body
two haploid cells produced by the primary oocyte following the first meiotic division
ovum
is the mature, haploid cell that results from a oocyte being fertilized by sperm and dividing.
zygote
combination of a sperm and ovum
corpus luteum
formed from the remains of a vesicular follicle after ovulation. It secretes progesterone and some estrogen
progesterone
a hormone produced by the ovaries to help maintain the uterus in a read-to-receive state just in case fertilization occurs.