catabolism of fats
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Fat as an Energy Source
Fats are the most concentrated store of metabolic energy per gram due to being highly reduced and hydrophobic.
Why do fats release more energy than carbohydrates when oxidized?
Because fats are more reduced and have more C–H bonds, which release more energy upon oxidation.
Water-Free Storage of Fat
Fats are hydrophobic, so they are stored without water, unlike polysaccharides that bind water, making fat more energy-dense by weight.
Oxidation States of Carbon
In metabolism, carbon atoms in molecules can be oxidized step by step, losing electrons (usually as hydrogen atoms). Each oxidation step releases energy, which the body can use.
Alkane (C:3H)
Most reduced form → contains the most energy
Alcohol (C:3H:1O)
Slightly oxidized — hydroxyl group added
Aldehyde/Acid (C:1H:2O)
More oxidized — carbon double bonded to O, fewer Hs
Carbon dioxide (C:0H:2O)
Final oxidation product
Most oxidized form of carbon → no more energy can be extracted
what happens here is step by step more oxidation is happening so alkane oxidized becomes alcohol, alcohol oxidized becomes aldehyde and so on
Consider that the following four compounds are completely
oxidized to CO2
(i) CH3-CH 3 (Alkane) (2C:6H)
(ii) CH 3CHO (Aldehyde) (2C:4H:1O)
(iii) CH 3CH 2OH (Alcohol) (2C:6H:1O)
(iv) CCHH33 CCOOOOHH (Carboxylic Acid) (2C:4H:2O)
The relative quantities of free energy released under
standard conditions are:
A (i)>(iii)>(ii)>(v)
B. (iv)>(ii)>(iii)>(i)
C. (ii)>(iii)>(i)>(iv)
D. (iii)>(ii)>(i)>(iv)
A
Remember from above - the most energy comes from alkane, then alcohol, then aldehyde, then carboxylic acid, then co2
The one that is the most reduced already releases the most energy
What is the order in which the body uses energy stores during fasting?
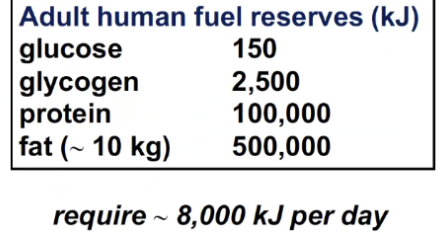
so the body uses glucose first, then glycogen, than fat, then proteins
fat i the largest energy store but its harder to mobilize then glucose or glycogen
proteins are broken down during cases of starvation
Triacylglycerols (TAGs)
The main storage form of fatty acids in the body; composed of three fatty acids attached to a glycerol backbone.
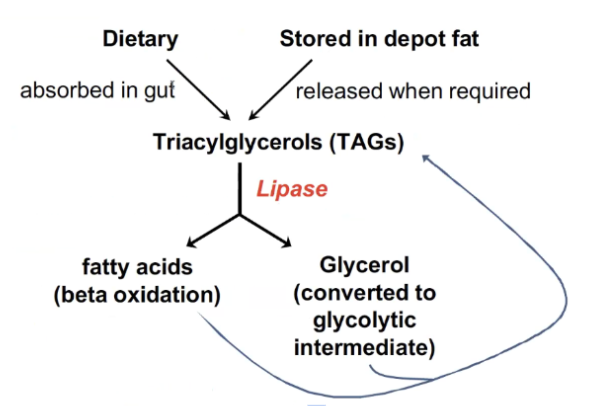
The fats gets converted into TAGs and then broken down into fatty acids and glycerols
Lipase
Enzyme that breaks down TAGs into free fatty acids and glycerol for energy use.
Complete Oxidation of Fatty Acids
A three-stage process by which fatty acids are fully broken down into CO₂, H₂O, and ATP.
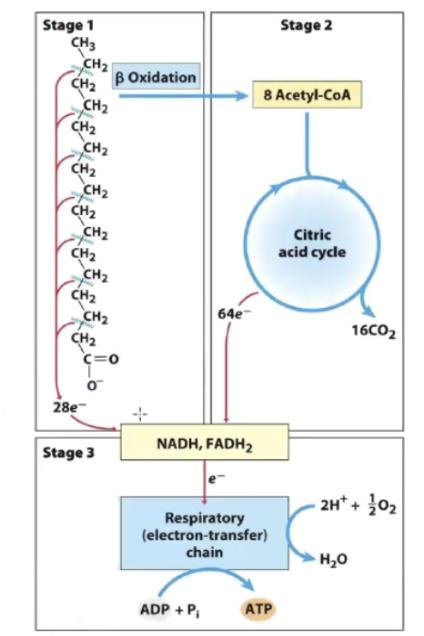
What are the three stages of complete fatty acid oxidation?
beta oxidation → Fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria to form acetyl-CoA and reduced cofactors (NADH, FADH₂).
citric acid cycle → Acetyl-CoA enters this cycle to generate CO₂, NADH, and FADH₂.
ETC → Electrons from NADH and FADH₂ are transferred to the ETC to drive ATP production and form H₂O.
What is produced during beta oxidation of fatty acids?
Acetyl-CoA, NADH, and FADH₂
Beta Oxidation history
Franz Knoop discovered that fatty acids are broken down 2 carbons at a time by tagging their ends with phenyl groups and analyzing dog urine after they ate the fats.
This experiment showed that:
Even-carbon fatty acids produce phenylacetic acid (2-carbon end product)
Odd-carbon fatty acids produce benzoic acid (1-carbon end product)
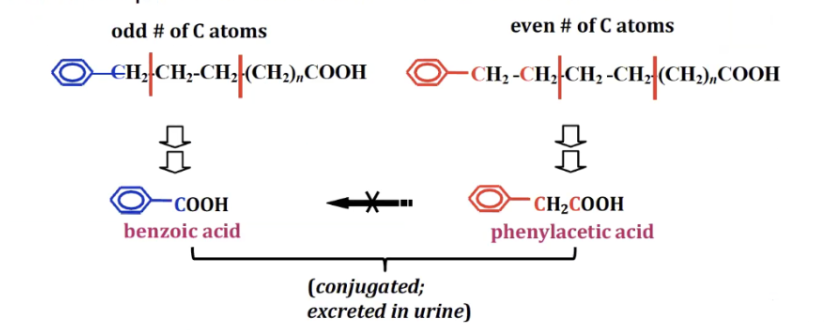
conclusion: fatty acids are catabolized 2 at a time
True or false, all naturally occuring fatty acids have even numbers of carbons?
True, its because we break fatty acids down in twos.
How are fatty acids prepared for catabolism?
The carbons need to be be activated in order to be more reactive.
What is the activated form that fatty acids need to be in to initatie beta oxidation?
fatty acyl-CoA
Synthetase
an enzyme that combines two small molecules to form a larger molecule with the help of ATP energy
Synthase
an enzyme that combines two small molecules to form a larger molecule without the help of ATP energy
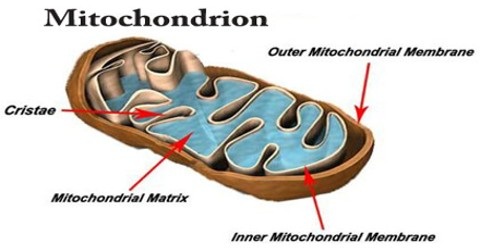
Where does the actiavtion occur?
on the outter mitochondrial membrane
What is the reaction for the activation of fatty acids
Fatty Acid+CoA+ATP→Fatty Acyl-CoA+AMP+PPi
so pretty easy fatty acid and coA and some energy to get the reaction started - ATP was needed to attach CoA to the fatty acid
irreversible reaction
What enzyme activates fatty acids?
Acyl-CoA synthetase, which forms fatty acyl-CoA from fatty acid + CoA + ATP.
Acyl-CoA synthetase, which forms fatty acyl-CoA from fatty acid + CoA + ATP.
ATP is converted to AMP + PPi, which is equivalent to using 2 ATP.
How many steps dpes fatty acid activation need to take place?
2
fatty acid activation step
step 1. The nucleophilic oxygen of the fatty acid attacks the alpha phosphate of ATP.
this forms PPi and acyl adenylate.
The PPi is hydrolyzed to 2Pi
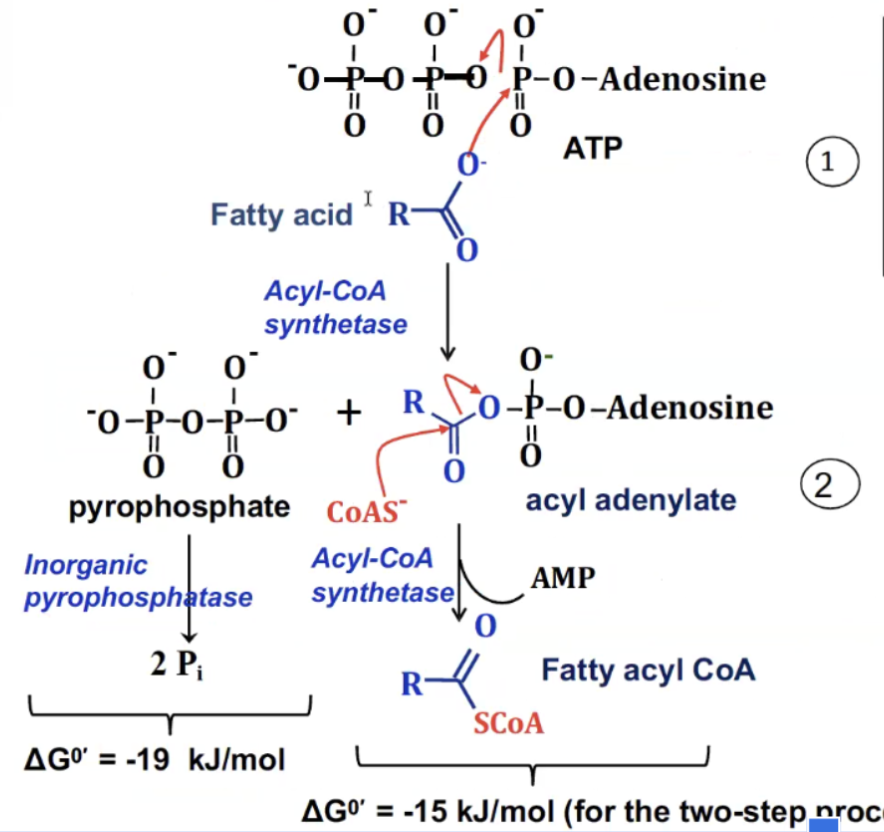
Step 2. The Thiol (-SH) group on coenzyme A acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acyl-adenylate intermediete.
AMP leaves, and the final product is fattyacyl-CoA
Where does fatty acid activation take place?
Fatty acids are activated in the cytoplasm outside the mitochondria
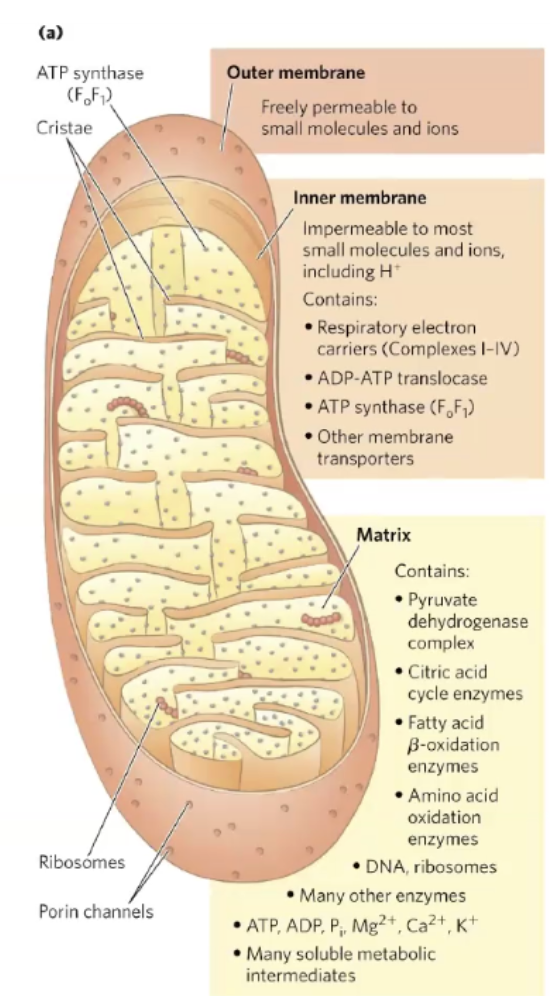
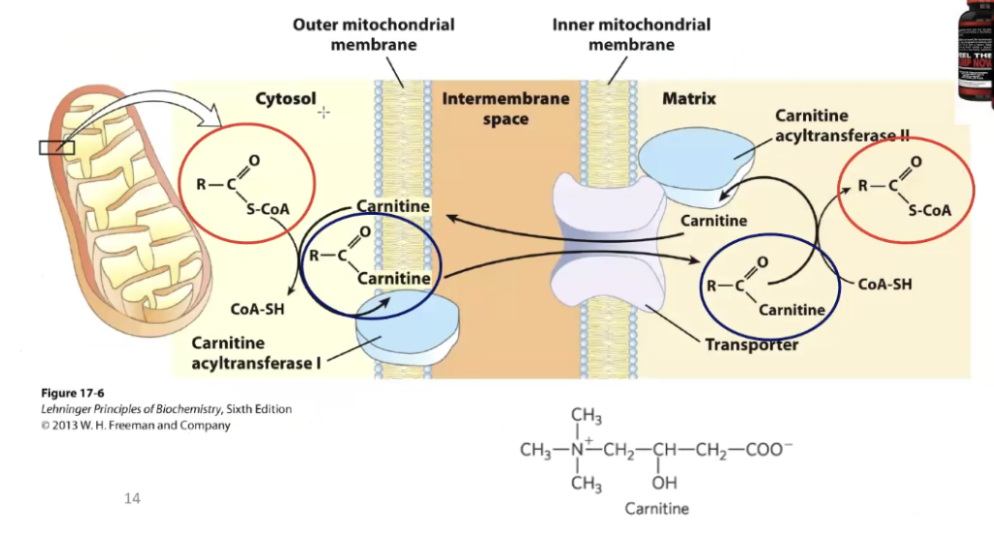
Where does beta oxidation take place?
In the mitochondrial matrix, but fatty acyl-CoA (our new product) can pass through the outer membrane but cannot pass through on its own (especially true for longer fatty acids).
it needs a shuttle to enter the matrix.
This shuttle involves carnitine.
The Carnitine shuttle system
We need to attach fatty acyl-coA to carrier carnitine and it transports it across the inner membrane and releases it into the matrix, carnitine can be recelyed to the cytoplasm.