Interactions of Radiation with Matter: Neutrons
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts related to the interactions of radiation with matter, particularly focusing on neutrons and their various sources and reactions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Neutron Sources
Neutrons can be generated from various sources including (α,n) reactions, (γ,n) reactions, nuclear fission, and particle accelerators. There are no naturally occuring radioisotopes that decay only emitting neutrons.
(α,n) Reactions
Reactions where alpha particles interact with target nuclei to produce neutrons. Combining alpha emitting radionuclide (Po-210, Ra-226, Pu-239) with light metal (Be, B). Continuous energy spectrum.
(γ,n) Reactions
Neutrons produced by gamma interactions with light elements, such as 9Be(γ,n)8Be. Radioisotopes with a single y-ray, monoenergetic neutrons can be produced.
Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
A technique for elemental analysis involving the absorption of neutrons, inducing radioactivity in the target.
Thermal Neutrons
Neutrons with energies around 0.025 eV, indistinguishable from gas molecules in their environment.
Fast Neutrons
Neutrons with kinetic energies greater than 0.1 MeV, capable of penetrating nuclei.
Elastic Scattering
An interaction where the neutron bounces off a nucleus without losing energy, typically observed with low-Z nuclei.
Inelastic Scattering
Occurs when a neutron strikes a high-Z nucleus, transferring energy and causing the nucleus to emit gamma radiation.
Neutron Diffusion Length
The average distance traveled by neutrons before being absorbed, includes fast-diffusion and thermal diffusion lengths.
Charge Particle Emission
Reactions involving slow neutrons that results in the emission of charged particles like protons or alpha particles.
Neutrons from Accelerators
Neutrons generated through nuclear reactions facilitated by particle accelerators, such as the D-T reaction producing 14 MeV neutrons.
Neutron Absorption Cross-Section
A measure of the probability of neutron absorption by a nucleus, energy-dependent and described by 1/v law.
Neutron Capture
A process where neutrons are absorbed by a nucleus, leading to various reactions such as (n,γ) and (n,p).
Spontaneous Fission
Neutron emission from heavy nuclei as part of their decay process, often occurring for isotopes like 252Cf.
Neutron Emission Rate
The number of neutrons emitted per unit time from a source, critical for understanding neutron generators.
Energy Distribution of Neutrons
Refers to the variation in neutron energies produced in reactions, typically characterized by an average and most probable energy.
Neutron Reactions Important to Health Physicists
Key neutron interactions that affect biological tissues, contributing to radiation doses in various medical and health physics applications.
Deuterium-Deuterium Fusion
Produces a 2 Mev neutron
Deuterium-Tritium Fusion
Produces a 14 MeV neutron.
Classification of neutrons
Classified according to their energy
Thermal
Around 0.025 eV
Epithermal, resonance, slow
Between 0.01 MeV and 0.1 MeV
Fast
Greater than 0.1 MeV and less than 20 MeV
Relativistic
Greater than 20 MeV
Probable Energy
Emp=KT
Average Energy
E=3/2KT
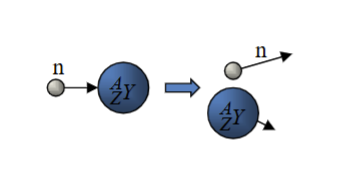
Elastic Scattering
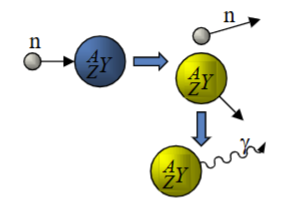
Inelastic Scattering
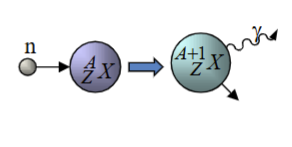
Radiative Capture
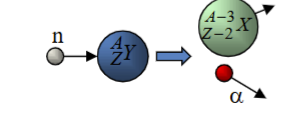
Charged-Particle Reactions
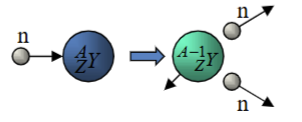
Neutron-Producing Reactions
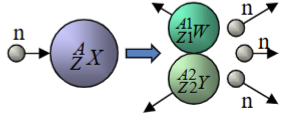
Fission
Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
A highly sensitive technique that involves bombarding a sample with neutrons to induce a radioactive state, then measuring the characteristic gamma rays emitted as the induced radioactive isotopes decay.