Chapter 9 Vocab - Agriculture
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Human Geography key terms on agriculture
Last updated 3:28 PM on 2/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Agricultural Revolution
The process that began when human beings first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering
2
New cards
Second Agricultural Revolution
An increase in agricultural activity through the improvement of crop rotation and breeding of livestock beginning in the UK in the seventeenth century; the development of improved sanitation, storage, and fertilization techniques, allowing for greater food output; coincided with the Industrial Revolution in England and a higher population growth rate
3
New cards
Third Agricultural Revolution
Also known as the Green Revolution, started in Mexico to increase wheat production and led to the creation of miracle seeds, new fertilizers, pesticides, and GMOs
4
New cards
Green Revolution
The rapid diffusion of new agricultural technology, especially high-yield seeds and fertilizers; also known as the Third Agricultural Revolution
5
New cards
Primary Economic Activity
Any economic activity pertaining to the collecting, harvesting, and obtaining of raw materials; extraction from Earth (growing chickens, planting soybeans, oil drilling, lumberjack, mining, fishing)
6
New cards
Secondary Economic Activity
Any economic activity pertaining to the manufacturing of useful products through processing, transforming, and assembling raw materials (slaughter, packaging, polishing minerals, making plywood)
7
New cards
Tertiary Economic Activity
Any economic activity pertaining to the provision of services (transportation, banking, retailing, education, marketing, stocking stores, teachers, truck drivers, hairdressers)
8
New cards
Quaternary Economic Activity
Any economic activity pertaining to the collection, processing, and manipulation of information, capital, and culture; evaluation and decision-making (finance, government, insurance, legal services, scientist, urban planner)
9
New cards
Quinary Economic Activity
High education and high decision-making power (high level in gov. or business, president)
10
New cards
Subsistence Agriculture
The providing of food for direct consumption by the farmer and farmer's family
11
New cards
Intensive Subsistence Agriculture
A form of subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a parcel of land
12
New cards
Crop Rotation
The planting of different crops each year to replenish the soil's nutrients that were lost to a previous crop and avoids exhausting the soil (Subsistence)
13
New cards
Shifting Cultivation
The moving of farm fields after several years in search of more productive soil after depleting the previous one (Subsistence)
14
New cards
Pastoral Nomadism
A form of subsistence agriculture based on herding domesticated animals (Subsistence)
15
New cards
Commercial Agriculture
The farming of products for sale off the farm
16
New cards
Market Gardening and Fruit Farming
Relatively small-scale production of fruits, vegetables, and other horticulture crops (Commercial)
17
New cards
Truck Farming
Gardening and fruit farming, so titled because the name came from a Middle English word meaning "bartering" (Commercial)
18
New cards
Plantation Agriculture
Agriculture performed on a large farm in tropical and subtropical climates that specializes in the production of one or two crops for sale, usually to a more developed country (Commercial)
19
New cards
Dairy Farm
A form of commercial agriculture that specializes in the production of milk and other dairy products (Commercial Intensive)
20
New cards
Ranching
Livestock graze over an extensive area (Commercial)
21
New cards
Mixed Crop and Livestock Farming
The integration of crops and livestock; most of the crops are fed to animals rather than consumed directly by humans (Commercial)
22
New cards
Conservation Tillage
A method of oil cultivation that reduces soil erosion and run-off
23
New cards
Monocropping (Monoculture)
The practice of growing the same single crop every year
24
New cards
No Tillage
A farming practice that leaves all of the soul undisturbed and the entire residue of the previous year’s harvest left untouched on the fields
25
New cards
Transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures
26
New cards
Aquaculture (Aquafarming)
The cultivation of seafood under controlled conditions
27
New cards
Organic Agriculture
Plants grown without green technology
28
New cards
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
Organisms whose genetic material has been modified for increased agricultural output
29
New cards
Herbicide
A chemical to control unwanted plants
30
New cards
Paddy
The Malay word for wet rice, increasingly used to describe a flooded field
31
New cards
Pesticide
A substance to control pests, including weeds
32
New cards
Sawah
A field deliberately flooded for growing rice
33
New cards
Wet Rice
Rice planted on dry land in a nursery, then moved to a deliberately flooded field to promote growth
34
New cards
Luxury Crops
Crops like tobacco that are grown for profit but are not necessarily needed by a population
35
New cards
Crop
A yield of a plant that is grown in abundance to be harvested as food, fodder, fuel, or commercial sale
36
New cards
Cash Crop
A crop that is grown for sale rather than the farmer’s own use (tobacco)
37
New cards
Cereal Grain
A grass with starchy grains, which are used in many different foods
38
New cards
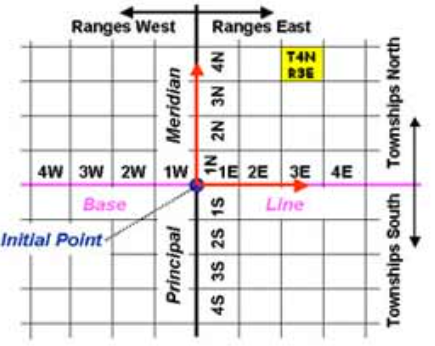
Township and Range Survey System
Uses longitude, latitude, baselines, grids, and cardinal directions
39
New cards
Rectangular Survey System
idk
40
New cards
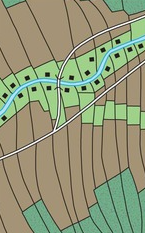
Long-Lot Survey System
Narrow parcels by transportation
41
New cards
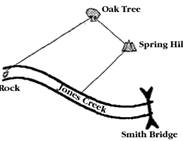
Metes and Bounds Survey System
Short distances from key features
42
New cards
Agribusiness
Commercial agriculture is characterized by the integration of different steps in the food-processing industry, usually through ownership by large corporations; a term referring to every business involved in commercial farming in one - farms, factories, suppliers, ad agencies, processing, etc
43
New cards
Agriculture
The deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth’s surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic growth; the raising of animals or the growing of crops on tended land to obtain food for primary consumption by a farmer's family or for sale off the farm
44
New cards
Desertification
The extreme deterioration of land in arid/semiarid regions due to loss of vegetation and soil moisture, excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting
45
New cards
Dietary Energy Consumption
The amount of food that an individual consumes, measured in kilocalories
46
New cards
Food Security
Physical, social, and economic access at all times to safe and nutritious food sufficient to meet dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life
47
New cards
Horticulture
The growing of fruits, vegetables, and flowers
48
New cards
Milkshed
The area surrounding a city from which milk is supplied
49
New cards
Undernourishment
Dietary energy consumption that is continuously below the minimum requirement for maintaining a healthy life and carrying out light physical activity