Calculating and Dispensing
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is considered a hazardous drug?
o A drug is considered to be hazardous if it exhibits one or more of the following characteristics in humans or animals:
§ Carcinogenicity
§ Teratogenicity
§ Developmental toxicity
§ Reproductive toxicity
§ Organ toxicity at low doses
§ Genotoxicity or structure and toxicity profiles of new drugs that mimic existing hazardous drugs.
What is the workflow process for chemotherapy medications?
-The chemotherapy is ordered
-After the order is check the chemotherapy is prepared
-Final verification and dispensing takes place
-The chemotherapy is then administered to the patient
-After administration the chemotherapy is disposed of
How do you dispose of chemotherapy?
-Yellow Basket ( trace chemotherapy): < 3% of original amount of chemotherapy is left
-BlackBasket ( bulk chemotherapy): > 3% of original amount of chemotherapy is left
When you are going through workflow what information do you look at about the patient before chemotherapy treatment is administered?
-During this process you gain an overview of the patient.
-You verify the patient’s cancer diagnosis
-Ensure treatment plan matches the diagnosis
What are the steps involved to ensure that the treatment plan matches the diagnosis?
§ Obtaining approval from insurance company to receive a particular medical service, treatment, or prescription drug.
§ Verify with the clinal notes and the patient’s current course of therapy that the correct medication, dosage form, product has been chosen.
§ Ensure the treatment parameters that are required have been met by the patient ( lab monitoring, imaging, etc.)
§ Ensure the necessary pre-medications have been ordered and have met criteria based upon the patient’s overall health.
§ Ensure correct supportive care medications are ordered based on the regimen type.
When you are trying to plan the the chemotherapy regimen what things do you consider?
-you review pertinent literature
-look at the time for treatment
-review appropriateness of regimen
-figure out chemotherapy dose
-chemotherapy sequence
What things do you have to consider about a patient on chemotherapy renal function?
-Check their CrCl
-Patient risk factors
-Look at medication related causes for renal dysfunction
A patient is on chemotherapy , what do you check in order to monitor for myelosuppression:
o Check RBCs, WBCs, ANC, and PLTs.
o Medication induced causes.
What do you check on a patient on chemotherapy to monitor their liver function?
o LFTs (AST and ALT)
o Metastatic disease ( see if disease has spread to the liver)
o Medication induced causes.( see if medication is causing the liver function to decline)
What do you check in a patient on chemotherapy to monitor their pulmonary function?
o PFTs
o Metastatic disease ( has the cancer spread to the lungs)
o Medication related causes. ( what medications are deceasing pulmonary function)
What test do you use to monitor the Cardiac Function in patients on chemotherapy?
-You monitor the Ejection Fraction using a ECHO
How do you calculate chemotherapy dosing using BSA?
· Calculate GB’s Rituxan dose if the standard rituximab dose is 375 mg/m2 and his BSA= 1.81 m2
· (375 mg/m^2)(1.81 m^2)= 679 mg
How do you calculate chemotherapy dosing using weight-based dosing?
· Calculate the patients’ dose of bevacizumab. The standard dose of bevacizumab is 15 mg/kg and their TBW= 72 kg
· (15 mg/kg)(72 kg)=1080 mg
What is advantage of flat dosing?
· Limited potential dose calculation mistakes.
What are some examples of medications with a flat dosing?
o Pertuzumab
o pembrolizumab
AUC dosing for Carboplatin:
· Carboplatin dose (mg) = Target AUC x (CrCl+25)
What are dosing considerations when calculating chemotherapy regimen by AUC?
o Maximum CrCl= 125 mL/min
o Minimum SCr=0.7 mg/dL
o For CrCl calculation, multiply by 0.85 if female.
· LT, 57 yo male with a 58 pack-year smoking history with newly diagnosed stage IV NSCLC with no targetable driver mutations. He will begin first-line treatment with carboplatin (AUC 5) + pemetrexed + pembrolizumab. What is the dose of Carboplatin for LT?
· TBW: 70 kg
· Ht: 170 cm
· SCr: 0.5 mg/dL ( but the minimum SCr for carboplatin is 0.7 mg/dL, so that is what we have to use)
o 1st step would be to find the CrCl:
§ ((140-57)(70))/(0.7)(72)=115 mL/min
o 2nd Step would be to determine if the CrCl has reach the maximum of 125 mL/min:
§ If it has not reach 125 mL/min than you can use the CrCl you found.
§ If the CrCl is greater than 125 mL/min then you can only use 125 mL/min for the CrCl in the formula.
o 3rd step would be to plug everything into the formula; Target AUC * (CrCl +25):
§ In the scenario it says the target AUC is 5.
§ 5 * (115 + 25)= 700 mg
What is the AUC formula for dialysis patients?
o Carboplatin dose= Target AUC * 25
What medications have some dose/weight caps?
§ Vincristine IV: 2 mg
§ Carfilzomib: 2.2 m^2 (BSA)
§ Brentuximab vedotin: 100 kg
Calculate GB’s vincristine dose if standard vincristine dose is 1.4 mg/m^2 and his BSA is 1.81 m^2
· (1.4 mg/m^2)(1.81 m^2)= 2.5 mg , but the max is 2 mg , so you give GB vincristine 2 mg IV.
Calculate a patient’s carfilzomib dose if the standard carfilzomib dose is 56 mg/m^2 and their BSA is 2.8 m^2
· Since the maximum BSA for Carfilzomib is 2.2 m^2 you must use that in the formula.
· 56 mg/m^2 * 2.2m^2= 123 mg
When do you recalculate the dose?
§ Recalculate dose if weight changes by > 10% from baseline.
Which chemotherapy medications have their doses tracked?
o Anthracyclines:
§ Doxorubicin
§ Epirubicin
§ Daunorubicin
§ Idarubicin
o Anthracenedione:
§ Mitoxantrone
o Bleomycin
o Carmustine and lomustine
o Mitomycin
How do you monitor chemotherapy toxicities?
· Identify chemo-induced toxicities.
· Supportive care regimen assessment.
· Patient allergies, drug-drug interactions.
What is the steps in the order verification process?
· Check drug calculations.
· Do an admixture assessment.
· Administration considerations.
What things can be checked in final chemotherapy verification?
§ Drug
§ Dose (volume)
§ Reconstitution diluent type and volume
§ Diluent type and volume
§ Expiration dates
§ Tubing type
§ Filters (if needed)
§ Use of closed-system transfer devices for compounding of hazardous medications
§ Appropriate auxiliary labels
§ Light and temperature storage conditions
Appropriate non-PVC/DEHP bags for taxanes, etoposide, and temsirolimus
What medications are look alike sound alike medications?
§ Taxol (paclitaxel) , Taxotere (docetaxel)
§ Taxol (paclitaxel), Abraxane (nab-paclitaxel)
§ Carboplatin, Cisplatin
§ Herceptin (trastuzumab), Kadcyla (ado-trastuzumab emtansine), Enhertu (fam-trastuzumab)
How can you prevent medication errors involving chemotherapy agents?
§ 2nd person verification
§ Ordering medications by reference dose (mg/m2, mg/kg or AUC) unless flat dose
§ TALLman Lettering
§ Clear labeling
Drug storage separation
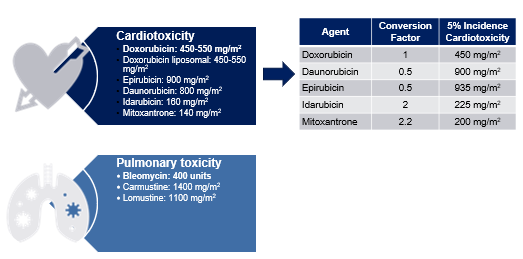
Medications with lifetime dosing:
What is USP 795?
§ Non-sterile compounding standards.
What is USP 797?
§ Sterile compounding standards.
What is USP 800?
§ Hazardous compounding standards.
What PPE is used when compounding hazardous drugs?
gloves
gowns
shoe covers
hair cover
beard cover, if applicable
mark
respirator
What is the policy for gloves while compounding hazardous drugs?
· Two pairs of sterile gloves should be worn when compounding chemotherapy.
· 1st pair is under the gown cuffs and 2nd pair is over the gown’s cuffs.
· Must change gloves every 30 minutes or when torn, punctured, or contaminated.
What are the requirements for gowns for compounding hazardous drugs?
· Must resist permeability.
· Close in the back.
· Long-sleeved
· Closed cuffs.
When are respirators required?
o Monthly BSC hood decontamination.
o Chemotherapy spills.
Where are chemotherapy compounded?
§ Inside biological safety cabinet (BSC) or chemotherapy isolator vented externally.
What is the goal of using a closed system transfer device
§ Reduce the risk of chemotherapy exposure.
What are the ways to administer chemotherapy?
§ IV push
§ IV infusion:
· Peripheral IV
· Central Venous Catheters:
o PICC Line
o Implanted Port
§ Subcutaneous
§ Intramuscular
intravitreal
Intrathecal
Intrathecal:
· Ommaya reservoir is an alternative intrathecal site.
· Ventricular access device for the purpose of repetitive access to the intrathecal space.
-Labeled as Intrathecal
-Preservative free formulation
What medications is intrathecal chemotherapy commonly used?
o Methotrexate
o Cytarabine
o Trastuzumab
o Rituximab
Which class of medications do you not use intrathecal administration?
o Vinca alkaloids because administration this way is fatal.
Which chemotherapy medications are commonly given via ambulatory infusion pumps?
§ Fluorouracil
§ Doxorubicin
§ Ifosphamide
§ Etoposide