Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
1/63
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
How do offspring acquire genes from parents?
By inheriting chromosomes
what is the transmission of traits frm one generation to the next called?
inheritance or HEREDITY
Offsprings are ___________________ copies of either parent or pf their siblings
not identical
Along with inherited similarity, there is ___________
variation
what are genes
units of heredity
What are genes made of?
made up of segments of DNA
how are genes passed to the next generation
via reproductive cells called gametes (sperm and eggs)
how is most DNA packaged
into chromosomes
how many chromosomes do humans have (not the # of pairs)
46
what are somatic cells
all cells of the body except gametes and their precursors
where are the 46 chromosomes in humans
in the nuclei of their somatic cells
what is a locus
a gene’s specific position along a chromosome
how does asexual reproduction work
a single individual passes all of its genes to its offspring w/o the fusion of gametes
what is a clone
a clone is an individual or group of genetically identical individuals from the same parent
how does sexual reproduction work?
two parents give rise to offspringf that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents
what is a (sexual) life cycle?… (chromosomes?)
a life cycle is the generation to generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism
the behavior of chromosomes are related to the human lifecycle and other types of sexual life cycles
how many pairs of chromosomes do human somatic cells have?
23 pairs
what is a karyotype
an ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell
what are the two chromosomes in each pair called?
homologous chromosomes or homologs
how are chromosomes in a homologous pair?
they have the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern
They also carry genes controlling the same inherited ccharacters
what are the sex chromosomes, which determine the sex of the individual, called
X and Y
female sex chromosomes:
XX
Male sex chromosomes:
XY
what are the remaining (non sex chromosomes) called?
autosomes
what does each pair of homologous chromosomes include?
one chromosome from each parent; the 46 chromosomes in a human somatic cell are two sets of 23: one from the mother and one from the father
what is a diploid cell?
(2n) has two sets of chromosomes
for humans what is the diploid number?
46 or 2n = 46
in a dcell in which DNA synthesis has occurred, each chromosome is ______________
replicated
what does each replicated chromosome consist of ?
sister chromatids
what is a gamete
a sperm or egg
is a gamete a diploid or a haploid cell?
haploid (n) → contains a single set of chromosomes
what is the haploid number for humans
n = 23
in an unfertilized egg (ovum), what is the sex chromosome
X
in a sperm cell, the sex crhomosomes may be …
X or Y
what is fertilization
the union of gametes (the sperm and the egg)
what is a fertilized eggs called?
called a zygote and has one set of chromosomes from each parent
how does a zygote produce somatic cells
produces somatic cells by mitosis and develops into an adult
which organs produce gametes
the ovaries and testes produce haploid gametes
gametes are the only type of human cells produced by ___.
meiosis
what does meiosis result in (pertaining to chromosomes and sets)
meiosis results in one set of chromosomes in each gamete
______________ and __________ alternate in sexual life cycles to maintain chromosome number
fertilization
meiosis
teh alternation of meiosis and fertilization is _____________________ to ____ organisms that reproduce sexually
common
all
the three main types of sexual life cycles differ ijn the timing of _______________ and ___________
meiosis
fertilization
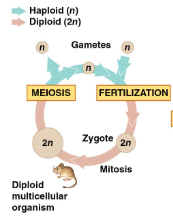
what is the life cycle of an animal
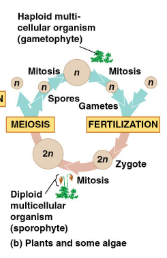
what is the life cycle of plants and some algae
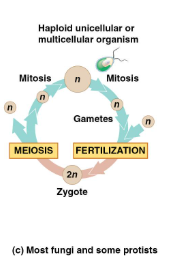
what is the life cycle of most fungii and some protists
_________________ are the only haploid cells in most animals
gametes
how are gametes produced
by meiosis and undergo no further cell division before fertilization
how do gametes debvelop into a multicellular organism
gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote that divides by mitosis to develop into a multicellular organism
what life forms exhibit an alternation of generations?
plants and some algae
do the life cycles of plants and some algae exhibit a diploid &/or a haploid multicellular stage
both diploid ajd haploid stages are present