sound waves
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Circular Motion
Motion in a circular path.
Periodic Motion [ eg.]
Repeated motion in a regular interval of time
planets revolving around the sun
Oscillation
A type of periodic motion in which an object moves to and fro at regular intervals of time about its equilibrium position
Such as a swinging pendulum or vibrating string.
true or false : All the oscillatory motions are periodic
True, all oscillatory motions are periodic, but not all periodic motions are oscillatory.
Amplitude (a)
The magnitude of maximum displacement to one side from its equilibrium position is amplitude
period (T) [ equation] [ unit]
The time taken for one oscillation is called period(T).
period = total time / no. of oscillation
T = t / n
unit of period is seconds (s).
FREQUENCY(f) [ equation ] [unit]
number of oscillation in one second is frequency
frequency = no. of oscillation / time taken
f = n/t
unit of frequency = hertz (Hz).
relation between frequency and period [equation]
Inversely proportional to each other; as frequency increases, the period decreases.
f = 1/ T
natural frequency
When an object vibrates freely, it vibrates in its innate frequency. This is the natural frequency of that object.
Factors Influence Natural Frequency (increases)
Length of the object ( dreases)
Size/mass of the object (increases)
Elasticity (increases)
Nature of the material
Forced Vibration
Forced vibration is the vibration of an object induced by an external vibrating object.
ex: phones vibration making a table vibrate
Resonance
If the natural frequency of the forcing object and that of the forced object are equal, the objects are said to be in resonance.
• The objects undergoing resonance will vibrate with maximum amplitude.
Applications of forced vibration and resonance
• MRI scanning • Radio tuning
• In musical instruments like guitar, violin, veena, harmonium, mridangam etc.
• A stethoscope used to listen to even a feeble sound in the body
• In instruments like megaphones, horns and musical instruments such as trumpets and nagaswaram
wave motion
Wave motion is one of the modes of transfer of energy from one part of the medium to other parts. -
- The continuous propagation of energy from one part to the other parts through oscillations is called wave motion
which are the 2 types of wave and how is it classified
mechanical wave ( medium required)
electromagnetic wave( medium not required )
mechanical wave has 2 types
longitudinal wave
Transverse wave
Longitudinal wave [ eg:]
Longitudinal waves are those in which the particles in the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave ( C – Compression , R - Rarefaction) one cycle of longitudinal wave include C&R
• Sound wave • Seismic waves
• Ultra Sound • Vibration of Spring
Transverse wavE
When the particles of a medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave they are called transverse waves.
one cycle of transverse wave include crest and trough
characteristics of tranverse wave
• AMPLITUDE
• PERIOD
• FREQUENCY
• WAVE LENGTH
AMPLITUDE [TW]
Maximum height of the crest or the trough
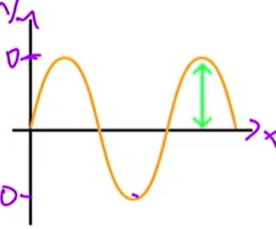
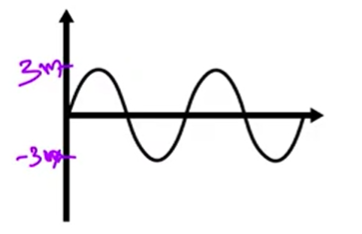
what is the amplitude
3
PERIOD [TW]
It is the time taken for one complete vibration
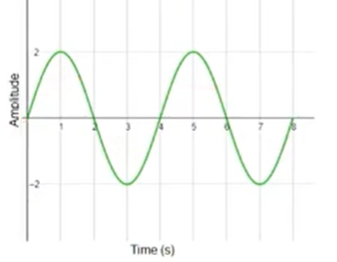
FIND THE PERIOD
T = t/n
8/2=4
FREQUENCY [TW]
no. of cycles in one second
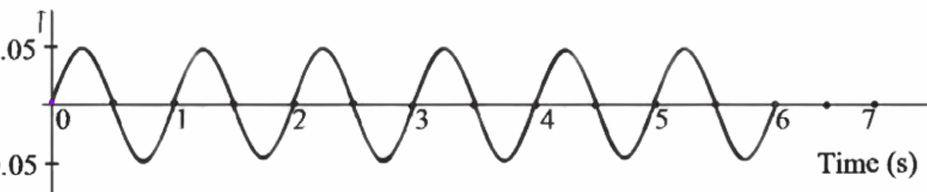
find the freaquency
f = n/t
6/6 = 1
WAVE LENGHT [ TW] ( UNIT & SYMBOL)
Distance between two adjescent Crest or trough
unit =m

SPEED OF WAVE ( UNIT & SYMBOL)
V = DISTANCE TRAVELLED BY THE WAVE /TIME
= frequency * wave length
unit = m/s

Relation btw frequency and wave length
frequency = 1/ wave length
Multiple Reflection of sound
Reflected sound waves get reflected again. This is multiple reflection of sound.
Echo
Echo is the sound heard after a while due to the reflection of the initial sound.
Reasons for echo
• Persistence of hearing
• Minimum Distance should be more than 17.5 m
Reverberation
Reverberation is the lingering of sound, even after the original sound has ceased. It is due to the multiple reflection of sound and the boom fades away gradually.
what can we do to reduce reverberation
to make the walls rough
limits of audiility
20Hz to 20000Hz
Infrasonic [eg.]
less than 20Hz
seismic waves
ultrasonic [eg.]
more than 20000Hz
dogs bats cats
Uses of Ultrasonic waves
• To crush small stones in the kidneys.
• In physiotherapy
• To take images of internal organs such as kidney, liver, gall bladder and uterus.
• For cleaning spiral tubes, irregular machine parts, electronic components etc.
Seismic Waves
• Seismic waves are those that travel through the Earth's crust as a result of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and massive explosions.
• Seismology is the study of seismic waves.
• The intensity of earthquakes is determined by the Richter scale.
Tsunami
• Earthquakes that occur at the bottom of oceans or along coastal areas can sometimes trigger tsunami waves.
• Tsunami is a series of gigantic ocean waves caused by the displacement of large volumes of water in the sea