25-26 Cell Membrane
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
cell
structural unit of all living things
3 parts of cell
plasma mem
cytoplasm
nucleus
all cells composed of
CHNO
trillions of cells
28-36 trillion
what is plasma mem
defines extent of cell
separates intracellular from extracellular
function- selectively permeable barrier
fluid mosaic model plasma mem
thin structure
bilayer of lipids wt dispersed proteins
→ “sea of lipids wt floating iceburgs”
what do proteins do in plasma mem
form a constantly changing mosaic pattern
lipid bilayer consists of
Phospholipids (75)
Cholesterol (20)
Glycolipids (5)
Phospholipids orient themselves in aqueous solutions such that
the polar heads face the interior and exterior of the cell with the tails forming center of membrane
bc of lipid content interior of mem is
hydrophobic
glycolipids (5%)
phospholipids wt attached sugar
→ fatty acid tail nonpolar
glycolipids are found ONLY
on the outer plasma mem surface
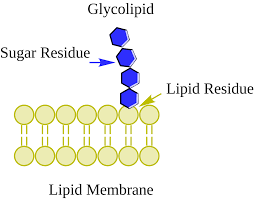
glycolipids
cholesterol (20%)
hydrocarbon rings btw phospholipid tails
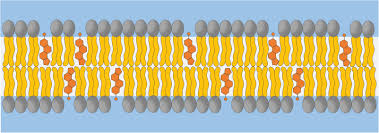
what does cholesterol do
stabilizes mem and fluidity of the mem
mem proteins
½ the mass
responsible for most specialized mem functions
mem proteins are either
integral (part in wt trails other out) or peripheral (either inside/outside mem) proteins
function of mem proteins
formation of channel
transporter proteins
receptor proteins
cell identity marker
linker
act as enzyme
linker
anchor proteins in cell mem or to other cells, allow cell movement, cell shape, and structure
glycocalyx
sticky carb/sugar coating on cell surface that is made up of glycolipids and glycoproteins
→ attached to mem proteins and lipids
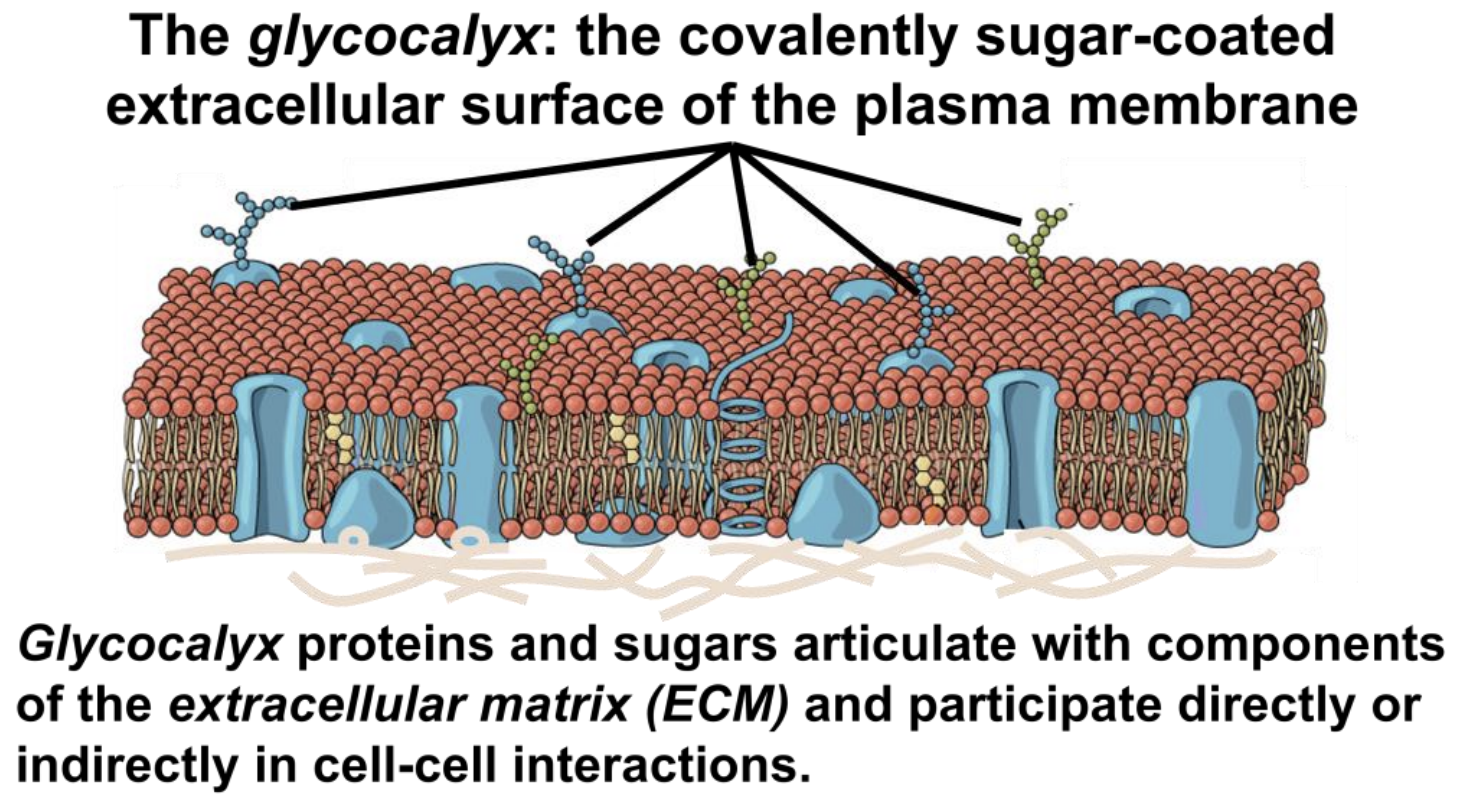
each cell hv diff pattern of sugars
glycocalyx provides highly specific bio makers by which cells recognzie eachother
fluid nature of cell mem
dynamic- not stiff and constantly moving
lipids in cell mem move
freely from side to side buy can NOT flip flop
proteins in cell mem move
some move freely
which protein movement restricted
peripheral proteins- b/c it is attatched to the intracellular cytoskeleton
microvilli
special feature of mem
small fingerlike extensions of mem that project from free or exposed cell surfacem cire if actin filaments
SMALLEST
function of microvilli
increase surface area of plasma mem → SMALLEST
microvilli are absorptive cells in
intestines and kidney tubules (usally on top)
cilia
extensions from surface of cell
microtubules covered in plasma mem
beat in coordinated wave-like motion
function of cilia
move things over surface of sheet cells as they beat in coordinated fashion
flagellum
only in human sperm cells
microtubules covered in plasma mem
propell entire cell
3 factors bind cells tg
glycoprotein of glycocalyx (sticky) act as an adhesive
wavy contours of mem of adjacent cells fit tg in a tounge and groove fashion (PUZZLE PIECES)
Special mem junctions
→ tight junctions
→ GAP junctions
→ Desmosomes
Tight junctions
dont want to leak out
mem proteins hold tg/meet in middle
EX: bladder stores urine tight junctions seal space btw cells
keep inside lumen
connexon proteins
proteins in GAP junctions
GAP junctions
allows ions flow from cell to cell
→ communication to sen message thru ions
important in muscle (heart)
→ upper chamber of cell floods and contractcs at same time
connexon proteins
desmosomes
protein plaques
→ send out proteins (linker proteins) intracellular space to hold tg
each like button: hold tg so don’t pull apart
EX: skin (tension)
→ takes force over one and sitributes among all cells
hemi-desmosome anchors to BM
hemi desmosome
½ desmosome