Kartlar: IB Biology - Water, Carbs., Lipids, Proteins | Quizlet
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Polar
having an uneven distribution of charge
Nonpolar
having an even distribution of charge
Hydrogen bond
A weak bond that forms between water molecules.
Covalent bond
A bond that is found within water molecules.
Cohesion
An attraction between water molecules
Adhesion
An attraction between water molecules and other charged or polar substances
Surface tension
A force that acts on the surface of water
Capillary action
The tendency of water to rise through the veins of a plant
High specific heat
A property of water that allows it to absorb a lot of heat before increasing in temperature.
Solvent properties
A property of water that allows it to easily dissolve and transport many substances.
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds that are energy sources and energy storage molecules
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
The elements that make up carbohydrates and lipids
Monosaccharide
The monomer for a carbohydrate
Glucose
A monosaccharide that provides a source of quick energy
Fructose
A monosaccharide that is found in fruits
Galactose
A monosaccharide that is found in dairy products
Sucrose
A disaccharide that is composed of glucose and fructose
Maltose
A disaccharide that is composed of two glucose molecules
Lactose
A disaccharide that is composed of glucose and galactose
Starch
A polysaccharide that stores energy in plants
Glycogen
A polysaccharide that stores energy in animals
Cellulose
A polysaccharide that forms the cell wall in plants
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate that is composed of two monosaccharides
Polysaccharide
A carbohydrate that is composed of many monosaccharides
Condensation reaction / Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction in which water is used to break apart a molecule
Hydroxyl group
an -OH group
Fatty acid
The monomer of a lipid
Saturated
A term describing a fatty acid with all single bonds in its hydrocarbon chain
Unsaturated
A term describing a fatty acid with at least one double bond in its hydrocarbon chain
Glycerol
A molecule that combines with fatty acids to form triglycerides
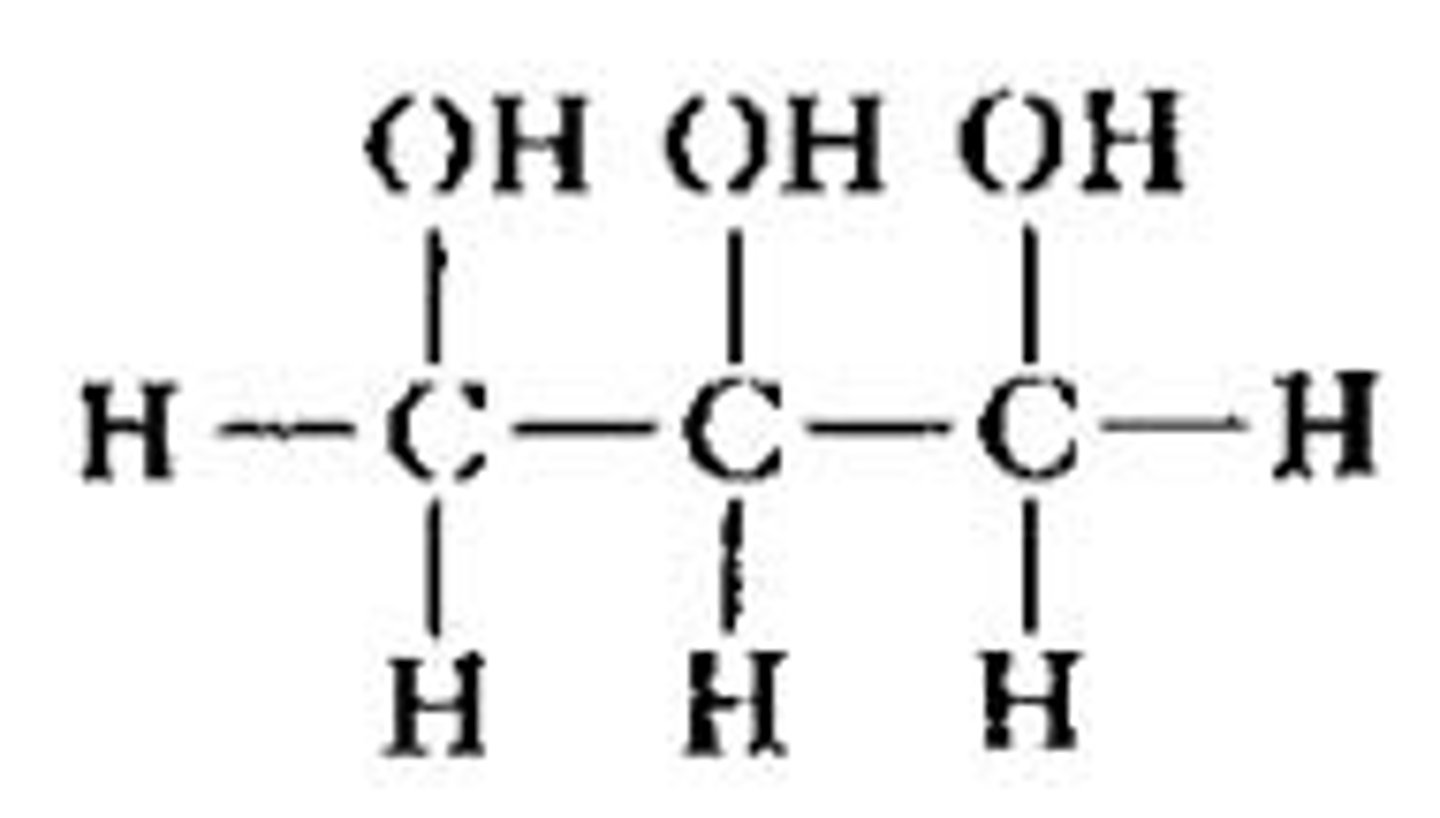
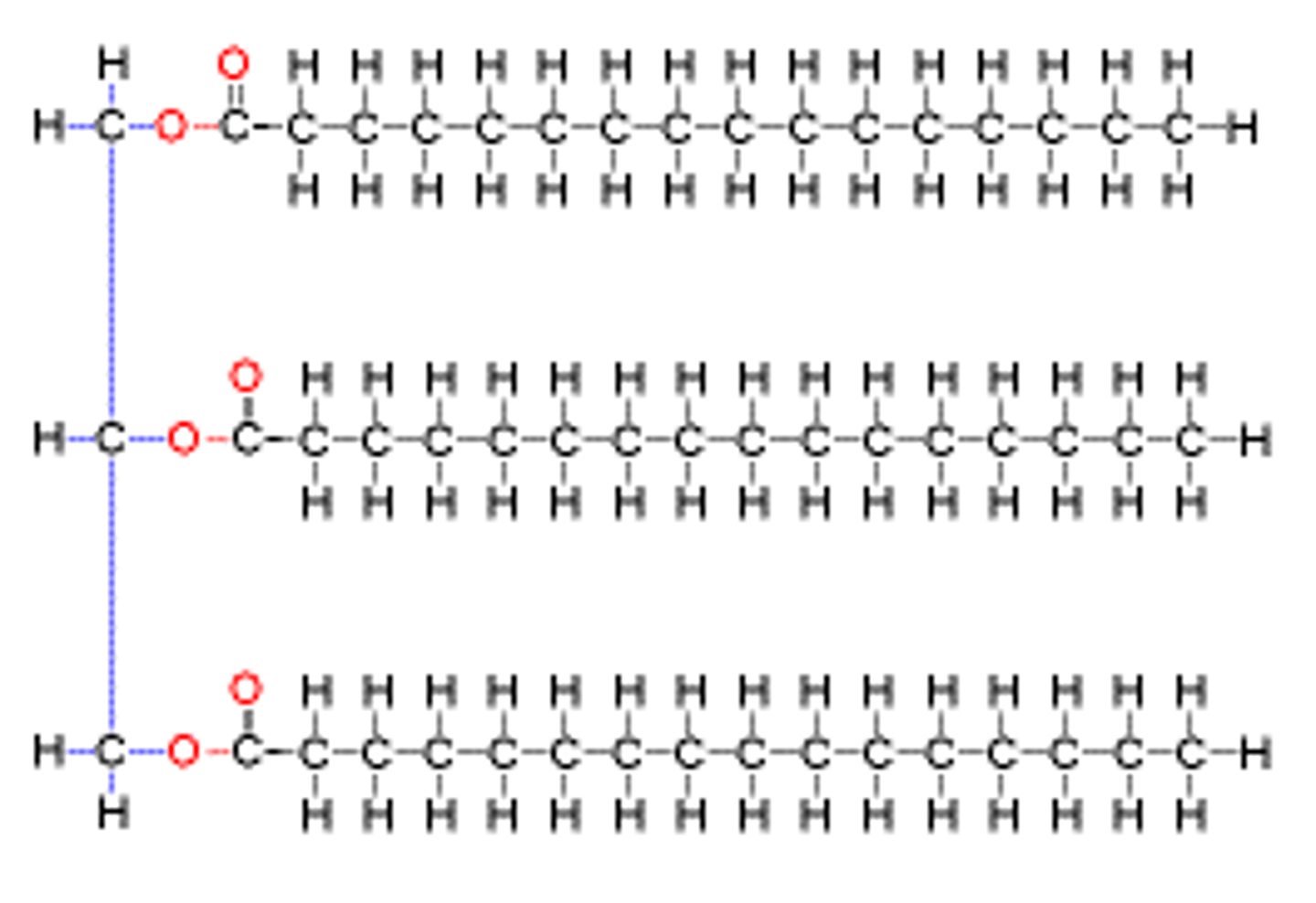
Triglyceride
A polymer used to store fatty acids
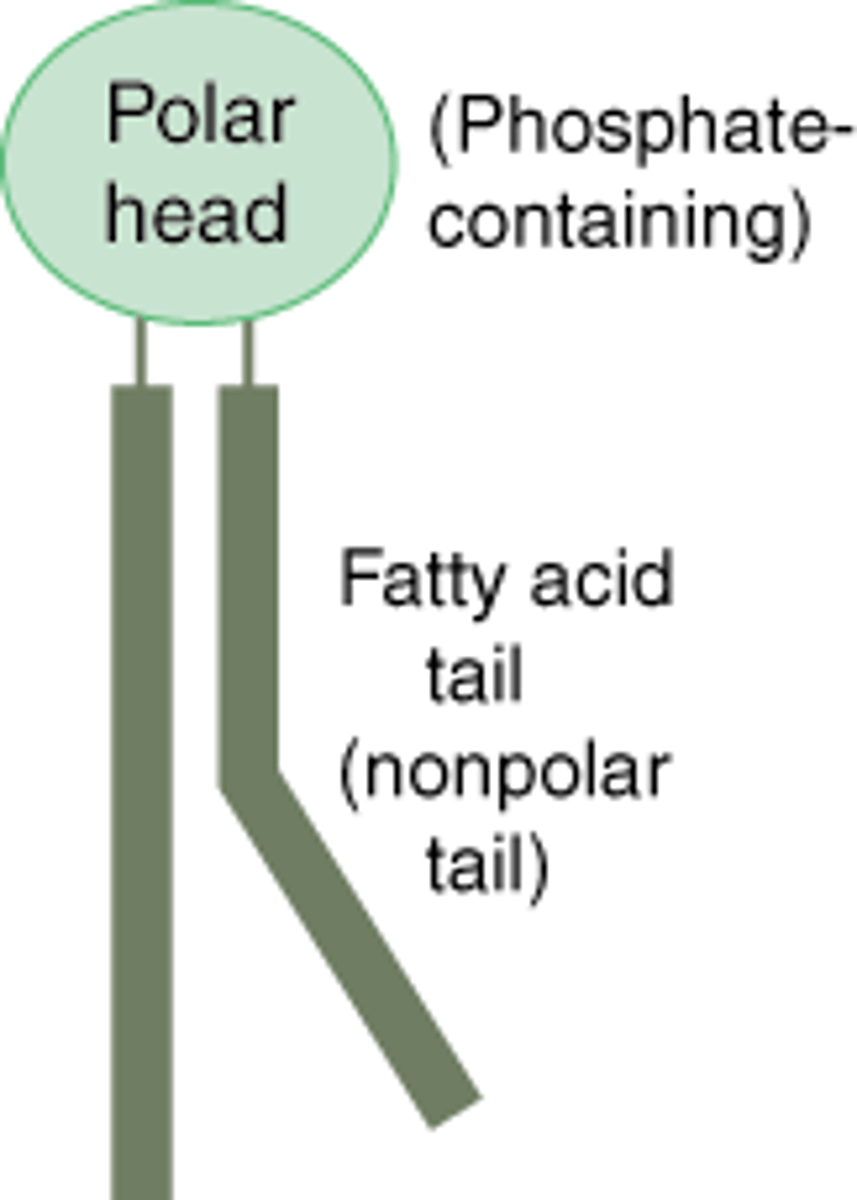
Phospholipid
A lipid that makes up the cell membrane
Hydrophobic
Water fearing (non polar)
Hydrophilic
Water loving (polar)
Steroid
A lipid hormone with four fused carbon rings. It can diffuse through plasma membranes.
Amino acid
The monomer of a protein
Peptide bond
A bond that joins two amino acids
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
Primary structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.
Secondary structure
The second level of protein structure consisting of alpha helices or beta pleated sheets
Tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure that results in a three-dimensional shape due to interactions between R groups
Quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure that results from the bonding of two or more polypeptide chains
Denature
A change in the shape of a protein that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH
Dipeptide
Two amino acids bonded together