Radioactivity
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is activity measured in
Becquerels Bq
1 Becquerel =
1 decay per second
define the term half life
The activity of a radioactive sample decreases over time.
The half-life of a radioactive sample is the average time taken for half of the original mass of the sample to decay.
what is a count rate
number of radioactive particles detected per second.
how does photographic film detect radiation
darkens on exposure to radiation and light, light cannot penetrate the badge but ionising radiation can. darkening of the film indicates that a person has been exposed to too much radiation
radioactivity can be detected using…
photographic film or a Geiger counter
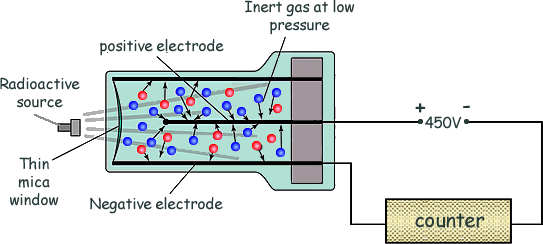
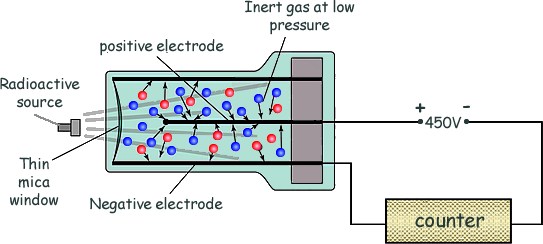
how does the geiger tube detect radioactivity
radiation produces ions in a low pressure gas between a central positively charged electrode & the outer negatively charged tube. a pulse of current then flows that is registered by the counter. the thin mica window allows the least penetrating radiation (alpha) to enter the tube. Gamma radiation and most beta can enter through the sides of the metal tube
give an example of a natural substance on earth
air, food, rocks, soil
give an example of a natural background radiation from space
cosmic rays (high energy particles) mainly from the sun
give an example of radiation from living things
carbon-14
artificial background radiation due to human activity
nuclear waste, fallout from nuclear weapons testing
background radiation
background nuclear radiation low-level ionizing radiation that is produced all of the time
explain radon gas
about 50% of natural background radiation
isotopes: radon 222 + radon 220 are produced by the radioactive decay of uranium and thorium in the Earth’s crust
this gas seeps into atmosphere & can build up foundations of buildings
explain cosmic rays
produce high energy particles, bombarding the Earth
atmosphere protects us from cosmic radiation
natural background radiation
produced by nuclear reactions in stars & supernovas
explain internal radiation
radioactive sources inside our bodies
some are natural, others man-made
explain artificial radiation
man-made events/procedures
some due to leakage and accidents or due to fall-out from nuclear weapon testing
radioactive tracers are used in industry & medicine
normally accounts for a small % of background radiation
uses of radioactivity
smoke detectors, automatic thickness monitoring, tracing underground leaks in pipes, radiotherapy, medical tracers in diagnosis, sterilisation
radioactivity in smoke detectors
a radioactive source inside the alarm emits alpha particles which ionise air in an air gap so that it conducts electricity
in a fire, smoke particles block the alpha radiation, reducing ionisation
this causes a drop in electric current which sets off the alarm
properties requires of radioactivity in smoke detectors
a source of alpha radiation must be used
a long half-life source must be used
radioactivity in automatic thickness monitoring
the amount of radiation received by the detector depends on the thickness of the aluminium foil
if the thickness increases then the detector reading falls and will cause the computer to bring the rollers closer together & so decrease the foil thickness
properties required of radioactivity in automatic thickness monitoring
a source of beta radiation must be used
a long half-life source must be used
radioactivity in tracing underground leaks and pipes
a radioactive tracer can be added to a fluid where a leak occurs will be shown by an increase in the count rate detected
why must you use a beta source in radioactivity in thickness monitoring
alpha wouldn’t pass through the thinnest aluminium and gamma wouldnt be affect by any thickness charge
why do you need a long half life source in radioactivity in automatic thickness monitoring
or else a false thickness increase will be detected as the activity of the source decreases
whats a suitable source with a long half life for radioactivity in automatic thickness monitoring
a suitable isotope is stronium-90, a beta emitter with a half life of 29 years
why do you need to use an alpha source in radioactivity in smoke detectors
beta or gamma wouldn’t cause sufficient ionisation & they wouldn’t come sufficient ionisation and wouldn’t be blocked by smoke
why do you need a long half life source in radioactivity in smoke detectors
or else a drop in current would set off the alarm
whats a commonly used alpha emmitter with a long half life for radioactivity in smoke detectors
the commonly used isotope Americum-241 an alpha emitter with a half life of 433 years
properties required of radioactivity in tracing underground leaks in pipes
if liquid can escape and pool in the ground, or if it is in a plastic pipe wall, what source will be used
beta can be used
if leakage is in a metal pipe underground then what source will be used
gamma
why must gamma be used if leakage is in a metal pipe underground
because gamma radiation wouldn’t give a count rate whether or not a leak was present. However, there would be an increased count rate at the site of the leak due to less absorption
why must you need a long half life for radioactivity in underground leaks and pipes
to remain reasonably active over the period of investigation but not too long so that it doesn’t remain a hazard to the environment