L1 - Mouth
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Length of GI tract from mouth to anus in vivo
6-7m
The four processes carried out by the GI tract
digestion
secretion
absorption
motility
Where do contents of vomit come from
Chyme from small intestine & stomach
Digestive secretions mostly consist of what
water
How many ml of water is taken in per day
1200 ml
How many g of solids is ingested per day
800 g
ml of salivary secretions per day
1500ml
(3x my water bottle!!!)
ml of gastric secretions per day
2000ml
ml of bile secretions per day
500ml
ml of pancreatic secretions per day
1500ml
ml of intestinal secretions per day
1500ml (primarily small intestine)
How many ml are absorbed from the small intestine into the blood per day
6700ml
How many ml are absorbed from the large intestine into the blood per day
1400ml
Total fluid ml excreted per day
1500ml
How much of the total excretions per day (1500ml) are through faeces
100ml
How much solids are excreted per day
50g
Mechanical digestion in the mouth
Teeth and tongue
Chewing action
Mechanical digestion
Reflex and Voluntary
Tongue shapes food into bolus and pushes bolus towards pharynx
Motility
Pharynx
Helps crush food digestion
Closes nasal opening when swallowing motility
Functions of the saliva
1. Lubrication prior to swallowing
2. Digestion
Digestive enzymes break down food
Amylase, Lipase
3. Dissolve food
For sensing of content
Taste buds for the five tastes
4. Antibacterial actions (tooth decay prevention)
Washing action
Mucus coating of mouth
Alkaline pH: buffers acids in food, from bacteria and gastric acids
Bactericidal
Antibodies

name the 4 salivary gland (3 proper & 1 isn’t really a gland)
Parotid
Submandibular
Sublingual glands
Buccal (not really a gland but secretes saliva)
Salivary flow rate
0.5ml/min to 4ml/min
What would cause saliva flow rate to increase
Mint/Lemon on tongue
Initial saliva (isotonic fluid) is produced by _________
acinar cells
Initial saliva(isotonic fluid) produced by acinar cells is modified by what
Ductal epithelial cells
Is initial saliva or secreted saliva more like plasma
Initial saliva is more like plasma as it is isotonic (not hypotonic (less water, higher solute) like secreted saliva) and has similar concentrations of Na⁺, Cl⁻, K⁺, and HCO₃⁻.
What happens to initial saliva as it passes through ductal cells
As the saliva passes through the ductal cells, it undergoes reabsorption and secretion of ions, making the final saliva hypotonic
Na⁺ and Cl⁻ are reabsorbed out of the saliva
K⁺ and HCO₃⁻ are secreted into the saliva
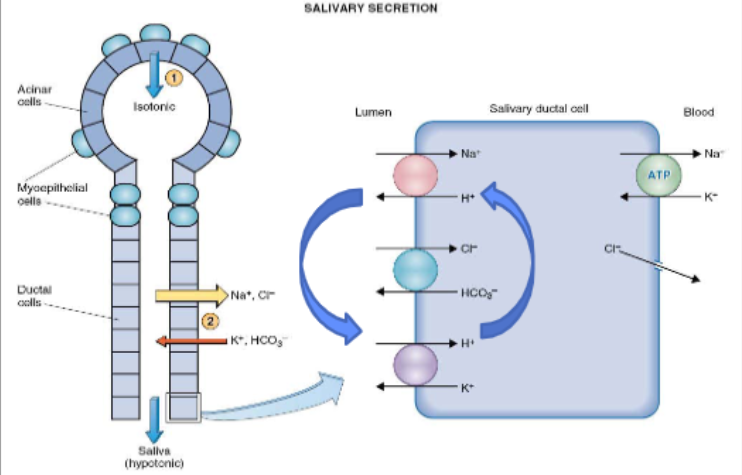
What regulates the process of saliva production
active transport mechanisms, including Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase pumps, which maintain ion gradients.
How do the concs of Na+, HCO3-, Cl- an K+ change with increased salivary flow rates
High Flow Rateleads to:
↑ Na⁺, ↑ Cl⁻ : less time for reabsorption of these ions out of saliva so more of it is secreted with saliva
↑ HCO₃⁻ : secretion is actively stimulated at higher flow rates. This helps buffer acidic pH, important during active digestion.
↓ K+ : not enough time to enter saliva as it is actively secreted into saliva.
What did Pavlov do
He proved that you could condition a reflex
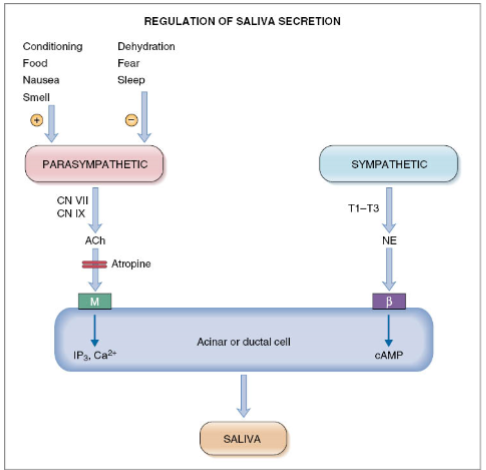
What controls the production/secretion of saliva from acinar/ductal cells