AP Macro Unit 4
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
1
New cards
Financial Sector
→ network of institutions that link borrowers and lenders
→ includes banks, mutual funds, pension funds, and other financial intermediaries
→ includes banks, mutual funds, pension funds, and other financial intermediaries
2
New cards
Assets
anything tangible or intangible that has value
3
New cards
Interest Rate
the amount a lender charges borrowers for borrowing money--the "price" of a loan
4
New cards
Interest-bearing Assets
assets that earn interest over time
5
New cards
Market Risk
when you lose money from fluctuations in market prices
6
New cards
Default Risk
when companies/individuals are unable to fulfill their payment/debt obligations
7
New cards
Inflation Risk
when the value shrinks from inflation
8
New cards
Liquidity
the ease with which an asset can be converted to a medium of exchange (in general, the higher the liquidity = the lower the rate of return)
→ cash and demand deposits are the two most liquid forms of money
→ cash and demand deposits are the two most liquid forms of money
9
New cards
Demand deposit
deposits by customers that can be withdrawn at anytime (EX. checking accounts)
10
New cards
Risks of Buying Assets
( 1 ) Market Risk
( 2 ) Default Risk
( 3 ) Inflation Risk
( 2 ) Default Risk
( 3 ) Inflation Risk
11
New cards
Bonds
(securities) loans or IOUs that represent debt that the government, businesses, or individuals must repay to the lender
12
New cards
Stocks
(equities) represent ownership of a corporation and the stockholder is often entitled to a portion of the profit paid out as dividends
13
New cards
Bond Prices and Interest Rates
→ a bond is issued at a specific interest rate that doesn't change throughout the life of the bond
→ bond price and interest rates are inversely related
→ bond price and interest rates are inversely related
14
New cards
Real Interest Rates
the percentage increase in purchasing power that a borrower pays (adjusted for inflation)
Real = nominal interest rate -- expected inflation
Real = nominal interest rate -- expected inflation
15
New cards
Nominal Interest Rate
the percentage increase in money that the borrower pays (not adjusted for inflation)
Nominal = real interest rate + expected inflation
Nominal = real interest rate + expected inflation
16
New cards
The Time Value of Money
you can determine the future value of any amount of money ($X) if you know the interest rate (ir) and the number of years (N)
Equation to calculate future value:
$X in N Years = $X(1 + ir)^N
(ir is expressed as a decimal)
Equation to calculate future value:
$X in N Years = $X(1 + ir)^N
(ir is expressed as a decimal)
17
New cards
Present Value of Money
the current worth of some future amount of money
Equation to calculate present value:
($X) / (1 + ir)^N
Equation to calculate present value:
($X) / (1 + ir)^N
18
New cards
The Barter System
goods and services are traded directly; there is no money exchanged
Problems with the Barter System
( 1 ) before trade could occur, each trader had to have something the other wanted--this is called the "Double Coincidence of Wants"
( 2 ) some goods cannot be split
Problems with the Barter System
( 1 ) before trade could occur, each trader had to have something the other wanted--this is called the "Double Coincidence of Wants"
( 2 ) some goods cannot be split
19
New cards
Money
anything that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services
→ NOT the same as wealth or income (wealth is the total collection of assets, income is a flow of earnings per unit of time)
→ NOT the same as wealth or income (wealth is the total collection of assets, income is a flow of earnings per unit of time)
20
New cards
Commodity Money
something that performs the function of money and has intrinsic value
EX.) gold, silver, cigarettes, etc.
EX.) gold, silver, cigarettes, etc.
21
New cards
Fiat Money
something that serves as money but has no other value or uses
EX.) paper money, coins, digital currency
EX.) paper money, coins, digital currency
22
New cards
3 Functions of Money
( 1 ) A Medium of Exchange
( 2 ) A Unit of Account (Measure of Value)
( 3 ) A Store of Value
( 2 ) A Unit of Account (Measure of Value)
( 3 ) A Store of Value
23
New cards
A Medium of Exchange
money can easily be used to buy goods and services with no complications of barter system
24
New cards
A Unit of Account (Measure of Value)
money measures the value of all goods and services: money acts as a measurement of value
25
New cards
A Store of Value
money allows you to store purchasing power for the future
26
New cards
What backs the money supply?
there is no gold standard, money's value comes from our collective belief that it is valuable
27
New cards
What makes money effective?
( 1 ) Generally Accepted → buyers and sellers have confidence it is legal tender
( 2 ) Scarce → money must not be easily transported and divided
( 3 ) Portable and Dividable → money must be easily transported and divided
( 2 ) Scarce → money must not be easily transported and divided
( 3 ) Portable and Dividable → money must be easily transported and divided
28
New cards
Purchasing Power
the purchasing power of money is the amount of goods and services a unit of money can buy
→ inflation decreases purchasing power, hyperinflation decreases acceptability
→ inflation decreases purchasing power, hyperinflation decreases acceptability
29
New cards
M1 (Highest Liquidity)
( 1 ) Currency in circulation
( 2 ) Checkable bank deposit (checking accounts)
( 3 ) Savings Accounts
( 2 ) Checkable bank deposit (checking accounts)
( 3 ) Savings Accounts
30
New cards
M2 (Near-Moneys)
( 1 ) Everything in M1
( 2 ) Time deposits (CDS = certificate of deposits)
( 3 ) Money market funds
( 2 ) Time deposits (CDS = certificate of deposits)
( 3 ) Money market funds
31
New cards
Fractional Reserve Banking
when banks hold a portion of deposits to cover potential withdrawals and then loans the rest of the money out
32
New cards
The Money Multiplier
1 / Reserve Requirement
33
New cards
Bank Balance Sheets
a record of a bank's assets, liabilities, and net worth
(demand deposits in a bank are liability for the bank, asset to the depositor)
(demand deposits in a bank are liability for the bank, asset to the depositor)
34
New cards
Required Reserves
the percent that banks must hold by law
35
New cards
Excess Reserves
the amount that the bank can loan out
36
New cards
The Demand for Money
( 1 ) Transaction Demand for Money → people hold money for everyday transactions
( 2 ) Asset Demand for Money → people hold money since it is less risky than other assets
( 2 ) Asset Demand for Money → people hold money since it is less risky than other assets
37
New cards
What is the opportunity cost of holding money in your pocket or checking account?
the interest rate you could be earning from other financial assets like stocks, bonds, and real estate
38
New cards
Interest Rate and the Quantity of Money Demanded
there is an inverse relationship
→ when interest rates increase, quantity demanded falls because individuals would prefer to have interest-earning assets instead
→ when interest rates decrease, quantity demanded increases, there is no incentive to convert cash into interest earning assets
→ when interest rates increase, quantity demanded falls because individuals would prefer to have interest-earning assets instead
→ when interest rates decrease, quantity demanded increases, there is no incentive to convert cash into interest earning assets
39
New cards
Money Demand Shifters
( 1 ) Change in price level
( 2 ) Change in income
( 3 ) Change in technology
( 2 ) Change in income
( 3 ) Change in technology
40
New cards
Money Supply
the U.S. Money Supply is set by the central bank and is independent from the interest rate
41
New cards
The Federal Reserve
the Fed is a nonpartisan government office that adjusts the money supply to influence the economy → this is called Monetary Policy
42
New cards
Increasing the Money Supply
if the money supply increases, a temporary surplus of money will occur; the surplus will cause the interest rate to fall
increase money supply → decrease interest rate → increase investment → increase AD
increase money supply → decrease interest rate → increase investment → increase AD
43
New cards
Decreasing the Money Supply
if the money supply decreases, a temporary shortage of money will occur; the shortage will cause the interest rate to rise
decrease money supply → increase interest rate → decrease investment → decrease AD
decrease money supply → increase interest rate → decrease investment → decrease AD
44
New cards
Money Supply Shifters
the Fed adjusts MS by changing:
( 1 ) The Reserve Requirement (ratios)
( 2 ) The Discount Rate
( 3 ) Open Market Operations
( 1 ) The Reserve Requirement (ratios)
( 2 ) The Discount Rate
( 3 ) Open Market Operations
45
New cards
Discount Rate
the interest rate that the Fed charges commercial banks
46
New cards
Open Market Operations
when the Fed buys or sells government bonds (securities)
→ this is the most important + widely used monetary policy
→ this is the most important + widely used monetary policy
47
New cards
Federal Funds Rate
the interest rate that banks charge on another for one-day loans of reserves
48
New cards
Actions the Fed could take to decrease the MS
increase discount rate, increase reserve ratios, sell bonds
49
New cards
Actions the Fed could take to increase the MS
decrease discount rate, decrease reserve ratios, buy bonds
50
New cards
Modern Changes to Banking
( 1 ) Interest on Reserves (IOR)
→ the interest rate that the Federal Reserve pays commercial banks to hold reserves
→ IOR and the discount rate are examples of administered rates
( 2 ) Administered Rates
→ interest rates set by the Fed rather than determined in a market
→ reserves at the Fed have no risk, therefore, banks have no incentive to lend money at an interest rate that is lower than what they can get from the Fed
→ the interest rate that the Federal Reserve pays commercial banks to hold reserves
→ IOR and the discount rate are examples of administered rates
( 2 ) Administered Rates
→ interest rates set by the Fed rather than determined in a market
→ reserves at the Fed have no risk, therefore, banks have no incentive to lend money at an interest rate that is lower than what they can get from the Fed
51
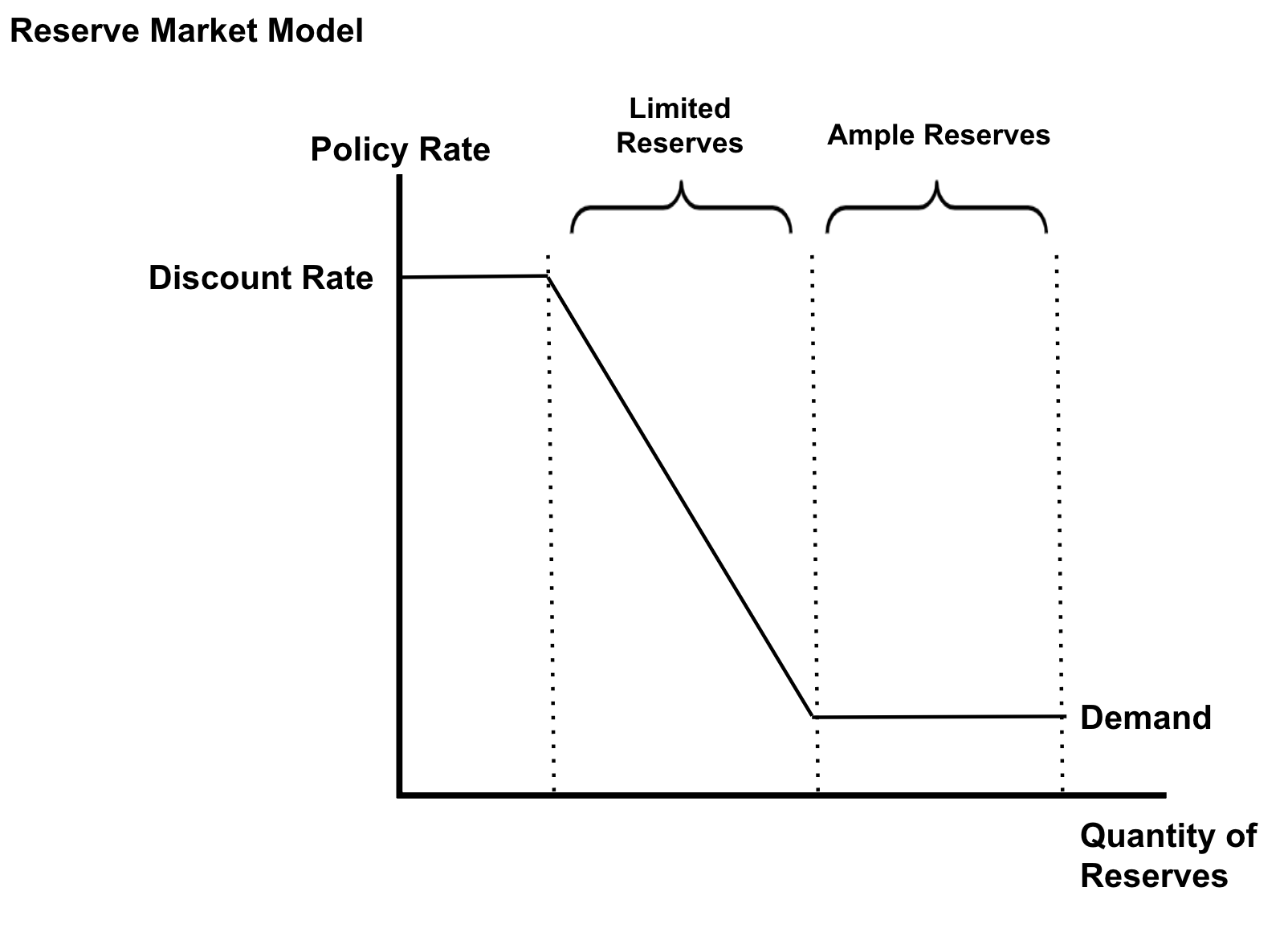
New cards
Limited Reserves
when there are limited reserves:
→ banks deposit fewer reserves with the central bank
→ small changes in the money supply can affect interest rates
→ the central bank conducts monetary policy by changing the reserve requirement or the discount rate or by using open market operations
→ banks deposit fewer reserves with the central bank
→ small changes in the money supply can affect interest rates
→ the central bank conducts monetary policy by changing the reserve requirement or the discount rate or by using open market operations
52
New cards
Ample Reserves
when there are ample reserves:
→ banks deposit a lot of reserves with the central bank
→ changing the money supply has little to no effect on interest rates
→ the central bank conducts monetary policy by changing its administered rates (IOR or discount rate)
→ banks deposit a lot of reserves with the central bank
→ changing the money supply has little to no effect on interest rates
→ the central bank conducts monetary policy by changing its administered rates (IOR or discount rate)
53
New cards
Reserve Market Model
→ inverse relationship between the Federal Funds Rate and the quantity of reserves demanded
→ when the Policy Rate is high, banks want to hold less reserves
→ when the Policy Rate is low, banks want to hold more reserves
→ when the Policy Rate is high, banks want to hold less reserves
→ when the Policy Rate is low, banks want to hold more reserves
54
New cards
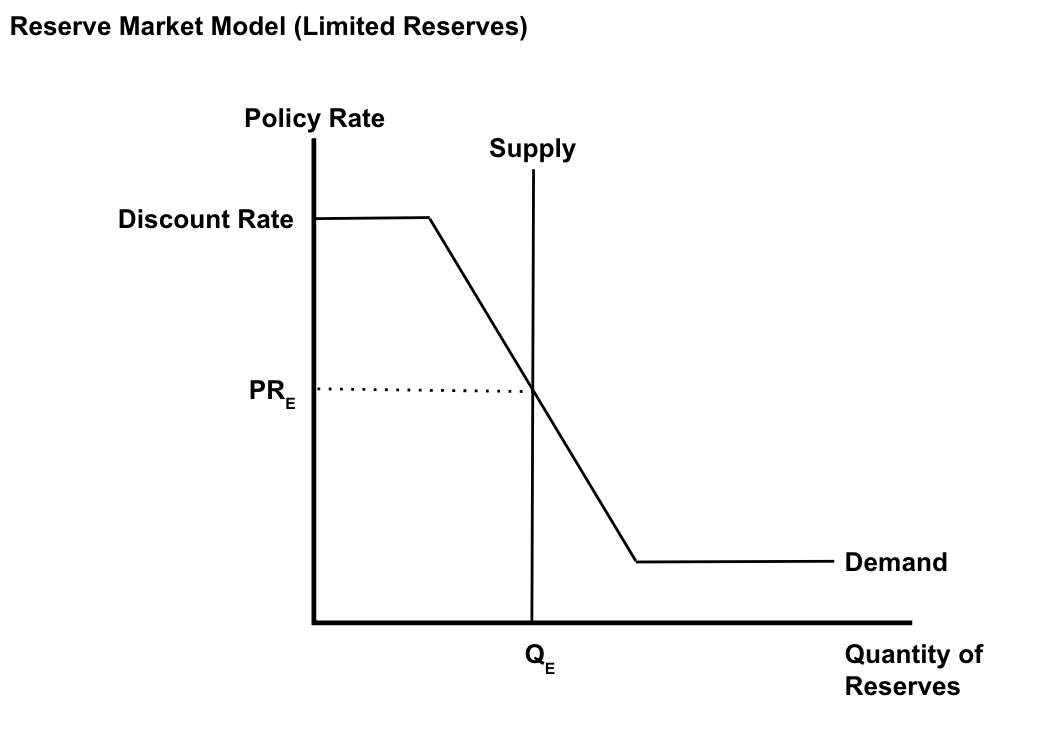
Reserve Market Model (Limited Reserves)
55
New cards
Monetary Policy Used (Limited Reserves)
( 1 ) Reserve Ratios
( 2 ) Discount Rate
( 3 ) Open Market Operations
( 2 ) Discount Rate
( 3 ) Open Market Operations
56
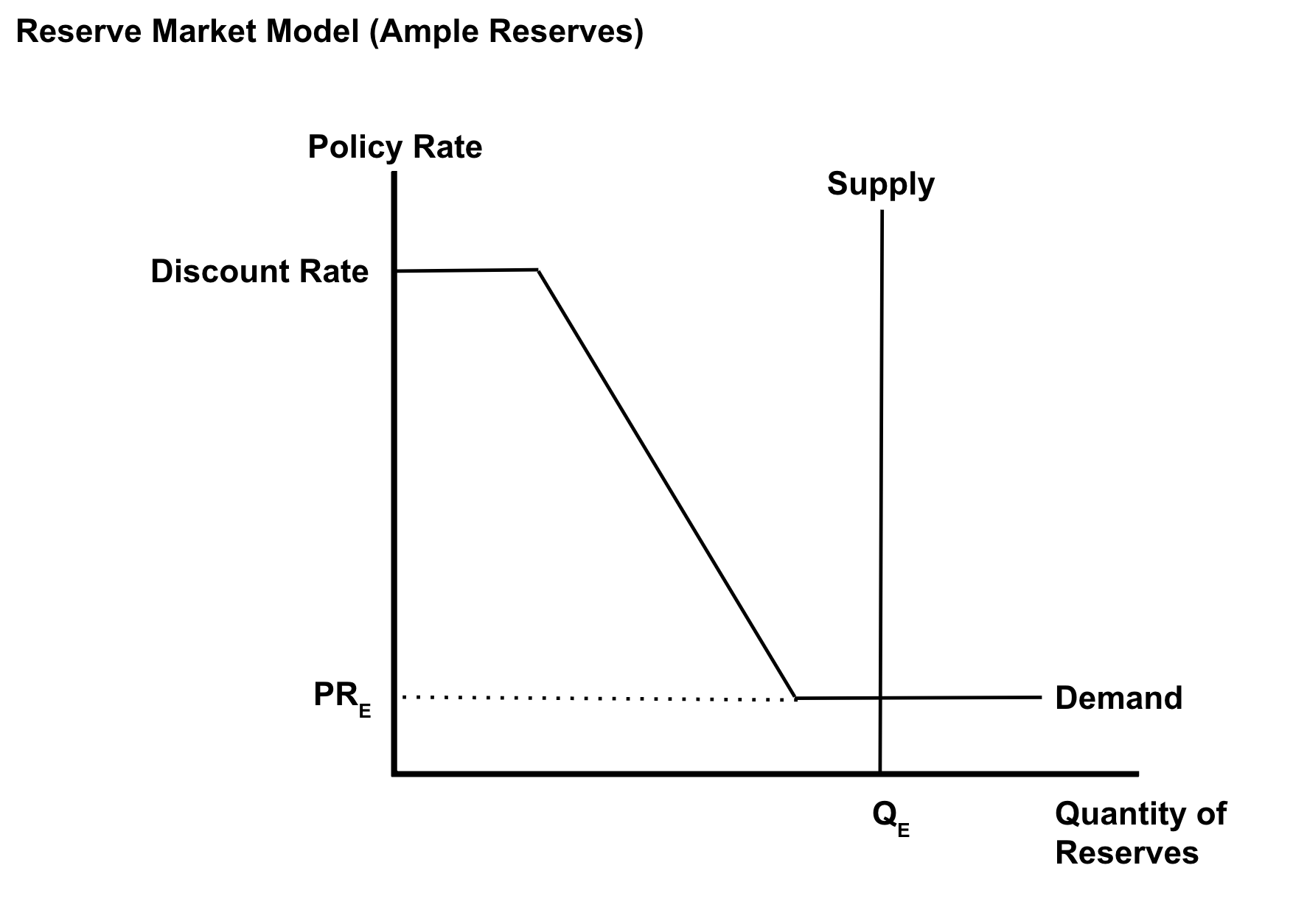
New cards
Monetary Policy Used (Ample Reserves)
(Administered Rates)
( 1 ) Interest On Reserves
( 2 ) Discount Rate
( 1 ) Interest On Reserves
( 2 ) Discount Rate
57
New cards
Reserve Market Model (Ample Reserves)
58
New cards
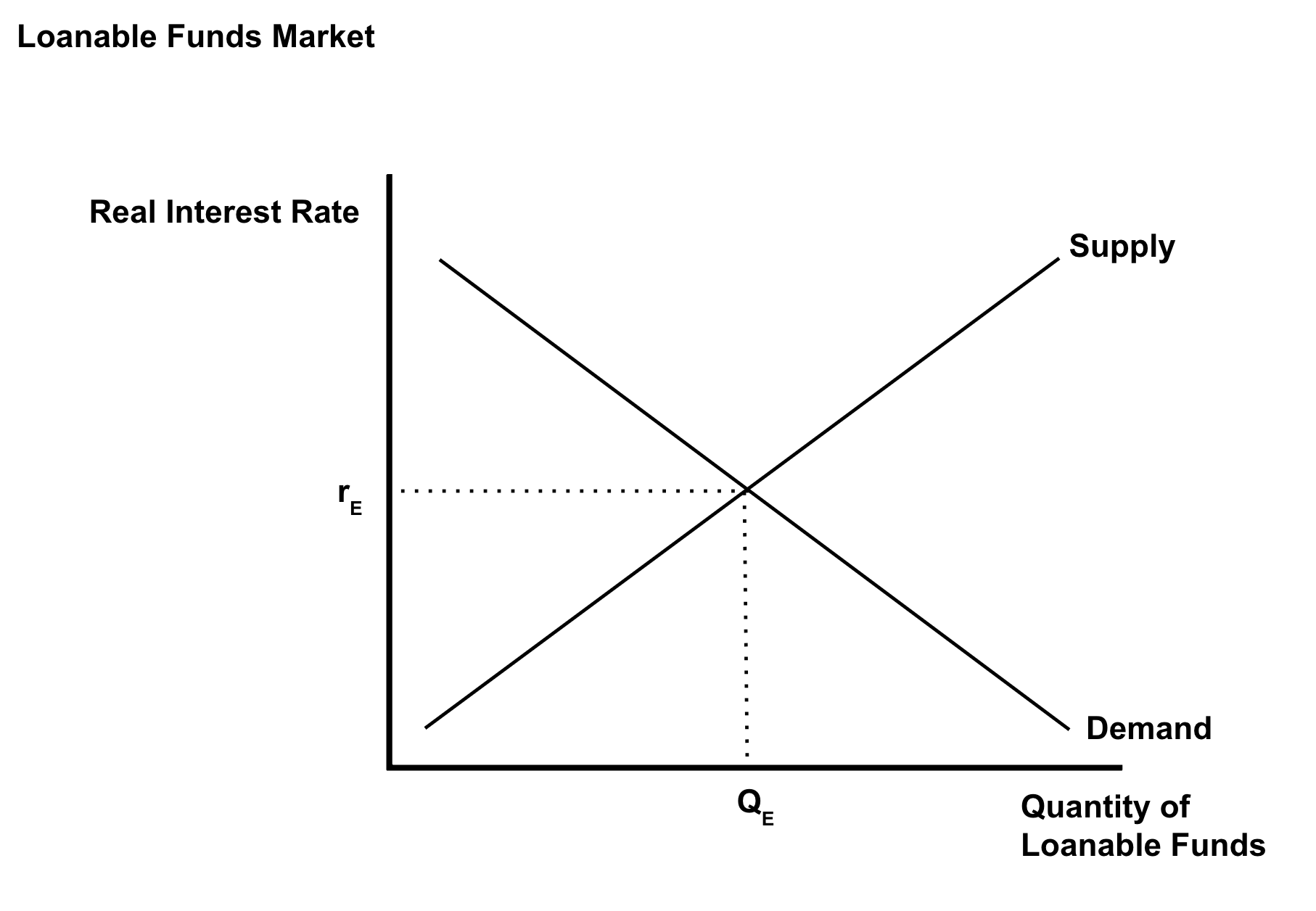
Loanable Funds Market
shows the supply and demand of loans and shows the equilibrium interest rates
→ demand has an inverse relationship between real interest rate and quantity loans demanded
→ supply has a direct relationship between real interest rate and quantity loans supplied
→ at the equilibrium real interest rate, the amount that borrowers want to borrow equals the amount lenders want to lend
→ demand has an inverse relationship between real interest rate and quantity loans demanded
→ supply has a direct relationship between real interest rate and quantity loans supplied
→ at the equilibrium real interest rate, the amount that borrowers want to borrow equals the amount lenders want to lend
59
New cards
Private Saving
the amount that households save instead of consume
60
New cards
Public Saving
the amount that the government saves instead of spends
61
New cards
National Savings
public saving + private saving
62
New cards
Capital Inflow
the amount of money entering the country
63
New cards
Capital Outflow
the amount of money leaving the country
64
New cards
Net Capital Inflow
capital inflow -- capital outflow
65
New cards
Private Investment
borrowing by businesses and consumers
66
New cards
Government Borrowing
deficit spending when government spending is greater than tax revenue
67
New cards
Loanable Funds Market Demand Shifters
( 1 ) Changes in borrowing by consumers
( 2 ) Changes in borrowing by businesses
( 3 ) Changes in borrowing by the government (ex. deficit spending)
( 2 ) Changes in borrowing by businesses
( 3 ) Changes in borrowing by the government (ex. deficit spending)
68
New cards
Loanable Funds Market Supply Shifters
( 1 ) Changes in private savings behavior
( 2 ) Changes in public savings behavior
( 3 ) Changes in foreign investment (ex. more inflow of foreign financial capital)
( 2 ) Changes in public savings behavior
( 3 ) Changes in foreign investment (ex. more inflow of foreign financial capital)
69
New cards
Loanable Funds Market Supply & Demand
→ demand for loans comes from borrowers/investors
→ supply for loans comes from lenders/savers
→ supply for loans comes from lenders/savers
70
New cards
Monetary Base
includes money in circulation and bank reserves