Ch 8 Nucleic Acids
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
What are the 4 major roles nucleotides play in celullar metabolism?
Energy currency in metabolic transactions
Essential chemical links in the response of cells to hormones and other extracellular stimuli
Structural components of an array of enzyme cofactors and metabolic intermediates
Constituents of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acids (RNA)
Do nucleic acids act as a repository or a functional expression of biological information? Or both?
Both
The transmission of biological information relies on what?
Molecular complementarity
What are the largest molecule in any cell?
Chormosomes
What are chromosomes?
Polymers composed of a small set of common nucleotides, with information embedded in the nucleotide sequence
Is potential for variable sequence and complementarity, and thus information storage and transmission a property of any other class of biological molecule?
No
Is DNA damage a constant? If so, what is the result of it?
Yes which results in occasional mutation
Biological information is subject to what 2 principle factors?
Natural damage and change
What are the 3 principle ways we can use biological information in the laboratory?
Access it
Interpret it
Alter it
What is the ultimate product of catabolic pathways?
ATP (Adenosine tri phosphate)
Nucleoside triphosphates occupy what type of role in cellular metabolism? How do they serve this function?
NTPs occupy a central role in cellular metabolism serving as an energy currency and as important regulatory signals.
What role does ATP serve in anabolic pathways?
Fuel
What is an example of a nucleic acid that stores genetic info?
DNA
What is an example of a nucleic acid that aids in transmission of genetic information?
mRNA
What is an example of a nucleic acid that is used for processing of genetic information?
Ribozymes
What is an example of 2 nucleic acids that are used for protein synthesis?
tRNA and rRNA
Nucleotides are also used in monomer form for cellular functions primarily what 3?
Enzyme for metabolism (ATP)
Enzyme cofactors (NAD+)
Signal transductions (cAMP)
How is rRNA primarily used?
Component of ribosomes
How mRNA primarily used?
Intermediates in protein synthesis
What is tRNAs primary function?
Adapter molecules that translate the information in mRNA into a specific amino acid sequence
Do noncoding RNAs serve a specific function or a wide variety of function?
A wide variety
What is a nucleotide made up of?
Nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine)
Pentose
Phosphate
What is a nucleoside made up of?
Nitrogenous base (Purine or pyrimidine)
Pentose
What is the major difference between a nucleotide and a nucleoside?
A nucleoside lacks the phosphate group which a nucleotide has.
In a cyclic nitrogenous base are only carbons numbered or carbon and nitrogen atoms?
Both carbon and nitrogen atoms are numbered
What charge does the phosphate group have at a neutral pH?
Negative
At what carbon on a nitrogenous base is the phosphate group typically attached to?
C5
Nucleic acids are built using what version of the nucleotide?
5’-triphosphates (ATP, GTP, TTP, CTP)
Completed nucleic acids contain how many phosphate moiety per nucleotide?
One
In special function cases of nucleotides the phosphate group may or may not be attached to other positions?
It may differ in position
The pentose form used may or may not differ in some nucleic acids and nucleotides?
It may differ in a variety of puckered conformations
What specific form of pentose is used in RNA
Beta-d-ribofuranose
What specific form of pentose is used in DNA?
Beta-2’-deoxy-d-ribofuranose
What type of molecule are nitrogenous bases?
Nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic molecules
Are nitrogenous bases planar or non-planar?
Planar
In what spectrum and at what wave length do nitrogenous bases absorb light?
UV light around 250-70nm
What three nitrogenous bases are found in both DNA and RNA?
Cytosine
Adenine
Guanine
What nitrogenous base is only found in DNA?
Thymine
What nitrogenous base is only found in RNA?
Uracil
Are nitrogenous bases good H-bond donors and acceptors?
Yes
At pH 7 what charge do nitrogenous bases have?
Neutral

What molecule is this? Give the nucleotide and nucleoside names as well as the 3 symbols that represent it
Nucleotide: Deoxyadenylate (deoxyadenosine 5’-monophosphate)
Nucleoside: Deoxyadenosine
Symbols: A, dA, dAMP

What molecule is this? Give the nucleotide and nucleoside names as well as the 3 symbols that represent it
Nucleotide: Deoxyguanylate (deoxyguanosine 5’-monophosphate)
Nucleoside: Deoxyguanosine
Symbols: G, dG, dGMP
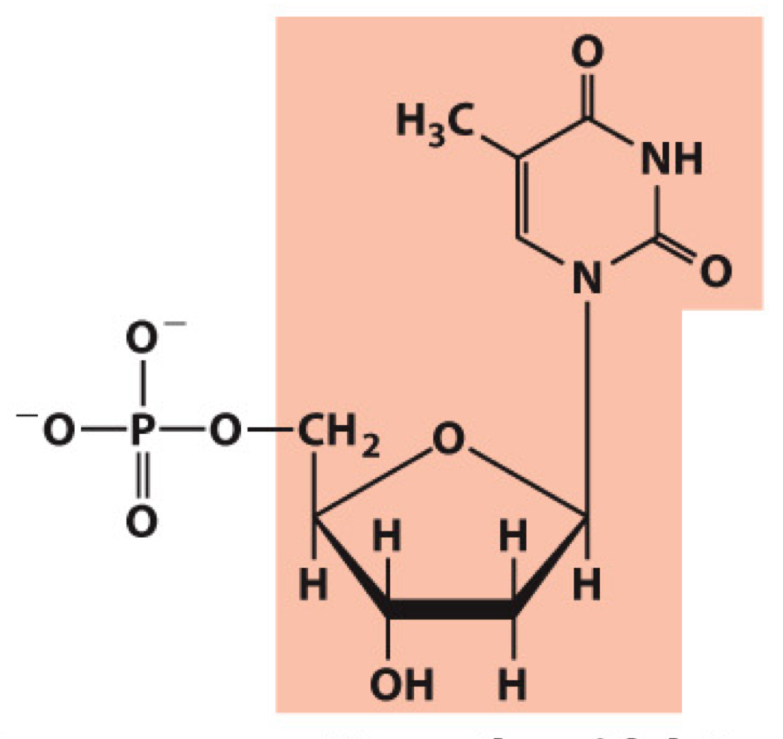
What molecule is this? Give the nucleotide and nucleoside names as well as the 3 symbols that represent it
Nucleotide: Deoxythymidine (deoxythymidine 5’-monophosphate)
Nucleoside: Deoxythymidine
Symbols: T, dT, dTMP
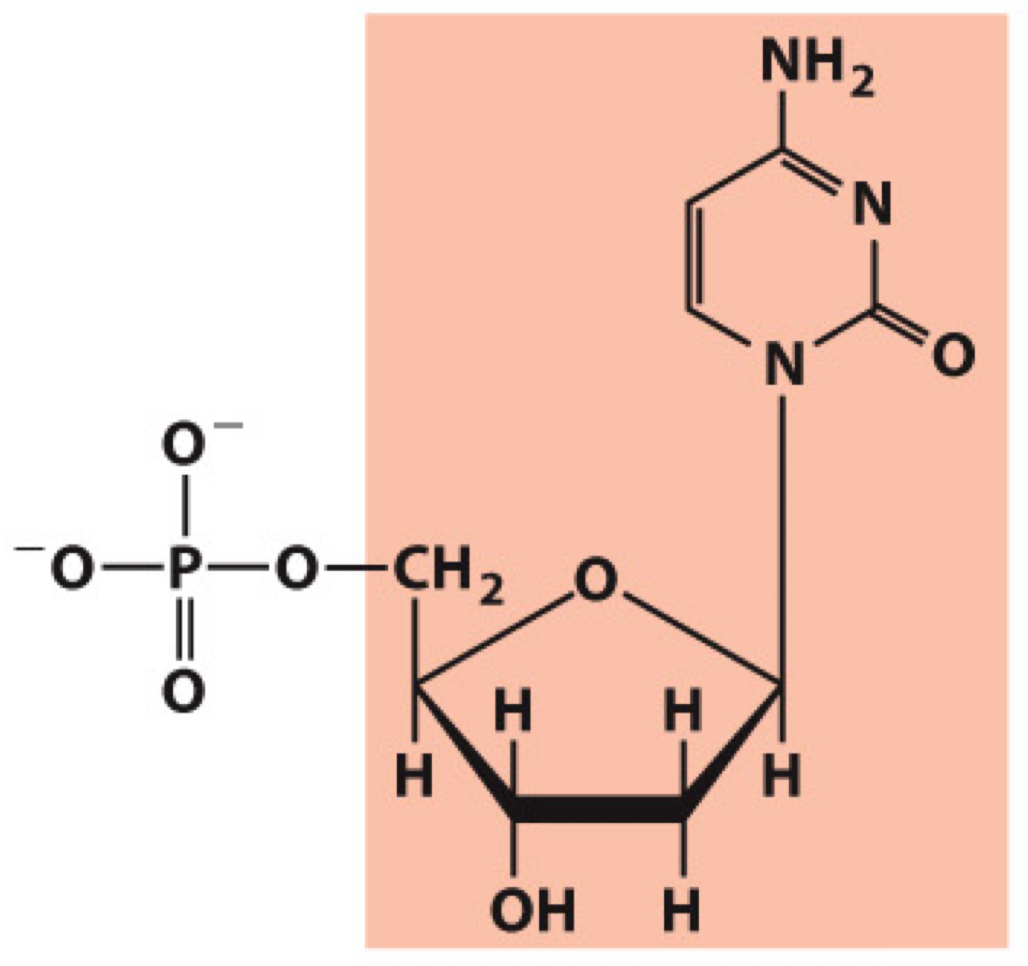
What molecule is this? Give the nucleotide and nucleoside names as well as the 3 symbols that represent it
Nucleotide: Deoxycytidylate (deoxycytidine 5’-monophosphate)
Nucleoside: Deoxycytidine
Symbols: C, dC, dCMP
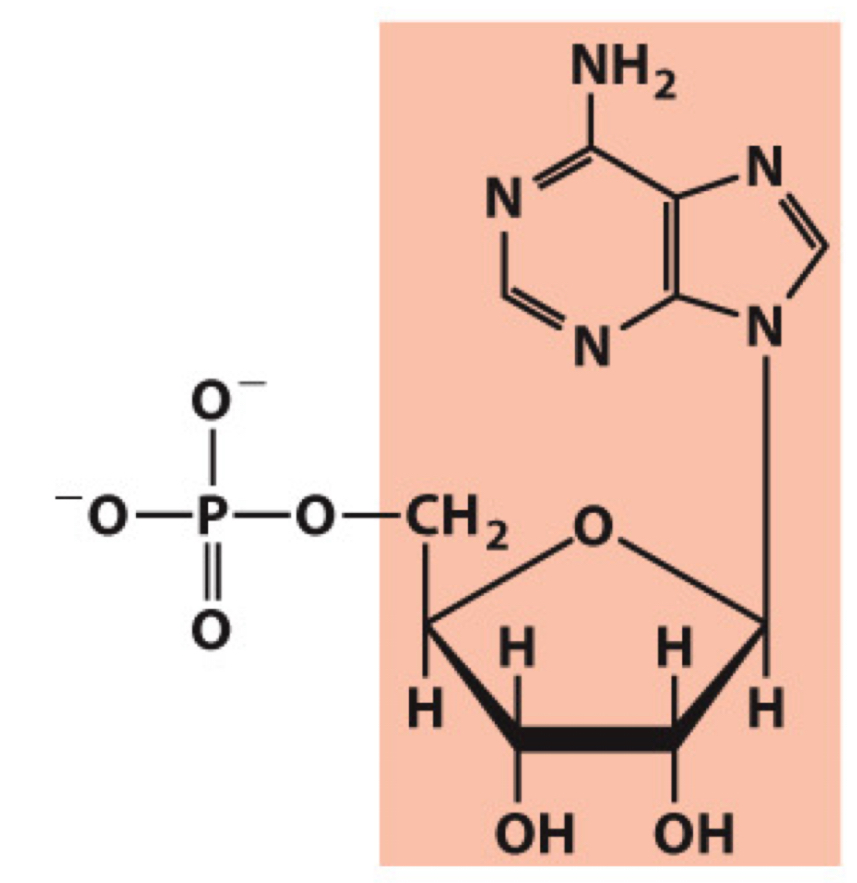
What molecule is this? Give the nucleotide and nucleoside names as well as the 3 symbols that represent it
Nucleotide: Adenylate (adenosine 5’-monophosphate)
Nucleoside: Adenosine
Symbols: A, AMP
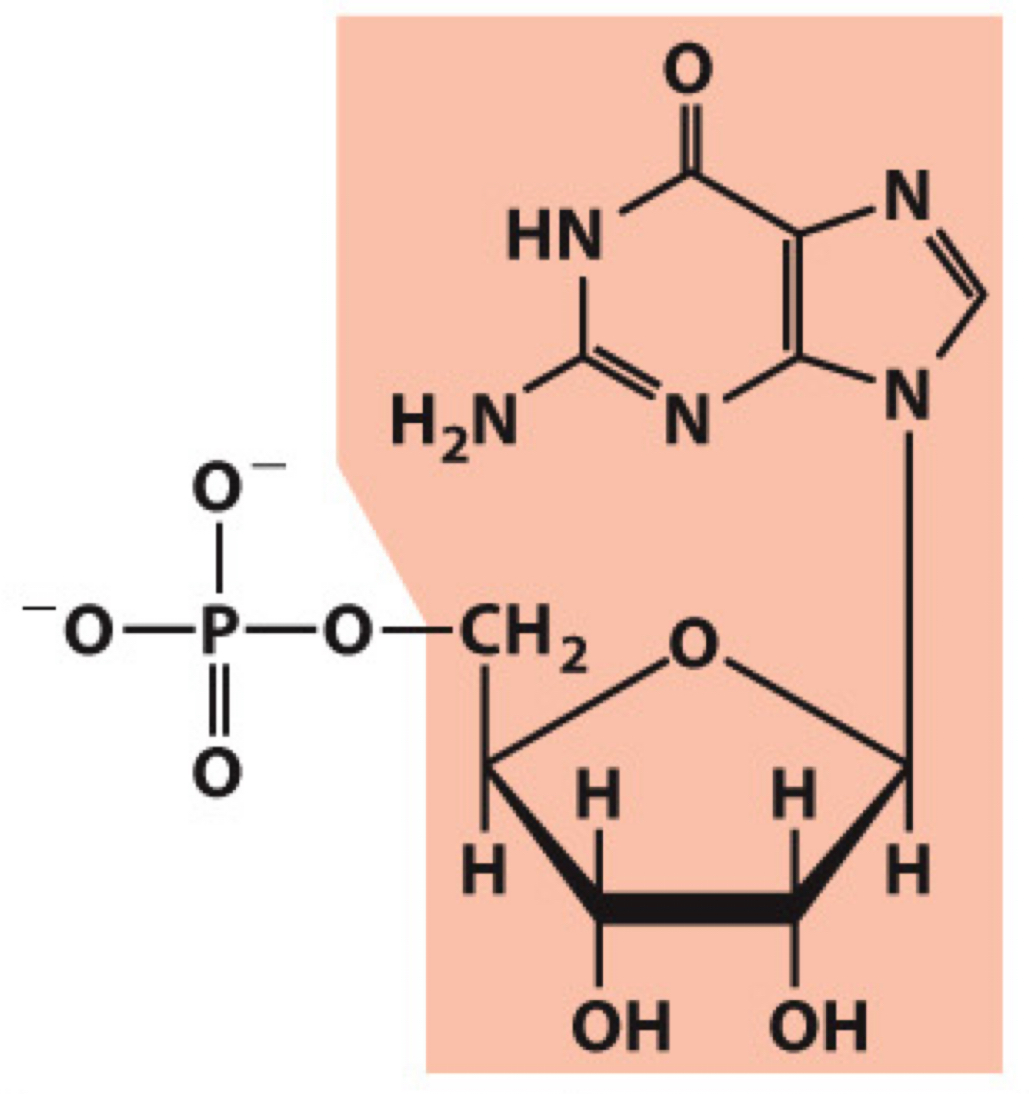
What molecule is this? Give the nucleotide and nucleoside names as well as the 3 symbols that represent it
Nucleotide: Guanylate (guanosine 5’-monophosphate)
Nucleoside: Guanosine
Symbols: G, GMP
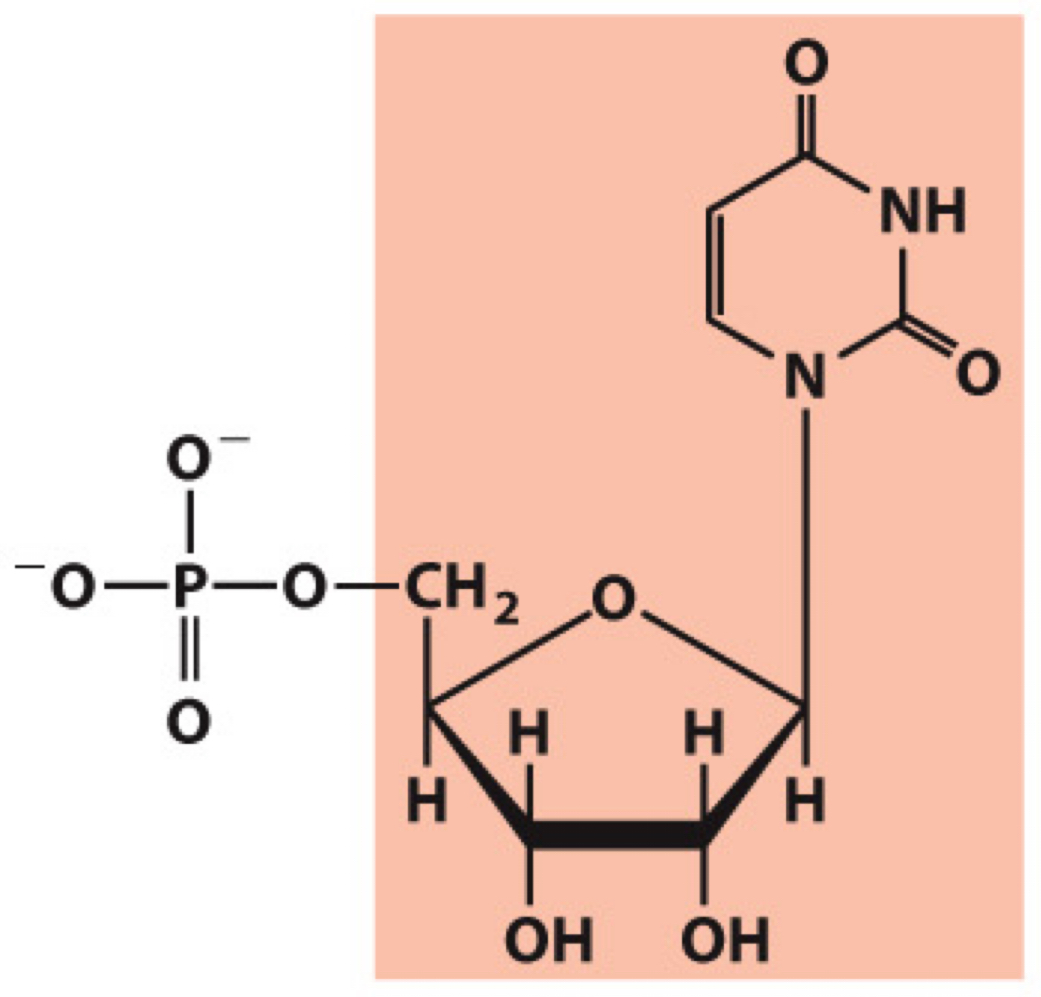
What molecule is this? Give the nucleotide and nucleoside names as well as the 3 symbols that represent it
Nucleotide: Uridylate (uridine 5’-monophosphate)
Nucleoside: Uridine
Symbols: U, UMP
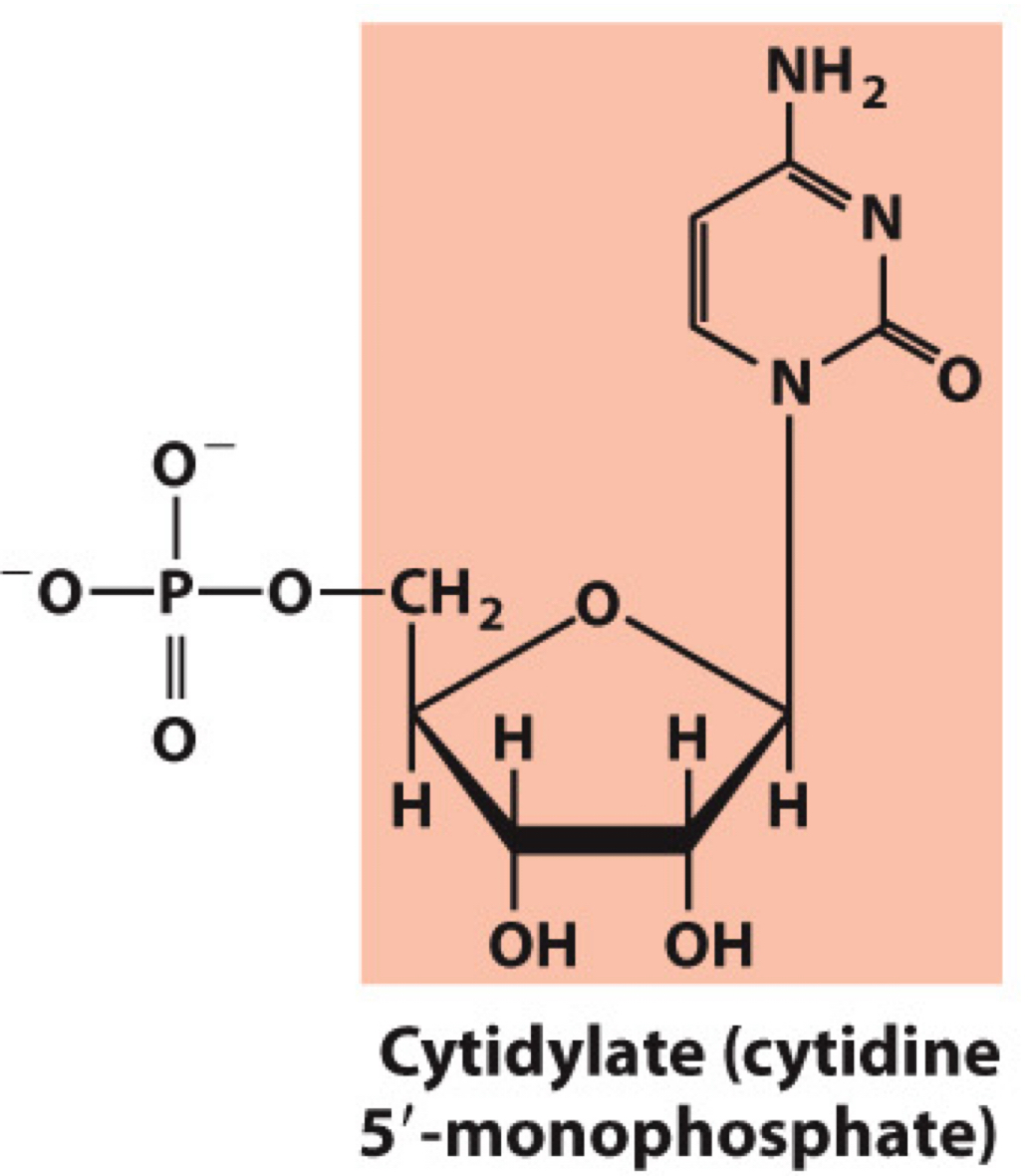
What molecule is this? Give the nucleotide and nucleoside names as well as the 3 symbols that represent it
Nucleotide: Cytidylate (cytidine 5’-monophosphate)
Nucleoside: Cytidine
Symbols: C, CMP
In nucleotides the pentose ring is attached to the nitrogenous base via what type of bond?
N-glycosidic bond
In nucleotides the anomeric carbon of the sugar is in what configuration?
Beta
The N glycosidic bond in pyrimidines is formed at what position?
N1
The N glycosidic bond in purines is formed at what position?
N9
The N-glycosidic bond is quite stable toward what lysis process? Particularly so in pyrimidines or purines?
Quite stable toward hydrolysis, especially in pyrimidines
Bond cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond can achieved through what reaction process?
Acid catalysis
Describe the solubility of nucleotides in pH 7.0 water and what interactions may occur
Hydrophobic
Relatively insoluble
Leads to stacking interactions (van der Waals and dipole-dipole)
Describe the solubility of nucleotides at acidic or alkaline pH values
More soluble than at pH 7.0
Charged
In free nucleotides what type of rotation can occur about the
N-glycosidic bond?
Free rotation
An angle near 0 degrees corresponds to what type of nucleotide conformation?
Synconformation
An angle near 180 degrees corresponds to what type of nucleotide conformation?
Anti conformation
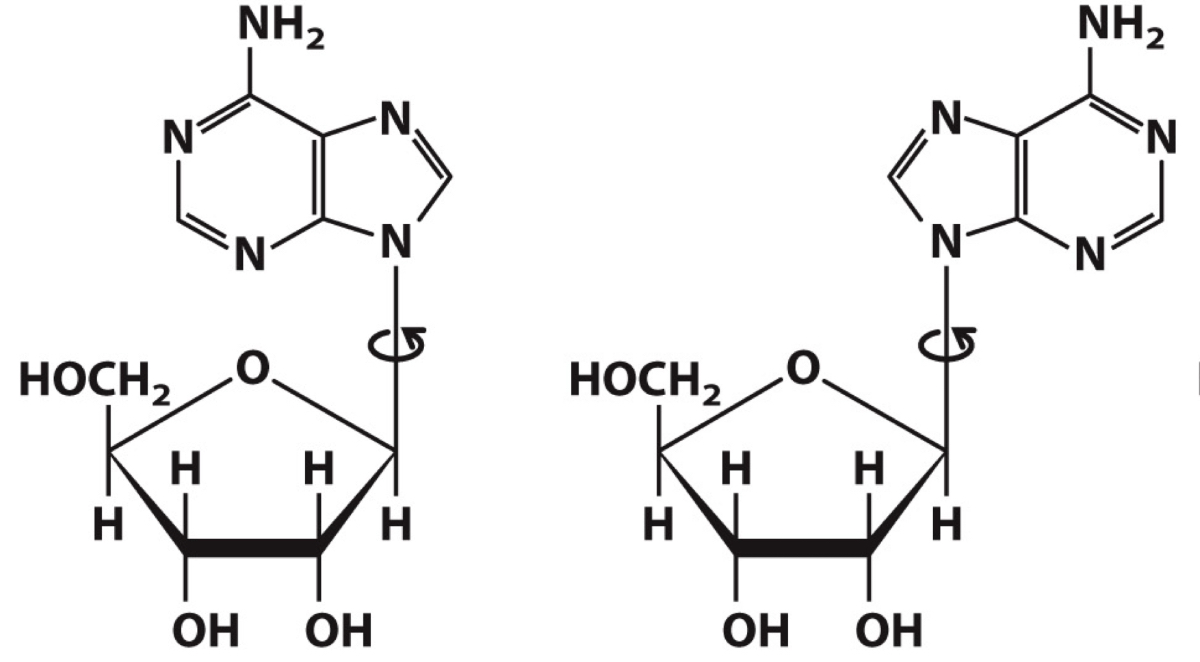
Identify which adenosine is in the synconformation and which is in the anti conformation
Synconformation adenosine is on the left
Anti conformation adenosine is on the right
What nucleotide conformation is found in normal B-DNA?
Anti conformation
What are prototropic tautomers?
Structural isomers that differ in the location of protons
What type of tautomerism is common in ketones?
Keto-enol tautomerism
What type of tautomerism is occurs in some heterocycles?
Lactam-lactim
Do nitrogenous bases have tautomers?
Yes
What type of tautomerism occurs in Uracil?
Lactam-lactim
In lactam-lactim tautomerism both tautomers exist in solution but at a neutral pH (7.0) which forms are predominant?
Lactam forms are predominant at neutral pH.
What RANGE of UV light wavelengths can Nucleobases absorb?
250-270nm
When measuring light absorption for mixtures of nucleotides what specific wavelength is used?
260nm
What can UV light absorption measurements be used to tell us about the nucleic acids in a solution?
Can be utilized to quantify the concentration of nucleic acids in a solution
What spectrum range do nucleobases absorb light from?
The UV range
Are there minor nucleosides in DNA and RNA?
Yes
When does modifications of nucleosides occur?
After DNA synthesis
What modified nucleoside is common in eukaryotes and also found in bacteria?
5-Methylcytosine
What modified nucleoside is common in bacteria but not found in eukaryotes?
N6-Methyladenosine
What is another term for the modifications of DNA?
Epigenetic markers
How do prokaryotes utilize epigenetic markers?
Use them as a way to mark own DNA so that cells can degrade foreign DNA
How do eukaryotes utilize epigenetic markers?
Use them as a way to mark which genes should be active
Could the environment turn genes on and off in an inheritable manner?
Yes
What is inosine? How is it made? What is its use?
A modified nucleoside in RNA sometime found in the “wobble position” of the anticodon in tRNA. Made by de-aminating adenosine. It provides a richer genetic code.
What is unique about Pseudouridine as a modified nucleoside?
It’s modification occurs after RNA synthesis
What is Pseudouridine? Where is it found? How is it made? What are its uses?
Pseudouridine is a modified nucleoside in RNA. It is found widely in tRNA and rRNA. ~every 10-20 nucleosides. More commonly found in eukaryotes but also found in eubacteria. Made from uridine by enzymatic isomerization after RNA synthesis. It may help stabilize the tRNA structure and may help in folding of rRNA
Are modified nucleotides functionally relevant?
Yes
How do you synthesize DNA or RNA from individual nucleotides?
Phosphoryl group transfer reaction
The phosphorous atom in phosphate groups is an “easy target” for what type of attack?
Nucleophilic
Hydrolysis of a phosphodiester bond in nucleoside triphosphates can be coupled commonly to what type of reaction?
Creation of a phosphodiester bond between two nucleotides
What is DNA synthesized 5’ → 3’ only?
Because the 3’ OH is the only free reactive hydroxyl group where new nucleotides can be added
What type of bond and linkage are required to form polynucleotides?
Covalent bonds which are formed via phosphodiester linkages
What charge does the backbone of polynucleotides possess?
Negative
Which backbone is more stable DNA or RNA?
DNA
In water how long can RNA last?
A few years
In cells how long can mRNA last?
It is degraded in a few hours
What enzyme is responsible for accelerated hydrolysis of DNA?
DNAse
Is the structure of polynucleotides linear, branched, or linear with cross-links
Linear
How are polynucleotides read?
From 5’ → 3’
Two bases can form what to make a base pair?
Hydrogen bond(s)
Monomers or polynucleotides which has more base pair possibilities?
Monomers
A pairs with what?
T