IED Unit 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:57 AM on 10/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
Forced Association
Ideas created by mentally forcing the association of two seemingly unrelated items

2
New cards
Assess
To thoroughly and methodically analyze accomplishment against
specific goals and criteria.
specific goals and criteria.

3
New cards
Assessment
evaluation technique for technology that requires analyzing benefits and risks, understanding the trade-offs, and determining the best action to take in order to ensure that the desired positive outcomes outweigh the negative consequences. Techniques used to analyze accomplishments against specific goals and criteria. Ex. tests, surveys, observations, and self-assessment.

4
New cards
brainstorm
A group technique for solving problems, generating ideas, stimulating creative thinking, etc. by unrestrained spontaneous participation in discussion.

5
New cards
Client
A person using the services of a professional person or organization.

6
New cards
Creativity
The ability to make or bring a new concept or idea into existence

7
New cards
Critieria
A means of judging. A standard, rule, or test by which something can
be judged.
be judged.
8
New cards
Constraint
1. A limit to a design process. Can be things such as appearance, funding, space, materials, and human capabilities. 2. A limitation or restriction.

9
New cards
Design
1. An iterative decision-making process that produces plans by which resources are converted into products or systems that meet human needs and wants or solve problems.
2. A plan or drawing produced to show the look and function or workings of something before it is
built or made.
2. A plan or drawing produced to show the look and function or workings of something before it is
built or made.

10
New cards
Design Brief
A written plan that identifies a problem to be solved, its criteria, and its constraints. Used to encourage thinking of all aspects of a problem before attempting a solution.

11
New cards
Design Process
A systematic problem-solving strategy, with criteria and constraints, used to develop many possible solutions to solve a problem or satisfy human needs and wants and to winnow (narrow) down the possible solutions to one final choice.

12
New cards
Design Statement
A part of a design brief that challenges the designer, describes what a design solution should do without how to solve the problem, and identifies the degree to which the solution must be executed.

13
New cards
Designer
A person who designs any of a variety of things. This usually implies the task of creating drawings or in some ways uses visual cues to organize his or her work.

14
New cards
Engineer
A person who is trained in and uses technological and scientific knowledge to solve practical problems.

15
New cards
Engineering Notebook
A book in which an engineer will formally document, in chronological order, all of his/her work that is associated with a specific design project.

16
New cards
Innovation
An improvement of an existing technological product, system, or method of doing something.

17
New cards
Invention
A new product, system, or process that has never existed before, created by study and experimentation.
18
New cards
Iterative
A process that repeats a series of steps over and over until the desired outcome is obtained.

19
New cards
Justifiable
Capable of being shown as reasonable or merited according to accepted standards.

20
New cards
Piling-on
An idea that produces a similar idea or an enhanced idea.

21
New cards
Problem Identification
The recognition of an unwelcome or harmful matter needing to be dealt with.

22
New cards
Product
A tangible artifact produced by means of either human or mechanical work, or by biological or chemical process.

23
New cards
Prototype
A full-scale working model used to test a design concept by making actual observations and necessary adjustments.

24
New cards
Research
The systematic study of materials and sources in order to establish facts and reach new conclusions.
25
New cards
Valid
Well-founded on evidence and corresponds accurately to the real world.

26
New cards
What does shading do for your drawing?
Shading makes your drawings appear more realistic by adding depth and contrast
27
New cards
What is the acronym for brainstorming, say it.
SCAMMPERR
S
Substitute something . . .
C
Combine it with something else . . .
A
Adapt something to it . . .
M
Magnify or add to it . . .
M
Modify it . . .
P
Put it to some other use . . .
E
Eliminate something . . .
R
Rearrange it . . .
R
Reverse it . . .
S
Substitute something . . .
C
Combine it with something else . . .
A
Adapt something to it . . .
M
Magnify or add to it . . .
M
Modify it . . .
P
Put it to some other use . . .
E
Eliminate something . . .
R
Rearrange it . . .
R
Reverse it . . .
28
New cards
What is the design process?
1. Define the Problem
2. Generate Concepts
3. Develop a Solution
4. Construct and Test a Prototype
5. Evaluate the Solution
6. Present the Solution
2. Generate Concepts
3. Develop a Solution
4. Construct and Test a Prototype
5. Evaluate the Solution
6. Present the Solution
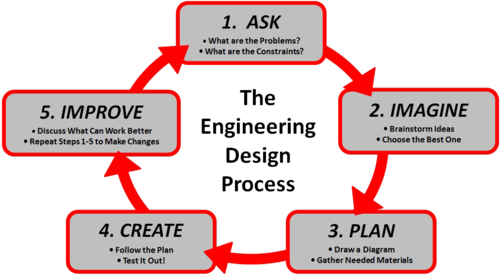
29
New cards
Don't criticize other peoples ideas while brainstorming, t/f?
True. Don't be that guy
30
New cards
What is a decision matrix?
A tool used to compare design solutions against one another, using specific criteria.
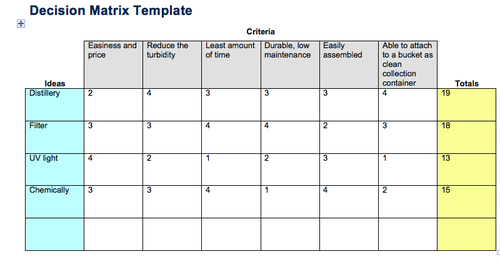
31
New cards
Who is the Client?
Although it may be the target consumer, the client is anyone who will buy the product.
Example, Wilson may buy a basketball hoop made by a company, for they are in the basketball business
Example, Wilson may buy a basketball hoop made by a company, for they are in the basketball business

32
New cards
Who is the Target Consumer
The person actually using the product
Someone in a wheelchair would use the wheelchair stop from rolling back thing. Or, a family might buy a hoop to play basketball in.
Someone in a wheelchair would use the wheelchair stop from rolling back thing. Or, a family might buy a hoop to play basketball in.
33
New cards
What is the problem statement?
a brief summary of the problem written in present tense, describing the situation.
Basketball rims, although an important piece in basketball, hurt when you 360 dunk on them.
Basketball rims, although an important piece in basketball, hurt when you 360 dunk on them.

34
New cards
Design statement
Always start with,
Design build and test a device to...
(what I said above) allow those who can dunk to do so without any pain in their hands after dunking.
Design build and test a device to...
(what I said above) allow those who can dunk to do so without any pain in their hands after dunking.

35
New cards
Constraints(MEASURABLE)
Things that your product must do or follow.
1. Cannot fall off of the rim after a dunk is made
2. Must be able to withstand rain or wind
3. Must be able to fit on any basketball hoop
4. Must be able to withstand 300 pounds of downward force.
1. Cannot fall off of the rim after a dunk is made
2. Must be able to withstand rain or wind
3. Must be able to fit on any basketball hoop
4. Must be able to withstand 300 pounds of downward force.
36
New cards
What is Research?
The systematic study of materials and sources in order to establish facts and reach new conclusions.

37
New cards
Primary v Secondary Research
Primary Research
Generating original information
Secondary Research
Gathering information that has already been generated
Generating original information
Secondary Research
Gathering information that has already been generated
38
New cards
Primary Research
Original research
Generates current information
Includes methods such as observation, experiments, surveys, and interviews
Analyzes, synthesizes, and evaluates all information and data
Generates current information
Includes methods such as observation, experiments, surveys, and interviews
Analyzes, synthesizes, and evaluates all information and data

39
New cards
Advantages to Primary Research
Advantages:
Is directly applicable to the need
Can result in extremely detailed, accurate, and relevant information or data
Can result in new information that cannot be found in secondary sources
Results in expert knowledge
Is directly applicable to the need
Can result in extremely detailed, accurate, and relevant information or data
Can result in new information that cannot be found in secondary sources
Results in expert knowledge
40
New cards
Disadvantages to Primary Research
Disadvantages:
Time consuming
Requires extensive planning
Can be expensive
May depend on the participation of unreliable sources for results
Time consuming
Requires extensive planning
Can be expensive
May depend on the participation of unreliable sources for results
41
New cards
Secondary Research
Look to see what has been written/done before on a topic
Includes:
Published works: books, journals, magazines, newspapers
Unpublished works: business reports, operating manuals, master's theses, doctoral dissertations, web pages
Is the most commonly conducted type of research
Includes:
Published works: books, journals, magazines, newspapers
Unpublished works: business reports, operating manuals, master's theses, doctoral dissertations, web pages
Is the most commonly conducted type of research
42
New cards
Advantages to Secondary Research
Requires less time and little to no cost in comparison to primary research
Helps the researcher to either focus or expand his/her scope
Elicits a sense of credibility and authority in that it shows others that the researcher has done his/her homework
Helps the researcher to either focus or expand his/her scope
Elicits a sense of credibility and authority in that it shows others that the researcher has done his/her homework

43
New cards
Disadvantages to Secondary Research
Researcher may have to sift through a tremendous amount of information
Sources may not be authoritative or reliable
Sources may not be authoritative or reliable

44
New cards
Big 4 fields of engineering
Chemical
Civil
Electrical
Mechanical
Civil
Electrical
Mechanical
45
New cards
Chemical Engineering
Apply scientifically the principles of chemistry, physics, and engineering to design an operation of plants for the production of materials that undergo chemical changes during their processing
Responsible for new and improved products and processes:
New fuels for rockets, reactors, and booster propulsion
Medicines, vaccines, serum, and plasma
Plastics, synthetics and textiles
Responsible for new and improved products and processes:
New fuels for rockets, reactors, and booster propulsion
Medicines, vaccines, serum, and plasma
Plastics, synthetics and textiles

46
New cards
Civil and Construction Engineering
Plan, design, and supervise the construction of facilities in both the public and private sectors
Projects vary widely in nature, size, and scope:
Space satellites
Launch facilities
Offshore structures
Bridges
Buildings
Highways
Transit systems
Dams
Airports
Irrigation projects
Tunnels
Treatment and distribution facilities for water
Collection and treatment for wastewater
Projects vary widely in nature, size, and scope:
Space satellites
Launch facilities
Offshore structures
Bridges
Buildings
Highways
Transit systems
Dams
Airports
Irrigation projects
Tunnels
Treatment and distribution facilities for water
Collection and treatment for wastewater

47
New cards
Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Deals with the motion of electrons in metals
Work focused on:
Large electrical systems
Motors and generators
Electrical circuits in Buildings
Power transmission systems
Electrical generation plants
Electronics engineering deals with the passage of charged particles in a gas, vacuum, or semiconductor.
Work focused on:
Large electrical systems
Motors and generators
Electrical circuits in Buildings
Power transmission systems
Electrical generation plants
Electronics engineering deals with the passage of charged particles in a gas, vacuum, or semiconductor.

48
New cards
Mechanical Engineering
Apply the principles of mechanics and energy to the design of machines and devices
Most often associated with devices that move but includes thermal designs as well as HVAC
Vibration analysis
Lubrication
Gears and bearing
Most often associated with devices that move but includes thermal designs as well as HVAC
Vibration analysis
Lubrication
Gears and bearing
49
New cards
Aeronautical Engineering
Deals with flight and the movement of fluids in the earth's atmosphere.
Specializing in the following work areas:
Aerodynamics
Propulsion
Controls
Structure
Specializing in the following work areas:
Aerodynamics
Propulsion
Controls
Structure

50
New cards
Aerospace and Astronautical Engineering
Deals with environments not found on Earth
Specialization in work areas centered on:
Propulsion cryogenics
Materials navigation
Thermodynamics cosmic radiation
Specialization in work areas centered on:
Propulsion cryogenics
Materials navigation
Thermodynamics cosmic radiation
51
New cards
Agricultural Engineering
blends engineering knowledge with soil systems, land management, and environmental control.
Five specialty fields:
Soil and water
Food
Power Machinery
Structures
Electric Power Generation
Five specialty fields:
Soil and water
Food
Power Machinery
Structures
Electric Power Generation

52
New cards
Architectural Engineering
Works with architects focusing on structural integrity and safety of design
Structural engineering and this field are very similar; the main difference is the concern for aesthetics
Structural engineering and this field are very similar; the main difference is the concern for aesthetics

53
New cards
Automotive Engineering
Design and build all types of vehicles:
Automobiles
Trucks
Tractors
Bulldozers
Motorcycles
Addresses:
Engine design
Structural design
Tire design
Automobiles
Trucks
Tractors
Bulldozers
Motorcycles
Addresses:
Engine design
Structural design
Tire design
54
New cards
Biomedical Engineering
Bridges engineering, physical, and life sciences in identifying and solving medical and health-related problems
Three general divisions:
Bioengineering
Medical Engineering
Clinical Engineering
Three general divisions:
Bioengineering
Medical Engineering
Clinical Engineering

55
New cards
Difference between Clinical, Medical, and Bioengineering.
1. Bioengineering, a research activity, applies engineering techniques to biological systems (kidney dialysis)
2. Medical Engineering develops medical instrumentation, artificial organs, prosthetic devices, and materials
3. Clinical Engineering concerns itself with the hospital systems; decontaminating airlines, removing anesthetics gases from operating rooms
2. Medical Engineering develops medical instrumentation, artificial organs, prosthetic devices, and materials
3. Clinical Engineering concerns itself with the hospital systems; decontaminating airlines, removing anesthetics gases from operating rooms
56
New cards
Computer Engineering
The design and organization of computers:
Hardware
Software
Who is the largest consumer of computers today?
Automotive Industry
Hardware
Software
Who is the largest consumer of computers today?
Automotive Industry

57
New cards
Industrial Engineering
The design, improvement, and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, and energy to produce a product at the lower possible cost
Deals with:
Design of systems for the manufacture of products
Raw materials to machines
Workforce to operate machinery
Removal of finished products
Maintenance of machinery
Analysis of manufacturing processes for cost
Deals with:
Design of systems for the manufacture of products
Raw materials to machines
Workforce to operate machinery
Removal of finished products
Maintenance of machinery
Analysis of manufacturing processes for cost

58
New cards
Manufacturing Engineering
Design of a manufacturing facility for a product or products
Deals with:
Physical plant layout
Use of existing machines or new
Purchase or rental of facilities
Purchase of nonproducing facilities and equipment
Packaging of product
Shipping to market
Deals with:
Physical plant layout
Use of existing machines or new
Purchase or rental of facilities
Purchase of nonproducing facilities and equipment
Packaging of product
Shipping to market

59
New cards
What do you use during the First Step of the Design Process
Design Statement
60
New cards
What do you use during the Second Step of the Design Process?
Decision Matrix
61
New cards
What do you use during the Third Step of the Design Process
Technical Drawings, Like CAD
62
New cards
What do you use during the Fourth Step of the Design Process
Test Report: You can use CAM for the prototype