AQA 8525 GCSE Computer Science
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
Algorithm
A sequence of steps that can be followed to complete a task.
Decomposition
Breaking a problem into a number of sub-problems, so that each sub-problem accomplishes an identifiable task.
Abstraction
The process of removing unnecessary detail from a problem.
Variable
A storage location paired with an associated name used to describe it. It can be changed.
Constant
A storage location paired with an associated name used to describe it. It cannot be changed.
Boolean
A data type, can be either true or false.
Char
A single character.
String
A collection of characters.
Integer
A whole number.
Real
A decimal number.
Boolean Operator - AND
Two conditions, true only if both are true
Boolean Operator - OR
Two conditions, true if atleast one is true
Boolean Operator - NOT
Single condition, returns the opposite of the condition
Sequence
Following programming commands one after another in the order that they have been typed.
Selection
A type of programming statement that uses a boolean condition to determine whether or not to run a certain block of statements.
Iteration
A type of programming statement that repeats a block of statements if or until a condition is met.
Subroutine
A small program inside a large one. Used when the same series of commands are repeated multiple times. Examples include functions and procedures.
Function
A subroutine that returns a value.
Procedure
A subroutine that doesn't return a value.
Parameter
A special kind of variable used in a subroutine to refer to one of the pieces of data provided as an input to the subroutine.
Argument
A variable passed into a subroutine
Local variable
Can only be used within the subroutine in which it was declared.
Global variable
Can be used anywhere within a program
Syntax Error
Occurs when there is a mistake in the source code such as a typo or calling on an object that does not exist.
Logic Error
Occurs when there is a fault in the logic or structure of the problem. They do not cause the program to crash however can cause unexpected results.
Trace Tables
Used to keep track of variables and their changing values to make sure there are no logic errors.
High-Level languages
Strongly resemble English and is easy for humans to read and write. However computers require a translator to convert it into machine code before running it.
Low-Level languages
Difficult and slow for humans to read and write, however they are much faster to convert and run.
Compilers
Software used to convert high-level code into machine code. Translates all of the source code at the same time and creates one executable file.
Assemblers
Software that converts assembly languages into machine code
Interpreters
Software used to convert high-level code into machine code. Translates and runs the source code one instruction at a time, but doesn't create an executable file.
NOT Gate
A logic gate that takes a single input and outputs the opposite value
AND Gate
A logic gate that takes in 2 inputs and only outputs True if both inputs are True
XOR Gate
A logic gate that takes two inputs and outputs true if the inputs are different.
OR Gate
A logic gate that takes two inputs and outputs True if either input is True
Binary
A representation of the flow of electricity within a computer. 1 is flow, 0 is not.
Data units and sizes
Bit (b), Nibble, Byte (B), Kilobyte (KB), Megabyte (MB), Gigabyte (GB), Terabyte (TB)
Binary shifts
The method to multiply or divide a binary number by 2 by moving a binary number to the left to multiply and to the right to divide.
Hexadecimal
A base-16 number system, consisting of the 16 symbols 0 through 9 and A through F.
ASCII
Each character is given a 7-bit binary code, meaning it can represent a total of 128 different characters.
Unicode
A character code that enables most languages, it uses multiple bytes for each character.
Bitmap
A type of image comprised of pixels.
Formula for calculating the number of colours stored in a pixel
2 to the power of the colour depth.
Analogue signal
A continuous signal that varies in amplitude or frequency with the information being transmitted. The form of data that sound is recorded as; that must be converted to digital data to be read by a computer.
Sampling
The process of converting analogue data into digital data through sampling the amplitude of the wave at regular intervals.

Sample resolution
The number of bits used to store the value of each sample. The higher the number of bits the more accurately the value is stored..
Formula for calculating the size of a sound file
Sample rate (in Hz) sample resolution length (in secs).
Sample rate
The number of samples taken per second, measured hertz.
Data compression
Reducing the amount of space needed to store a piece of data
Lossy compression
A data compression technique that permanently removes some data from the file. Used for MP3, AAC, JPEG.
Lossless compression
A data compression technique that temporarily removes data. The original version of the data can be restored.
Run-Length-Encoding (RLE)
A form of lossless compression that looks for consecutive repeating data in a file. It stores the number of times it repeats and one copy of the data.
Huffman coding
Encoding more frequent letters/pixels with shorter bit representations and less frequent ones with longer bit representations.

What are embedded systems
Computers built into other devices such as a dishwasher, they are usually dedicated systems. They are most often used as control systems.
What are the advantages of embedded systems
They're usually easier to design, cheaper to produce and more efficient than a general purpose computer due to them being dedicated to one task
What are the 5 main parts of the CPU
The Control Unit (CU), the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Registers, Clock, Buses
Control unit (CU)
The part of the CPU that is in overall control of the CPU, its primary job is to execute program instructions by following the fetch-decode-execute cycle.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The part of the CPU that carries out calculations and logical operations.
The Clock
A part of the CPU that sends out a signal that continually cycles between 1 and 0 at a constant rate.
Buses
A collection of wires that are used to transmit data between components of the CPU, and to other parts of the computer system.
Cache Memory
High-speed memory that stores frequently needed instructions or data. Stores copies of data or instructions from the RAM that are accessed very regularly.
Registers
Small, high-speed storage locations that temporarily hold data and instructions, stored within the processor.
Von Neumann architecture
Storing instructions and data in the same memory and using one bus to access both.
Harvard Architecture
Storing instructions and data in seperate memory locations and using a seperate bus to access each.
Fetch-decode-execute cycle
Retrieves a program instruction from memory, determines what actions the instruction requires, and carries out those actions. One action is carried out per clock tick.
RAM
Can access any storage location directly. It is used as the main memory in a computer, it can be read or written to and is volatile. Is where all data, files and programs are stored while they are being used.
Volatile memory
Storage that is wiped clean when power is cut off from a device
ROM
Non-volatile memory that comes on a small, factory made-chip built into the motherboard. It contains the BIOS (Basic Input Output System) which are the instructions required to boot up a computer.
Clock speed
The number of instructions a single processor core can carry out per second.
CPU cores
Each core in a CPU can process data independently of the rest. The more cores a CPU has, the more instructions it can carry out at once, so the faster it can process a batch of data.
Cache type
There are different levels - L1, L2, L3. The higher the level, the higher the capacity but the lower the level the faster it can access data.
Primary storage
Memory that can be accessed directly by the CPU.
Secondary storage
Memory that isn't directly accessible by the CPU, it is where all data is stored when not in use. Data stored is kept even if the computer is powered off.
Hard disk drives (HDD)
Comprised of a stack of magnetised spinning metal disks. Data is stored magnetically in small areas called sectors within circular tracks. Read/write heads on a moving arm are used to access sectors on the disks.
Solid state drives
They are internal storage devices with no moving parts, most of them use a type of flash memory, an electronic type of memory storage that allows data to be electrically erased and reprogrammed.
Magnetic tape
A type of magnetic storage made of a plastic material, resembling a cassette tape that stores data sequentially. It has an extremely low cost per GB, however due to being read/write sequentially it can take a long time to find specific data.
Optical disks
Data is stored as microscopic indentations on the shiny surface of the disk which represents binary, a pit being equivalent to 0 and a land equivalent to 1. The disk is spun inside a player and read using a laser as pits are not reflective while lands are.
Cloud storage
A service where files can be uploaded via the internet to a secure remote server fore storage.
Operating system (OS)
Is a complex piece of software that that manages: input and output devices, applications, user interface, memory, processing, files, security and user accounts.
Device drivers
Utility software used by the operating system to communicate with (I/O) devices.
Places where utility software is used
Defragmentation, disk health, system cleanup, compression, backup, encryption, virus scanners
Defragmentation
As files are moved and deleted, gaps of free space appear on the disk and whole files cannot be stored together. This process removes the gaps and rearranges files to be together.
Local area network
A network that covers a small geographical are located on a single site.
Wide area network
A network covering a very wide geographical area, connecting, smaller, LAN networks together.
Personal area network
A network usually centred around a single person, that connects devices across a very short. Commonly uses wireless technology, such as bluetooth.
Switch
Used to connect devices on a LAN.
Router
Used to connect multiple LAN's together.
Wireless Access Point
Allows devices to connect to a network using wireless technology.
Network Interface Card
A piece of hardware inside a device that allows it to connect to networks, in both wired and wireless connections
Types of cables
Fibre optic, Ethernet, Coaxial cables.
Network
A group of computers linked together to share resources.
Bandwidth
The amount of data that can be sent across a network in a given time.
Wireless networks
A type of network that uses radio waves to transmit data.
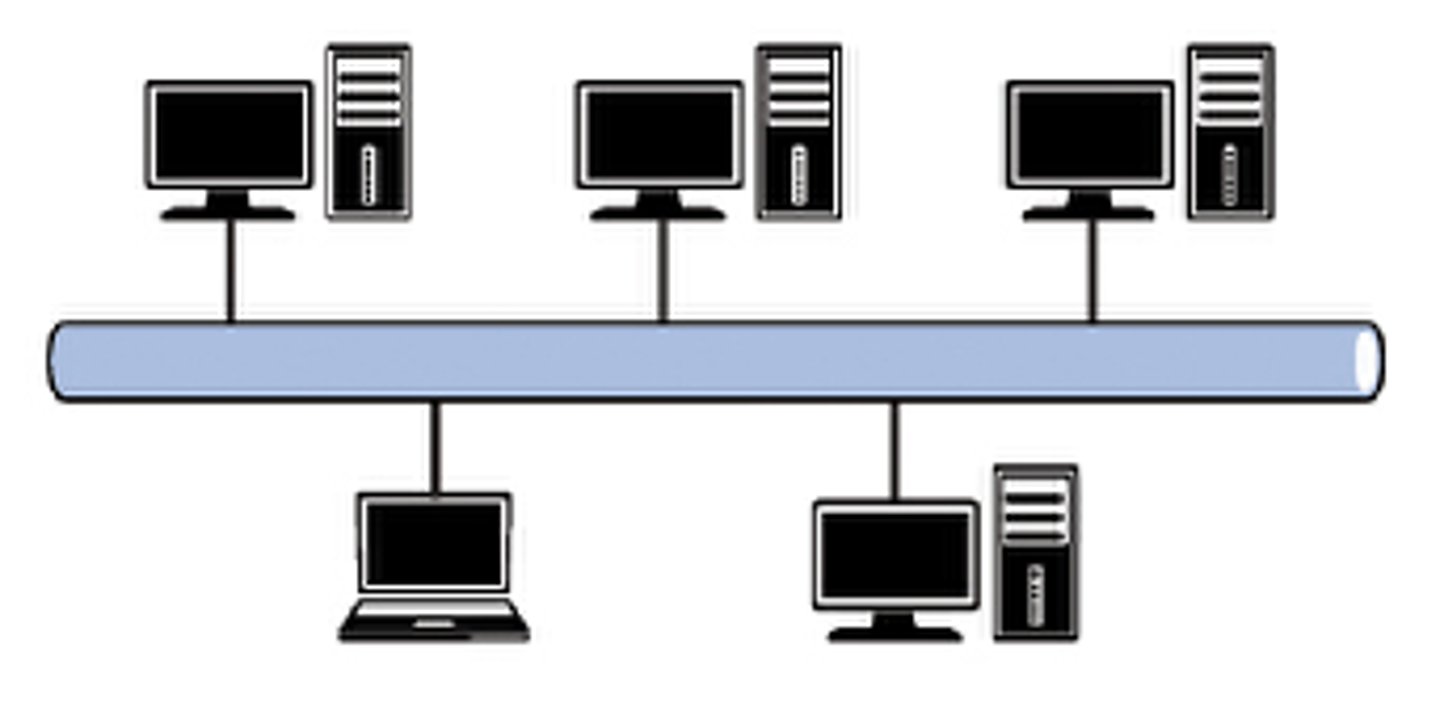
Bus Topology
A wired network layout comprised of one main cable (the backbone), to which all devices are directly connected.
Star Topology
An either wired or wireless network layout in which all devices are connected to a single central device, such as a switch or a hub.

Advantages of a Bus Topology
Very cheap, as it requires minimal amount of cabling.
Easy to add or remove computers.
Advantages of a Star Topology
If one cable fails, only the device attached to it is isolated from the network. Faults are easy to find.
Disadvantages of a Bus Topology
Failure in the main cable will cause failure of the network. The network can be significantly slowed by high network traffic.
Disadvantages of a Star Topology
Lots of cable, which means more expensive to install than other topologies.
Network protocol
Specifies the rules and format of communication between devices on a network.