extraoral radiography- cephalometric & skull proj
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
skull projection definition
radiographs of the whole head (craniofacial skeleton)
cephalometric radiographs definition
type of skull projection w standardized projection geometry and known magnification (reproducible- can compare images over time)
cephalometric projections are predominantly used for
orthodontic and orthognathic surgical dx and tx planning
what is cephalometry
measurement and comparison of specific points, distances, and lines within the facial skeleton
since cephalometric projections are reproducible, what can they be used to monitor
growth and tx progress and outcomes
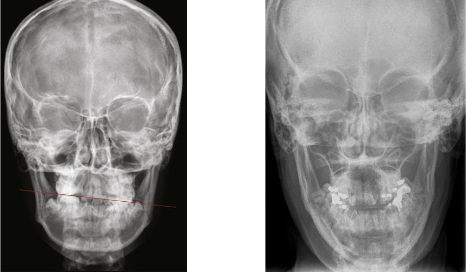
what are they types of cephalometric projections
lateral and posteroanterior
what is a cephalostat
device that maintains a constant relationship between the skull, the receptor, and the x-ray beam; also helps stabilize and immobilize pt
in cephalometric projections, the measurement scale on the nasion stabilizer allows for…
determination of magnification on the radiograph
how is magnification minimized in cephalometric projections
long source-to-object distance (150 cm)
short object-to-receptor distance (15-20 cm)
in cephalometric projections, are structures closer to the receptor magnified more or less than those located closer the source
closer to the receptor are magnified less than those closer to the source
lateral cephalometric projections are most used…
in orthodontics
what is the pt positioning in lateral cephalometric projections (4)
mid-sagittal plane vertical, paralleling receptor
Frankfort plane horizontal
maximum intercuspation
pt R side toward the receptor
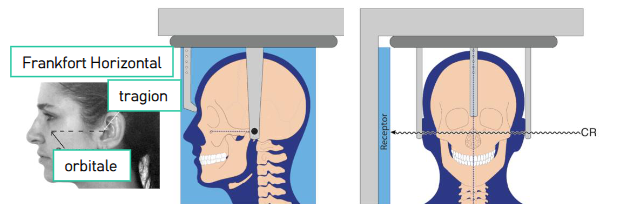
in lateral cephalometric projections, to better image the anterior facial soft tissue profile, is the amount of radiation to area dec or inc
dec
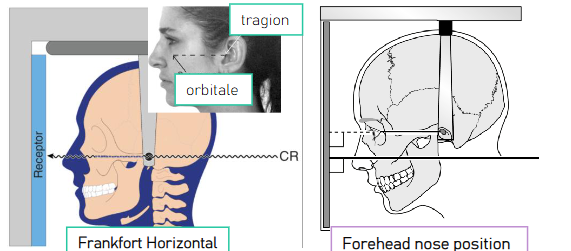
in posteroanterior projections, what is the pt positioning (4)
pt facing receptor
mid-sagittal plane vertical, perpendicular to receptor
Frankfort plane horizontal, perpendicular to the receptor or forehead-nose position
maximum intercuspation
posteroanterior projections show…
mid-facial skeleton
allows assessment of mediolateral and vertical dimensions