Light dependent stage
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the light dependent stage?
Energy from sunlight is absorbed and used to form ATP.
Hydrogen from water is used to reduce coenzyme NADP to reduced NADP.
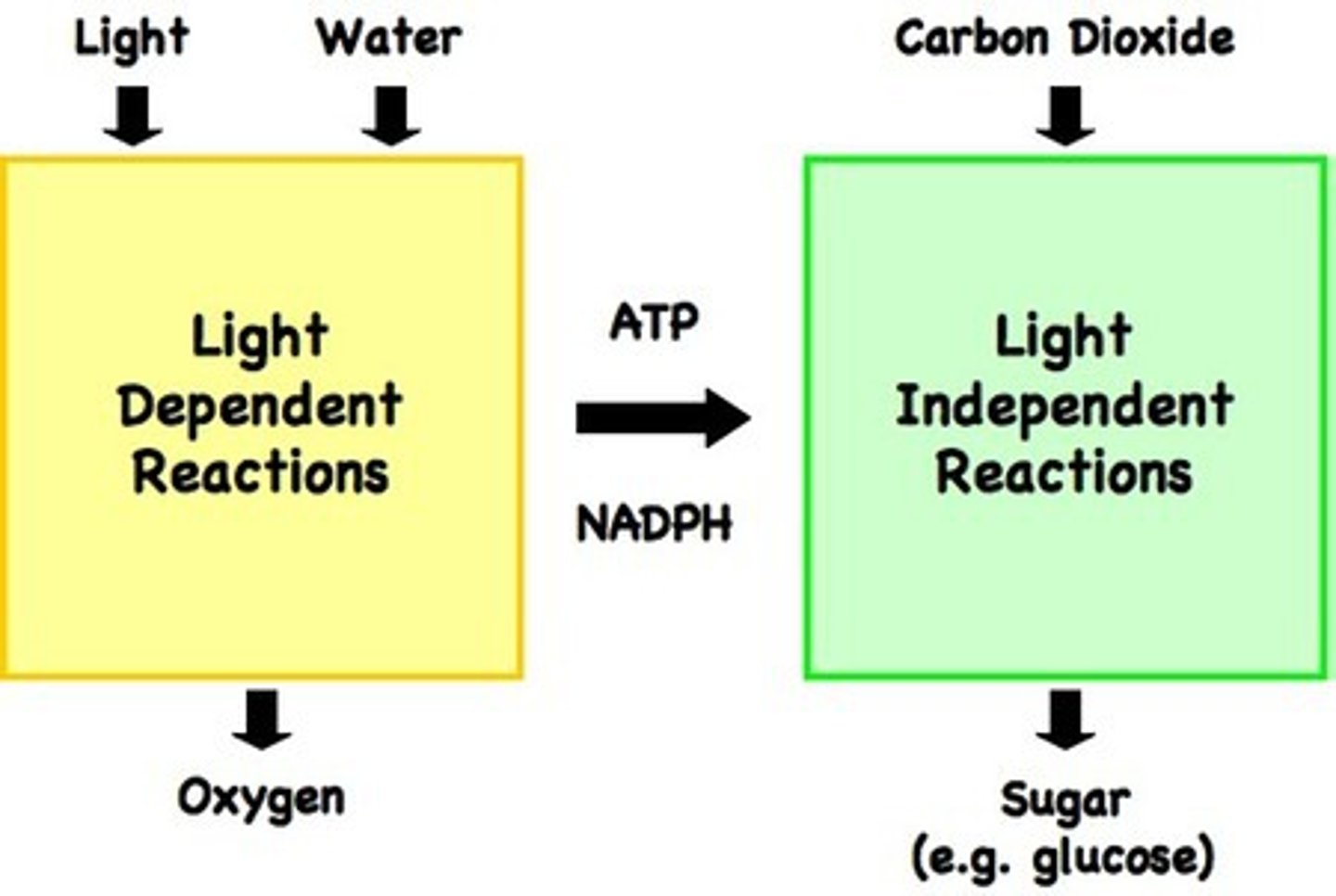
Where does the light dependent stage occur?
Thylakoid membrane
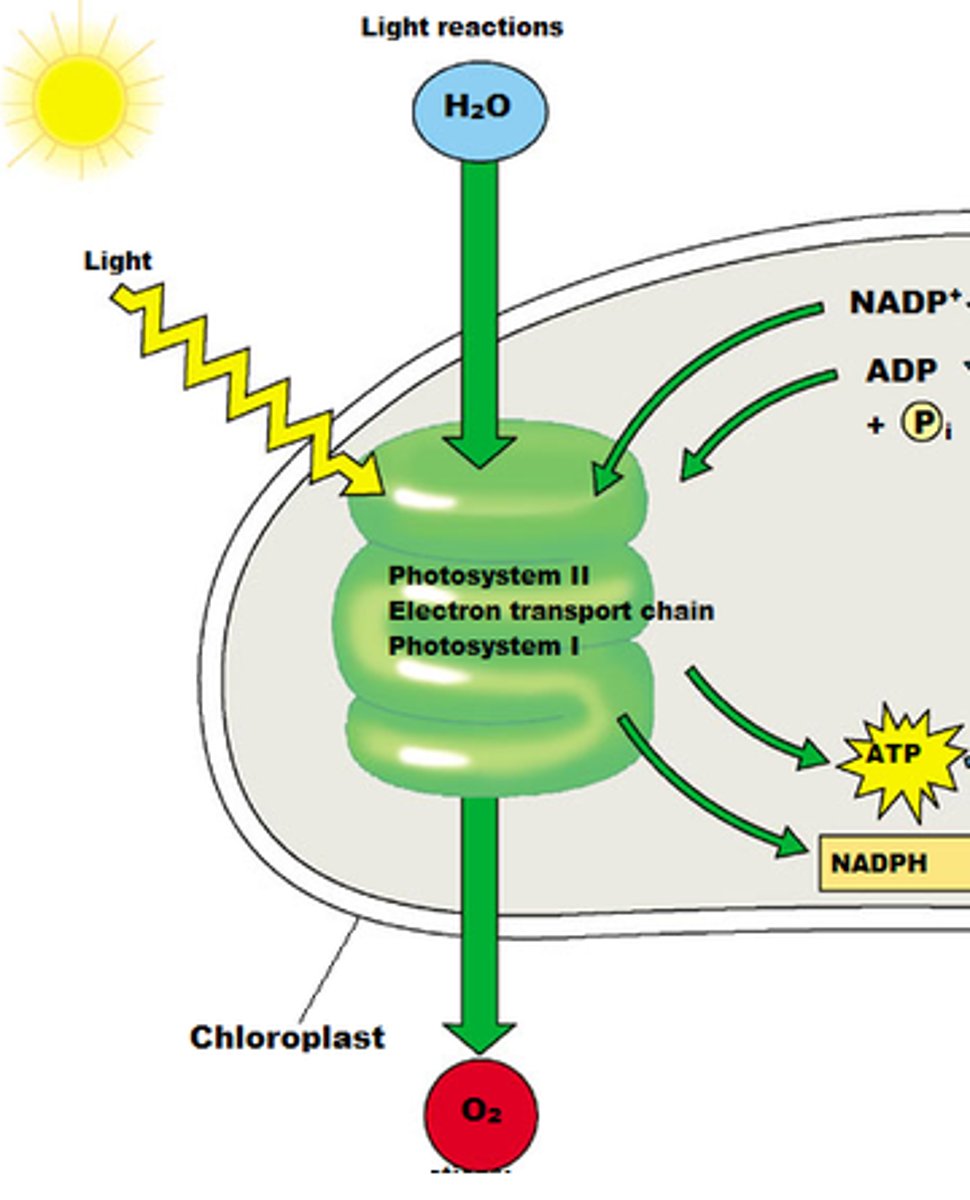
PSII
Water is absorbed from the roots, travels up to the leaf and goes into the thylakoid membrane.
Water is first at PSII
What is PSII also known as?
P680
Because chlorophyll a in this system has a max absorption at 680nm
What about PSI?
P700
Chlorophyll a in this system has a max absorption of light at 700nm
Photolysis
Light from the sun hits the leaf, and the light energy is used to break this water molecule down.
1/2 O₂ has been released
2 H⁺ are also made
Electrons are released from the water molecule, go into PSII, and they get excited because of the light energy.
Why is this process called photolysis?
Light energy break down
4)
The 2e⁻ from the water molecule are transported in structures called electron carriers. They electrons will go through the electron transport chain
Electron transport chain
ETCs play a major role in ATP synthesis. It's the same one in respiration (oxidative phosphorylation)
6)
These electrons eventually lose their energy as they go along a series of electron carriers, and reach PSI. In the process, they will make ATP, releasing energy
7)
PSI absorbs light energy from the sun, and again, the electrons get excited and travel via an electron carrier again
Cyclic Photophosphorylation
The electrons can either go back down to PSI to release more energy, or continue with the cycle. This depends on what the plant needs - if the plant is lacking in ATP, it will travel back down to PSI, releasing ATP again
ADP + Pi → ATP
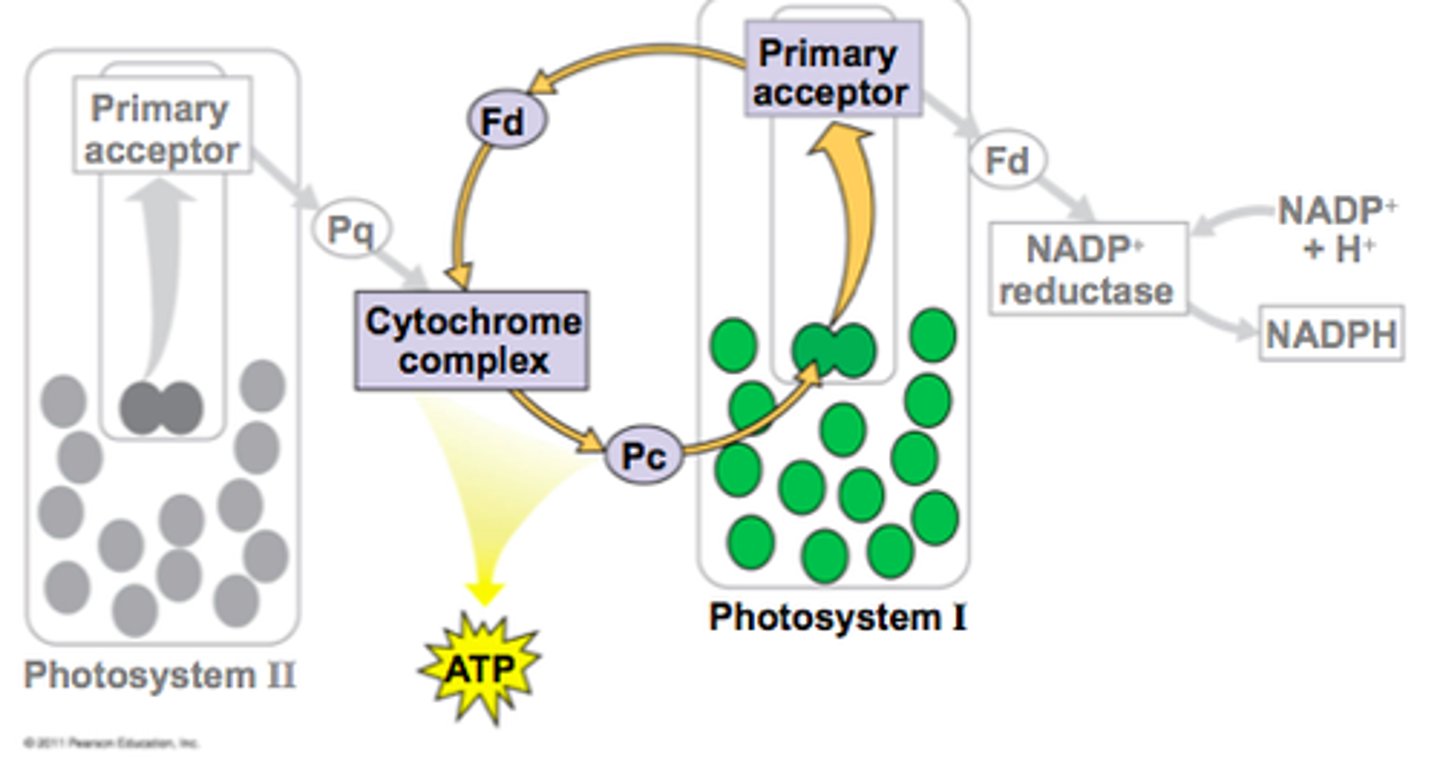
8)
The electrons can continue with the cycle, arriving at an enzyme called NADP reductase
9)
NADP will receive the 2 electrons and 2H⁺ from the water molecule at the beginning
The 2e⁻ and 2H⁺ will combine with the NADP to produce reduced NADP
NAD
Coenzyme in respiraton
NADP
Coenzyme in photosynthesis
12)
When the 2H⁺ is travelling to NADP reductase, it also passes an enzyme called ATP synthase.
ATP synthase releases energy in the form of ATP (ADP+Pi → ATP)
What's the process called when the electrons continue with the cycle from PSI?
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
Proton gradient
There's a build up of protons in the intermembrane space. This establishes a proton gradient, so H⁺ moves through ATP synthase, down its electrochemical gradient, in a process called chemiosmosis to make ATP
15)
The hydrogen ion that's come through the ATP synthase will be added on to NADP along with the e⁻ to form NADPH