ANSC 221 (Exam 3): Homework & Pre-lecture
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Match the terms to the correct description: Mitosis
Division of the nucleus
Match the terms to the correct description: Interphase
G1,S, and G2 phase
Match the terms to the correct description: Prophase
Chromosomes start to condense
Match the terms to the correct description: Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm
Match the terms to the correct description: Metaphase
Chromosomes align on the plate
Match the terms to the correct description: Prometaphase
Condensation of chromosomes is completed
Match the terms to the correct description: Telophase
Two daughter nuclei form in the cell and the chromosomes uncoil
Match the terms to the correct description: Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate
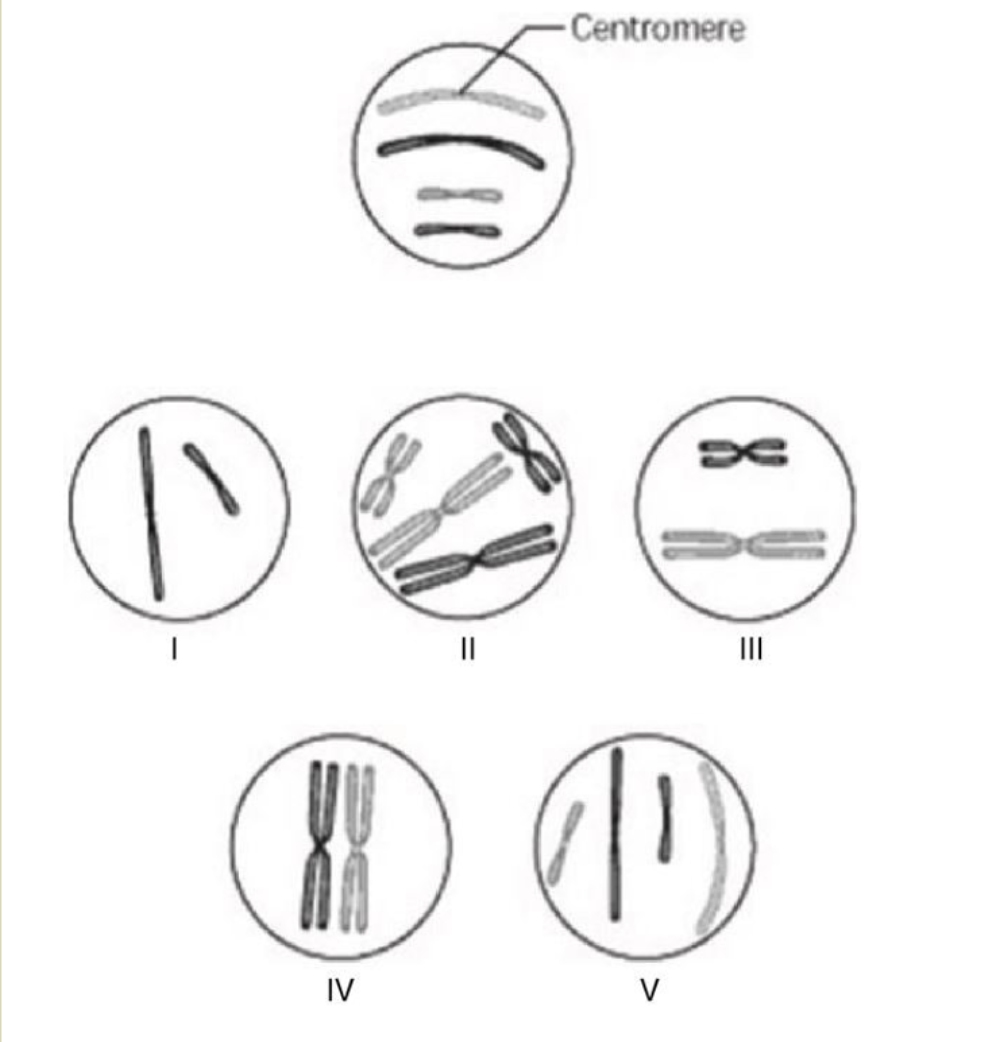
Which chromosomal configuration would be observed in one daughter cell after telophase of mitosis?
V
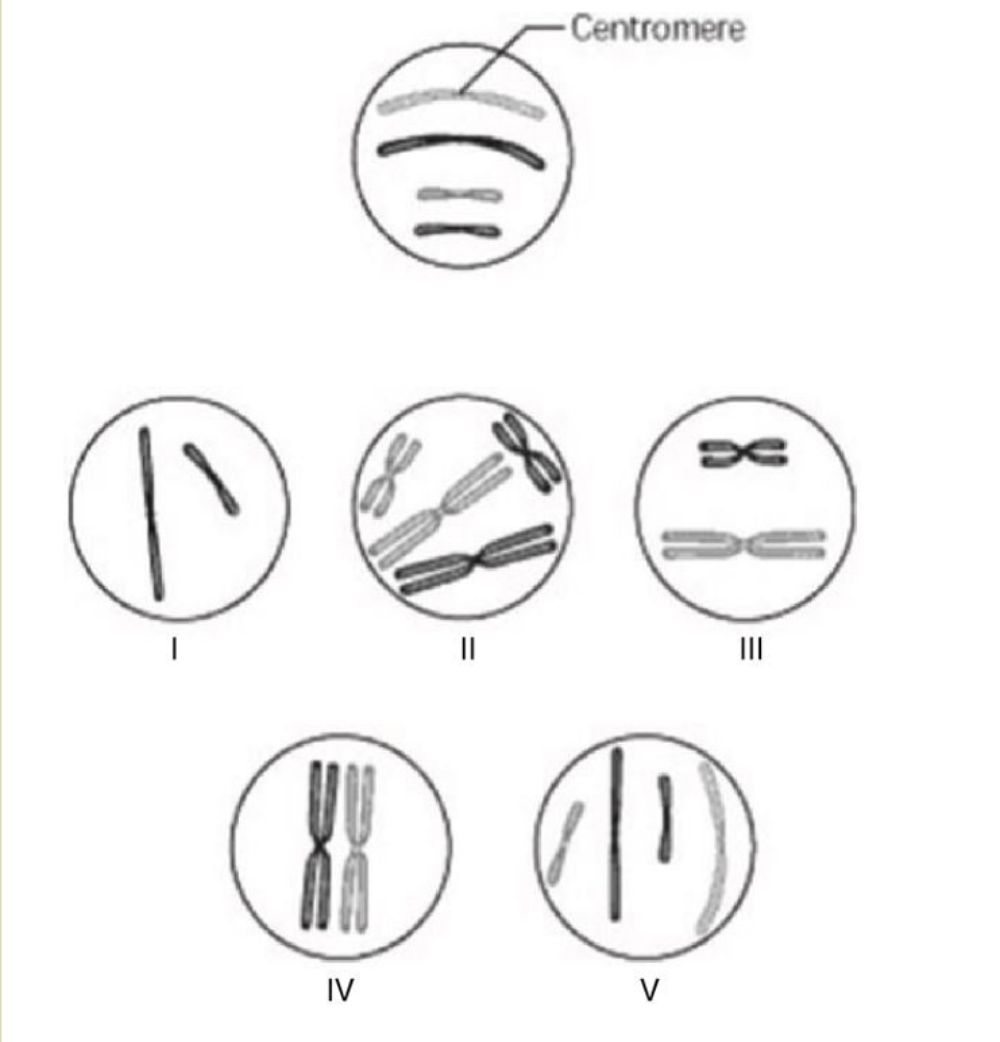
Which chromosomal configuration would be observed at prometaphase of mitosis?
II
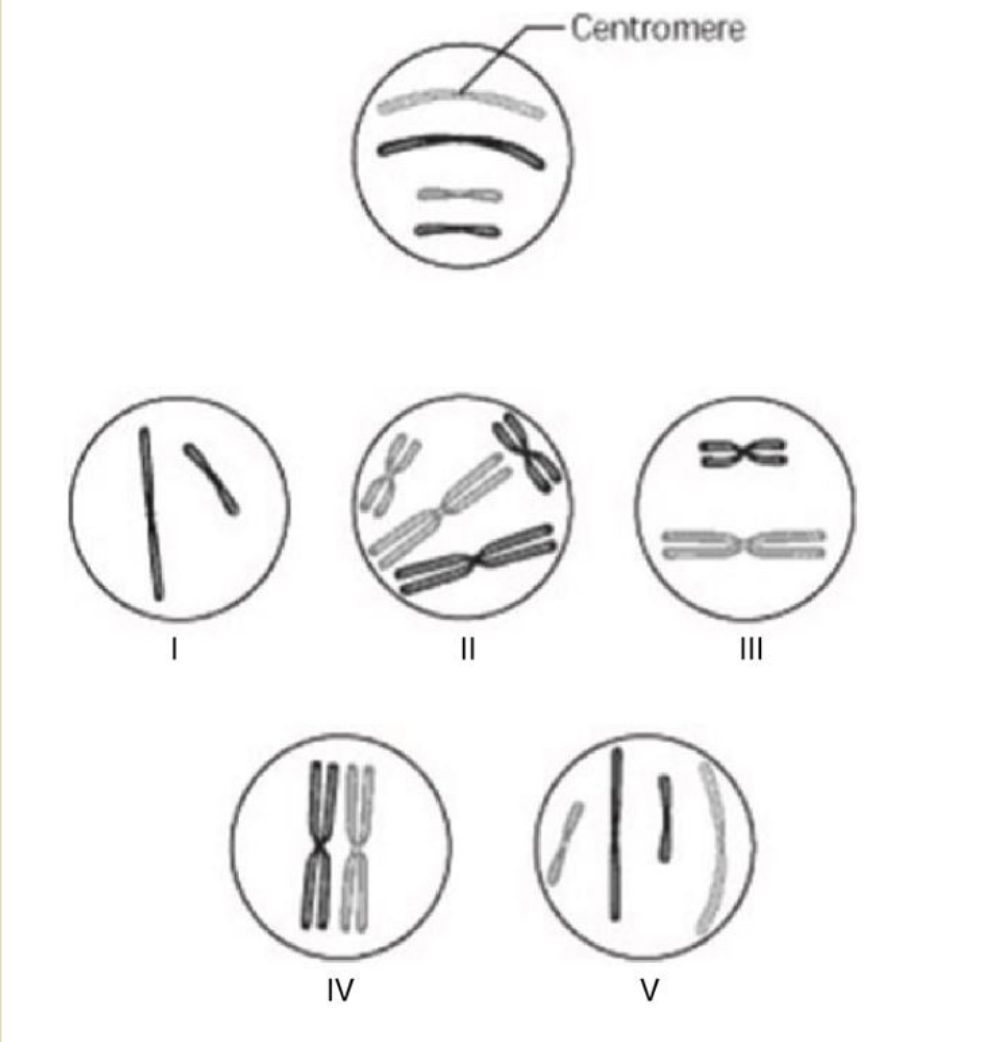
How many chromosomes are present in cell V?
Four chromosomes
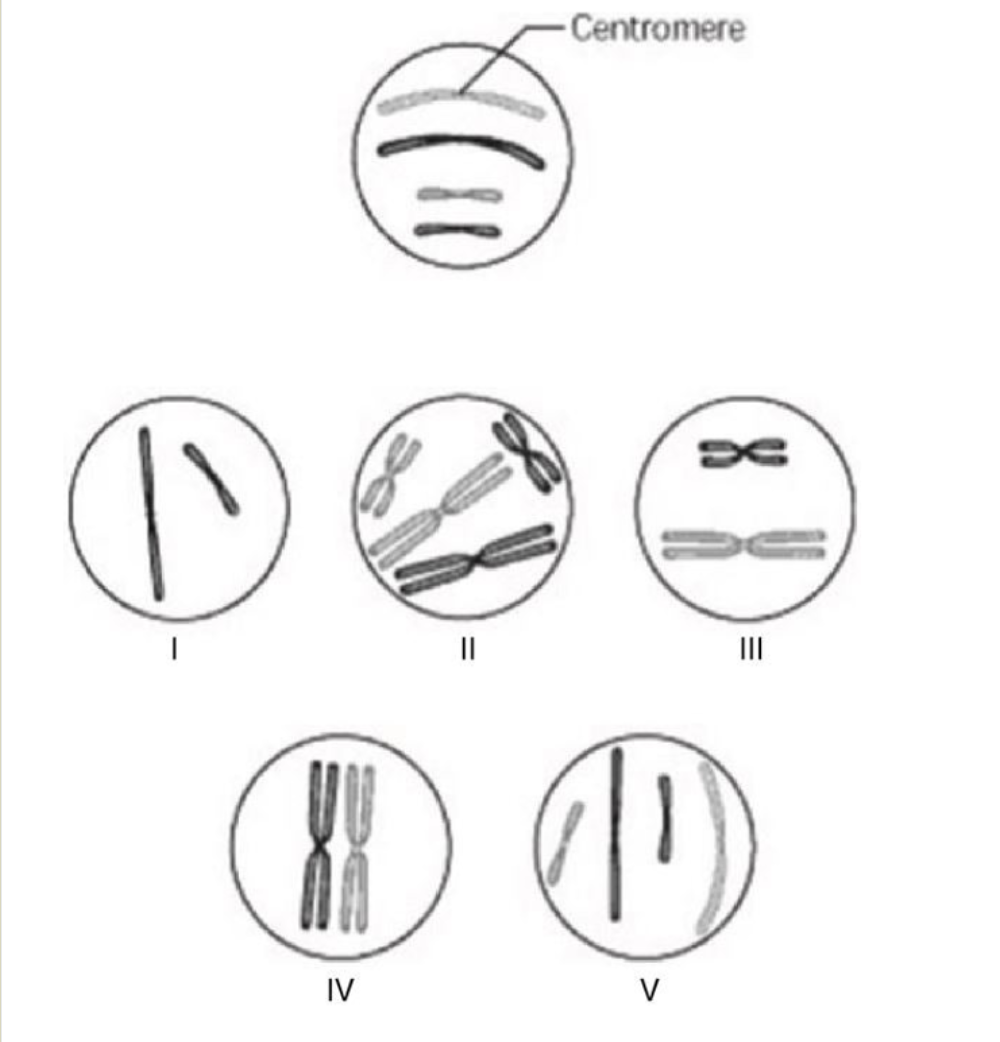
How many sister chromatids are present in cell IV?
Four sister chromatids
A hamster cell has 22 duplicated chromosomes migrating to one cell pole and 22 duplicated chromosomes migrating to another cell pole. What is the cell stage of this cell? *A Chinese hamster has a diploid number of 44 (2n=44).*
Anaphase I
A hamster cell has 22 chromatids migrating to one cell pole and 22 chromatids migrating to another cell pole. What is the cell stage of this cell? *A Chinese hamster has a diploid number of 44 (2n=44).*
Anaphase II
Match the events of meiosis with the stages listed: Metaphase I
Homologous chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate
Match the events of meiosis with the stages listed: Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate (Anaphase II)
Match the events of meiosis with the stages listed: Telophase II
Four haploid cells form containing joined sister chromatids
Match the events of meiosis with the stages listed: Anaphase I
Separation of homologous chromosomes
Match the events of meiosis with the stages listed: Telophase I
Two daughter cells from containing a complete haploid set of duplicated chromosomes
Match the events of meiosis with the stages listed: Metaphase II
Alignment of chromosomes to the metaphase plate
Match the events of meiosis with the stages listed: Prophase I
Exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
Students in a biology lab isolated cells in various phases of the cell cycle. A population of cells that have 1 1/2 times (1.5x) the DNA of G1 phase cells was most likely isolated from which of the following parts of the cell cycle?
In the S phase
Pigs have 38 chromosomes in each somatic cell (2n=38). One pig somatic cell undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are formed, and what is the chromosome number in each daughter cell?
Two cells with 38 chromosomes in each cell
Which of the following events would be most likely to produce cells with several nuclei?
Repeated mitosis without cytokinesis
If there are 24 centromeres in a cell at anaphase of mitosis, how many chromosomes will be found in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
12
Movement of the chromosomes during anaphase would be most directly affected by a drug that prevents which of the following events?
Shortening of microtubules
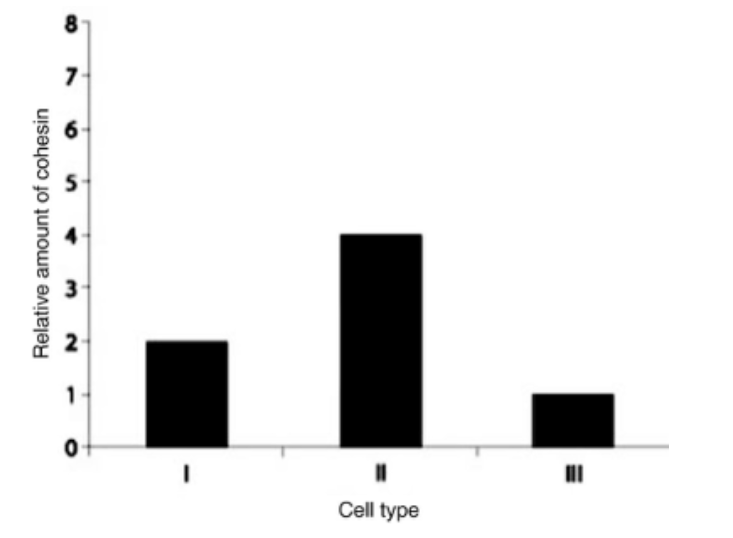
Which sample is consistent with a cell that has completed meiosis?
Cell type III completed meiosis
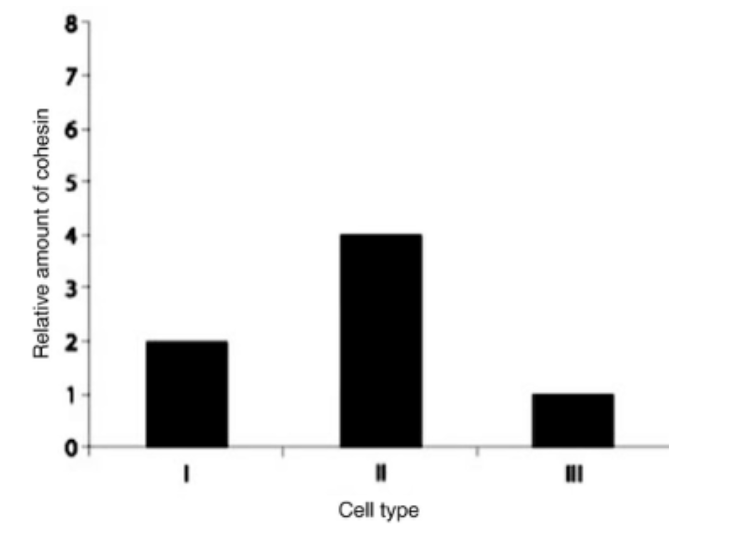
Which sample is consistent with a cell that is in metaphase I?
Cell type II is in metaphase I
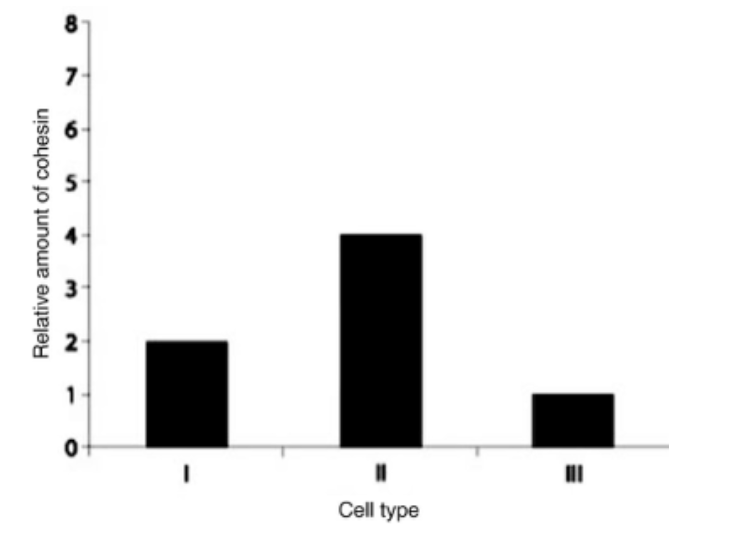
Which sample is consistent with a cell that is in telophase I?
Cell type I
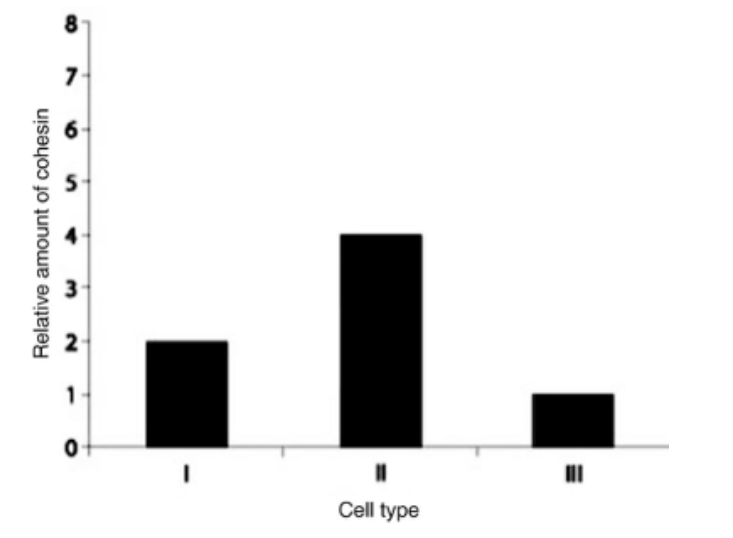
Which sample is consistent with a cell that has completed mitosis?
Cell type III is consistent with completing mitosis
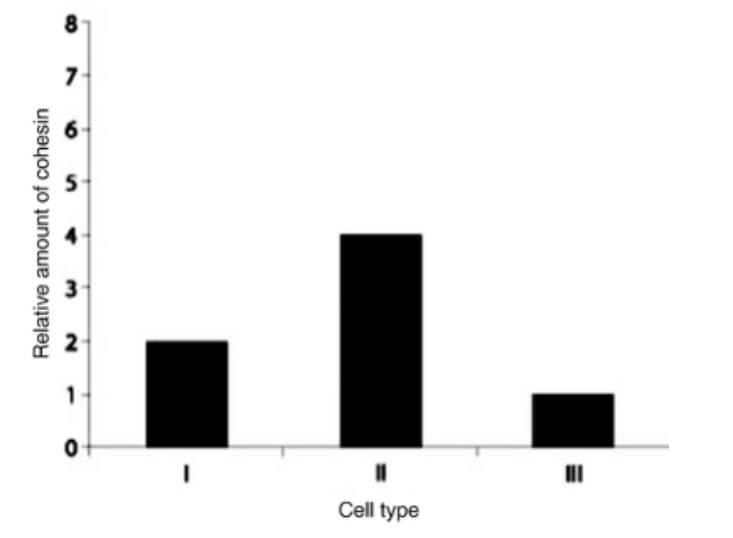
Which sample is consistent with a cell that is entering mitosis?
Cell type II is consistent with a cell that is entering mitosis
Select the differences between somatic cells and gamete cells.
Somatic cells are all body cells except for reproductive cells
Somatic cells have double the chromosomes of gametes cells
What are the phases of interphase?
G1
S phase
G2
Which of the following statements correctly describes the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication?
The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5'→ 3' direction, while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in the 5'→ 3' direction.
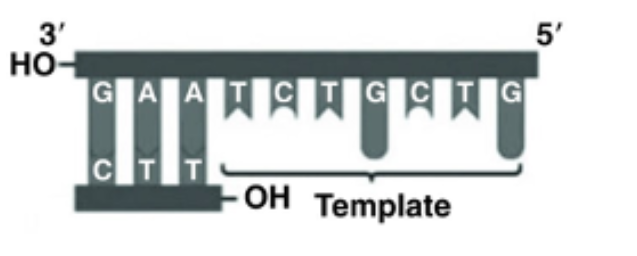
Referring to the figure below, what bases will be added as DNA replication proceeds on the bottom strand?
5′ A G A C G A C 3′
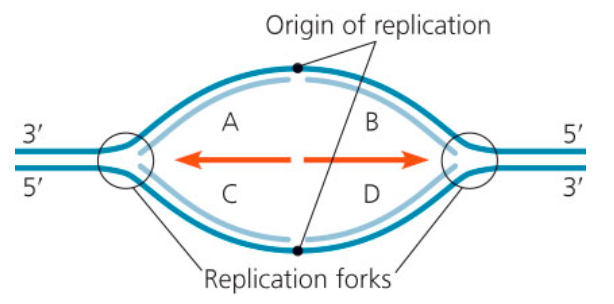
Considering that a new DNA strand can elongate only in the 5′ → 3′ direction. Use the figure below to mach the question to its answer. Which of the four segments of new DNA (lighter blue) could be leading strands?
B and C
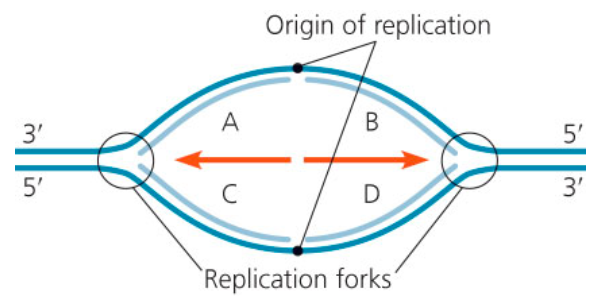
Considering that a new DNA strand can elongate only in the 5′ → 3′ direction. Which of the segments of new DNA (lighter blue) would be lagging strands, synthesized as a series of smaller Okazaki fragments?
A and D
Match the protein to its function in DNA replication: DNA polymerase I
Removes nucleotides from the RNA primer that is used for initiation DNA synthesis
Match the protein to its function in DNA replication: Topoisomerase
Relieves the strain in the DNA ahead of the replication fork caused by the untwisting of the double helix
Match the protein to its function in DNA replication: DNA polymerase III
Adds nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing DNA strand
Match the protein to its function in DNA replication: DNA ligase
Plays role in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA replication, joining Okazaki fragments together
Match the protein to its function in DNA replication: Helicase
Unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork
Match the protein to its function in DNA replication: Single-strand DNA binding protein
Helps to hold the DNA strands apart while they are being replicated
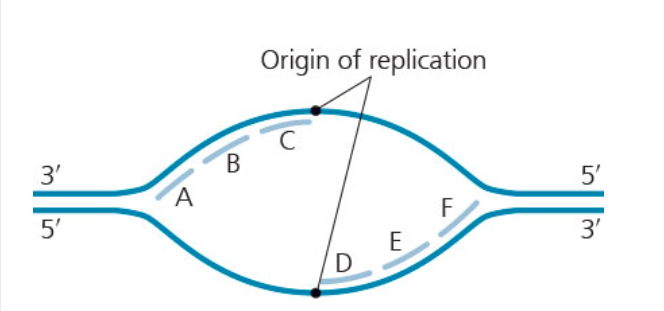
Which of the labeled Okazaki fragments would be the first two to be synthesized? (The leading strands are nor shown)
D and C would be synthesized first
Which of the following combinations of base pairs will be found in a molecule of DNA?
A + C = G + T
A sample of double-stranded DNA contains 42% cytosine. Approximately what percent of the nucleotides in this sample will be thymine?
8%
42 ×2= 84
100 - 84= 16
16/2 = 8%
The sequence of nucleotides below is present at a DNA location where the chain opens to form a replication fork:
3' C C T A G G C T G C A A T C C 5'
An RNA primer is formed starting at the underlined T (T) of the template. Which of the following represents the primer sequence?
5' A C G U U A G G 3'
The spontaneous loss of amino groups from adenine in DNA results in hypoxanthine, an uncommon base, opposite thymine. What combination of proteins could repair such damage?
nuclease, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase
A mutation in a gene called dnaB prevents the helicase from binding at the origin of replication. Which of the following events would you expect to occur as a result of this mutation?
No replication fork will be formed.
True or False: Okazaki fragments only form on the leading strand
False it forms on the lagging strand
DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the ____ end of a preexisting chain
3’
DNA replication follows a _______ model
Semiconservative
The law of segregation
It describes the inheritance of different alleles relative to one another.
The law of independent assortment
It describes the inheritance of different genes relative to one another.
Which of the following statements correctly describes how Mendel explained why traits disappeared in the F1 generation and then reappeared in the F2 generation?
Traits can be dominant or recessive, and the recessive traits were "hidden" by the dominant ones in the F1.
A diploid animal is dihybrid at the Head shape (H) and Tail length (T) loci (HhTt). Which of the following gamete genotypes can it produce?
Ht
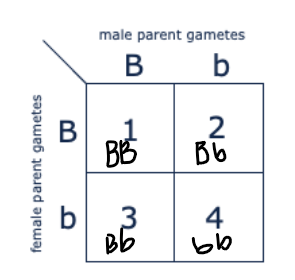
Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to dogs with heterozygous genotype?
2 and 3 only
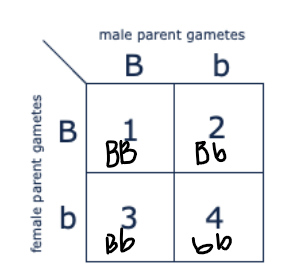
Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to dogs that will be true-breeding?
1 and 4 only
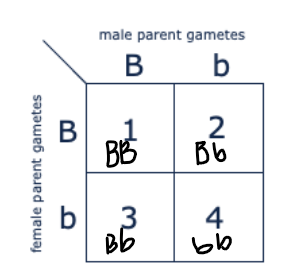
Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to dogs with brown coat color?
4 only
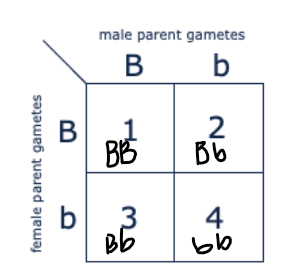
Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to dogs with black coat color?
1,2 and 3
When Mendel set up a Parental cross between true breeding purple (PP) and white (pp) flowered plants to generate the F1 (Pp) and then allowed the F1 to self-pollinate to generate the F2 he saw a dominant to recessive ratio of 3:1. What phenotypic ratio would be expected if he crossed the F1 with the original purple parent?
4:0
PP x Pp …
PP
PP
Pp
Pp
They are all going to show all the purple phenotype and no white bc white is pp
How many unique gametes could be produced through independent assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE?
8
Mendel crossed true breeding yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants and then allowed the offspring to self-pollinate to produce an F2 generation. The results were as follows: 6,022 yellow and 2,001 green (8,023 total). Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship of the allele for green seeds to the allele for yellow seeds?
The green allele is recessive to the yellow allele.
Albinism is a recessive trait where an individual does not produce the pigment melanin. A man and woman both produce melanin, but both have one parent with albinism. What is the probability that their first child will have albinism?
1/4
In a particular plant, green seed color is dominant to blue. If two plants with green seeds were crossed and resulted in 302 green and 98 blue seed plants, what was the most probable genotype of each parent?
Gg × Gg
A brown dog crossed with a yellow dog produced 12 brown offspring. A second brown individual was obtained. When the yellow dog was crossed with this animal, six brown and six yellow offspring were born. Which of the following best explains the results of the second cross?
yellow is a recessive trait; brown is a dominant trait
Character
Heritable feature with variance among individuals
Trait
Variants of heritable features
Alleles
Alternate versions of a gene
Homozygote
Organism with pair of identical alleles for a gene encoding a character
Genotype
Genetic makeup
Phenotype
Observable traits
A tool used for predicting allele composition of offspring resulting from crossing individuals with known genetic makeup is
Punnet square
Codominance
Phenotypes of both alleles are exhibited in the heterozygous.
Incomplete dominance
Phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes.
Pleiotropy
A single gene affects more than one character.
Complete dominance
Phenotypes of heterozygote and dominant homozygote are the same.
In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous (R1R2) offspring of red (R1R1) and white (R2R2) homozygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in the ratio of 1 red:2 roan:1 white?
roan (R1R2) × roan (R1R2)
R1R2 x R1R2
R1R1
R1R2
R1R2
R2R2
1 red (R1R1), 2 roan (R1R2), & 1 white (R2R2)
Which of the following statements correctly explains the observation that parents with two different phenotypes produced offspring with a phenotype that is a blend of the two parental varieties?
Neither of the parental alleles is dominant over the other.
Which of the following inheritance patterns describes the ability of a single allele to have multiple phenotypic effects?
Pleiotropy describes the ability of a single allele to have multiple phenotypic effects
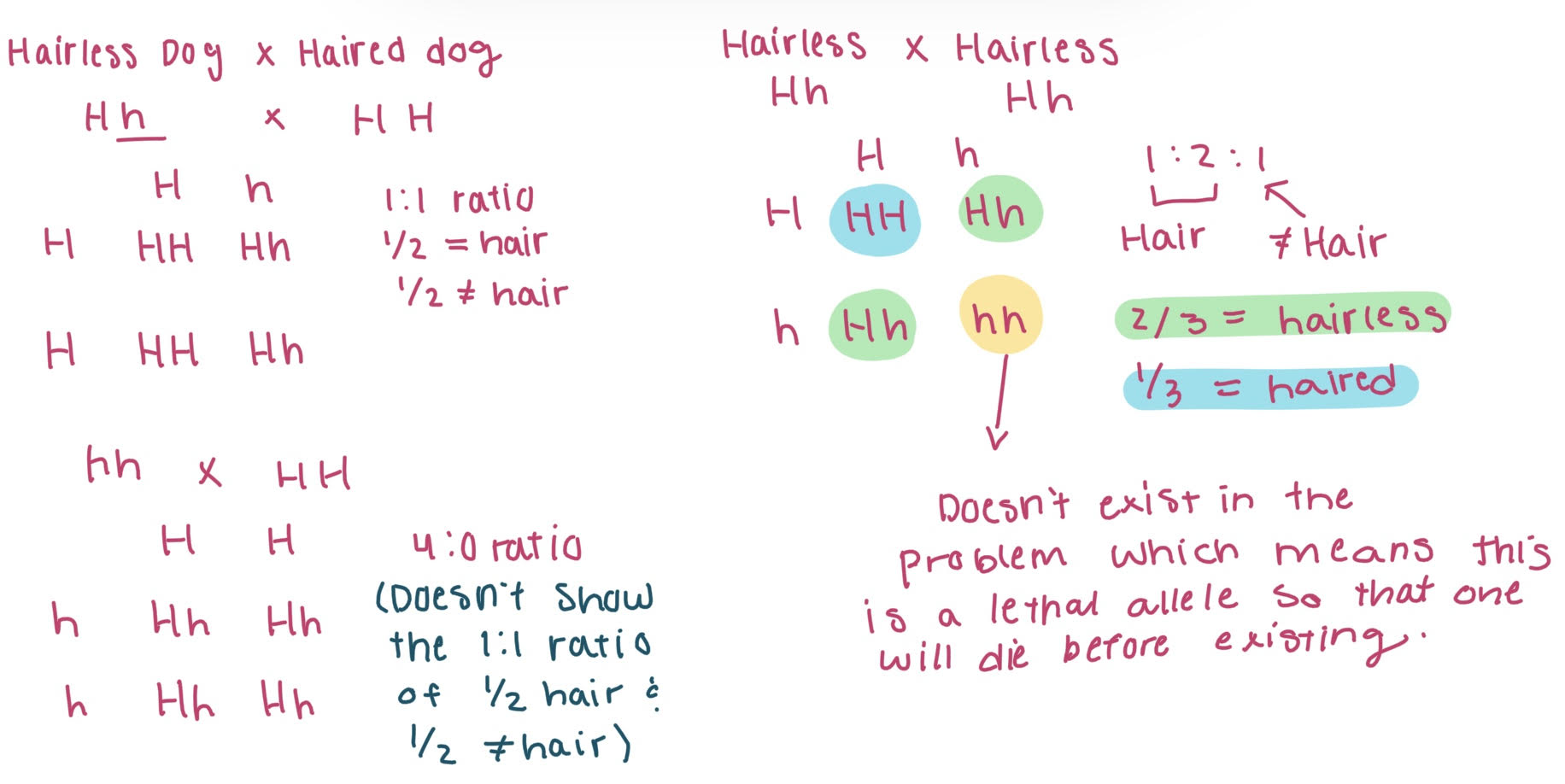
Mexican hairless dogs have a mutation that affects the development of ectodermal tissues such as hair and teeth. When a Mexican hairless dog is mated to another breed of dog about 1/2 of the offspring are hairless and 1/2 have hair. However, when two Mexican hairless dogs are mated about 2/3 are hairless and 1/3 have hair. What can we suggest about inheritance hairless?
Mexican hairless dogs are heterozygous for hairless allele; embryos homozygous for hairless are lethal (die before birth).
A gene for the MN blood group has codominant alleles M and N. If both children in a family are of blood type M, which of the following situations is possible?
each parent is either M or MN
Which of the following relationships among alleles of a single gene best explains the observation that a single change in the gene encoding α-keratin results in chickens with frizzled feathers, increased food consumption, higher heart rate and delayed sexual maturity?
This relationship is pleiotropy
Crossing a red and white flower in the P generation, and getting a pink flower in the F1 generation is an example of
Incomplete dominance
________ is when phenotypic expression of a gene in one locus alters the phenotypic expression of another gene at another locus
Epistasis
True or false: skin color is an example of monogenic inheritance
False skin color is not an example of monogenic inheritance. Monogenic inheritance means a pattern where a trait is determined by a single gene. Skin is polygenic inheritance.
_____ is when two alleles affect the phenotype in their own separate, distinguishable ways
Codominance
If two black Labrador retrievers mate and the F1 generation has 9 black, 3 brown, and 4 yellow labs, this is an example of
Epistasis (occurs in Labradors masking/modifying the expression of another gene)
True or false: the additive effect of multiple genes on a single phenotypic character is called polygenic inheritance
True polygenic inheritance means the inheritance of a trait controlled by two or more genes, resulting in a wide range of phenotypes due to the cumulative effect of these genes, such as human height, skin color, and eye color.
If sperm is 1/2 (Rr) and Egg is 1/2 (Rr), the probability that the offspring is RR is ____ (See figure 14.9 to guide your answer)
¼ will be RR
Rr is described as?
Heterozygote
rr is describes as
Homozygous recessive
True or False: We can exactly predict with certainty the number of progeny of different genotypes that will result from a genetic cross
False because sometimes there could be other factors
What was Morgan's choice for an experimental organism?
Fruit fly
What is not an example of an X-linked disorder?
Huntington's disease
Feather color in budgies is determined by two different genes: Y for pigment on the outside of the feather, and B for pigment on the inside of the feather. YYBB, YyBB, or YYBb is green; yyBB or yyBb is blue; YYbb or Yybb is yellow; and yybb is white. A blue budgie is crossed with a white budgie. Which of the following results in the offspring is most possible?
blue and white offspring
Feather color in budgies is determined by two different genes: Y for pigment on the outside of the feather, and B for pigment on the inside of the feather. YYBB, YyBB, or YYBb is green; yyBB or yyBb is blue; YYbb or Yybb is yellow; and yybb is white. Two blue budgies were crossed. Over the years, they produced 22 offspring, five of which were white. What are the most likely genotypes for the two blue budgies?
yyBb and yyBb
Epistasis
One gene interferes with the expression of another gene, leading to a specific phenotype.
Polygenic
Phenotype expression depend on an additive effect of many genes.
Skin color in a certain species of fish is inherited via a single gene with four different alleles. Each allele confers a unit of color darkness such that having allele S1 confers one unit of color, S2 has two units, S3 has three units, and S4 confers four units. A fish of this type has the genotype S1S3, and its mate has the genotype S2S4. What proportion of their offspring would be expected to have five units of color?
½