4.1 - 4.3 Niche
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Habitat
The space where an organism lives
Population
- a group of interbreeding individuals of the same species found in an area
Community
all the various populations in a habitat
Species evennesss
the number of species within a habitat
Species richness
Number of individuals of each species
Endemism
Habitat diversity
range of different ecosystems or habitats within a particular area or region
Habitat diversity: High biodiversity
The larger the number of different habitats within an area, the more likely it is to have a high biodiversity
Species diversity
the number of different species in an ecosystem, and their abundance.
Benefits of High species divesity
The higher the species diversity, the more stable the ecosystem is
More resilient to environmental changes
Genetic diversity
the variety of alleles in the gene pool
Gene pool
All the alleles of all the genes present in a population of a species
Causes of genetic diversity
mutation
Random assortment
Crossing over
Populations occupy different ranges, different selection pressure, different allele frequencies
Genetic diversity importance
helps population to adapt to, and survive, changes in the environment
Causes of low genetic diversity
inbreeding in small isolated populations can lead to a high proportion of homozygous individuals, resulting in lower biodiversity
Genetic disease caused be recessive alleles are more common in a population.
Human factors affecting biodiversity
Habitat destruction
Overexploitation
Hunting
Agriculture
Climate change
How has variety of life changed over time?
Variety increases as new species form
Human activity is threatening much of the life on the planet.
Distribution of a species
how a species is spread throughout the ecosystem
Species abundance
the number of individuals of that species
Random sampling
Using quadrats, convert sampling area into grid format
Label each square
Use a random number generator to pick sample points
Record the organisms and numbers
Other sampling techniques to for animals
Sweeping nets
Pitfall traps
Kick-sampling
ALWAYS USE SAME SAMPLING METHOD
ALWAYS USE SAME SAMPLING METHOD
Measuring genetic diversity with phenotype
Different alleles are responsible for the variety of phenotypes within a species
The greater the variety of phenotypes within a species, the higher the genetic diversity
Measuring genetic diversity with genotype
An organisms genotype is determined by the different alleles found within cells
The higher the number of different alleles for a characteristic, the greater the genetic diversity
Heterozygosity Index
The higher the proportion of heterozygotes in a population, the greater the genetic diversity
Heterozygosity index

Index of diversity formula
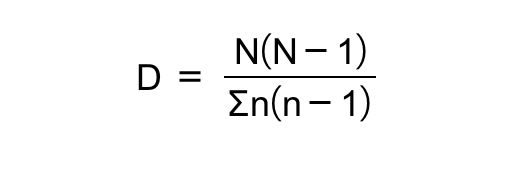
Units of the index of diversity formula

Niche
the role of an organism in its environment
How many species can occupy a niche
Niche only occupied by one species
What happens if more than one species occupy a niche?
competition for same resources
one species outcompetes the other
other species use occupy new niche or extinction
Adaptations to abiotic and biotic factors
Anatomical
Behavioural
Physiological
Anatomical adaptations
observable structures of organisms - external or upon dissection - that help them survive or reproduce
Behavioural adaptations
actions taken by organisms that help them survive or reproduce
Physiological adaptations
features of the internal workings of organisms that help them to survive or reproduce