Chapter 27 Recall (Glycosides, Lactose, Glycoproteins, and Glycolipids)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
activated (converted to sugar nucleotides)
Carbohydrates must be ________ before they can be used in the synthesis of glycoconjugates
glycoconjugates
molecules such as proteins, lipid, or other organic substances containing glycosidic bonds to sugars
1. A sugar phosphate reacts with a nucleotide (NTP) to form a sugar nucleotide (NDP-sugar)
2. This reaction is catalyzed by NDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase and releases 2 phosphates
Describe how sugar nucleotides are made
1. Their formation is irreversible; this "tags" carbs to set aside as a pool for biosynthetic reactions
2. The nucleotide moiety provides binding interactions that help with catalysis
3. The nucleotidyl group is an excellent leaving group, facilitating formation of new glycosidic bonds
Describe the 3 reasons why sugars must be converted to sugar nucleotides
UDP-glucose
The activated form of glucose is ....
- The sugar is transferred from the UDP to an alcohol or other nucleophile to form a glycosidic bond
- This is catalyzed by sugar transferases
How is UDP-glucose is used in biosynthesis?
glycosides
glycoconjugates in which a sugar is bound, via glycosidic bond, to a molecule other than a carbohydrate, lipid, or protein
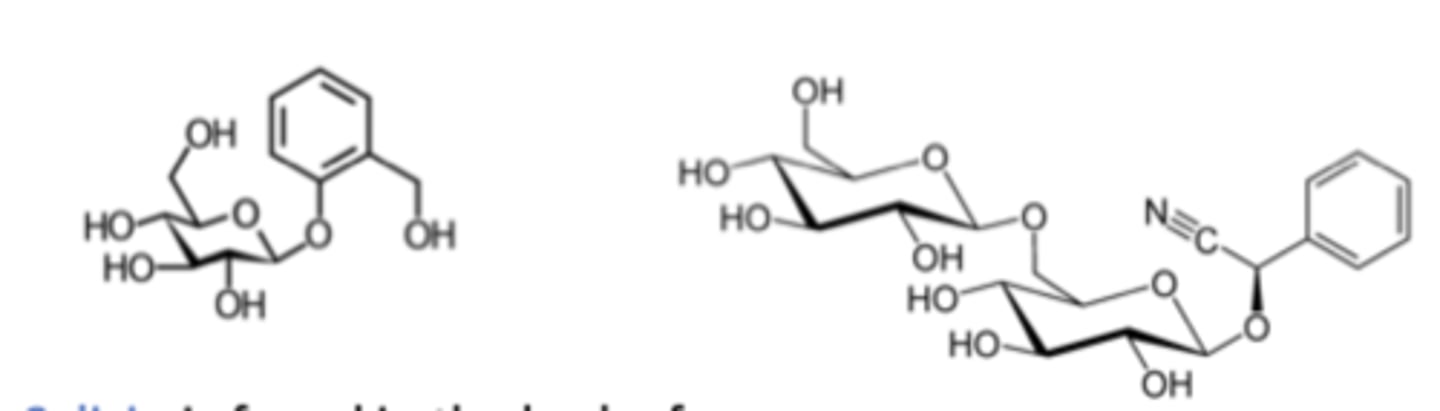
salicin
glycoside found in the bark of trees; has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties
amygdalin
glycoside found in the pits of cherries, apricots, and other fruits; lysis facilitates the release of cyanide
The sugar in both these glycosides is glucose, and the anomeric carbons are in the B conformation. Thus, these molecules are classified as B-glucosides.
The sugar in both these glycosides is ________, and the anomeric carbons are in the ________ conformation. Thus, these molecules are classified as ________.
glucuronides
glycoconjugates containing glucuronate, the product of oxidation of C6 in glucose to a carboxyl group
- UDP-glucose is oxidized at C6 to form UDP-glucuronate; this is catalyzed by UDP-glucose dehydrogenase
- UDP-glucuronate is converted to glucuronide by UDP-glucuronate transferase, which transfers xeniobiotics/drugs onto the molecule and UDP is the leaving group (this occurs primarily in the liver)
- Glucuronide is then eliminated in the bile or urine
How are glucuronides formed?
1. The negative charge of the carboxylate ion and the polor hydroxyl groups increase the water-solubility of hydrophobic hormones, drugs, or xeniobiotics bound to the glucuronide
2. Glucuronate also acts as a 'marker' for cellular export
What 2 factors facilitate the elimination of glucuronides?
billirubin
a degradation product of heme that is formed in the reticuloendothelial system
it is conjugated with 2 glucuronates to form bilirubin diglucuronide
Bilirubin is transferred, bound to serum albumin, to the liver, where ....
bile
Conjugated bilirubin is secreted in the ________, and thus eventually eliminated in the stool and urine.
the buildup of bilirubin in tissues, causing jaundice
Inability of the liver to conjugate and/or eliminate bilirubin results in ....
Laboratory tests can measure total, indirect (unconjugated), and direct (conjugated) serum bilirubin levels in order to facilitate diagnosis of the cause of jaundice.
Laboratory tests can measure total, indirect (________), and direct (________) serum bilirubin levels in order to facilitate diagnosis of the cause of jaundice.
hepatic bilirubin glucuronyltransferase
- transfers glucuronates from UDP to bilirubin
Infantile jaundice is most frequently caused by low activity of ....
During lactation in the mammary gland
When and where is lactose synthesized in the body?
- Galactosyltransferase
- a-lactalbumin
Lactose synthase consists of what 2 enzymes?
prolactin
a-lactalbumin is expressed after childbirth in response to the hormone ....
- In the absence of a-lactalbumin, galactosyltransferase has a very low affinity for glucose
- Instead of transferring galactose from UDP-galactose to glucose to make lactose, it will transfer galactose from UDP-glucose to glycoproteins
In the absence of a-lactalbumin, how does galactosyltransferase work?
UDP-galactose may be synthesized from UDP-glucose
this is why women with dietary galactose restrictions (bc of lactose intolerance or galactosemia) are still able to breastfeed
Where else can we get galactose besides from the diet?
- UDP-glucose is converted to UDP-galactose using UDP-glucose 4-epimerase
this enzyme is also used in galactose metabolism
How is UDP-galactose made from UDP-glucose?
glucose
All of the different sugars found in glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins, glycolipids, and other compounds in the body can be synthesized from ________
glucosamine 6-phosphate
gets its amino group from glutamine
All of the nitrogen-containing sugars are derived from ________
glycoproteins
proteins that contain short chains of carbohydrates linked at either ser/thr or asn residues
glycosylated
almost all of the secreted and membrane-associated proteins of eukaryotic cells are ________
mucins
a class of glycoproteins secreted by mucus-producing cells
N-acetylneuraminic acid
NANA =
galactose
Gal =
N-acetylglucosamine
GlcNAc =
mannose
Man =
fucose
Fuc =
1. Cell-cell recognition and attachment
2. Binding of bacteria and viruses to cell surfaces
3. Binding of hormones and transport proteins to cell surfaces
Describe the 3 functions of carbohydrates attached to glycoproteins
ER
The protein portion of glycoproteins is synthesized in the ....
the lumen of the ER and the Golgi complex
The carbohydrate chains are attached to the protein in ....
They are recognized by receptors, facilitating their transport to lysosomes
What happens when the mannose residues on glycoproteins are phosphorylated?
- A condition in which the phosphoryltransferase that makes mannose-P is deficient
- This causes lysosomal hydrolases to be secreted from the cell
- Junk accumulates in the lysosomes and forms inclusion bodies
What is I-cell disease? What causes it?
- Skeletal abnormalities
- Coarse facial features
- Delayed development of motor skills
What are the 3 clinical signs of I-cell disease?
- They are synthesized in the ER directly on the peptide chain
- It involves the action of glycosyltransferases and occurs directly on Ser or Thr residues
How are O-linked glycoproteins synthesized?
- They are synthesized in the ER directly onto dolichol phosphate
- The oligosaccharide is then transferred to Asn residues in target proteins
- They are further process in the ER and Golgi complex
How are N-linked glycoproteins synthesized?
Dolichol phosphate
a hydrophobic molecule that inserts itself into the ER membrane
glycolipids
derivatives of the lipid sphingosine; they contain ceramide; they are important cell-recognition factors and are produced in the Golgi
cerebrosides
(i.e. galactocerebroside or glucocerebroside)
contain only one sugar residue attached to a ceramide
gangliosides
contain several sugar residues, and will always have at least one NANA residue (N-acetylneuraminic acid)
the expression of glycosyltransferases
Differences in ________ result in different blood types
H substance (oligosaccharide)
All of the blood groups begin with a common core:
N-acetylglucosamine
In type A blood, a ________ residue is added to the H substance
Galactose
In type B blood, a ________ residue is added to the H-substance
gangliosidoses
lysozomal storage diseases resulting from defects in the degradation of gangliosides; they result in the accumulation of partially degraded gangliosides in lysosomes, causing disruption of neuronal function
autosomal recessive
Gangliosidoses are inherited in an ________ pattern, and most present with neurological degeneration
Gaucher disease
Gangliosidoses are usually fatal before early childhood, with the exception of ....
Hexoaminidase A
- Causes accumulation of the ganglioside GM2
Tay-Sachs disease is caused by a deficiency in which enzyme? What substrate accumulates?
- Infantile onset with rapid progression of neurodegeneration and blindness
- Cherry-red spot on macula
- Muscular weakness and seizures
What are the common symptoms of Tay-Sachs Disease?
Sphingomyelinase
- Causes accumulation of Sphingomyelin
Neimann-Pick disease is caused by a deficiency in which enzyme? What substrate accumulates?
- Infantile onset with rapid progression of neurodegeneration and blindness
- Cherry-red spot on macula
- Hepatosplenomegaly
What are the common symptoms of Neimann-Pick disease?
B-glucosidase
- Causes accumulation of glucocerebrosides
most common lysosomal storage disease
Gaucher disease is caused by a deficiency in which enzyme? What substrate accumulates?
- Onset at any age, but generally after childhood
- No neurodegeneration
- Bone involvement, causes weakness with pathologic fractures and bone pain
- Hepatosplenomegaly
What are the common symptoms of Gaucher disease?